Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cpar 1
Uploaded by
this isn't aiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cpar 1
Uploaded by
this isn't aiaCopyright:
Available Formats
HUMANITIES STYLE
Humanus means human, cultured, refined. Peculiar way in which an artist sees his subject, forms
Study of how people process and document the his ideas, and expresses them.
human experience FORM
Through the arts, we come to the know changing image Organization, arrangements or framework of an
of mankind as s/he journeys across time, sifts through artwork.
layers of reality, and strives to achieve the ideals that
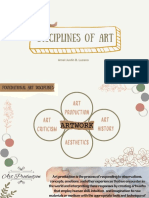
make for the meaningfulness of life. THE FOUR COORDINATES OF ART CRITICISM
THE SUBJECT
HOW TO STUDY THE HUMANITIES AND ARTS THE ARTIST
TEXT THE AUDIENCE
Any primary source refer to its medium (that is, what it ITS FORM
is made of), its forms (its outward shape), and its
content (the subject it describes). SUBJECT MATTER
CONTEXT 2 TYPES
Describes the historical and cultural background or REPRESENTATIONAL OR FIGURATIVE ART
environment of the artwork Depicts something other than its own form
SUBTEXT NON-REPRESENTATIONAL OR NON-OBJECTIVE ART
Secondary and implied meanings. Represents nothing except its own form
ART THE ARTIST
Expression or application of human creative skills and • Based on the viewpoint of the artist
imagination • Art is a means of expression
• A medium for communicating an idea
3 TYPES OF ART • An emotion or some human experiences
VISUAL ARTS • An impression of life
Are collectively called for those art forms that we • A vision of beauty
perceive with our eyes and which occupy space.
AUDITORY ARTS THE AUDIENCE
Art forms that can be heard and are expressed in time. Importance of art to the audience is its value, function,
COMBINED ARTS and significance.
Combination of visual and auditory Art is an experience
Also known as PERFORMING ARTS • What is a poem if no one can read it?
• What is a painting if no one can see it?
VALUES OF ART • What is a sonata if no one can hear it?
AESTHETIC VALUE
Quality appeals to our sense of beauty. FORM
INTELLECTUAL VALUE Medium
Enriches our mental life by making us realize What does it made of
fundamental truths about ourselves, about other What is depicted
human beings, and about the world around us.
SUGGESTIVENESS
Emotional power of art.
SPIRITUAL VALUE HOW TO CRITIQUE ARTWORKS
Elevates the spirit by bringing our moral values which DESCIBE WHAT YOU SEE
makes us a better person. • Artist’s name
PERMANENCE • Title of work
Can be viewed again and again as each encounter gives • Type of artwork
fresh delight and new insights and opens new world of • The subject
meaning and experience. • Objects
UNIVERSALITY • Colors used
Great art is timeless and timely. Forever relevant and • Shapes and textures
appeals to one and all anytime. • Light saturation
ANALYZE THE ARTWORK
• In-depth examination of how the technical
elements were utilized
• Color
• Shapes and forms
• Texture
• Light and shadow
• Technical element that contributes to the
mood, meaning, and aesthetic sensation of
artwork
INTERPRET THE ARTWORK
• Artist’s message conveyed
• Expound the feeling conveyed
• Explain what you feel the artist’s purpose of
creating the artwork
• Identify symbols
EVALUATE THE ARTWORK
• The summation of the art criticism
• Using your analysis and interpretation to draw
out conclusions
Explain its strength and weaknesses (the values)
USE ART VOCABULARY IN YOUR ART CRITIQUE
• Your goal is not to say whether the artwork is
good or bad, but rather to impart the best you
can to impart criticism.
