Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communication Barriers To Effective Communication
Communication Barriers To Effective Communication
Uploaded by
Charmaine JohnsonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communication Barriers To Effective Communication
Communication Barriers To Effective Communication
Uploaded by
Charmaine JohnsonCopyright:
Available Formats
OLD HARBOUR HIGH SCHOOL
OFFICE ADMINISTRATION MRS. J. LEWIN
COMMUNICATION PART 3
GRADE 10 BUSINESS/GENERAL
NOVEMBER 22,2021
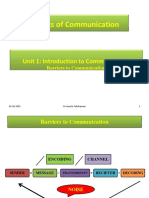
TOPIC: BARRIERS TO COMMUNICATION
WHAT ARE COMMUNICATION BARRIERS?
• Barriers to Communication are anything that impedes, block or otherwise interferes with
the communication of a thought from one individual to another.
• Barriers to Communication are things that hinders the transmission and/or receipt of
information.
• A communication barrier is anything that impedes the communication process.
Barriers to Communication
• Perceptual bias – means bias against or for something based on sensory inputs (sight,
hearing, smell, taste, touch). For example you may love a radio station and your parents may
think its too much noise.
• Cultural bias – making judgments based on your own culture.
• Personal bias – is your own beliefs and responses.
• Semantics – are caused when people of different cultures or language cannot identify with the
meaning of a word or expression.
• Language – if one person is talking to another in a language that he/she
doesn’t understand.
• Literacy skills – poor literacy skills affects effective communication.
• Internal and external barriers – miscommunication within and outside the organization.
Forms of Business Structure
• A basic responsibility of the management of an organization is to develop an effective business
structure. Forms of decision–making business structures:
OLD HARBOUR HIGH SCHOOL
OFFICE ADMINISTRATION MRS. J. LEWIN
COMMUNICATION PART 3
GRADE 10 BUSINESS/GENERAL
NOVEMBER 22,2021
• Centralised: Entreprenuerial/centralised.
OLD HARBOUR HIGH SCHOOL
OFFICE ADMINISTRATION MRS. J. LEWIN
COMMUNICATION PART 3
GRADE 10 BUSINESS/GENERAL
NOVEMBER 22,2021
• Decentralised
1. pyramid;
2. matrix; and,
3. independent.
Centralised: Entreprenuerial/centralised.
In a centralised organization, the main responsibilities and decisions are carried out by the head
office.
• Decentralised – Departmental managers can make their own decisions without going
through any chain of command.
Forms of Decentralised Structure
• pyramid – shows an organization that has progressively more people at each lower level. Strategic
decisions will be made by senior managers at the top level, but day-to-day decisions will
be made by staff lower down the pyramid.
Executives
Middle Management
Supervisor
Staff/employees
Forms of Decentralised Structure
• Matrix – is often found in organizations that deal with special “one-off” projects. These companies
may be working on several projects at once such as building a hotel, a sports facility and shopping
centre in different Caribbean territories.
• Independent – exists when individuals can make their own decisions about their operations, even
if they work as a part of a large enterprise.
You might also like
- Large Language Model (LLM) Bias Index-LLMBIDocument14 pagesLarge Language Model (LLM) Bias Index-LLMBIbosheng dingNo ratings yet
- FR KhanhDocument3 pagesFR KhanhVuong Hong Dam (FUG CT)No ratings yet
- Barriers of CommunicationDocument15 pagesBarriers of CommunicationPallavi KuchewarNo ratings yet
- Hindrances To Good Human Relation StrategiesDocument4 pagesHindrances To Good Human Relation StrategiesCarol Neng Calupitan100% (2)
- Language As A Barrier To CommunicationDocument12 pagesLanguage As A Barrier To CommunicationVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 & 11 (Unit 1 - Barriers To Communication)Document23 pagesLecture 10 & 11 (Unit 1 - Barriers To Communication)siddharthaNo ratings yet
- The Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument7 pagesThe Barriers To Effective CommunicationSimran PillayNo ratings yet
- Reformed Church University: Assignment Mark FormDocument9 pagesReformed Church University: Assignment Mark FormEvans MulamboNo ratings yet
- HBO Chapter 3Document31 pagesHBO Chapter 3milanlagundiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective Communication 1Document6 pagesBarriers To Effective Communication 1Waleed RasoolNo ratings yet
- Communication (Unit II)Document11 pagesCommunication (Unit II)aniket yadav0006No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 HoDocument24 pagesChapter 2 Hoyukta jainNo ratings yet
