Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Important Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74
Uploaded by
MohanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74
Uploaded by
MohanCopyright:
Available Formats
Important Articles of
Indian Constitution
[UPSC Notes]
List of Important Articles of Indian Constitution
Articles are the guidelines given in the Constitution of India. There are currently 448
articles in the constitution of India. Following are some important Articles of the Indian
Constitution.
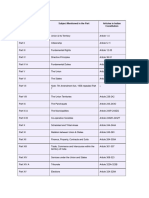
Parts of Indian Subjects Mentioned Articles in
Constitution Constitution
Part I Union and its Territories Article 124
Part II Citizenship Article 5 to 11
Part III Fundamental Rights Article 12 to 35
Part IV Directive Principles Article 36 to 51
Part IV-A Fundamental Duties Article 51A
Part V The Union Article 51 to 151
Part VI The States Article 152 to 237
Part VII 7th Amendment Act(Repealed) —
Part VIII The Union Territories Article 293 to 242
Part IX The Panchayat Article 243 to
243O
Part IX-A The Municipalities Article 243p to
243ZG
Part IX-B Cooperative Societies Article 243 ZH to
243ZT
Part X Schedule and Tribal Areas Article 244 to
244A
Part XI Relation Between Union and States Article 245 to 263
Part XII Finance Property Contracts And Suits Article 264 to
300A
Part XIII Trade Commerce and Intercourse Within Article 301 to 307
The Territory of India
Part XIV Services Under The Union And States Article 308 to 323
Part XIV-A Tribunals Article 323A to
323B
Part XV Elections Article 324 to
329A
Part XVI Special Provisions Relating To Certain Article 330 to 342
Classes
Part XVII Official Languages Article 343 to 351
Part XVIII Emergency Provisions Article 352 to 360
Part XIX Miscellaneous Article 361 to 367
Part XX Amendment of the Constitution Article 368
Part XXI Temporary Transitional and Special Article 369 to 392
Powers
Part XXII Short Title Commencement Authoritative Article 393 to 395
Text in Hindi and Repeals
Description of the Articles of Indian Constitution
Below we have described the Articles of Indian Constitution.
Part 1 - Article 1 to Article 4
Article 1- name and Territory of the union.
Article 2- admission and establishment of the new state.
Article 3- formation of new states and alteration of areas boundaries and name of
existing States.
Part 2 - Article 5 to Article 11
Article 5- Citizenship at the commencement of the constitution.
Article 6- rights of citizenship of a certain person who has migrated to India from
Pakistan.
Article10- continuance of rights of citizenship.
Article 11- Parliament two regulates the right of citizenship by law.
Part 3 - Article 12 to Article 35
Article 12- definition of the state.
Article 13- loss inconsistent with or in derogation of the fundamental right.
Articles of Indian Constitution on Fundamental Rights
All the citizens of India are provided with 6 fundamental rights. These 6 fundamental
rights are-
1. Right to Equality
Article 14- equality before law
Article 15- prohibition of discrimination on the grounds of religion, race, caste,
sex, or place of birth
Article 16- equality of opportunity in matters of public employment
Article 17- abolition of untouchability
Article 18- abolition of titles
2. Right to Freedom
Article 19- guarantees to all the citizens the six rights-
a. Freedom of speech and expression
b. Freedom to assemble peaceably and without arms
c. Freedom to form associations or unions
d. Freedom to move freely throughout the territory of India
e. Freedom to reside and settle in any part of the territory of India
f. Omitted
g. Freedom to practice any profession or to carry on any occupation trade or
businesses
Article 20- protection in respect of conviction for offenses
Article 21- protection of life and personal liberty
Article 22- protection against arrest and detention in certain cases
3. Right Against Exploitation
Article 23- prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labor
Article 24- prohibition of employment of children under the age of 14 in factories
and mines
4. Right to Freedom of Religion
Article 25- freedom of conscience and free professional practice and propagation
of religion
Article 26- freedom to manage religious affairs
Article 27- freedom as to pay taxes for promotion of any particular region
Article 28- freedom from attending religious instruction
5. Cultural and Educational Right
Article 29- protection of interest of minorities
Article 30- right to minorities to establish and administer educational institutions
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies
Article 32- remedies for enforcement of fundamental rights
Part 4 - Article 36 to Article 51( Directive Principal of State Policy)
Article 36- definition.
Article 37- application of DPSP.
Article 39A- equal justice and free Legal Aid.
Article 40- organization of a village panchayat.
Article 41- right to work, to education, and to public assistants in certain cases.
Article 43- living wages for workers.
Article 43A- participation of workers in the management of industries.