You might also like
- Sq3r Practical GuideDocument7 pagesSq3r Practical GuideMark ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Phenomenology - PPT 9-1-12Document16 pagesPhenomenology - PPT 9-1-12Dilshad Shah100% (2)
- Art Appreciation DiscussionDocument7 pagesArt Appreciation DiscussionAlexis Gee100% (2)
- Contingency TheoryDocument20 pagesContingency TheoryEAC School of Pharmacy ManilaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Creativity-Imagination-ExpressionDocument38 pages1.2 Creativity-Imagination-ExpressionmaricrisandemNo ratings yet
- Meaning of ArtDocument100 pagesMeaning of ArtDominic BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction of Art AppreciationDocument26 pagesLesson 1 Introduction of Art AppreciationMr. YosoNo ratings yet
- Art AppDocument67 pagesArt AppNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Art Education and Appreciation: Jeremich G. SeraficaDocument57 pagesArt Education and Appreciation: Jeremich G. SeraficaAiziel OrenseNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary InterventionDocument22 pagesVocabulary InterventionChrysa PetridouNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document138 pagesLesson 1Adrem RabinoNo ratings yet
- Merged PPT. of CAADocument107 pagesMerged PPT. of CAAVia NaduraNo ratings yet
- Art and Creative LiteracyDocument9 pagesArt and Creative LiteracyRowly Pearl Iradiel Nedic0% (1)
- Lesson 2 ART APPRECIATIONDocument21 pagesLesson 2 ART APPRECIATIONcham shayne89% (9)
- Quiz 1 - Practical Research 1Document1 pageQuiz 1 - Practical Research 1Airah SantiagoNo ratings yet
- 00 B1 Practice Test 1 IntroductionDocument6 pages00 B1 Practice Test 1 IntroductionsalvaNo ratings yet
- Art 2019Document53 pagesArt 2019Laurence MaricolNo ratings yet
- Gec6-Reviewer FinalDocument27 pagesGec6-Reviewer FinalGdeity PlaysNo ratings yet
- Gec6 MergedDocument73 pagesGec6 MergedEme WritesNo ratings yet
- Humanities and Art First SessionDocument31 pagesHumanities and Art First SessionQuennie Kate RomeroNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument6 pagesArt Appreciationtantiana parangNo ratings yet
- Art App (Reviewer)Document5 pagesArt App (Reviewer)Dexter GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Art Education and AppreciationDocument122 pagesArt Education and AppreciationKarlyn RamosNo ratings yet
- ARTS ReviewerDocument11 pagesARTS ReviewerRachel ManaogNo ratings yet
- HUMA 1A - Imagination, Creativity, ExpressionDocument65 pagesHUMA 1A - Imagination, Creativity, ExpressionJeff Jeremiah PereaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Humanities and ArtDocument32 pagesLesson 1. Humanities and ArtPatrick SapieraNo ratings yet
- Art Rituals in The Classroom: "Practice Makes Anything Easier. Practice Builds Self-Esteem. Practice Builds Confidence."Document5 pagesArt Rituals in The Classroom: "Practice Makes Anything Easier. Practice Builds Self-Esteem. Practice Builds Confidence."Veligen BeruedaNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Art AppreciationDocument2 pages01 Introduction To Art AppreciationLara CalayagNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument6 pagesArt AppreciationJenny Dimarucut EspirituNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Lesson 2Document33 pagesContemporary Lesson 2John EspiqueNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Art Assumptions-CreativityDocument43 pages1.2 Art Assumptions-CreativitymaricrisandemNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Lecture 1Document18 pagesArt Appreciation Lecture 1Cresenciano MalabuyocNo ratings yet
- Art App Group 1Document18 pagesArt App Group 1Chelsy Coleen LonzamiaNo ratings yet
- Aa100 PrelimDocument13 pagesAa100 PrelimJasmine Angeli ObilloNo ratings yet
- ARTAP NOTES - Module 1Document4 pagesARTAP NOTES - Module 1Frankie CordovaNo ratings yet
- in Art Appreciation 1Document134 pagesin Art Appreciation 1Fredrex SalacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.ArtAppreeeDocument43 pagesLesson 1.ArtAppreeeRosalie G. FortunaNo ratings yet
- Notes On HUM 101Document7 pagesNotes On HUM 101Trisha LaidenNo ratings yet
- ART Appreciation:: Creativity, Imagination and ExpressionDocument16 pagesART Appreciation:: Creativity, Imagination and ExpressionErica CampusposNo ratings yet
- Art Appre 1Document8 pagesArt Appre 1kishidibagulun29No ratings yet
- Art Appreciation 1st ShiftingDocument9 pagesArt Appreciation 1st ShiftingRica UyNo ratings yet
- FFFFFDocument6 pagesFFFFFimie aldoyesaNo ratings yet
- Gec 5 PrelimsDocument3 pagesGec 5 PrelimsnianNo ratings yet
- Disciplines of Art: Arnel Justin B. LuzanoDocument10 pagesDisciplines of Art: Arnel Justin B. LuzanoArnold AbellaNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Bsis Ba 1b Hum 1Document53 pagesGroup 1 Bsis Ba 1b Hum 1Xavier MesaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Zefra T. Reamillo Social Science DepartmentDocument39 pagesProf. Zefra T. Reamillo Social Science Departmentgazzie rayNo ratings yet
- Haha ResetDocument9 pagesHaha ResetMelissa PioscaNo ratings yet
