Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry
Uploaded by
Safalsha BabuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry
Uploaded by
Safalsha BabuCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 5 – COMPOUNDS OF NON-METALS
1. Reactants used for the laboratory preparation of Ammonia are -------- and -------
2. Drying agent used in the laboratory preparation of ammonia is -----
3. In a reversible reaction the reaction from left to right is called ----
4. Which is the basic nature substance formed by the decomposition of ammonium chloride?
5. Write the backward reaction from the following reversible reaction.
6. Write the name of a concentrated aqueous solution of ammonia?
7. Which of the following is true about the reversible reaction?
i) Reaction stops after some time.
ii) Reaction attain equilibrium after some time
iii) Reaction takes place only in one direction.
8. What is the optimum temperature used in the manufacture of ammonia?
9. Which of the following substance is used as a refrigerant in ice plants?
10. Identify the reactions A and B
11. In which of the following reversible reactions the change in pressure does not influence the
equilibrium? What is the reason?
12. Calcium oxide (CaO) is used as a drying agent in the preparation of Ammonia in the laboratory. Can
concentrated H2SO4 be used as a drying agent instead of CaO? Justify your answer.
13. Analyse the following diagram and observations given below.
a) Which is the white substance formed here?
b) Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction?
14. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH 3 (g) + Heat
a) What change is to be made in pressure to get the maximum yield of the products?
b) What is the change in concentration of product is required for increasing the rate of the forward
reaction?
15. Ammonia is a gas that is highly soluble in water and it can be liquefied easily by applying pressure.
a) What is the name of a concentrated aqueous solution of ammonia?
b) What is the name of liquefied ammonia?
16. Ammonia is manufactured by the Haber process.
a) What is the optimum temperature used in this process?
b) Write any two uses of ammonia?
17. A reversible reaction can attain chemical equilibrium after some time.
a) Write any one characteristic of chemical equilibrium?
b) What happens when the concentration of reactants is increased at chemical equilibrium? 18. 2NO(g)
+ O2(g) ⇌ 2NO2 (g) + Heat
Identify the effect of the following changes in forward reaction.
a) Pressure is decreased.
b) Products are frequently removed from the system.
19. The graph for the reaction N2 +3H2 ⇌ 2NH3 is given below. Analyze it and answer the following
questions
a) Identify the reactions C and D
b) Which stage of the reaction is shown by the portion AB of the graph?
20. Take some ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) in a boiling tube and heat it. When a wet red litmus showed
at the mouth of the boiling tube it changes to blue.
a) Which are gases produced?
b) Write the chemical equation of the reaction that occurred here?
c) Which gas is responsible for the color change of the litmus paper?
21. a) What are the reactants used in the laboratory preparation of ammonia?
b) Write the balanced chemical equation of the reaction?
c) Which is a drying agent used?
d) Ammonia is collected in the gas jar by keeping the mouth downwards. Why?
22. N2(g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌ 2NH3 (g) + Heat.
What happens in the yield of ammonia when the following changes are made?
a) Concentration of Nitrogen is increased.
b) Temperature is decreased.
c) NH3 is removed from the system.
d) Pressure is increased.
CHAPTER 6 - NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS AND ISOMERISM
1. The general formula of alkanes is -----------
2. The general formula of alkynes is ----------
3. Find the odd one out
(C2H6, C3H8, C5H10, C6H14)
4. Find the missing member in the following homologous series.
C2H2, C3H4, C4H6 , ............. , C6H10
5. Which of the following is an unsaturated compound?
(C2H6, C3H4, C5H12, C6H14)
6. Which of the following is a saturated compound?
(C2H6, C3H6, C5H8, C6H12)
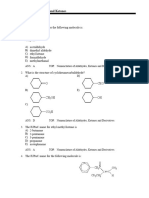
7. Name of the functional group OH is ---------
8. Write the structure of but – 2 – yne.
9. Molecular formulae of some hydrocarbons are given.
a) To which Homologous series do these belong?
b) Write its general formula?