Article 44- Uniform Civil Code.
Article 45- provision of free and compulsory education for children.
Article 46- promotion of the educational and economic interest of scheduled caste
Scheduled Tribes and other backward classes.
Article 47- duty of the state to raise the level of nutrition and the standards of living and
two to improve public health.
Article 48- organization of agriculture and animal husbandry.
Article 49- protection of monuments and places and objects of natural importance.
Article 50- separation of Judiciary from the executive.
Article 51- promotion of international peace and security.
Part 4A - Article 51A(Fundamental Duties)
With the 42nd amendment act 1976, there were 10 fundamental duties, later with the
86th amendment act 2002, one more duty was added to it. After that, we have a total of
11 fundamental duties.
Part 5 - Union: Article 52 to Article 151
Article 52- the president of India.
Article 53- executive power of the union.
Article 54- election of the president.
Article 61- procedure for impeachment of the president.
Article 63- the vice president of India.
Article 64- the vice president to be ex officio chairman of the Council of States.
Article 66- election of vice president.
Article 72- Pardoning powers of President.
Article 74- Council of Ministers to aid and advise the president.
Article 76- Attorney General for India.
Article 79- composition of parliament.
Article 80- composition of Rajya Sabha.
Article 81- composition of Lok Sabha.
Article 83- Duration of houses of parliament.
Article 93- the speakers and Deputy speakers of the house of people.
Article 105- powers privileges etc. of the house of parliament.
Article 109- special procedure and respect of money bills.
Article 110- definition of money bills.
Article 112- annual fiscal budget.
Article 114- appropriation bills.
Article 123- powers of the President to promulgate ordinances during Recess of
parliament.
Article 124- establishment of Supreme Court.
Article 125- salaries of judges.
Article 126- appointment of acting Chief Justice.
Article 127- appointment of Ad Hoc judges.
Article 128- attendance of retired judge at sitting of the supreme court.
Article 129- Supreme Court to be a court of record.
Article 130- the seat of the supreme court.
Article 136- special leaves for an appeal to the supreme court.
Article 137- review of judgments or orders by the supreme court.
Article 141- decision of Supreme Court of India binding on all the codes.
Article 148- Comptroller and Auditor General of India.
Article 149- duties and powers of Comptroller and Auditor General.
Part 6 - State: Article 152 to Article 237
Article 153- Governors of States.
Article 154- executive powers of governors.
Article 161- Pardoning powers of the governor.
Article 165- advocate general of the state.
Article 213- the power of the Governor to promulgate ordinances.
Article 214- high courts for States.
Article 215- high courts to be a court of record.
Article 226- the power of high courts to issue certain writs.
Article 233- appointment of district judges.
Article 235- control over subordinate courts.
Part 7- It is also known as “The States in Part B of the First
Schedule”.
It has only one article – that is, Article 238.
It was repealed by the Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956.
Part 8- Union Territories: Article 239 to Article 242
Part 9-Panchayats: Article 243 to Article 243
Article 243A- Gram Sabha.
Article 243B- constitution of Panchayat.
Part 9A- Municipalities: Article 243 P to Article 243 ZG
Part 10 -Scheduled and Tribal Areas: Article 244
Part 11- Centre-State Relations: Article 245 to Article 263
Part 12 - Finance, Properties, Contracts, Suits: Article 264 to Article
300A
Article 266- consolidated fund and public account fund.
Article 267- contingency fund of India.
Article 280- finance commission.
Article 300A- right to property.
Part 13 - Trade, Commerce, and intercourse within the territories of
India: Article 301 to Article 323
Article 301- freedom to trade commerce and intercourse.
Article 302- the power of Parliament to impose restrictions on trade, commerce, and
intercourse.
Part 14 - Services under Centre and State: Article 308 to Article 323
Article 312- all India services.
Article 315- Public Service commissions for the Union and for the states.
Article 320- functions of public service commission.
Part 14A - Tribunals: Article 323A to Article 323B
Article 323A- administrative tribunals.
Part 15 - Elections: Article 324 to Article 329
Article 324- Superintendence, direction, and control of elections to be vested in an
election commission.
Article 325- no person to be eligible for inclusion in or to claim to be included in a
special electoral roll on grounds of religion, race, caste, or sex.
Article 326- elections to the house of people and to the legislative assemblies of states
to be on the basis of adult suffrage.
Part 16 - Special Provisions to SC, ST, OBC, Minorities, etc: Article
338 to Article 342
Article 338- National Commission for scheduled caste and Scheduled Tribes.
Article 340- appointment of a Commission to investigate the conditions of backward
classes.