- Arts AppreciationDocument11 pagesArts Appreciationkathleen.cuyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Art: Introduction and AssumptionsDocument7 pagesWhat Is Art: Introduction and AssumptionsjunquelalaNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Reviewer MidtermDocument22 pagesArt Appreciation Reviewer MidtermZyNo ratings yet
- Lesson I: Introduction To Humanities and Art AppreciationDocument9 pagesLesson I: Introduction To Humanities and Art AppreciationJoyce Kayen BuisingNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction of Art AppreciationDocument28 pagesLesson 1 Introduction of Art Appreciationshanelleregala03No ratings yet
- Hum 101 - Topic 1Document19 pagesHum 101 - Topic 1Raechelle OmolonNo ratings yet
- Soc Sci Art Appreciation HumanitiesDocument38 pagesSoc Sci Art Appreciation HumanitiesJane PadillaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1Document14 pagesTopic 1ireliaakali007No ratings yet
- Cpar W1Document33 pagesCpar W1tolentinoalohamaeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document20 pagesLesson 1FilmaMenasqueRamboyongNo ratings yet
- Cpar Group 1Document85 pagesCpar Group 1Ashley Mc Ginn GacuyaNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO GEC AA Art AppreciationDocument23 pagesINTRODUCTION TO GEC AA Art AppreciationNiña Gel Gomez AparecioNo ratings yet
- Functional of Arts and Its PerspectiveDocument14 pagesFunctional of Arts and Its PerspectiveRaymon Sadsad CondesNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation RobbyargarinDocument29 pagesArt Appreciation RobbyargarinNj SarioNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ArtAppreDocument16 pagesReviewer ArtAppreJuliana David AustriaNo ratings yet
- Cpar Week 1Document64 pagesCpar Week 1John Harry BacudNo ratings yet
- AED Art Appreciation Module 1Document8 pagesAED Art Appreciation Module 1Armie Joy Embat CariazoNo ratings yet
- ARTSDocument7 pagesARTSAndrea Ericka CanawayNo ratings yet
- Research 1Document2 pagesResearch 1this isn't aiaNo ratings yet
- Cpar 2Document4 pagesCpar 2this isn't aiaNo ratings yet
- Research ProblemDocument5 pagesResearch Problemthis isn't aiaNo ratings yet
- PERDEVDocument1 pagePERDEVthis isn't aiaNo ratings yet
- Eng ReDocument1 pageEng Rethis isn't aiaNo ratings yet
- Types of SpeechesDocument2 pagesTypes of Speechesthis isn't aiaNo ratings yet
- Su16 Edld7431 Syllabus Stumpf 20160511Document11 pagesSu16 Edld7431 Syllabus Stumpf 20160511api-381991708No ratings yet
- Methodology-Mixed ClassDocument9 pagesMethodology-Mixed ClassYegana HuseynzadaNo ratings yet
- Unofficial TranscriptsDocument3 pagesUnofficial Transcriptsapi-255765082No ratings yet
- Perceived Effects of Lack of Textbooks To Grade 12Document10 pagesPerceived Effects of Lack of Textbooks To Grade 12Jessabel Rosas BersabaNo ratings yet
- (NAME) Model Citizen Applying ConventionsDocument3 pages(NAME) Model Citizen Applying ConventionsRohan GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mulu G TsadikDocument15 pagesMulu G TsadikYonasNo ratings yet
- Asking Questions, Its ImportanceDocument18 pagesAsking Questions, Its ImportanceTristan BabaylanNo ratings yet
- The Five Minds of A ManagerDocument8 pagesThe Five Minds of A ManagerAashutosh PandeyNo ratings yet
- ktp2019 Tra1996Document94 pagesktp2019 Tra1996Luchmee Devi GoorjhunNo ratings yet
- Panatang Makabayan English and Tagalog VersionDocument7 pagesPanatang Makabayan English and Tagalog VersionJENILOU100% (3)
- Facilitating Human LearningDocument8 pagesFacilitating Human LearningYaj CruzadaNo ratings yet
- May Semester 2010 Sbsc4103 - Measurement and Evaluation in Science Assignment (30%)Document4 pagesMay Semester 2010 Sbsc4103 - Measurement and Evaluation in Science Assignment (30%)Oscar ArthurNo ratings yet
- Reflective Portfolio Feedback and Marking RubricDocument2 pagesReflective Portfolio Feedback and Marking Rubricapi-512652362No ratings yet
- MopDocument47 pagesMopNishan DineshkaNo ratings yet
- Hope11 Q3 Week1 PDFDocument12 pagesHope11 Q3 Week1 PDFIan Joshua Sanchez100% (1)
- Law of The InstrumentDocument2 pagesLaw of The InstrumentMenesteroso DesgraciadoNo ratings yet
- Pangasinan State University Table of Specifications 2 Semester S.Y. 2018-2019 Midterm ExamDocument2 pagesPangasinan State University Table of Specifications 2 Semester S.Y. 2018-2019 Midterm ExamRenwel Jhon PagusanNo ratings yet
- Not Synonymous: Criticism and Critical AnalysisDocument3 pagesNot Synonymous: Criticism and Critical AnalysisEthel Joi Manalac MendozaNo ratings yet
- MSC Psychology SyllabusDocument25 pagesMSC Psychology SyllabusPravin AjaazNo ratings yet
- Critical Methodology Analysis: 360' Degree Feedback: Its Role in Employee DevelopmentDocument3 pagesCritical Methodology Analysis: 360' Degree Feedback: Its Role in Employee DevelopmentJatin KaushikNo ratings yet
- Case Study What A Waste of Time (Final)Document3 pagesCase Study What A Waste of Time (Final)Mizanur Rahman Peash100% (6)
- 8.he Couldn't Help - With ThemDocument3 pages8.he Couldn't Help - With ThemAlexNo ratings yet
- Tos 1ST Quarter Mapeh 10Document2 pagesTos 1ST Quarter Mapeh 10Dhan Mark BarlintangcoNo ratings yet
- Assess Aspects of Your DevelopmentDocument9 pagesAssess Aspects of Your DevelopmentCHRISTINE RANESESNo ratings yet