Professional Documents
Culture Documents
About Presentation Flower Hormone
Uploaded by
Medina0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pageshormone
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthormone
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesAbout Presentation Flower Hormone
Uploaded by
Medinahormone
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
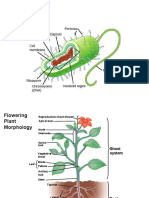
Plant hormones
(also known as phytohormones) are organic
substances that regulate plant growth and development.
Plant hormones may be part of a signal-transduction pathway, or
their presence may stimulate reactions that are signal and/or
causative agents for stress responses.
Plant hormones as signal molecules regulate cellular processes in
targeted cells locally and when moved to other locations of the
plant. They also determine the formation of the root, stem, leaf, and
flower and facilitate the shedding of leaves and the development
and ripening of fruits. Hormones shape the plant and affect seed
growth, time of flowering, sex of flowers, and senescence of leaves
and fruits. They affect which tissues grow upward and which grow
downward and even plant death. Hormones are vital to plant growth
and lacking them, plants would be mostly a mass of undifferentiated
cells.
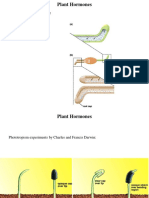
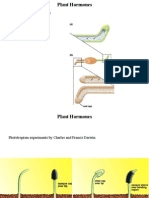
Phototropism- the orientation of a plant or other organism in
response to light, either toward the source of light (positive
phototropism) or away from it (negative phototropism).
Iz knjige podvuceno
In order to knowwhat causes the cells on the dark side to grow faster
than the cell on brogh side, Charles Darwin had done an experiment.
He noticed that if light is shone on a coleoptile (shoot tip) from one
side the shoot bends (grows) toward the light. The ‘bending’ did not
occur in the tip itself but in the elongating part just below it. Removing
the tip or covering it with foil meant that the shoot could no longer
‘bend’ toward the light. Covering the elongating part of the shoot did
not affect the response to light at all!
Darwin Concluded that: “Some influence is transmitted from the tip to the
more basal regions of the shoot thereby regulating growth and inducing
curvature- basically the shoot tip determines the wither the plant will grow
towards or away from the light
Role of abscisic acid (ABA) in plant development and stress response. Abscisic acid
regulates different developmental processes, such as seed dormancy and shoot and
root development. In leaves, ABA transport to the guard cells triggers stomatal
closure in response to biotic and abiotic stresses.
You might also like
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDocument19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To JoinDocument18 pagesPlant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To Joinmerit tutorials com NET JRF JAM TUTORIALSNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlDocument17 pages14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlRahulKwatraNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesPlant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacieda_89No ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Document12 pagesCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 Plant MorphologyDocument3 pagesBIO 2 Plant MorphologyMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- The Pressure-Flow Hypothesis: Gibberellins (Gas) AreDocument2 pagesThe Pressure-Flow Hypothesis: Gibberellins (Gas) AreMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Control and CoordinationDocument27 pagesPresentation On Control and CoordinationKunal TolaniNo ratings yet
- Plant ResponsesDocument24 pagesPlant Responsesk75544863No ratings yet
- Plant Hormones SummaryDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Name BabalolaDocument19 pagesName BabalolaDEBORAH BABALOLANo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToDocument6 pagesNervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response Pt. 2Document22 pagesCoordination & Response Pt. 2Yagna LallNo ratings yet
- How Do We Know They Exist?Document11 pagesHow Do We Know They Exist?Saumyaranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- Bio Written Report Ancheta and IñaDocument4 pagesBio Written Report Ancheta and IñaFerdinand RyanNo ratings yet
- BIOLAB Plant Hormones Exercise PDFDocument2 pagesBIOLAB Plant Hormones Exercise PDFRaphael MontierroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PLANTDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PLANTSedsed QuematonNo ratings yet
- 04 Growth - Regulators GA - ExptDocument8 pages04 Growth - Regulators GA - Exptjessenia oviedoNo ratings yet
- 2003 - Knowing When To Grow - Signals Regulating Bud DormancyDocument7 pages2003 - Knowing When To Grow - Signals Regulating Bud Dormancyjuan antNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlAlnedKirby Carijutan Mendiola100% (1)
- Bio T1 ApuntesDocument11 pagesBio T1 ApuntesGuillermo Corbi BallesterNo ratings yet
- Biology Auxin PhototropismDocument2 pagesBiology Auxin PhototropismAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- BIO02 - TropismDocument10 pagesBIO02 - TropismCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Can Plants CommunicateDocument19 pagesCan Plants CommunicateIemaaNaimaaNo ratings yet
- THE TROPISM, Nastic, Turgor Movements, Cycle and Rhythm, Senescence, Fruit Ripening and AbscissionDocument37 pagesTHE TROPISM, Nastic, Turgor Movements, Cycle and Rhythm, Senescence, Fruit Ripening and AbscissionJamaica NaridoNo ratings yet
- Laporan Acara Dominansi ApikalDocument2 pagesLaporan Acara Dominansi ApikalPuri Rahma100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Gaurav Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- 0 BooksDocument52 pages0 BooksletslearnwithsaneelaNo ratings yet
