Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Compound
Uploaded by
RUBY LYN PAGULONGOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Compound
Uploaded by
RUBY LYN PAGULONGCopyright:
Available Formats
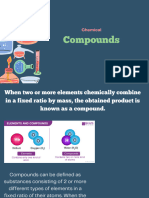
- When two or more elements chemically combine in a fixed ratio by mass,
the obtained product is known as a compound.
- Compounds can be defined as substances consisting of 2 or more
different types of elements in a fixed ratio of their atoms.
- chemical compound, any substance composed of
identical molecules consisting of atoms of two or more chemical
elements.
- Every element is designated by a unique symbol consisting of one, two,
or three letters arising from either the current element name or its
original (often Latin) name.
-
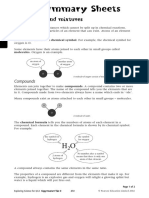
- Water, which is a chemical compound of hydrogen and oxygen in the
ratio two hydrogen atoms for every oxygen atom, contains H2O
molecules. Sodium chloride is a chemical compound formed
from sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) in a 1:1 ratio.
Classification of compounds
*Based on specific Element Present
Oxides - contain one or more oxygen atoms.
Hydrides - contain one or more hydrogen atoms, and halides contain one or
more halogen (Group 17) atoms.
Organic compounds - characterized as those compounds with a backbone of carbon
atoms, and all the remaining compounds are classified as inorganic.
*Based on the types of bonds that the compound contains
Organometallic compounds are organic compounds bonded to metal atoms.
Ionic compounds - contain ions and are held together by the attractive forces among
the oppositely charged ions.
Molecular compounds- contain discrete molecules, which are held together by sharing
electrons (covalent bonding).
*Based on reactivity
Acids - compounds that produce H+ ions (protons) when dissolved in water to produce
aqueous solutions. acids are defined as proton donors.
Bases - proton acceptors. The most common base is the hydroxide ion (OH−), which
reacts with an H+ ion to form a water molecule.
You might also like
- Chemistry - BSN 1Document6 pagesChemistry - BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Describing Matter 13-1 Notes Part 2Document7 pagesDescribing Matter 13-1 Notes Part 2Chenie CoronelNo ratings yet
- Substance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific PropertiesDocument8 pagesSubstance A Substance Is Matter Which Has A Specific Composition and Specific Propertiesaishajutt041No ratings yet
- 940 Elements Compounds MixturesDocument33 pages940 Elements Compounds MixturesEllen Grace Aguirre TobezaNo ratings yet
- A. Chemical Composition of The BodyDocument15 pagesA. Chemical Composition of The BodyShumail JANNo ratings yet
- Elements Compounds MixturesDocument33 pagesElements Compounds MixturesKunwar DaniyalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDocument3 pagesChemistry Form 4 Definition ListSyazana Mohd RosliNo ratings yet
- (CHEMISTRYDocument6 pages(CHEMISTRYcponnusamy411No ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListDocument3 pagesSPM Chemistry Form 5 Definition ListNursafika Bahira100% (1)
- Hidzqi SA - 15A - Assingment 3Document2 pagesHidzqi SA - 15A - Assingment 3hidzqiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Chemical Basis of LifeDocument6 pagesChapter 2: The Chemical Basis of LifeThalia LauNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Classifying MatterDocument14 pagesChapter 2 Classifying Matteranneth renteriaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Glossary and TermsDocument3 pagesChemistry: Glossary and TermsSIDDHANo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDocument3 pagesChemistry Form 4 Definition ListAliif IsmailNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDocument2 pagesChemistry Form 4 Definition ListRabbitNo ratings yet
- Compounds: From Elements To CompoundsDocument3 pagesCompounds: From Elements To CompoundsUnikeNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of LifeDocument8 pagesThe Chemistry of LifeAda Gay Olandia Serencio0% (1)
- Reviewer For Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesReviewer For Organic ChemistryJona MaeNo ratings yet
- SPM Definition ListDocument3 pagesSPM Definition ListWong Weng SiongNo ratings yet
- 3 CH 1 Sec 3 Compunds and Mixtures UploadDocument34 pages3 CH 1 Sec 3 Compunds and Mixtures Uploadapi-270861823No ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements & CompoundsDocument3 pagesAtoms, Elements & Compoundsalquran.queriesNo ratings yet
- Chemical Basis of LifeDocument38 pagesChemical Basis of LifeFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICS Notes 3Document3 pagesBIOENERGETICS Notes 3Hya LaniogNo ratings yet
- Form 1 2 Elements Compounds and Mixtures 1Document22 pagesForm 1 2 Elements Compounds and Mixtures 1Osmany MadrigalNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry Definition ListDocument2 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Definition ListYixin HowNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Matter: Atoms and MoleculesDocument6 pagesThe Nature of Matter: Atoms and Moleculesmelan pNo ratings yet
