Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Csec Study Guide Smoking
Uploaded by
Lynda BarrowOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Csec Study Guide Smoking
Uploaded by
Lynda BarrowCopyright:
Available Formats
Smoking
Addicted to smoking
• • If you smoke or know someone who smokes, you will know that
At the end of this topic you it is very hard to give up the habit. Smokers have a craving that
should be able to : is only prevented by having another smoke. That craving is partly
• state the main components of psychological but it is also physical. The body relies on the drug in
tobacco smoke tobacco smoke in order to function properly because its molecules
interact with synapses in our nervous system . That drug is nicotine
• describe the effects of tar on
and it is one of the most addictive substances known .
the airways
• explain why people become Nicotine is a stimulant. It stimulates the release of adrenaline leading
addicted to smoking to an increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This gives an increase
in mental alertness . Marijuana (ganga) contains a drug that has the
• outline the effects of nicotine
opposite effect. It has a calming effect and may induce a trance-like
and carbon monoxide on the
state and also cause hallucinations .
circulatory system .
a b
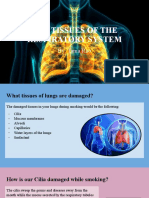
Dust These cells
particles make mucus
Synapses are tiny gaps between
nerve cel ls (see 8.4) . Many J.
drugs including heroin and
nicotine act on our synapses .
Figure 5.11.2 a Healthy lining of a bronchus of a non-smoker, b Lining of a
bronchus of a long-term smoker: the ciliated cells are replaced by
squamous cells.
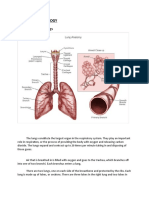
Damage to the lungs
tube
Tar is the black sticky material that collects in the lungs as smoke
cools. It does not pass into the bloodstream. Tar irritates the lining of
the airways stimulating the epithelial cells to produce more mucus.
Contents of This tends to accumulate, narrowing the airways. Smokers cough to
cigarette smoke:
make this material move to the back of the throat (Figure 5.11.1).
Nicotine
Tar Tar causes the cilia on the cells that line the air passages to stop
Carbon monoxide
Carcinogens beating. Mucus and the dust, dirt and bacteria that stick to it,
r ""
((
rr-- \
are not removed from the lungs. The mucus accumulates and
-(f'\ ( ) bacteria mUltiply. White blood cells congregate where this happens,
~, , -'-.
particularly in the bronchi . The bronchi become blocked with
phlegm (a mixture of mucus, bacteria and white blood cells), which
Figure 5.11.1 A simple smoking people attempt to cough up . This condition is chronic bronchitis.
machine. Scientists have
People with this condition find it difficult to breathe as the bronchi
used more sophisticated
machines to mimic our are partly blocked (Figure 5.11 .2) .
smoking behaviour to
analyse the contents of
tobacco smoke.
Particles, bacteria and tar reach the alveoli. White blood cells digest
a pathway through the lining of the alveoli to reach the bacteria.
Eventually this weakens the walls of the alveoli so much that they Tobacco plants produce nicotine
break down and burst, reducing the surface area for gas exchange. as an insecticide to kil l insects
This condition is emphysema, which leaves people gasping for that try to eat the leaves. Tobacco
breath . They cannot absorb enough oxygen or remove carbon dioxide farmers harvest the leaves and
efficiently. Many long-term smokers have both of these conditions. dry them; manufacturers make
tobacco products, such as cigars
and cigarettes .
Effects on transport of oxygen
Carbon monoxide combines permanently with haemoglobin in
red blood cells so reducing the volume of oxygen that the blood
can carry. There may be as much as a 10% decrease in the oxygen
transported . This is particularly dangerous for pregnant women .
Lung cancer
90% of cases of lung cancer occur in people who smoke or w ho
have smoked. The cause of lung cancer is the carcinogens in tar.
These substances promote changes, known as mutation, to occur in
the DNA of cells lining the airways. These mutations cause the ce lls
to grow and divide out of control. This growth is very slow and it Lung cancer is often
may take 20 years before there are any symptoms. The cells form a '---=:.-----' diagnosed by taking X- rays.
tumour. If this is not discovered it may grow to occupy a large area Compare this with the X-ray
of healthy lungs in 5.10 .
of the lung pushing against airways and blood vessels to block them .