- How To Overcome Physical Barriers?Document4 pagesHow To Overcome Physical Barriers?JOHN CARLO DE ASISNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Departmental CommunicationDocument43 pagesUnit IV Departmental Communicationsharmaabhinav6804No ratings yet
- Antim Prahar Busniess Communication 2023 PDFDocument22 pagesAntim Prahar Busniess Communication 2023 PDFJaskaran SinghNo ratings yet
- 3 Strategies To Avoid Communication BreakdownDocument17 pages3 Strategies To Avoid Communication BreakdownGreta ReyesNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument5 pagesBarriers To Effective CommunicationsangeethadurjatiNo ratings yet
- Course Title: ClassDocument12 pagesCourse Title: ClassMalik Muhammad Ijlal RazaNo ratings yet
- Welcome TO,: Barriers of CommunicationDocument12 pagesWelcome TO,: Barriers of CommunicationShraddhanjali SahooNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument7 pagesDocxMahnoor AwaisNo ratings yet
- Barriers To The Communication ProcessDocument5 pagesBarriers To The Communication ProcessdlukowskaNo ratings yet
- BarriersDocument4 pagesBarriersJonna May Delgaco-MotaNo ratings yet
- The Barriers To Effective Communication: Rupal JainDocument3 pagesThe Barriers To Effective Communication: Rupal JainMillyNo ratings yet
- Barrirs For CommunicationDocument35 pagesBarrirs For CommunicationShivu Yati100% (1)
- Informal and Formal Barriers To CommunicationDocument26 pagesInformal and Formal Barriers To CommunicationBaran RoyNo ratings yet
- Summer 2011-39Document12 pagesSummer 2011-39Amit JhaNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Marketing Management Submitted By:-Simranjeet Kaur Course: - Mba-2 ROLLNO:-22-MBA-006 Submitted To:-Dr - Vishal VinayakDocument12 pagesPresentation of Marketing Management Submitted By:-Simranjeet Kaur Course: - Mba-2 ROLLNO:-22-MBA-006 Submitted To:-Dr - Vishal VinayakSimran jeet kaurNo ratings yet
- Top 11 Barriers To CommunicationDocument3 pagesTop 11 Barriers To CommunicationAndrea Elizabeth Flores OrtizNo ratings yet
- Barriers of Communication-1Document12 pagesBarriers of Communication-1Yasheerah YaqootNo ratings yet
- BC AssignmentDocument9 pagesBC Assignmentshivam kumarNo ratings yet
- WalkerIMChapter17 GW2015Document13 pagesWalkerIMChapter17 GW2015Nazia EnayetNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication MOD 1Document23 pagesOral Communication MOD 1Kristal BandongNo ratings yet
- Buscom 1 PPT Pres. Module 1 Understanding Business CommunicationDocument47 pagesBuscom 1 PPT Pres. Module 1 Understanding Business CommunicationSamantha Ysabel PasayloNo ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument41 pagesCommunication Barrierskabibhandari100% (1)
- Lecture 6-Communication PDFDocument37 pagesLecture 6-Communication PDFJohn Ray CuevasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-Communication ProcessDocument41 pagesLesson 1-Communication ProcessAnagirl LynNo ratings yet
- Communication Barrier 1.define Communication BarrierDocument3 pagesCommunication Barrier 1.define Communication BarrierAshikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- U5E7 - Communication Challenges For Sustainability - EN - NotesDocument24 pagesU5E7 - Communication Challenges For Sustainability - EN - NotessilbersterneNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Business CommunicationDocument7 pagesBarriers To Business CommunicationFLORENTINANo ratings yet
- Coaching, Counseling, and Supportive CommunicationDocument31 pagesCoaching, Counseling, and Supportive CommunicationMd SelimNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument26 pagesBarriers To CommunicationArnav RastogiNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers of Chapter 2Document3 pagesQuestions and Answers of Chapter 2Kristina SimbolonNo ratings yet
- CH2&3 - Communication in An OrganizationDocument106 pagesCH2&3 - Communication in An OrganizationBarkhad HassanNo ratings yet
- Barriers TO Effective CommunicationDocument34 pagesBarriers TO Effective CommunicationSubratKumarNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Communication in BusinessDocument9 pagesUnit I: Communication in BusinessKrishnamoorthy RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Barriers or Gateways To CommunicationDocument14 pagesBarriers or Gateways To Communicationshreedhar koiralaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Business CommunicationDocument51 pagesCH 1 Business CommunicationHailemariam KibretNo ratings yet
- P 27S Comm BarrierDocument27 pagesP 27S Comm BarrierNi Made DwidianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Barriers To CommunicationDocument38 pagesChapter 4 Barriers To CommunicationAsad Latif BhuttaNo ratings yet
- HS 24 PC & LS Unit-1 & 2Document46 pagesHS 24 PC & LS Unit-1 & 21ms20ei002No ratings yet
