Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Geotechnical Engineering Is The Branch of Civil Engineering Concerned With The Engineering Behavior of Earth Materials
Uploaded by
ann valerie reyesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Geotechnical Engineering Is The Branch of Civil Engineering Concerned With The Engineering Behavior of Earth Materials
Uploaded by
ann valerie reyesCopyright:
Available Formats
Geotechnical engineering is the branch of civil engineering concerned with the engineering behavior of
earth materials. It uses the principles of soil mechanics and rock mechanics for the solution of its
respective engineering problems.
3 branches of Geotechnical Engineering
• Soil Mechanics
• Rock Mechanics
• Foundation Engineering
Foundation engineering is a branch of geotechnical engineering which applies soil mechanics, structural
engineering, and project serviceability requirements for design and construction of foundations for
onshore, offshore, and in-land structures.
A foundation is the lowest part of the building structure. It is the engineering field of study devoted to
the design of those structures which support other structures, most typically buildings, bridges or
transportation infrastructure.
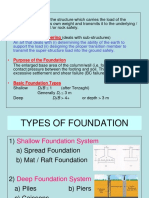
2 Types of Foundation
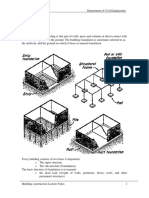
• Shallow Foundations
Foundations with a depth of embedment-to-width ratio of approximately less than four can be
considered as a shallow foundation.
2 Types of Shallow Foundations
Spread Footing- Enlargement of a load-bearing wall or column to spread
Mat Foundation- A concrete pad where the entire structure is supported
• Deep Foundations
Foundations with a depth of embedment-to-width ratio of foundations greater than four can be
considered as deep foundations
2 Types of Deep Foundations
Pile Foundation
FRICTION PILES - shear resistance along the surface of the pile
END BEARING PILES - load is transmitted at the tip to a firm stratum of soil
Drilled Shaft Foundation- -Shaft drilled in the subsoil is then filled with concrete
You might also like
- Presentation On FoundationsDocument14 pagesPresentation On FoundationsShiwangi NagoriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document82 pagesLecture 2Zuhal ZaeemNo ratings yet
- Foundation Engineering: Meaning and Types of FoundationDocument29 pagesFoundation Engineering: Meaning and Types of FoundationNasr UllahNo ratings yet
- 01 IntroductionDocument26 pages01 IntroductionJoshua OrcalesNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Lecture Note .2Document198 pagesBuilding Construction Lecture Note .2amu aytuNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Geotechnical EngineeringDocument23 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Geotechnical EngineeringAnthony Al LakissNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document27 pagesChapter 2aduyekirkosu1scribdNo ratings yet
- RR Study On Different Type of FoundationDocument28 pagesRR Study On Different Type of FoundationAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Module 01Document21 pagesModule 01Niña Criselle PasiaNo ratings yet
- BCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021Document21 pagesBCM-V U2 Part-A 19-07-2021hyperloop707 designNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Types of Foundations PDFDocument36 pagesLec 2 Types of Foundations PDFUsman AliNo ratings yet
- BACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4Document14 pagesBACLIG, LORNA G. (BSCE 4-2) - CENGR 4220 Assignment No. 4LORNA BACLIGNo ratings yet
- Foundations Engg, Lec 1, IntroductionDocument29 pagesFoundations Engg, Lec 1, IntroductionLearners of Civil Engineering100% (1)
- 13-Structural Foundation, Deep FoundationDocument37 pages13-Structural Foundation, Deep Foundationengsamim.walizadaNo ratings yet
- Foundation PlanDocument34 pagesFoundation PlanMagie MendozaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Foundation TypesDocument27 pages3 - Foundation TypesimaniNo ratings yet
- Builiding FoundationDocument16 pagesBuiliding FoundationSanjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Foundations: Silia Grover Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Architecture GNDU, AmritsarDocument34 pagesFoundations: Silia Grover Assistant Professor, Deptt. of Architecture GNDU, AmritsarPalakNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsDocument10 pages1.1 Introduction To Building Construction MethodsAlexNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document149 pagesModule 3Owsu KurianNo ratings yet
- 1 CHAPTER 1shallow Foundation in SoilDocument45 pages1 CHAPTER 1shallow Foundation in SoilAizat HermanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-22 FoundationDocument20 pagesChapter-22 Foundationdesubie bireNo ratings yet
- Types of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Document14 pagesTypes of Foundations and Its Uses Rahul Kumawat 08CE000137Rahul Kumawat100% (1)
- 4.CEE 4101 3 MarchDocument44 pages4.CEE 4101 3 MarchPranto KhanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 FoundationDocument34 pagesCHAPTER 4 Foundationashenafi.aNo ratings yet
- CH-2 Types of Shallow FoundationsDocument35 pagesCH-2 Types of Shallow Foundations19CE535 Mandar GawandeNo ratings yet