Worse, a part of the tumour may break off and spread into other
organs . If a tumour is discovered before it has spread then it may
be removed by surgery. If the tumour has spread, then the cancer is
much more difficult to treat (Figures 5.11.3 and 5.11.4).
SUMMARY QUESTIONS
1 State the components of tobacco smoke.
This cancer has spread
2 Smoking-related diseases are often classified as self-inflicted '---=-------' through the lung , blocking
diseases. Discuss whether or not this is true. blood vessels and airways.
3 Outline the effects of smoking on the gaseous exchange
system .
4 Explain why smokers find it hard to give up their habit.
1 Nicotine is the addictive substance in tobacco smoke.
2 Tar damages the lining of the airways, stimu lating excess
production of mucus and destroying ciliated cells .
3 Carcinogens in smoke cause lung cancer.
4 Carbon monoxide combines with haemoglobin in red blood
cel ls to reduce the blood's oxygen -carrying capacity.
You might also like
- Smoking PosterDocument1 pageSmoking PosterBryan TanNo ratings yet
- Effects of Smoking PresentationDocument59 pagesEffects of Smoking PresentationMEGA GAMINGNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 2 RespirationDocument13 pagesF3 Chapter 2 RespirationJue Hazea GoldshopNo ratings yet
- 5 Quarter 1 Module 5 Negative Effects of Cigarette SmokingDocument21 pages5 Quarter 1 Module 5 Negative Effects of Cigarette SmokingKathlyn Joy GeronimoNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIODocument15 pagesINTRODUCTIOVishwapranesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- Dangers of SmokingDocument3 pagesDangers of Smokingifeoluwasubomi.adeleyeNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 RespirationDocument30 pagesScience Chapter 2 RespirationWei LinNo ratings yet
- Effects of Tabacco SmokingDocument17 pagesEffects of Tabacco SmokingPedro Gomez GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Passive Smoking: CarcinogensDocument3 pagesPassive Smoking: Carcinogensapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Mapeh 8 Lesson 4. Dangers of Tobacco Use Know About SmokingDocument2 pagesMapeh 8 Lesson 4. Dangers of Tobacco Use Know About SmokingrheyNo ratings yet
- Report WVDocument9 pagesReport WVSEANo ratings yet
- Tobacco Smoking For Igcse BiologyDocument10 pagesTobacco Smoking For Igcse BiologyAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesImportance of Respiratory SystemnoorashidahNo ratings yet
- Apec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemDocument2 pagesApec Schools 1 Quarter S.Y. 2019 - 2020 Science 9 Lesson Handout #3: Coordinated Function - The Human Respiratory SystemEy ChuaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Smoking FinalDocument2 pagesEffect of Smoking FinalRufi RizwanNo ratings yet
- Your Teachers and Staff "Need To Know"Document19 pagesYour Teachers and Staff "Need To Know"Eng CirroNo ratings yet
- Chem 12 CompDocument12 pagesChem 12 CompVishwapranesh GanesanNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemDocument11 pagesF3 Chapter 1 Respiratory SystemFoh Lian HuaiNo ratings yet
- Smoking - To Die For!Document19 pagesSmoking - To Die For!Priya JainNo ratings yet
- Smokerss Body Rev PHL Ed 2010Document1 pageSmokerss Body Rev PHL Ed 2010Mayca Solomon GatdulaNo ratings yet
- A Smoker's BodyDocument1 pageA Smoker's BodyHensim Mae Cajes0% (1)
- Biology BrochureDocument3 pagesBiology BrochureMilton DownesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document8 pagesChapter 10Olusoga AdeyigaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Lungs: Viii. PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The Lungs: Viii. PathophysiologyShin EscaresesNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and SmokingDocument20 pagesGas Exchange and SmokingAnggraeni Kusuma WardaniNo ratings yet
- HEALTH Module 4thDocument4 pagesHEALTH Module 4thpogi90No ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: EmphysemaDocument11 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: EmphysemarielNo ratings yet
- Date: Topic: Harmful Chemical in Cigarettes. Aim: List The Diseases That Effects The Respiratory SystemDocument17 pagesDate: Topic: Harmful Chemical in Cigarettes. Aim: List The Diseases That Effects The Respiratory SystemIbrahim AhmadNo ratings yet