10. A structure of hydrocarbon is given below
CH3 −CH2 −CH2 −CH2 −CH2 −CH3
a) Write its IUPAC name?
b) In which homologous series does this compound belongs?
11. Details regarding an unsaturated hydrocarbon are given below.
• There are five carbon atoms in the main chain.
• A double bond is present between the second and third carbon atoms.
a) Write the structure of this compound?
b) Write the IUPAC name of the compound?
12. A student writes the IUPAC name of an organic compound as 2-ethyl Pentane. The teacher says that
it is wrong.
a) Draw the structure of this compound.
b) Write its correct IUPAC name.
Each question from 13 to 14 carries 3 marks
13 Analyse the given structures and answer the following questions.
a) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – O – CH3
b) CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH
c) CH3 – CH2 – O – CH3
i) Identify the isomer pair from the above compounds.
ii) Which type of isomerism is exhibited?
iii) Write the structural formula of the position isomer of compound (b)?
14. Structure of alcohol is given below. Analyze and answer the following questions.
CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – OH
a) Write the IUPAC name of this compound?
b) Write the structure and IUPAC name of a functional isomer of this Compound?
15. Analyse the structure and answer the following questions.
a) How many carbon atoms are in the main chain?
b) what is the position of the branch?
c) What is the name of the branch?
d) Write its IUPAC name?
16. Complete the table
17. Structural formulas of some organic compounds are given below
a) Write the structure of the chain isomer of the compound (i)
b) Which compounds have the same molecular formula?
c) Write the structural formula and IUPAC name of a functional isomer of the compound (iii)
CHAPTER 7 CHEMICAL REACTIONS OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
1. Which is the monomer of Teflon?
2.CH3 - CH2 -CH3 ⟶ A + CH4
What is the molecular formula of compound A?
3. Which is the main component of LPG?
4. Which of the following molecule can undergo an addition reaction?
(Methane, Ethane, Propane, Butane)
5.CH3 - CH = CH2 + H2 ⟶ A
Write the IUPAC name of compound A.
6.
a) What is the IUPAC name of compound A?
b) To which type does this reaction belong?
(Addition reaction, Substitution reaction, Combustion, Polymerisation)
7. a) Which is the main component of LPG?
b) What are the products obtained by the combustion of LPG?
8. CH3 - CH2 -CH3 ⟶ A + CH4
a) Write the structural formula of compound A.
b) Which type of chemical reaction is this?
9. Given below are two chemical equations.
a) Identify the products X and Y.
b) By which name this type of reaction is known?
10. Complete the following equations
11. Match the columns A, B, and C suitably.
12. The given table is related to different types of reactions of hydrocarbons. Fill in the blanks.
You might also like
- BIO-VISION SSLC Set III Chemistry em - A Pre Model 2024 MalappuramDocument2 pagesBIO-VISION SSLC Set III Chemistry em - A Pre Model 2024 Malappuramnairvinodkumar79No ratings yet
- Problem Set - Organic ChemDocument7 pagesProblem Set - Organic ChemGela EcalNo ratings yet
- BIOKMOR N01 3rd ExamDocument8 pagesBIOKMOR N01 3rd ExamMacy MarianNo ratings yet
- Chapter_09Document15 pagesChapter_09Sara NameerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 MergedDocument38 pagesChapter 08 MergedreemNo ratings yet
- CH7 Alcoholsphenols and Ethers HHW WorksheetDocument4 pagesCH7 Alcoholsphenols and Ethers HHW WorksheetAaditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chem c2 Exer1Document3 pagesChem c2 Exer1jalrizal7No ratings yet
- Prelims Review: Organic Chemistry QuestionsDocument12 pagesPrelims Review: Organic Chemistry QuestionsMarjorie Ann GabuatNo ratings yet
- Class X Term Ii Fa Science PDFDocument15 pagesClass X Term Ii Fa Science PDFgodwinmodernschoolNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample Paper 2Document6 pagesChemistry Sample Paper 2Koushiki Chakraborty 10 f 27No ratings yet