- BIO109P Module 2. Differentiation & MorphogenesisDocument28 pagesBIO109P Module 2. Differentiation & MorphogenesisJet DelimaNo ratings yet
- Biologychapter 17Document52 pagesBiologychapter 17anchal kumariNo ratings yet
- Movement Part 1 SCDocument14 pagesMovement Part 1 SCgsvpjdq9wmNo ratings yet
- Totipotency and MorphogenesisDocument17 pagesTotipotency and MorphogenesisApratim SinghNo ratings yet
- Sevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BDocument3 pagesSevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BJoyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- Tropic ResponsesDocument4 pagesTropic ResponsesMuhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Plant Coordination: Pudica, Ivy Vines That Cling To Walls, Trapping of InsectDocument2 pagesPlant Coordination: Pudica, Ivy Vines That Cling To Walls, Trapping of InsectArif UllahNo ratings yet
- AUXINDocument23 pagesAUXINJose S. Cabato IIINo ratings yet
- Magazine: Apical DominanceDocument2 pagesMagazine: Apical DominancejessicaNo ratings yet
- CaphyDocument10 pagesCaphyHằng NgôNo ratings yet
- Auxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyDocument33 pagesAuxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyAyushi MandloiNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument3 pagesPlant Hormonesministore kmcNo ratings yet
- Senescence MechanismDocument15 pagesSenescence Mechanismrheen_shanticaNo ratings yet
- 06 Plant HormonesDocument4 pages06 Plant HormonessureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Plant Morphology - WikipediaDocument57 pagesPlant Morphology - WikipediaBashiir NuurNo ratings yet
- Axunis BDocument49 pagesAxunis BAbebe fikaduNo ratings yet
- Science Material - Plants Move (Tropismn) (II)Document4 pagesScience Material - Plants Move (Tropismn) (II)Fransiska ArethaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4wienna1987No ratings yet
- LR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Document19 pagesLR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Kate Jewel CullamatNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument29 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Plant HormonesDocument13 pagesGroup 6 Plant HormonesJv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Biology Note For WK 7 Grade 11Document14 pages1st Term Biology Note For WK 7 Grade 11Adeola YusufNo ratings yet
- Tropism 1Document5 pagesTropism 1Eiann Jasper LongcayanaNo ratings yet
- MidtemDocument6 pagesMidtemkhahoaNo ratings yet
- Regulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesDocument30 pagesRegulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesMoath EnnabNo ratings yet
- O-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYDocument21 pagesO-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYayikoyoroy10No ratings yet
- Plant GrowthDocument6 pagesPlant Growthj_sheriNo ratings yet
- 27 IrritabilityDocument8 pages27 Irritabilitymcalmontsarah612No ratings yet
- 5th Form Biology-Movement in Plants-TropismsDocument25 pages5th Form Biology-Movement in Plants-TropismsJharell CaravlhoNo ratings yet
- Topics For EvolutionDocument1 pageTopics For EvolutionMedinaNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis Online I 2 I 3 MYPDocument32 pagesPedigree Analysis Online I 2 I 3 MYPMedinaNo ratings yet
- Pedigree WorksheetDocument3 pagesPedigree WorksheetAbed ZaghalNo ratings yet
- Dna Technology I Online I MypDocument45 pagesDna Technology I Online I MypMedinaNo ratings yet
- Online Viruses I MypDocument62 pagesOnline Viruses I MypMedinaNo ratings yet
- ONLINE Questions Protein SynthesisDocument1 pageONLINE Questions Protein SynthesisMedinaNo ratings yet
- Online PPT Protein Synthesis I MypDocument45 pagesOnline PPT Protein Synthesis I MypMedinaNo ratings yet
- Topics For EvolutionDocument1 pageTopics For EvolutionMedinaNo ratings yet
- Mass Extinctions 2015 PosterDocument1 pageMass Extinctions 2015 PosterMedinaNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Stem CellsDocument1 pageMindmap Stem CellsMedinaNo ratings yet
- Clone WorksheetDocument2 pagesClone WorksheetMedinaNo ratings yet
- Online Viruses I MypDocument62 pagesOnline Viruses I MypMedinaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPDocument36 pagesDNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPMedinaNo ratings yet
- Dna Technology I Online I MypDocument45 pagesDna Technology I Online I MypMedinaNo ratings yet
- Pedigree WorksheetDocument3 pagesPedigree WorksheetAbed ZaghalNo ratings yet
- Clone WorksheetDocument2 pagesClone WorksheetMedinaNo ratings yet
- ONLINE Questions Protein SynthesisDocument1 pageONLINE Questions Protein SynthesisMedinaNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Stem CellsDocument1 pageMindmap Stem CellsMedinaNo ratings yet
- Pedigree Analysis Online I 2 I 3 MYPDocument32 pagesPedigree Analysis Online I 2 I 3 MYPMedinaNo ratings yet
- Mass Extinctions 2015 PosterDocument1 pageMass Extinctions 2015 PosterMedinaNo ratings yet
- Online PPT Protein Synthesis I MypDocument45 pagesOnline PPT Protein Synthesis I MypMedinaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPDocument36 pagesDNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPMedinaNo ratings yet
- Plants MovementDocument8 pagesPlants MovementMedinaNo ratings yet
- The Life of A Flowering PlantDocument19 pagesThe Life of A Flowering PlantMedinaNo ratings yet
- RevisionDocument16 pagesRevisionMedinaNo ratings yet
- Preparation For Test First PartDocument8 pagesPreparation For Test First PartMedinaNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic CellDocument90 pagesEukaryotic CellMedinaNo ratings yet
- II1 IB RevisionDocument3 pagesII1 IB RevisionMedinaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones & Response To StimuliDocument9 pagesPlant Hormones & Response To StimuliMedinaNo ratings yet
- 35 Plant Structure Growth and DevelopmentDocument62 pages35 Plant Structure Growth and DevelopmentMedinaNo ratings yet