- Advbio CH 2 Student Notes 13-14Document4 pagesAdvbio CH 2 Student Notes 13-14Mary MaxwellNo ratings yet
- Laboratories For Their Reducing Properties.: 3 Hybridization)Document3 pagesLaboratories For Their Reducing Properties.: 3 Hybridization)nydia sierraNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument6 pagesDefinitionsali ahsan khanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3.1: Chapter 3: Periodicity - GlossaryDocument4 pagesWorksheet 3.1: Chapter 3: Periodicity - GlossaryNeha KabraNo ratings yet
- Unit# 2: Basics of Organic Chemistry: by Doc Hira Younas (DPT, Isrs)Document28 pagesUnit# 2: Basics of Organic Chemistry: by Doc Hira Younas (DPT, Isrs)Muaaz Tahir Muaaz TahirNo ratings yet
- Science DictionaryDocument14 pagesScience DictionaryLuhan BernasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compound - WikipediaDocument7 pagesChemical Compound - Wikipediatsvmpm1765No ratings yet
- CompoundsDocument7 pagesCompoundsapi-578650113No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Chemistry of LifeDocument23 pagesChapter 2 - The Chemistry of LifeDorothy AtilanoNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminology in ChemistryDocument4 pagesBasic Terminology in ChemistryHaider JalalNo ratings yet
- LQ 2 NotesDocument42 pagesLQ 2 NotesThe BluemanNo ratings yet
- Basic Oil-Field Chemistry Elements, Compounds, and MixturesDocument4 pagesBasic Oil-Field Chemistry Elements, Compounds, and MixturesAnonymous QM0NLqZONo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesAna Pinto MouraNo ratings yet
- Fred Redmore - ChemistryDocument12 pagesFred Redmore - ChemistryMark Anthony SantosNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument1 pageCHEMISTRYzoya last nameNo ratings yet
- Global Indian International School Uppal, Hyderabad Subject: Chemistry Chapter 3 .Atoms and MoleculesDocument13 pagesGlobal Indian International School Uppal, Hyderabad Subject: Chemistry Chapter 3 .Atoms and MoleculesKhatrasNo ratings yet
- O LVL Chem Definitions ListDocument6 pagesO LVL Chem Definitions Listacsbr4science170% (10)
- Chemistry SPM DefinitionsDocument3 pagesChemistry SPM DefinitionsUchiha Kimono80% (5)
- Quarter 2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesQuarter 2 Reviewervinz hanzel aguarillesNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument4 pagesAtoms and MoleculesHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- Guide QuestionsDocument8 pagesGuide QuestionsReading HubNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Central Science NotesDocument8 pagesChemistry The Central Science Noteslucykipper100% (1)
- Nature of MoleculesDocument41 pagesNature of MoleculesOentoeng JahjaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1Winrich Louise M. MontanoNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry Definition ListDocument3 pagesSPM Chemistry Definition ListLooiNo ratings yet
- Answers - For Questions 1 To 12Document3 pagesAnswers - For Questions 1 To 12jokish0% (1)
- Chemistry DefinitionDocument4 pagesChemistry DefinitionJaima Nahin NisheNo ratings yet
- Introduction-to-ChemistryDocument38 pagesIntroduction-to-ChemistryEGAS JAYSON RABENo ratings yet
- Bccaefce b01b 4dfd 9d12 46b537fd41feDocument23 pagesBccaefce b01b 4dfd 9d12 46b537fd41feSaltanat TurarovaNo ratings yet
- Science Dictionary Grade 9Document4 pagesScience Dictionary Grade 9Kristel Kaye BasasNo ratings yet
- 1610assignment 1 ListDocument7 pages1610assignment 1 Listapi-341205347No ratings yet
- Important Topics of ChemistryDocument7 pagesImportant Topics of ChemistrystrangeankitNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument1 pageCarbohydratesRUBY LYN PAGULONGNo ratings yet
- Light and SoundDocument1 pageLight and SoundRUBY LYN PAGULONGNo ratings yet
- Post Activity Report TemplateDocument3 pagesPost Activity Report TemplateRUBY LYN PAGULONGNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Week 1Document4 pagesScience 8 Week 1RUBY LYN PAGULONGNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideFrom EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesFrom EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Practical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationFrom EverandPractical Approaches to Method Validation and Essential Instrument QualificationNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 2: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNo ratings yet
- Dust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesFrom EverandDust Explosion and Fire Prevention Handbook: A Guide to Good Industry PracticesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsFrom EverandGuidelines for Integrating Process Safety into Engineering ProjectsNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionFrom EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Lime and Limestone: Chemistry and Technology, Production and UsesFrom EverandLime and Limestone: Chemistry and Technology, Production and UsesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)