Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cutting Room Activities
Uploaded by
Piyush singh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesOriginal Title
CUTTING ROOM ACTIVITIES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views6 pagesCutting Room Activities
Uploaded by
Piyush singhCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
9/21/2020 SPME
ASSIGNMENT-1
PIYUSH KUMAR SINGH
BFT/19/594
DFT SEM 3
CUTTING ROOM ACTIVITIES
Cutting is the process of separating a spread into garment
components as a replica of pattern pieces on a marker. It also
involves transferring marks and notches from the marker to
garment components to facilitate sewing.
The process flow in the cutting department is given below:
LAY PLANNING
It is a process that positions pattern templates onto fabric in
the most economical way. This prevents excess wastage of
fabric and as such ensures the garment is as cheap as it can be
to make. In the garment industry, computer aided design (CAD)
programs are used to facilitate this process.
MARKER PLANNING
Marker is a long thin paper which contains all necessary pattern
pieces for different sizes for a particular style of garments. The
pattern pieces are placed in the marker in such a way so that
the wastage would be least. Marker making can be done
manually and also automatically.
FABRIC SPREADING
The main aim of the spreading process is to lay the several
fabric plies essential for the production process to the marker
length without any tension on the fabric. The lay height
depends on the order size, volume of production, thickness of
fabric and equipment used.
FABRIC CUTTING PROCESS
After spreading is done, the cutting part comes. Purpose of
cutting is to separate fabric plies as replicas of the patterns in
the marker plan. It also involves transferring marks and notches
from the marker to garment components to facilitate sewing
Generally, there are two types of fabric cutting techniques, they
are portable cutting and stationary cutting.
PREPARATION FOR CUTTING
After the laying process has been completed, the spreader has
to recount the numbers of plies as in the cutting ticket. Then
the following additional steps have to done prior to cutting.
Moving the spreading machine aside
Facilitating shrinkage of the lay
Rechecking the marker
Fastening the marker to the spread
PREPARATION FOR ASSEMBLING PROCESS
NUMBERING: In this process, each garment component is
marked with a serial number of the layer in the cut. Normally
the numbering code contains garment size (e.g. Small, Medium,
Large), Marker number and layer sequence. The worker can set
the numbering format for each style and marker as desired.
PURPOSE OF NUMBERING:
1.To identify the right garment components of a garment (size,
color, and shade) when operators stitch the garment.
In case, sewing operator stitches a garment taking components
from different layers, there might a chance of shade variation in
the finished garment. This process helps factory to reduce
quality issue related to shade variation.
Most of the times, more than one sizes of the garment is
loaded in the production line. When bundles are open and
move on the machines, there might be a chance of taking
garment parts from different bundles of garment sizes. This
layer number helps an operator to identify correct size of the
component.
SORTING: In this process patterns are sorts according to size
and design and makes bundles of them. This step requires
much precision because making bundles of mismatched
patterns can create severe problems. On each bundle there are
specifications of the style size and the marker too is attached
with it.
BUNDLING: In this process as per the production line
requirement, a certain number of pieces with all components
are tied together. Each bundle is marked with bundle number,
style name, size number and quantity of pieces in that bundle.
At this stage, cuttings are ready to send to a production line for
stitching.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF RESIN
MATERIAL USED FOR FUSING.
1.Polyethylene Coated Interlining: Polyethylene is used as
resin coating. The effect of varying the density of the resin is to
give a greater resistance to dry cleaning solvents and a higher
softening point with increasing density. This type of interlining
is used in collar, cuff of shirt. The fabric attached with this type
of interlining can be washed in water.
2.Polyamide Coated Interlining: Polyamide is used as resin
coating. Poly-amides are very widely used in dry cleanable
garments. High temperature fusing is done for the garments,
which are washed with water at 60ºc.
3.PVC Coated Interlining: Poly vinyl chloride is used as resin
coating This type is suitable for both dry cleanable and
washable garments. PVC coated interlining is widely used for
making the coat type garments.
