Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPT
Uploaded by
Arpitha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views19 pagesOriginal Title
Control and Coordination ,Class 10 ,Module 2.3 ,Ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPT
Uploaded by
ArpithaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
BY
SMT. RENUKA BALA BHAKAT
AECS , NARWAPAHAR
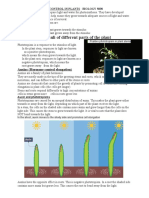
TYPES OF MOVEMENTS
1. TROPIC MOVEMENTS
2. NASTIC MOVEMENTS
Movement of plant towards
the stimulus is called tropic
movement .
Phototropism – Movement of plant
towards light is called phototropism.
Shoot grow towards light.
Shoot is positively phototropic while
root is negatively phototropic .
Movement of plants in response to
gravity is called geotropism .
Roots are positively geotropic and
shoots are negatively geotropic .
Growth of plants towards water
is called hydrotropism .
Roots grow towards water.
Movement of plants towards
chemicals is called chemotropism .
Growth of pollen tube towards
ovule is an example of
chemotropism.
Nasticmovement is not a
directional movement of
the plant part with response to the
stimulus. In nastic movement, from
whichever direction the stimulus is
applied, it affects all the parts of
the organ of a plant equally and
they always move in the same
direction .
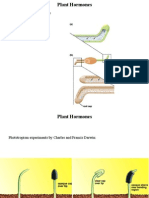
Mimosa pudica (touch me not)
Planthormones are signal molecules,
produced within plants, that occur in
extremely low concentrations. Plant
hormones control all aspects of plant growth
and development, from embryogenesis to
regulation of organ size, pathogen defense,
stress tolerance and reproductive
development.
The auxin group of hormones has a wide range of
uses in a plant. Auxin molecules are found in all
tissues in a plant. However, they tend to be
concentrated in the meristems, growth centres
which are at the forefront of growth. These
centres release auxin molecules, which are then
distributed towards the roots. In this way, the
plant can coordinate its size, and the growth and
development of different tissues based on the
gradient of the auxin concentration.
Cytokinins (CK) are a class of plant growth
substances (phytohormones) that promote
cell division, or cytokinesis, in plant roots
and shoots. They are involved primarily in
cell growth and differentiation, but also
affect apical dominance, axillary bud
growth, and leaf senescence.
Abscisic acid (ABA) is often referred to as a inhibitory
rather than stimulatory hormone. It is involved in the
closure of stomata, bud and seed dormancy and is
known to inhibit other hormonal actions.
Stimulates the closing of stomata in the epidermis.
Inhibits plant metabolism and seed germination.
Mainly involved in regulating abscission and dormancy
Induces dormancy in seeds and helps in withstanding
desiccation and other unfavorable growth factors.
It acts as a growth promoter as well as
inhibitor. It is a gaseous hormone .
Functions
1.Stimulating fruit ripening.
2.Helps in determining the sex of a flower.
3.It is involved in the production of female flowers in a
male plant.
4.Promotes Apo-geotropism in roots.
5.Helps in the root initiation and pollination.
6.Ethylene increases the speed of leaf and flower
senescence.
7.Induces seed germination.
8.Induces root growth to increase the capability of water
and mineral absorption.
You might also like
- Can Plants CommunicateDocument19 pagesCan Plants CommunicateIemaaNaimaaNo ratings yet
- Topic 9.3: Growth in PlantsDocument17 pagesTopic 9.3: Growth in Plantssalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Comparison of Fertilizer Cost Between Chemical and Bio FertilizerDocument5 pagesComparison of Fertilizer Cost Between Chemical and Bio FertilizerJohn DAcquisto, D.Sc.No ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument19 pagesPlant HormonesWu YiruiNo ratings yet
- Devt-Psych ReviewerDocument226 pagesDevt-Psych ReviewerJudy Mae OmanioNo ratings yet
- KVS Jammu Sample Paper for Class X MathsDocument115 pagesKVS Jammu Sample Paper for Class X MathsArpitha100% (1)
- Plant Hormones SummaryDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones SummaryRamesh Kumar MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlDocument27 pagesPlant and Animal Chemical and Nervous ControlAlnedKirby Carijutan MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Exploring Biology in The Laboratory Pendarvis PDFDocument2 pagesExploring Biology in The Laboratory Pendarvis PDFJulie0% (6)
- Plant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesPlant Hormone: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacieda_89No ratings yet
- Plant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To JoinDocument18 pagesPlant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To Joinmerit tutorials com NET JRF JAM TUTORIALSNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlDocument17 pages14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlRahulKwatraNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth & Development: Morphology, Physiology, FactorsDocument3 pagesPlant Growth & Development: Morphology, Physiology, FactorsMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- BIO02 - TropismDocument10 pagesBIO02 - TropismCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesGrowth Regulatorsirfan shahNo ratings yet