- All About Smoking - Quit SADocument4 pagesAll About Smoking - Quit SAkogul_remo92No ratings yet
- Environmental ThreatsDocument5 pagesEnvironmental ThreatsAstra CardinalNo ratings yet
- Effects of SmokingDocument15 pagesEffects of SmokingAslanNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Respiratory SystemDocument9 pagesWeek 1 Respiratory SystemCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- 13-2 Smoking and Your Health WebDocument8 pages13-2 Smoking and Your Health WebKelli McDaniel MarchbanksNo ratings yet
- Smoking and Lung DamageDocument11 pagesSmoking and Lung DamageAbdulHadi IrfanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary Two ScienceDocument16 pagesCambridge Secondary Two SciencearenestarNo ratings yet
- Biology Mouth To Mouth Resuscitation and SmokingDocument5 pagesBiology Mouth To Mouth Resuscitation and SmokingBrassette BalenciagaNo ratings yet
- What's in Cigarettes?: Smoking KillsDocument2 pagesWhat's in Cigarettes?: Smoking Kills34rfdsNo ratings yet
- Substance Abuse (Autosaved)Document10 pagesSubstance Abuse (Autosaved)glenNo ratings yet
- Effects of SmokingDocument4 pagesEffects of SmokingScribd UserNo ratings yet
- Process of Respiration: Human Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesProcess of Respiration: Human Respiratory Systemnalinda avishkaNo ratings yet
- B6.2 Revision Notes ZwhjilDocument3 pagesB6.2 Revision Notes ZwhjilwellingtonNo ratings yet
- BreathingDocument5 pagesBreathingvictory IsaacNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Document34 pagesRespiration: Prepared By: PN - Tan Seoah Chee SMK Desa Skudai 2010Hazmaniran HarunNo ratings yet
- How Cigarettes-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesHow Cigarettes-WPS OfficeSofrialdi Imam Bukhori NasutionNo ratings yet
- F3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - RespirationDocument2 pagesF3 Chapter 1 (SOALAN) - Respirationleong cheng liyNo ratings yet
- Smoking - Pharcare 2 - Public HealthDocument11 pagesSmoking - Pharcare 2 - Public HealthEj AmbaganNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and Smoking XI312 RAMADocument1 pageGas Exchange and Smoking XI312 RAMAMuhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- The Tissues of The Respiratory System: By: Tania RaoDocument7 pagesThe Tissues of The Respiratory System: By: Tania RaoTania RaoNo ratings yet
- Smoking and Its EffectsDocument65 pagesSmoking and Its EffectsElvyn Fabellore HerreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesChapter 2 Tutorial 1Tanisa SaminNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Respiratory Systemxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- FreebaseDocument8 pagesFreebaseAmber Mohanty100% (1)
- Asthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesAsthma Ineffective Airway ClearanceEdmr SlzarNo ratings yet
- B3A Animal Physiology Edexcel Gcse BiologyDocument5 pagesB3A Animal Physiology Edexcel Gcse BiologySuki ChanNo ratings yet
- PSYC 231 Caffeine and Nicotine 2017Document51 pagesPSYC 231 Caffeine and Nicotine 2017arenpetersNo ratings yet
- Smoking Hand OutDocument4 pagesSmoking Hand Outrosana f.rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Tobacco and Its Effect: Format: Information Sharing and Display of Various Health Effect Posters and Anti-Smoking PostersDocument7 pagesTobacco and Its Effect: Format: Information Sharing and Display of Various Health Effect Posters and Anti-Smoking Posterssannu ahmedNo ratings yet