Part 17 - Official Languages: Article 343 to Article 351
Article 343- official languages of the union.
Article 345- official languages or languages of a state.
Article 348- languages to be used in the supreme court and in the High Court.
Article 351- directive for development of Hindi languages.
Part 18 - Emergency: Article 352 to Article 360
Article 352- the proclamation of National Emergency.
Article 356- state emergency by president rule.
Article 360- financial emergency.
Part 19 - Miscellaneous: Article 361 to Article 367
Article 361- protection of president and governors.
Part 20 - Amendment of Constitution: Article 368
Article 368- powers of Parliament to amend the constitution.
Part 21 - Special, Transitional, and Temporary Provisions: Article 369
to Article 392
Article 370- temporary provision for the erstwhile state of Jammu and Kashmir.
Article 371A- special provision with respect to the state of Nagaland.
Article 371J- special status for Hyderabad in the Karnataka region.
Part 22 - Short Text, Commencement, Authoritative Text in Hindi and
Repeals: Article 392 to Article 395
Article 393- short title, this constitution may be called the constitution of India.
Schedules and Important Articles of Indian Constitution
The schedules and important articles of the Indian constitution are as follows:
Schedules of Indian Constitution Articles in Indian Constitution
First Schedule Article 1 and Article 4
Second Schedule Articles:
59
65
75
97
125
148
158
164
186
221
Third Schedule Articles:
75
84
99
124
146
173
188
219
Fourth Schedule Article 4 and Article 80
Fifth Schedule Article 244
Sixth Schedule Article 244 and Article 275
Seventh Schedule Article 246
Eighth Schedule Article 344 and Article 351
Ninth Schedule Article 31B
Tenth Schedule Article 102 and Article 191
Eleventh Schedule Article 243G
Twelfth Schedule Article 243W
You might also like
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesParts of The Indian Constitutionserryserry362No ratings yet
- Articles India ConstitutionDocument3 pagesArticles India ConstitutionYash KumbleNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution, Complete ListDocument12 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution, Complete ListJacob JrNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Parts Vs Corresponding ArticlesDocument3 pagesIndian Constitution Parts Vs Corresponding ArticlesTharun CloudNo ratings yet
- Parts of Indian Constitution ExplainedDocument2 pagesParts of Indian Constitution Explainedjharbifno0% (1)
- Imp articles, Parts & Schedule (4)Document7 pagesImp articles, Parts & Schedule (4)Akash PatelNo ratings yet
- Important Articles in Indian Constitution for UPSC ExamsDocument17 pagesImportant Articles in Indian Constitution for UPSC ExamsAditya SuriNo ratings yet
- Parts and Important Articles of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesParts and Important Articles of The Constitutioncoolsumitan100% (1)
- Detailed Important Articles in Indian Constitution (UPSC Indian Polity Notes)Document19 pagesDetailed Important Articles in Indian Constitution (UPSC Indian Polity Notes)amanankit211No ratings yet
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesParts of The Indian ConstitutionAmisha BhandariNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument4 pagesParts of The Indian ConstitutionAmisha BhandariNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesDocument5 pagesIndian Constitution - Parts, Fundamental Rights and SchedulesShiva KumarNo ratings yet
- Bbaa2d9b d1da 4f8b 9eea 54cad7ca97ef GKMaterialDocument2 pagesBbaa2d9b d1da 4f8b 9eea 54cad7ca97ef GKMaterialHarsh SaravatNo ratings yet
- NTSE Sheet 3 PDFDocument8 pagesNTSE Sheet 3 PDFVed bukhariyaNo ratings yet
- How Many Articles Are There in The Indian ConstitutionDocument1 pageHow Many Articles Are There in The Indian ConstitutionsaumyaNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Notes by NIKHIL TYAGIDocument143 pagesGeneral Knowledge Notes by NIKHIL TYAGIShivani Yadav 10 CNo ratings yet
- Parts of ConstitutionDocument4 pagesParts of ConstitutionFake MailNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Indian ConstitutionDocument1 pageParts of The Indian ConstitutionAmisha BhandariNo ratings yet
- eBOOK 22091914205956Document42 pageseBOOK 22091914205956Kuwar NikhilNo ratings yet
- ConstitutionDocument70 pagesConstitutionakshay100% (1)
- Constitution of IndiaDocument134 pagesConstitution of IndiarajdeeppawarNo ratings yet