4.Polyester Coated Interlining: Polyester is used as resin
coating Polyester resins are used in dry cleanable and washable
garments because polyester is less water absorbent than
polyamide. It can be used as in all types of garments. This is
called ideal interlining Available in market but costly in price.
5.Polypropylene Coated Interlining: Polypropylene coated
interlining. The resin is similar to the properties of polyethylene
coated interning Comparatively high temperature fusing is
done. The fabric attached with this interlining can be washed
with water.
6.PVA Coated Interlining: PVA coated interlining. Poly vinyl
acetate is used as resin coating PVA coated interlining is not dry
cleanable and it has limited wash ability Low temperature and
pressure is required. Basically, it is used between the leather
and fur materials. The resin is normally in the form of a
continuous plasticized coating on the base fabric. This type is
rarely used in garments industry.
You might also like
- Complete Book of Sewing Techniques, New 2nd Edition: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterFrom EverandComplete Book of Sewing Techniques, New 2nd Edition: More Than 30 Essential Sewing Techniques for You to MasterRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Cutting Processes Garment Industry EbookDocument22 pagesCutting Processes Garment Industry Ebookkarthikeyan100% (1)
- Process Flow of Cutting and Cutting EquipmentDocument8 pagesProcess Flow of Cutting and Cutting EquipmentarunkadveNo ratings yet
- Marker PlaningDocument11 pagesMarker Planingtextile028100% (1)
- Improve Cutting Room Process with Customized Cut-PlansDocument3 pagesImprove Cutting Room Process with Customized Cut-Plansaadarsh mahajanNo ratings yet
- Spreading and Cutting of Apparel ProductsDocument77 pagesSpreading and Cutting of Apparel ProductskbalabalaNo ratings yet
- Katle GoDocument17 pagesKatle GoKenewendo Kapinga ThebeNo ratings yet
- Garments Manufacturing Process: Stepwise Garments ManufacturingDocument24 pagesGarments Manufacturing Process: Stepwise Garments ManufacturingAnamika Priyadarshini100% (1)
- GCT Lec 2 Cutting Room 2014Document42 pagesGCT Lec 2 Cutting Room 2014Eshetu DeribNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Processes (Cutting Part 1) : Learn Apparel Merchandising Learn Fashion DesigningDocument7 pagesPreparatory Processes (Cutting Part 1) : Learn Apparel Merchandising Learn Fashion DesigningZaman ParvezNo ratings yet
- Cutting Room ManagementDocument6 pagesCutting Room ManagementRH NiloyNo ratings yet
- Kura AaaaaaaDocument18 pagesKura AaaaaaaKurabachew BekeleNo ratings yet
- Marker MakingDocument6 pagesMarker MakingBharti Pahuja100% (1)
- Introduction To Cutting Room: Lecturer-1Document8 pagesIntroduction To Cutting Room: Lecturer-1nahidNo ratings yet
- Cutting Room OverviewDocument3 pagesCutting Room OverviewraindfNo ratings yet
- Organizational Areas in Garment ManufacturingDocument7 pagesOrganizational Areas in Garment ManufacturingIshan RastogiNo ratings yet
- Fabric Spreading and Cutting Section of Garments Industry: Textile AssignmentDocument16 pagesFabric Spreading and Cutting Section of Garments Industry: Textile AssignmentJulie MerrillNo ratings yet
- Marker Making Preparation and Its FactorsDocument10 pagesMarker Making Preparation and Its Factorsmorshed_mahamud7055100% (1)
- Garment Production Starts With The Cutting ProcessDocument3 pagesGarment Production Starts With The Cutting ProcessrajasekaranvgNo ratings yet
- Garment Production Process OverviewDocument10 pagesGarment Production Process OverviewAbu UmarNo ratings yet