- 2017 2018 Dis Org (TR) 1 Komite Soru8 DuzeltilmisDocument10 pages2017 2018 Dis Org (TR) 1 Komite Soru8 DuzeltilmisTiba MohammedNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by Hart DownloadDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry A Short Course 13th by Hart Downloaddannyriddle05051994ieq100% (23)
- Revision ChemDocument32 pagesRevision ChemNada AlbuainainNo ratings yet
- Aromatic Compounds Chapter 5 ReviewDocument23 pagesAromatic Compounds Chapter 5 ReviewKayeNo ratings yet
- Che 232 Test 1b 2016 AnsDocument12 pagesChe 232 Test 1b 2016 AnsBONOLO RANKONo ratings yet
- JR Chemistry Imp Vsaq 2023-24Document4 pagesJR Chemistry Imp Vsaq 2023-24masarathbegum94No ratings yet
- International Indian School Chemistry Worksheet on Carbon CompoundsDocument4 pagesInternational Indian School Chemistry Worksheet on Carbon CompoundsRaghav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid - Xii Group-2-2023Document14 pagesAldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic Acid - Xii Group-2-2023Shashwat R TripathyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its CompoundDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Carbon and Its Compoundomm2500100% (1)
- Examen 1Document12 pagesExamen 1Sahimara de JesúsNo ratings yet
- A-Level Organic Chemistry Test: Key Concepts CoveredDocument5 pagesA-Level Organic Chemistry Test: Key Concepts CoveredTubocurareNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Q1 M 5-6Document12 pagesGen Chem 1 Q1 M 5-6Joselito UbaldoNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument6 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundsPramod SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Practice Paper-3Document4 pagesHydrocarbon Practice Paper-3sandysrilakshmiNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde Ketone &carboDocument18 pagesAldehyde Ketone &carboFaraz KhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 4-Carbon and Its CompoundDocument2 pagesCHAPTER - 4-Carbon and Its CompoundHimanshu JainNo ratings yet
- DIAGNOSTIC EXAM IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument4 pagesDIAGNOSTIC EXAM IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRYMANUEL, BUSTY P.No ratings yet
- Set 2Document6 pagesSet 2sanjith4arisNo ratings yet
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set 4Document5 pagesCBSE Sample Paper Class 12 Chemistry Set 4Sidharth SabharwalNo ratings yet
- Exam Three Practice TestDocument13 pagesExam Three Practice TestBUCH203100% (1)
- Chapter 11 and 12 Alcohol and Ether ReviewDocument8 pagesChapter 11 and 12 Alcohol and Ether ReviewREGINE CUEVASNo ratings yet
- 2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 1Document9 pages2nd PU Chemistry Model QP 1Prasad C M100% (2)
- Organic Chem (With Solution) 2Document75 pagesOrganic Chem (With Solution) 2vlNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem Intro Qs 3.: (Total 1 Mark)Document7 pagesOrganic Chem Intro Qs 3.: (Total 1 Mark)Nika Johanne SCHOLTENo ratings yet
- Practice Exam I - Organic ChemsitryDocument14 pagesPractice Exam I - Organic ChemsitryDave KowalczykNo ratings yet
- TS - JR - Chemistry - Imp - Questions 2023-24Document6 pagesTS - JR - Chemistry - Imp - Questions 2023-24chatlanagababu1986No ratings yet
- Chapter Sk027 OverviewDocument12 pagesChapter Sk027 OverviewNor AfidahNo ratings yet
- Alkenes TutorialDocument8 pagesAlkenes TutorialVarshLokNo ratings yet
- Grade12Pre Boardexamination QPChemistryQPSET1Document7 pagesGrade12Pre Boardexamination QPChemistryQPSET1BigsmokeNo ratings yet
- Exercise: AlkaneDocument17 pagesExercise: AlkaneHenerita RayNo ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - FinalDocument65 pagesXII Chemistry Sample Question Paper - Finalkrishnapradhani091No ratings yet
- QP-Chemistry-12-Practice Paper-1Document8 pagesQP-Chemistry-12-Practice Paper-1piyushchampion2006No ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY QUESTION PAPERDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRY QUESTION PAPERRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science - Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science - Carbon and Its CompoundsAbhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes Test Questions 20aug2023Document3 pagesHaloalkanes Test Questions 20aug2023Robert DanielNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SET C QPDocument9 pagesChemistry SET C QPowenknight3456No ratings yet