- 1.1 The Human Breathing Mechanism 1.2 The Transport of Oxygen in The Human Body 1.3 The Importance of A Healthy Respiratory SystemDocument24 pages1.1 The Human Breathing Mechanism 1.2 The Transport of Oxygen in The Human Body 1.3 The Importance of A Healthy Respiratory SystemChang Yin YinNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Study GuideDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesis Study GuideLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- 4th Form Biology Pretest 1 - Print - QuizizzDocument9 pages4th Form Biology Pretest 1 - Print - QuizizzLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesSexual and Asexual ReproductionLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- Csec Study Guide BreathingDocument2 pagesCsec Study Guide BreathingLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- 4th Form Biology Pretest 1revDocument4 pages4th Form Biology Pretest 1revLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- Biology Intro Lesson NotesDocument1 pageBiology Intro Lesson NotesLynda BarrowNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Lab ActivityDocument7 pagesRespiratory System Lab Activitywelfred indino100% (1)
- Obestetrics Gynecology PDFDocument192 pagesObestetrics Gynecology PDFdrazam5314No ratings yet
- Updated - Science 7Document187 pagesUpdated - Science 7Mushtaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nursing Lecture RespiratoryDocument13 pagesNursing Lecture RespiratoryAedge010100% (1)
- Circulation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceDocument29 pagesCirculation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceHasan Mahmud Maruf 1621513630No ratings yet
- ICU Checklist - TEN FASTHUGSSS v3.0Document35 pagesICU Checklist - TEN FASTHUGSSS v3.0gxjjsjejdu100% (3)
- Gas Exchange and Transport (Physiology)Document31 pagesGas Exchange and Transport (Physiology)Arsalan khanNo ratings yet
- The Basic Safety Rules of FREEDIVINGDocument3 pagesThe Basic Safety Rules of FREEDIVINGAbdul Halim ReveloNo ratings yet
- CHN Non Communicable Diseases and OthersDocument90 pagesCHN Non Communicable Diseases and OthersEllenare Racion100% (1)
- I. Objectives:: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology-IiDocument19 pagesI. Objectives:: A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in General Biology-IiMhimi ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Ray InterpretationDocument3 pagesChest X-Ray InterpretationHaluk AlibazogluNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 2 Structure and Functions in Living Organisms - Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument30 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 2 Structure and Functions in Living Organisms - Edexcel Biology IGCSENatala WillzNo ratings yet
- Oxygen InsufficiencyDocument70 pagesOxygen InsufficiencydaisyNo ratings yet
- How To Read Chest X-RayDocument4 pagesHow To Read Chest X-RaydrrajkumarsoniNo ratings yet
- 7 1 2 B SR Autopsyreporttemplate 6Document4 pages7 1 2 B SR Autopsyreporttemplate 6api-457390058No ratings yet
- Spiders Nerv SystemDocument3 pagesSpiders Nerv Systemelcrack1231No ratings yet
- PART A: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesPART A: Multiple Choice QuestionsDarshini SankerNo ratings yet
- Pranvaha - Rahim FileDocument6 pagesPranvaha - Rahim FileRahimshaikhNo ratings yet
- 1B Chapter 7 (Gas Exchange) Exercise SolutionDocument3 pages1B Chapter 7 (Gas Exchange) Exercise SolutionSarahHung100% (1)
- Erasmus Et Al-2016-Transplant InternationalDocument8 pagesErasmus Et Al-2016-Transplant InternationalkibatanNo ratings yet
- FA Pulmo PDFDocument32 pagesFA Pulmo PDFNARENDIRAN P MNo ratings yet
- Biology Anotomy VertebrateDocument17 pagesBiology Anotomy VertebrateAhmad ZuhudyNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Infarction - Radiology Reference ArticleDocument7 pagesPulmonary Infarction - Radiology Reference ArticleHieu PhanNo ratings yet
- Lung AbscessDocument10 pagesLung AbscessCherlotte TbNo ratings yet
- Merkaba Meditation by Drunvalo MelchizedekDocument10 pagesMerkaba Meditation by Drunvalo MelchizedekDani Ka BioNo ratings yet
- Krok 2 - 2014 (Pediatrics)Document47 pagesKrok 2 - 2014 (Pediatrics)Heeb WardaNo ratings yet
- HAL S3201 - Brochure 2011 - NopricesDocument6 pagesHAL S3201 - Brochure 2011 - NopricesOmar García MuñozNo ratings yet
- Summary Form 3Document26 pagesSummary Form 3Prakkash RajanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ENT Assessment GuideDocument3 pagesRespiratory ENT Assessment GuidepriyaNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION: Bronchial Asthma: Fatima University Medical CenterDocument36 pagesCASE PRESENTATION: Bronchial Asthma: Fatima University Medical CenterVan MacabioNo ratings yet