- Garment Manufacturi NG: Assignment-4Document25 pagesGarment Manufacturi NG: Assignment-4You Kno WhoNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Steps: 1.receiving FabricsDocument22 pagesManufacturing Steps: 1.receiving FabricsHaq ChandioNo ratings yet
- Garment Manufacturing and Quality AssuranceDocument9 pagesGarment Manufacturing and Quality AssuranceGaurav BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Sample Section:It Is The First Section Of: Garment Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 pagesSample Section:It Is The First Section Of: Garment Manufacturing ProcesssantumysoreNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument11 pagesAssignmentAshraful Islam Sagor100% (1)
- Knitwear Technology (Cutting & Sewing) - APM 7402 - Note Book-1Document25 pagesKnitwear Technology (Cutting & Sewing) - APM 7402 - Note Book-1shahinrezaNo ratings yet
- Cutting Room in Apparel IndustryDocument25 pagesCutting Room in Apparel IndustryPriyanka RoyNo ratings yet
- Clothing 6Document6 pagesClothing 6Nahabwe ElisaNo ratings yet
- English Assingment GarmentsDocument8 pagesEnglish Assingment GarmentsKhalid abdiwasicNo ratings yet
- Marker Making ParametersDocument20 pagesMarker Making ParametersRavi Shankar100% (1)
- Cutting and Spreading Fabric EfficientlyDocument7 pagesCutting and Spreading Fabric EfficientlyAlemu HaileNo ratings yet
- SMEDA-JICA Best Practices for Garments CuttingDocument65 pagesSMEDA-JICA Best Practices for Garments CuttingRafayMalikNo ratings yet
- SopDocument23 pagesSopAl Arafat RummanNo ratings yet
- Cutting PortionDocument20 pagesCutting PortionAbdul RafayNo ratings yet
- Cutting Room PlanningDocument33 pagesCutting Room PlanningSreedhara AkankshaNo ratings yet
- Apparel Manufacturing PPTDocument21 pagesApparel Manufacturing PPTkaleabandebet7No ratings yet
- Fabric Cutting and Spreading Process ExplainedDocument18 pagesFabric Cutting and Spreading Process ExplainedAmeesha PawarNo ratings yet
- Scap Assessment Jayesh ThoolDocument26 pagesScap Assessment Jayesh ThoolJayesh ThoolNo ratings yet
- Smeda-Jica Industry Support Program: Small and Medium Enterprises Development AuthorityDocument65 pagesSmeda-Jica Industry Support Program: Small and Medium Enterprises Development AuthoritySAILAYS100% (2)
- Cutting Room Planning: ATDC, BhubaneswarDocument37 pagesCutting Room Planning: ATDC, BhubaneswarBinoy MundaNo ratings yet
- Scap By: Chandra Shekhar Kumar Dipti Kumar Louhit Manuraj KumarDocument19 pagesScap By: Chandra Shekhar Kumar Dipti Kumar Louhit Manuraj KumarNikita KalraNo ratings yet
- Factory Report 2Document6 pagesFactory Report 2Chen Wei Sassei-KetsuNo ratings yet
- SpreadingDocument7 pagesSpreadingsporti1412No ratings yet
- Production Process of Garments Manufacturing UnitDocument6 pagesProduction Process of Garments Manufacturing UnitNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF FASHION TECHNOLOGY, MUMBAIDocument38 pagesNATIONAL INSTITUTE OF FASHION TECHNOLOGY, MUMBAIPrakriti100% (4)
- Textile IndustryDocument11 pagesTextile IndustryPRATHIYUMAN JNo ratings yet
- Module-3 Marker PlanningDocument17 pagesModule-3 Marker PlanningMadhurendra Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument13 pagesConcept NoteVaswee Dubey100% (1)
- National Institute of Fashion Technology: HyderabadDocument40 pagesNational Institute of Fashion Technology: HyderabadGreeshmaNo ratings yet
- Garment Manufacturing: History of Garment IndustryDocument7 pagesGarment Manufacturing: History of Garment IndustryVictoria RolloNo ratings yet
- Objective of Marker Planning and Marker MakingDocument4 pagesObjective of Marker Planning and Marker MakingSanthosh KannanNo ratings yet