- Volume 1 TN JSE 1Document20 pagesVolume 1 TN JSE 1Rama ChandranNo ratings yet
- General Knowledge Social Science Capsule For ICAR Technician 2022 ExamDocument98 pagesGeneral Knowledge Social Science Capsule For ICAR Technician 2022 ExamHritik SharmaNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution Parts & Articles SummaryDocument6 pagesIndian Constitution Parts & Articles SummaryKavalla Bhimarao67% (3)
- Odisha Police Exam GuideDocument51 pagesOdisha Police Exam GuideAlokNo ratings yet
- ArticleDocument7 pagesArticleshivankur sharmaNo ratings yet
- PolityDocument22 pagesPolitySudhanshu ShekharNo ratings yet
- Constitution: Useful LinksDocument7 pagesConstitution: Useful LinkssatyajitNo ratings yet
- PolityDocument22 pagesPolityDilip LatiyalNo ratings yet
- Parts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A VDocument10 pagesParts Subject Matter Articles Covered I II III IV Iv-A Vrakesh kumarNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONDocument31 pagesCONSTITUTIONpcbranch.copNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India Fundamental Rights GuideDocument44 pagesConstitution of India Fundamental Rights Guidesoumya612No ratings yet
- POLITY For RRB NTPC 2020-21 ExamDocument26 pagesPOLITY For RRB NTPC 2020-21 ExamSamu ThapaNo ratings yet
- IMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument8 pagesIMP Articles of Indian ConstitutionNandita NanditaNo ratings yet
- Must Know Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesMust Know Articles of Indian Constitutionnur mdNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetDocument43 pagesNew Microsoft Office Excel WorksheetbilbobaggingsNo ratings yet
- Points ConstitutionDocument6 pagesPoints Constitutionchoosypandit81No ratings yet
- Parts of Indian ConstitutionDocument1 pageParts of Indian Constitutionvishalbeniwal1712No ratings yet
- Understanding the Parts, Articles and Schedules of the Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesUnderstanding the Parts, Articles and Schedules of the Indian ConstitutionAnonymous iz83EL9No ratings yet
- Polity Capsule: Ga Power Capsule For Indian Polity/Civis For Defence Exams 2018-19Document18 pagesPolity Capsule: Ga Power Capsule For Indian Polity/Civis For Defence Exams 2018-19pankaj soniNo ratings yet
- Constitution of India 1Document7 pagesConstitution of India 1pratapsinghashutosh12No ratings yet
- Indian Constitution .Document18 pagesIndian Constitution .kiranbarki63No ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument1 pageConstitution of IndiaDeva GnanamNo ratings yet
- List of Important Articles of The Constitution of India - GK Notes PDF!Document12 pagesList of Important Articles of The Constitution of India - GK Notes PDF!Akash BhowalNo ratings yet
- List of Important Articles of The Indian ConstitutionDocument2 pagesList of Important Articles of The Indian ConstitutionAarthi SnehaNo ratings yet
- GS Series - Polity: Polity Notes For SSCDocument12 pagesGS Series - Polity: Polity Notes For SSCParshant MalikNo ratings yet
- Panchayati Raj: Amendment Act in 2011Document7 pagesPanchayati Raj: Amendment Act in 2011Chandu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Polity 2Document18 pagesPolity 2Swayam SwastikNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs Merged PDFDocument157 pagesCurrent Affairs Merged PDFabesh sinhaNo ratings yet
- Polity Notes for SSC ExamDocument13 pagesPolity Notes for SSC Examdick kumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity Black Book PDF 1Document19 pagesIndian Polity Black Book PDF 1Anirudh ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- Polity Notes 50 Questions For SSC CGL Tier 2 ExamDocument30 pagesPolity Notes 50 Questions For SSC CGL Tier 2 Examuttamprajapati0601No ratings yet
- parts of constitutionDocument3 pagesparts of constitutionKABADDI RISINGNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution 2020 47e939c5Document12 pagesIndian Constitution 2020 47e939c5KriNo ratings yet
- General Awareness Capsule For AFCAT II 2021 ExamDocument146 pagesGeneral Awareness Capsule For AFCAT II 2021 ExamRitikNo ratings yet
- The Indian Constitution: Key Parts and SchedulesDocument9 pagesThe Indian Constitution: Key Parts and SchedulesRitwik PatraNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of Indian ConstitutionDocument5 pagesImportant Articles of Indian ConstitutionSingh Jora0% (1)