- Ch2 IMDocument33 pagesCh2 IMshahdad sayedNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Introduction To Communication2023nDocument37 pagesCH1 - Introduction To Communication2023nHANA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument40 pagesCommunication BarriersCarl Andrie MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Written Report 2 - Eunice Dimple CaliwagDocument6 pagesWritten Report 2 - Eunice Dimple CaliwagEunice Dimple CaliwagNo ratings yet
- MISCOMMUNICATIONDocument20 pagesMISCOMMUNICATIONNeha Apa100% (2)
- Barriers To Effective of Communication SkillsDocument4 pagesBarriers To Effective of Communication Skillsa_j1988No ratings yet
- Name: Arun Goel Roll No. 40232 Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument5 pagesName: Arun Goel Roll No. 40232 Barriers To Effective CommunicationArun GoelNo ratings yet
- Module-2 Individual Behaviour: Faculties - DR Deepali Pai, MR T S NarayananDocument115 pagesModule-2 Individual Behaviour: Faculties - DR Deepali Pai, MR T S NarayananAMRUD GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Ch. 4 Barriers To CommunicationDocument38 pagesCh. 4 Barriers To CommunicationMiyamoto MusashiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument50 pagesBarriers To CommunicationachsurajNo ratings yet
- The Art of Communication How to Communicate Effectively: Self help, #4From EverandThe Art of Communication How to Communicate Effectively: Self help, #4No ratings yet
- SDCL Pract 3Document6 pagesSDCL Pract 3Mahesh DarvankarNo ratings yet
- Thesis Progress Report SampleDocument5 pagesThesis Progress Report Samplegj84st7d100% (1)
- Recommended Browsers For Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12Document16 pagesRecommended Browsers For Oracle E-Business Suite Release 12vivek_khoslaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer Programming (C++) : Course ObjectivesDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Computer Programming (C++) : Course ObjectivesAlina RafeeqNo ratings yet
- Understanding Group Policy: James Michael StewartDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Group Policy: James Michael Stewartmohammedfereje suliemanNo ratings yet
- Enki Speaks: Enki & Ninmah Breed Girls Till She Curses HimDocument5 pagesEnki Speaks: Enki & Ninmah Breed Girls Till She Curses HimDejan VajagicNo ratings yet
- RamanaDocument2 pagesRamananaga212067No ratings yet
- Umc DTM ManualDocument60 pagesUmc DTM Manualjuan_fimNo ratings yet
- Project 1 Lesson Plan Around TownDocument8 pagesProject 1 Lesson Plan Around Townjmobando1No ratings yet
- Lesson 14Document35 pagesLesson 14Lucky YasayNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable NounsDocument12 pagesCountable and Uncountable NounsjaimejoseNo ratings yet
- BHELComputer ScienceDocument7 pagesBHELComputer ScienceManjunath ItagiNo ratings yet
- Digital Simulation of Numerical Relay Using MatlabDocument6 pagesDigital Simulation of Numerical Relay Using MatlabthavaselvanNo ratings yet
- Thiruppavai English - AR SwamyDocument134 pagesThiruppavai English - AR SwamyData ScienceNo ratings yet
- Y2 Phonics ModuleDocument36 pagesY2 Phonics ModulepusatlatihanstemnknNo ratings yet
- Opencv2refman PDFDocument899 pagesOpencv2refman PDFrosasilbusNo ratings yet
- Technology: AutoformDocument8 pagesTechnology: AutoformAnonymous ZGcs7MwsLNo ratings yet
- Letter Compendium NO NOA ENDocument9 pagesLetter Compendium NO NOA ENBoban TrpevskiNo ratings yet
- Representative Texts and Authors From Europe Literature of The Ancient GreeceDocument13 pagesRepresentative Texts and Authors From Europe Literature of The Ancient GreeceMylen ObreroNo ratings yet
- Oc All Dist - Gsrao GK GroupsDocument5 pagesOc All Dist - Gsrao GK GroupsTeja Vardhan BikkasaniNo ratings yet
- GGT Micro Report PDFDocument13 pagesGGT Micro Report PDFJZNIXCNo ratings yet
- Islamic Renaissance-The Real Task AheadDocument61 pagesIslamic Renaissance-The Real Task AheadMuhammad Azam KhalidNo ratings yet
- AS400 Automatically Logging Off Inactive WorkstationsDocument2 pagesAS400 Automatically Logging Off Inactive WorkstationsMiguel Ángel Macías MartínezNo ratings yet
- Im Not The Indian You Had in Mind - PoemDocument3 pagesIm Not The Indian You Had in Mind - PoemRobot BotNo ratings yet
- Victory Over TemptationsDocument23 pagesVictory Over TemptationsGmeet RecordsNo ratings yet
- Chatbot: A Deep Neural Network Based Human To Machine Conversation ModelDocument7 pagesChatbot: A Deep Neural Network Based Human To Machine Conversation ModelĐặng Phương NamNo ratings yet
- Collins Cambridge Checkpoint English Coursebook 8 Answers PDFDocument5 pagesCollins Cambridge Checkpoint English Coursebook 8 Answers PDFbelinda chikanda50% (2)
- A Little Girl Screamed at The Library at Her MotherDocument35 pagesA Little Girl Screamed at The Library at Her MotherDeiseree GarciaNo ratings yet