- Marker MakingDocument10 pagesMarker MakingRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Marker Making Guide: Layout, Efficiency, Methods & DuplicationDocument10 pagesMarker Making Guide: Layout, Efficiency, Methods & DuplicationM.José Copons GalloNo ratings yet
- SpreadingDocument8 pagesSpreadingsporti1412No ratings yet
- Marker PlanningDocument6 pagesMarker PlanningAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Apparel Production OverviewDocument121 pagesApparel Production OverviewBianca AndronacheNo ratings yet
- Cutting Room Cost ReductionDocument39 pagesCutting Room Cost ReductionSwapnil LalNo ratings yet
- Typs of Fabric LossDocument2 pagesTyps of Fabric LossarunkadveNo ratings yet
- Garment ManufacturingDocument9 pagesGarment ManufacturingSauumye Chauhan0% (1)
- Fundamentals Garment ConstructionDocument30 pagesFundamentals Garment ConstructionGashaw Fikir AdugnaNo ratings yet
- Critical ThikingDocument7 pagesCritical ThikingPiyush singhNo ratings yet
- CT AssignmentDocument17 pagesCT AssignmentPiyush singhNo ratings yet
- Sewn Product Machinery Equipment T-Shirt DiagramDocument10 pagesSewn Product Machinery Equipment T-Shirt DiagramPiyush singhNo ratings yet
- Ancient EgyptDocument6 pagesAncient EgyptPiyush singhNo ratings yet
- How Does VMI Works: Advantages of Vendor Managed InventoryDocument2 pagesHow Does VMI Works: Advantages of Vendor Managed InventoryPiyush singhNo ratings yet
- CKB 20104 - Reaction EngineeringDocument9 pagesCKB 20104 - Reaction EngineeringNoor FatihahNo ratings yet
- HW ID AmendmentDocument1 pageHW ID AmendmentZhu Chen ChuanNo ratings yet
- N 252Document34 pagesN 252miguelgg78No ratings yet
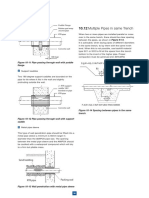
- Multiple Pipes in Same Trench: Figure 9-14Document1 pageMultiple Pipes in Same Trench: Figure 9-14norman moralesNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange and Titration Detn Co and NiDocument6 pagesIon Exchange and Titration Detn Co and NiHoang ThaoNo ratings yet
- Acronal LA 471 SDocument2 pagesAcronal LA 471 SrallemNo ratings yet
- BO-0475 - Const - Work - Pro - For Gasket Install (Rev 0) - 20150605Document35 pagesBO-0475 - Const - Work - Pro - For Gasket Install (Rev 0) - 20150605Rijwan MohammadNo ratings yet
- Materials Research Bulletin: H.S. Khalsa, M.D. Smith, H.-C. Zur LoyeDocument4 pagesMaterials Research Bulletin: H.S. Khalsa, M.D. Smith, H.-C. Zur LoyeLulueleNo ratings yet
- QUIMICAmarkscheme HL Paper2Document22 pagesQUIMICAmarkscheme HL Paper2Fiona DonovanNo ratings yet
- 1-2014 Aguilar Et Al Analysis of The Feasibility of The Recovery of Landfill Gas A Case Study of MexicoDocument8 pages1-2014 Aguilar Et Al Analysis of The Feasibility of The Recovery of Landfill Gas A Case Study of MexicoZero litaNo ratings yet
- CFD Study of Diesel Oil Hydrotreating Process in Thenon-Isothermal Trickle Bed ReactorDocument16 pagesCFD Study of Diesel Oil Hydrotreating Process in Thenon-Isothermal Trickle Bed Reactoramir_chemengNo ratings yet
- DBSTDocument25 pagesDBSTAnonymous Dyk8Z39evNo ratings yet
- Endonucleases (Comp)Document14 pagesEndonucleases (Comp)Fatima HabibNo ratings yet
- KFT SERUMDocument6 pagesKFT SERUMDeepanshu Singh KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Child Safety For Apparel ProductionDocument20 pagesChild Safety For Apparel ProductionAshraf AliNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 4: Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic ChemistryDocument14 pagesEdexcel IAL Chemistry A-Level: Unit 4: Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic ChemistryMer CyNo ratings yet
- Vibrational S Ctroso) In/: ReviewDocument9 pagesVibrational S Ctroso) In/: ReviewAchyut JamadagniNo ratings yet
- LAS 3 - Solution ProcessDocument2 pagesLAS 3 - Solution ProcessDaniella Izabelle SaguinNo ratings yet
- NORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For HearingDocument146 pagesNORSOK M-630 Edition 6 Draft For Hearingcaod1712100% (1)
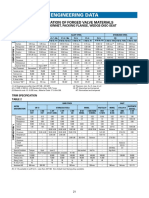
- Forged Engineering DataDocument4 pagesForged Engineering DataretrogradesNo ratings yet
- Triple Effect EvaporatorDocument9 pagesTriple Effect Evaporatorjnmanivannan100% (1)
- QUIZ Confined Space Rescue AnswersDocument3 pagesQUIZ Confined Space Rescue AnswersEdwardNo ratings yet
- Nitrobacter WinogradskyDocument7 pagesNitrobacter WinogradskyFerryKurniawanNo ratings yet
- Destilation Column InfoDocument33 pagesDestilation Column InfokumarNo ratings yet
- Welding of Nickel AlloysDocument12 pagesWelding of Nickel Alloysaj87_goswamiNo ratings yet
- MasterFormat - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesMasterFormat - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMartin SabahNo ratings yet
- Cabbage Production GuideDocument11 pagesCabbage Production GuideMbingose MwanzaNo ratings yet
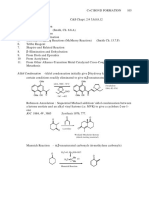
- C=C Bond Formation Reaction OverviewDocument12 pagesC=C Bond Formation Reaction Overviewaggelisgeorge8546No ratings yet
- A Review On Polymer-Layered Silicate NanocompositesDocument80 pagesA Review On Polymer-Layered Silicate Nanocompositesjyotiranjan_roulNo ratings yet
- Cetiol® Ultimate - SDS - Europe - en 191008Document14 pagesCetiol® Ultimate - SDS - Europe - en 191008mengyizhu668No ratings yet
- To Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryFrom EverandTo Pixar and Beyond: My Unlikely Journey with Steve Jobs to Make Entertainment HistoryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (26)
- $100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffFrom Everand$100M Leads: How to Get Strangers to Want to Buy Your StuffRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Bare Bones: I'm Not Lonely If You're Reading This BookFrom EverandBare Bones: I'm Not Lonely If You're Reading This BookRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Writing Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsFrom EverandWriting Screenplays That Sell: The Complete Guide to Turning Story Concepts into Movie and Television DealsNo ratings yet
- The Black Star of Kingston: Tales of Old Natalia 1From EverandThe Black Star of Kingston: Tales of Old Natalia 1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (152)
- Summary: Greenlights: by Matthew McConaughey: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Greenlights: by Matthew McConaughey: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- I Didn't Come Here to Make Friends: Confessions of a Reality Show VillainFrom EverandI Didn't Come Here to Make Friends: Confessions of a Reality Show VillainRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (47)
- They Can't Kill Us Until They Kill UsFrom EverandThey Can't Kill Us Until They Kill UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (36)
- The Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisFrom EverandThe Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (49)
- Altamont: The Rolling Stones, the Hells Angels, and the Inside Story of Rock's Darkest DayFrom EverandAltamont: The Rolling Stones, the Hells Angels, and the Inside Story of Rock's Darkest DayRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (25)
- Twilight of the Gods: A Journey to the End of Classic RockFrom EverandTwilight of the Gods: A Journey to the End of Classic RockRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (28)
- The Gardner Heist: The True Story of the World's Largest Unsolved Art TheftFrom EverandThe Gardner Heist: The True Story of the World's Largest Unsolved Art TheftNo ratings yet