- Must Know Articles of Indian Constitution - Clear IAS PDFDocument9 pagesMust Know Articles of Indian Constitution - Clear IAS PDFDiana JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- Final Article Attachemnt With Doi B 4141Document7 pagesFinal Article Attachemnt With Doi B 4141MohanNo ratings yet
- The Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor Etiology PDocument8 pagesThe Canine Transmissible Venereal Tumor Etiology PMohanNo ratings yet
- Important Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74Document8 pagesImportant Articles of Indian Constitution Upsc Notes 74MohanNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Proestrus Bleeding and Medical Treatment in An English Pointer DogDocument3 pagesProlonged Proestrus Bleeding and Medical Treatment in An English Pointer DogMohanNo ratings yet
- ICCT Colleges Foundation, Inc. Transfer and Business Taxation (Blo4) Chapter 1 - ActivityDocument2 pagesICCT Colleges Foundation, Inc. Transfer and Business Taxation (Blo4) Chapter 1 - ActivityJoyce Mae D. FloresNo ratings yet
- Case Digest by Adonis PDFDocument172 pagesCase Digest by Adonis PDFCarmela BautistaNo ratings yet
- HND-Equity & Trusts-Assignment BriefDocument7 pagesHND-Equity & Trusts-Assignment BriefadeebaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The Philippine ConstitutionDocument5 pagesEvolution of The Philippine ConstitutionLewy Katrin S. Cortez100% (2)
- Expresso Unious Exclusio Project ReportDocument10 pagesExpresso Unious Exclusio Project ReportIshaan Vashishth100% (1)
- Lorenzo vs. Posadas Jr. G.R. No. L-43082 June 18, 1937Document6 pagesLorenzo vs. Posadas Jr. G.R. No. L-43082 June 18, 1937Andrea IvanneNo ratings yet
- Legislative ProceduresDocument28 pagesLegislative ProceduresVipul PartapNo ratings yet
- Philippine Constitution Association v. Enriquez ruling on presidential veto powerDocument2 pagesPhilippine Constitution Association v. Enriquez ruling on presidential veto powerLucila MangrobangNo ratings yet
- NERI VDocument15 pagesNERI VVincent CruzNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 - JurisprudenceDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 - JurisprudencePARVEENA KAUR A P BALDEB SINGHNo ratings yet
- Property Law Project On Transfer of Property To Unborn ChildDocument18 pagesProperty Law Project On Transfer of Property To Unborn Childshivanika singla100% (1)
- SK Election Postponement ActDocument2 pagesSK Election Postponement ActDay BrilloNo ratings yet
- Articles of IncorporationDocument3 pagesArticles of IncorporationNini Lucero100% (1)
- Warren County Indiana Notes From Walter Salts - Judy Cox File IndexDocument10 pagesWarren County Indiana Notes From Walter Salts - Judy Cox File IndexmcphilbrickNo ratings yet
- Memory Aid of Wills Cases 0831Document8 pagesMemory Aid of Wills Cases 0831extraordinerizNo ratings yet
- Answers To Bar Questions-PilDocument1 pageAnswers To Bar Questions-PilAleah-Hidaya Ali Hadji RakhimNo ratings yet
- Dorotheo vs. CaDocument1 pageDorotheo vs. CakarlonovNo ratings yet
- Philippine Government and Politics Quiz 012018Document1 pagePhilippine Government and Politics Quiz 012018Mello Jane Garcia DedosinNo ratings yet
- GALLANOSA v. ARCANGEL (Escra Full Text)Document14 pagesGALLANOSA v. ARCANGEL (Escra Full Text)NOLLIE CALISINGNo ratings yet
- Aims Faculty Association By-LawsDocument2 pagesAims Faculty Association By-Lawsapi-27176213No ratings yet
- Deed Polls, Contracts, Affidavits, Statutory Declarations & Power of AttorneyDocument5 pagesDeed Polls, Contracts, Affidavits, Statutory Declarations & Power of AttorneyFinding flowNo ratings yet
- California Instestate SuccessionDocument32 pagesCalifornia Instestate SuccessionJenna AliaNo ratings yet
- Deed of Trust for Property SettlementDocument5 pagesDeed of Trust for Property SettlementutkarshNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. L-27526 (1974)Document3 pagesG.R. No. L-27526 (1974)MorphuesNo ratings yet
- Jose Lee Vs RTC of QCDocument2 pagesJose Lee Vs RTC of QCParis ValenciaNo ratings yet
- 1 Commencement Certificates - NA Order For Plotted DevelopmentDocument3 pages1 Commencement Certificates - NA Order For Plotted DevelopmentSethia DarshanNo ratings yet
- Abbas Vs ComelecDocument4 pagesAbbas Vs ComelecRaymond Roque100% (1)
- Territorial NexusDocument3 pagesTerritorial NexusVikash Kumar0% (1)
- Sema vs. ComelecDocument4 pagesSema vs. ComelecRikki BanggatNo ratings yet
- Office of ProfitDocument2 pagesOffice of ProfitDivyanshi JoshiNo ratings yet