- About Presentation Flower HormoneDocument2 pagesAbout Presentation Flower HormoneMedinaNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesPlant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument7 pagesControl and CoordinationKanish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- BBC - GCSE Bitesize - Plant HormonesDocument4 pagesBBC - GCSE Bitesize - Plant HormonessureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone - WikipediaDocument13 pagesPlant Hormone - WikipediaNageso FitoNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument29 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument3 pagesPlant Hormonesministore kmcNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Document12 pagesCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument8 pagesPlant Hormone: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDharmendra SinghNo ratings yet
- How Do We Know They Exist?Document11 pagesHow Do We Know They Exist?Saumyaranjan PradhanNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyhahahahaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell DifferentiationDocument3 pagesPlant Cell DifferentiationJoyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Control and CoordinationDocument27 pagesPresentation On Control and CoordinationKunal TolaniNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Plants: RadiateDocument14 pagesControl and Coordination in Plants: RadiateTaimoor Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Plant ResponsesDocument24 pagesPlant Responsesk75544863No ratings yet
- The Pressure-Flow Hypothesis: Gibberellins (Gas) AreDocument2 pagesThe Pressure-Flow Hypothesis: Gibberellins (Gas) AreMaikka IlaganNo ratings yet
- Dominansi Apikal: Telaah Pustaka dan Hasil PengamatanDocument2 pagesDominansi Apikal: Telaah Pustaka dan Hasil PengamatanPuri Rahma100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4wienna1987No ratings yet
- Regulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesDocument30 pagesRegulating Growth and Development The Plant HormonesMoath EnnabNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToDocument6 pagesNervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- The Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentDocument29 pagesThe Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentbeneNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone Signaling and the Greening ProcessDocument6 pagesPlant Hormone Signaling and the Greening ProcesskhahoaNo ratings yet
- P3 OrganogenesisDocument13 pagesP3 OrganogenesisPanca Ayu VirgirlNo ratings yet
- Bio Written Report Ancheta and IñaDocument4 pagesBio Written Report Ancheta and IñaFerdinand RyanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Part II Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesLesson 7 Part II Control and CoordinationDragonAffire 1No ratings yet
- Plant Physiology: Auxin and Cytokinin InteractionDocument7 pagesPlant Physiology: Auxin and Cytokinin InteractiondorynemoNo ratings yet
- Growth Regulators Functions in Horticultural Crops: Eknaik, V S S V PrasannaDocument6 pagesGrowth Regulators Functions in Horticultural Crops: Eknaik, V S S V PrasannaiajerNo ratings yet
- GLUCOSIDEDocument3 pagesGLUCOSIDEAngel Ellene MarcialNo ratings yet
- TEACHING MATERIALS ON PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENTDocument6 pagesTEACHING MATERIALS ON PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENTAndi NurhidayahNo ratings yet
- The Discovery and Functions of Auxin, the First Plant Growth HormoneDocument33 pagesThe Discovery and Functions of Auxin, the First Plant Growth HormoneAyushi MandloiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PLANTDocument3 pagesChapter 4 PLANTSedsed QuematonNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Plant HormonesDocument13 pagesGroup 6 Plant HormonesJv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Coordination in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination in Plants NotesAmna SaleemNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument3 pagesPlant HormonesAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument28 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsFaishol MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of CropsDocument17 pagesGrowth and Development of CropsSUSHMA PRIYANo ratings yet
- Plant HormoneDocument31 pagesPlant HormoneChristine De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Plant Coordination: Pudica, Ivy Vines That Cling To Walls, Trapping of InsectDocument2 pagesPlant Coordination: Pudica, Ivy Vines That Cling To Walls, Trapping of InsectArif UllahNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFDocument38 pagesKuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFRianNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Hormones: Chemical MessengersDocument1 pagePlant and Animal Hormones: Chemical MessengersEsther EkengNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Document8 pagesAdobe Scan 05 Dec 2022Gaurav Raj SharmaNo ratings yet