- Ujian 2 Form 5Document9 pagesUjian 2 Form 5Nazreen NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Che 232 Test 1 Sptember 2007Document16 pagesChe 232 Test 1 Sptember 2007BONOLO RANKONo ratings yet
- Chemsitry 09.12.2022Document4 pagesChemsitry 09.12.2022santhosNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- XII Chemistry Paper CBSEDocument3 pagesXII Chemistry Paper CBSESanjna ParikhNo ratings yet
- Exercise AlkaneDocument17 pagesExercise Alkanerudi_zNo ratings yet
- Exam Three Practice Test Answers PDFDocument19 pagesExam Three Practice Test Answers PDFBUCH203100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic Chemistry with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNo ratings yet
- Super ReportDocument21 pagesSuper ReportSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- ThedDocument15 pagesThedSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- DynaDocument19 pagesDynaSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- S A Niknamandv songmeneINLACO2013Document11 pagesS A Niknamandv songmeneINLACO2013Safalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Wing-In-ground-effect Craft A Case Study in AerodyDocument5 pagesWing-In-ground-effect Craft A Case Study in AerodySafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Axial Field Electrical MachinesDocument20 pagesAxial Field Electrical Machinesవారణాసిరవిసత్యలక్ష్మీనరసింహ. శాస్త్రి100% (1)
- 3Document19 pages3Safalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- CRDocument17 pagesCRSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- SuperDocument21 pagesSuperSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Awh Polytechnic College: Seminar ReportDocument6 pagesAwh Polytechnic College: Seminar ReportSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- NBCDocument27 pagesNBCSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Cryogenic Materials and Circuit Integration For Quantum ComputersDocument15 pagesCryogenic Materials and Circuit Integration For Quantum ComputersSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Sanu 39Document5 pagesSanu 39Safalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Transport Airplane, Which Is Purposely Deemed To Exploit Ground-Effect (8) - Some GroundDocument14 pagesTransport Airplane, Which Is Purposely Deemed To Exploit Ground-Effect (8) - Some GroundSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- NafihDocument6 pagesNafihSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Gyrobus Seminar Report Details Early Electric BusDocument24 pagesGyrobus Seminar Report Details Early Electric BusVara Lakshmi100% (1)
- Fig 1.1 Axial-Field Electrical MachineDocument26 pagesFig 1.1 Axial-Field Electrical MachineSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Ece Free Space OpticsDocument14 pagesEce Free Space OpticsSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Engine Heat Sink Thermal Energy Recovery SystemDocument10 pagesEngine Heat Sink Thermal Energy Recovery SystemSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Ece Free Space Optics Report PDFDocument24 pagesEce Free Space Optics Report PDFBhavya PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document17 pagesChapter 1Safalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- SreenathDocument6 pagesSreenathSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- SuperadobeDocument27 pagesSuperadobeSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Heat SinkDocument14 pagesHeat SinkSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Ece Free Space Optics Report PDFDocument24 pagesEce Free Space Optics Report PDFBhavya PatelNo ratings yet
- 2Document18 pages2Safalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- The Design and Fabrication of An Improved Diesel Powered Hydraulic Red Brick Molding MachineDocument8 pagesThe Design and Fabrication of An Improved Diesel Powered Hydraulic Red Brick Molding MachineSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- MUHAMMED - ASHIQ PT - Resume - 02-02-2023-13-23-28Document1 pageMUHAMMED - ASHIQ PT - Resume - 02-02-2023-13-23-28Safalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Axial Field Electrical MachinesDocument20 pagesAxial Field Electrical Machinesవారణాసిరవిసత్యలక్ష్మీనరసింహ. శాస్త్రి100% (1)