- Full Report On Isolated FootingDocument22 pagesFull Report On Isolated Footingabidur77100% (2)
- Tanvi Khanna - B.arch 3 Year - A - TOS - Assignment - 1 - FoundationsDocument12 pagesTanvi Khanna - B.arch 3 Year - A - TOS - Assignment - 1 - Foundationskritish duaNo ratings yet
- Types of FoundationsDocument30 pagesTypes of FoundationsFahad Areeb100% (1)
- Types of Foundations PDFDocument30 pagesTypes of Foundations PDFHuzaifa TanzeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 FoundationDocument53 pagesChapter-3 Foundationkader ArefeNo ratings yet
- CH 4 FoundationDocument43 pagesCH 4 FoundationEyoatem Teferi100% (1)
- 4 LectureDocument37 pages4 LecturePranto KhanNo ratings yet
- Structural Presentation2Document45 pagesStructural Presentation2Jherome ManuelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Design of Foundation LabDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Design of Foundation LabAmith Unnimadhavan UNo ratings yet
- Foundation 2Document34 pagesFoundation 2aamaniammuNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Pile FoundationDocument17 pagesAssignment: Pile Foundationsunil khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Pile FoundationDocument17 pagesAssignment: Pile Foundationsunil khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Chap - 2 FoundationsDocument12 pagesChap - 2 FoundationstekalignNo ratings yet
- Footings FoundationsDocument89 pagesFootings FoundationsAC Suarez100% (1)
- BCE - Module 4 - MaterialsDocument106 pagesBCE - Module 4 - MaterialsABHISHEK SHARMANo ratings yet
- Buildings-Types of FoundationsDocument5 pagesBuildings-Types of FoundationsRonit ChariNo ratings yet
- Always Try To Do The Best in Your LifeDocument79 pagesAlways Try To Do The Best in Your LifeNamrata PalNo ratings yet
- CEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringDocument36 pagesCEE 4101 Foundation EngineeringRamu KakaNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument41 pagesFoundationhamnahrico100% (1)
- Building Technology Assignment: Question and AnswerDocument6 pagesBuilding Technology Assignment: Question and AnswerBorel JasonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Foundation EngineeringDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Foundation EngineeringBinitaNo ratings yet
- Vineet Shrivastava: Associate Professor Department of Planning & Architecture Mizoram UniversityDocument25 pagesVineet Shrivastava: Associate Professor Department of Planning & Architecture Mizoram UniversityMZU Barch 2020No ratings yet
- Foundation PlanDocument50 pagesFoundation PlanShaina Habib-AgilNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To Foundation EngineeringDocument6 pages1 Introduction To Foundation EngineeringJhan SeenNo ratings yet
- Sub Structure FoundationDocument32 pagesSub Structure FoundationshingkeongNo ratings yet
- Foudation Ass 1Document1 pageFoudation Ass 1Jea LagahitNo ratings yet
- FoundationsDocument24 pagesFoundationsMohamed SanoosNo ratings yet
- Details of Construction-Ii - FoundationsDocument78 pagesDetails of Construction-Ii - Foundationspallabi banerjeeNo ratings yet
- Theory of Structures: Assignment 1Document16 pagesTheory of Structures: Assignment 1Sakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- FoundationsDocument49 pagesFoundationsManjeet CinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2aduyekirkosu1scribdNo ratings yet
- "In The Name of Allah, The Most Gracious, & The Most Merciful"Document37 pages"In The Name of Allah, The Most Gracious, & The Most Merciful"Uzair SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Materials and Construction - Part IIIDocument158 pagesBasic Building Materials and Construction - Part IIIGãlväñ Fôx100% (1)
- TRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 7Document1 pageTRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 7ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- TRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 5Document1 pageTRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 5ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- TRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 2Document1 pageTRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 2ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- TRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 1Document1 pageTRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 1ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- TRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 4Document1 pageTRANSPO-Mod12 (1) - 4ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- TRANSPO Mod12Document7 pagesTRANSPO Mod12ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Sampling 3Document1 pageSoil Investigation and Sampling 3ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Sampling 1Document1 pageSoil Investigation and Sampling 1ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and Sampling 2Document1 pageSoil Investigation and Sampling 2ann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- PFD Meyerhofs-TableDocument1 pagePFD Meyerhofs-Tableann valerie reyesNo ratings yet
- Soil Investigation and SamplingDocument3 pagesSoil Investigation and Samplingann valerie reyesNo ratings yet