- AuksinDocument8 pagesAuksinhabib arief prakosoNo ratings yet
- How Plants SurviveDocument5 pagesHow Plants SurviveChrisNo ratings yet
- Tropic ResponsesDocument4 pagesTropic ResponsesMuhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Laporan Tunas Lateral Plant Anatomy and PhisiologyDocument15 pagesLaporan Tunas Lateral Plant Anatomy and PhisiologyRizkaHasanahNo ratings yet
- Byjus Com Biology Plant Physiology (1) Pages 1 4Document4 pagesByjus Com Biology Plant Physiology (1) Pages 1 4Vikas PratikNo ratings yet
- English 12 SS 2Document24 pagesEnglish 12 SS 2ArpithaNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument14 pagesRevision QuestionsArpithaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Grammar Worksheet on DeterminersDocument10 pagesGrade 10 Grammar Worksheet on DeterminersArpithaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Reported SpeechDocument18 pagesGrammar - Reported SpeechArpithaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Modal VerbsDocument11 pagesGrammar - Modal VerbsArpithaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Subject Verb AgreementDocument10 pagesGrammar - Subject Verb AgreementArpitha100% (1)
- Grammar - TensesDocument11 pagesGrammar - TensesArpithaNo ratings yet
- CFPQ English10Document138 pagesCFPQ English10ArpithaNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTDocument19 pagesControl and Coordination, Class 10, Module 2.3, PPTArpithaNo ratings yet
- Populations Review Questions KEYDocument23 pagesPopulations Review Questions KEYtanusehdev17No ratings yet
- Don Bosco Splendid Home 1 Terminal Examination-2017 Class-VII G.KDocument2 pagesDon Bosco Splendid Home 1 Terminal Examination-2017 Class-VII G.KproodootNo ratings yet
- Nutrient Media Review for Orchid MicropropagationDocument15 pagesNutrient Media Review for Orchid MicropropagationRahmaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals ModuleDocument5 pagesReproduction in Animals ModuleMugdha SenguptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 ClusteringDocument48 pagesLecture12 ClusteringarjunNo ratings yet
- Lupasol PN 80 On PP Nonwoven - From StevenDocument6 pagesLupasol PN 80 On PP Nonwoven - From StevenSyed Owais Ali NaqviNo ratings yet
- Specimen 2019 (IAL) MS - Unit 3 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDocument8 pagesSpecimen 2019 (IAL) MS - Unit 3 Edexcel Biology A-Levelchipo activesonNo ratings yet
- Practice Test A2Document6 pagesPractice Test A2Khang Nguyen TienNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Week 1 2 Q2Document3 pagesSummative Test Week 1 2 Q2Jennifer AleaNo ratings yet
- M1CHAP3Document28 pagesM1CHAP3Eilla Marie GomosNo ratings yet
- MG I - TEMA 5 Limba EnglezaDocument2 pagesMG I - TEMA 5 Limba Englezaoana_matacheNo ratings yet
- BIO 104L Lab Report 1Document3 pagesBIO 104L Lab Report 1Kyle Sheen Saclolo CostillasNo ratings yet
- Gey 204 AssignmentDocument17 pagesGey 204 AssignmentAniefiok EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Materi Postural OntogenesisDocument14 pagesMateri Postural Ontogenesisdamha al bannaNo ratings yet
- Citrus Commodity Survey ReferenceDocument255 pagesCitrus Commodity Survey Referenceduong-hoai-an-6140No ratings yet
- Lab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIDocument10 pagesLab 3 Bacterial Staining Techniques IIErreneoNo ratings yet
- Science 161222 1userupload - inDocument150 pagesScience 161222 1userupload - inDinesh GaikwadNo ratings yet
- WMGS Newsletter Summer 2013 EditionDocument6 pagesWMGS Newsletter Summer 2013 EditionWestern Michigan Genealogical SocietyNo ratings yet
- What Is A GeneDocument11 pagesWhat Is A GeneetdsdgNo ratings yet
- A&P Course SyllabusDocument4 pagesA&P Course SyllabusChristopher Rey BurceNo ratings yet
- STS Module 5-6Document3 pagesSTS Module 5-6なるNo ratings yet
- Practice Test A - Reading Question 1-10Document6 pagesPractice Test A - Reading Question 1-10Silence alfa0% (1)
- AA3 My Favorite City - Comparing Places Ejercicio FinalDocument6 pagesAA3 My Favorite City - Comparing Places Ejercicio FinalCesar Augusto Triana AyalaNo ratings yet
- The Selection Process WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Selection Process Worksheetapi-256236481No ratings yet
- Laboratory Exercise No. 1Document6 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 1jasper pachingelNo ratings yet
- 2016 - Historical and Cultural Aspects of Pineal Gland - Comparison Between The Theories Provided by Spiritism in The 1940s and The Currents Cientific EvidenceDocument12 pages2016 - Historical and Cultural Aspects of Pineal Gland - Comparison Between The Theories Provided by Spiritism in The 1940s and The Currents Cientific Evidencedick_henriqueNo ratings yet
- Zinc PCA Inhibits UVA-Induced MMP-1 and Enhances CollagenDocument6 pagesZinc PCA Inhibits UVA-Induced MMP-1 and Enhances CollagenVIỆT NAM NUHANCIAM100% (1)