- Business Process Reengineering: A Recent Review: December 2014Document29 pagesBusiness Process Reengineering: A Recent Review: December 2014muhsin alamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 2 Term 1 2024Document11 pagesChemistry Form 2 Term 1 2024DenisNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry WorkbookDocument147 pagesYear 11 Chemistry WorkbookVikas86% (7)
- CH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Document37 pagesCH 14-VP-Stoichiometry - 2020Mlamuli MlarhNo ratings yet
- 1 Organic Chemistry of Aliphatic CompoundsDocument12 pages1 Organic Chemistry of Aliphatic CompoundsSholpanNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metallurgy 11638Document4 pagesSheet Metallurgy 11638moazmizo211No ratings yet
- 2.1 Molecules To MetabolismDocument44 pages2.1 Molecules To MetabolismJianing Claire LiNo ratings yet
- Chemestry CollageDocument85 pagesChemestry CollageET039 Sudhabrata SahooNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Unit3Document196 pagesGrade 10 Science Unit3BuddyNo ratings yet
- Learn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-ChemistryDocument32 pagesLearn: Chapter-10 Haloalkanes & Haloarenes Class-XII Subject-Chemistryprajaktac506No ratings yet
- Biochem TestADocument6 pagesBiochem TestAaby251188No ratings yet
- iGCSE Chemistry Section 1Document93 pagesiGCSE Chemistry Section 1irma.javashviliNo ratings yet
- Types of Chemical Reactions ExplainedDocument27 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions ExplainedSheena LidasanNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry-2: Action of Alkali On Certain MetalsDocument3 pagesAnalytical Chemistry-2: Action of Alkali On Certain MetalsManju YadavNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2nd MEDocument3 pagesGen Chem 2nd MEJay Cariel GastonesNo ratings yet
- DLL Matter G7 Q1.W4 5.D1Document6 pagesDLL Matter G7 Q1.W4 5.D1Rowena Sta Maria50% (2)
- Atomic Structure: 4.1 Defining The AtomDocument34 pagesAtomic Structure: 4.1 Defining The Atomnayef aNo ratings yet
- M4 Chemistry BondingDocument23 pagesM4 Chemistry BondingDalvie OliverosNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Org ChemDocument14 pagesFundamental of Org ChemLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology The Dynamic Science 4th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Biology The Dynamic Science 4th Editionoscines.filicide.qzie100% (45)
- Chemistry Final Exam Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesChemistry Final Exam Practice Problemssrinath parvatine100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solution ManualDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With Integrated Study Guide 5th Edition Gunstream Solution Manualelizabeth100% (25)
- 5070 s11 QP 11Document16 pages5070 s11 QP 11chuasioklengNo ratings yet
- Formula Mass/Molecular Mass: A. Moles To Number of Atoms/molecules/particlesDocument5 pagesFormula Mass/Molecular Mass: A. Moles To Number of Atoms/molecules/particlescjNo ratings yet
- Fundamental concepts in chemistryDocument38 pagesFundamental concepts in chemistryÂfñåņ AhmedNo ratings yet
- Vogel - Qualitative Inorganic Analysis, 5 EdDocument617 pagesVogel - Qualitative Inorganic Analysis, 5 EdThuane SalesNo ratings yet
- Polyatomic Ions ExplainedDocument4 pagesPolyatomic Ions ExplainedIBRAHIM ABOU EL NAAJNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-11-23 at 8.02.39 AMDocument84 pagesScreenshot 2023-11-23 at 8.02.39 AMNURUL IZZA HUSINNo ratings yet
- Science: Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesScience: Organic CompoundsCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases Salts WorksheetDocument5 pagesAcid Bases Salts WorksheetAvani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Matter TestDocument4 pagesChapter 2 Matter TestSheryl Jane P. SilangNo ratings yet