Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Script-Topic 3
Uploaded by
Anh Nguyễn Thị NgọcOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Script-Topic 3
Uploaded by
Anh Nguyễn Thị NgọcCopyright:
Available Formats
SCRIPT TOPIC 3
Định nghĩa GHG (nêu kịp thì nói)
Firstly to determine how GHG emissions rate changed during and after the
Covid19, let’s define what is GHG emissions. GHG emissions or greenhouse gas is a gas
that absorbs and emits radiant energy in the thermal infrared spectrum, resulting in the
greenhouse effect and deteriorating our earth.
Diễn giải toàn bộ bối cảnh GHG emissions thay đổi tại HQ
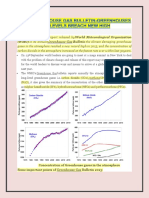
The obvious rate changes are in Urban CO2 concentration and air quality in the
atmosphere in Korea. According to Aerosol and Air Quality Research, the average and
excess concentrations of all measured atmospheric elements show a reduction in
February 2020 compared to 2019. Particularly, NO2 had the greatest drop in average and
background concentrations (-32.9% and -32.7%, respectively) among the three
greenhouse gasses NO2, CO, and CO2. CO decreases by -14.1% and -9.1% in average
and background concentrations, respectively, whereas CO2 decreases by -0.2% and -
0.1% in average and background concentrations, respectively. All recorded excess
amounts are lower in February 2020 compared to 2019, with declines of -34%, -23.8%,
and -4.4% for NO2, CO, and CO2, respectively.
kết luận
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a reduction in atmospheric
CO2 concentration and GHG emission changes in general. The COVID-19 virus has
caused tremendous socioeconomic damage; however, it has provided a positive outlook
regarding the potential for future climate change and greenhouse gas reduction. However,
when the pandemic ended, cities and people started everything that they were doing
before the pandemic and people even enjoy going out more after the pandemic which has
been leading to a high rate of GHG emissions like it was in the first place. Thank you for
listening.
You might also like
- Carbon Credits-A Case Study On GFLDocument39 pagesCarbon Credits-A Case Study On GFLsudesh1992No ratings yet
- Data Vis Final ReportDocument54 pagesData Vis Final ReporttheonlygodNo ratings yet
- Wmo Greenhouse Gas Bulletin-Greenhouses Gas Levels Breach New HighDocument5 pagesWmo Greenhouse Gas Bulletin-Greenhouses Gas Levels Breach New HighRamBabuMeenaNo ratings yet
- GHG 18 enDocument10 pagesGHG 18 enDhafin KlonNo ratings yet
- Dramatic Decline of Observed Atmospheric CO2 and CH4 During The COVID-19 Lockdown Over The Yangtze River Delta of ChinaDocument11 pagesDramatic Decline of Observed Atmospheric CO2 and CH4 During The COVID-19 Lockdown Over The Yangtze River Delta of Chinakok peng leongNo ratings yet
- WMO 2020 Green House Gas BulletinDocument9 pagesWMO 2020 Green House Gas Bulletinchenzhaoying6666No ratings yet
- Reduce Co2 With Sustainable ItDocument4 pagesReduce Co2 With Sustainable ItDoggiesBrownNo ratings yet
- Apec EnvironmentDocument6 pagesApec EnvironmentRura SilindungNo ratings yet
- Final Revision Lockdown Has Been Impactful To The Atmosphere Final Draft 1 5Document23 pagesFinal Revision Lockdown Has Been Impactful To The Atmosphere Final Draft 1 5api-548825228No ratings yet
- Eprs Bri (2021) 689336 enDocument8 pagesEprs Bri (2021) 689336 enbarakalami94hudahaiderNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Dioxide - WHO Guidelines For Indoor Air Quality: Selected PollutantsDocument52 pagesNitrogen Dioxide - WHO Guidelines For Indoor Air Quality: Selected Pollutants89kkNo ratings yet
- GHG Emissions Paint Industry JournalDocument6 pagesGHG Emissions Paint Industry Journalbhawani27No ratings yet
- EV10003 C6 Climate Change 2023Document51 pagesEV10003 C6 Climate Change 2023Saloni ShawNo ratings yet
- Zeng+et+al 2021 Environ. Res. Lett. 10.1088 1748-9326 Ac3f62Document25 pagesZeng+et+al 2021 Environ. Res. Lett. 10.1088 1748-9326 Ac3f62lucioNo ratings yet
- 6.4 (7) ArdlDocument17 pages6.4 (7) ArdlShijie TanNo ratings yet
- Envr1150 03 GHGDocument14 pagesEnvr1150 03 GHG1danielkang1210No ratings yet
- CO2 Capture and Separation Technologies For End-Of-pipe ApplicationsDocument19 pagesCO2 Capture and Separation Technologies For End-Of-pipe ApplicationsKhuram MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Climate Change PoliticsDocument7 pagesClimate Change PoliticsASNMURTYNo ratings yet
- CO2 Emissions Overview PDFDocument12 pagesCO2 Emissions Overview PDFHasan MasrurNo ratings yet
- Introduction 1Document3 pagesIntroduction 1Aishwarya SinghNo ratings yet
- UK Environmental Accounts 2023Document15 pagesUK Environmental Accounts 2023camhahuynh1982No ratings yet
- Trends in Global GHGs EmissionsDocument85 pagesTrends in Global GHGs EmissionswalaaeconNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0048969720357673 Main PDFDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S0048969720357673 Main PDFAngela Lucía NúñezNo ratings yet
- 8 PDFDocument4 pages8 PDFDaniela PatiñoNo ratings yet
- What Is Co2Document5 pagesWhat Is Co2elinebet03No ratings yet
- Engliah III (Technical Report Writing)Document2 pagesEngliah III (Technical Report Writing)Faiqa MalikNo ratings yet
- CO2 Emissions - Our World in DataDocument29 pagesCO2 Emissions - Our World in DataMuhammad Oki ZuheimiNo ratings yet
- EV10003 C5 Climate Change Aut2023Document54 pagesEV10003 C5 Climate Change Aut2023aditya10prakashiitNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution: Action in A Changing Climate: WWW - Defra.gov - UkDocument24 pagesAir Pollution: Action in A Changing Climate: WWW - Defra.gov - UkSomchai ChuananonNo ratings yet
- 1AC - Climate Aff: Plan: The United States Ought To Provide A Federal Jobs GuaranteeDocument19 pages1AC - Climate Aff: Plan: The United States Ought To Provide A Federal Jobs GuaranteeBobb JoeeNo ratings yet
- Ijerph 19 11076 v2Document19 pagesIjerph 19 11076 v2Pika SeptianiNo ratings yet
- EnvironmentDocument11 pagesEnvironmentمحمد علي كريم شكرNo ratings yet
- Friedlingstein Et Al NGeo 2010Document3 pagesFriedlingstein Et Al NGeo 2010John KellyNo ratings yet
- Bicol University College of Engineering Legazpi City Vista, Hermialyn B. Bsce-3DDocument10 pagesBicol University College of Engineering Legazpi City Vista, Hermialyn B. Bsce-3DHermialyn VistaNo ratings yet
- Articulo N°1 PDFDocument8 pagesArticulo N°1 PDFvaleriaNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Health Expenditure, CO Emissions, and Economic Growth in G7: Evidence From Heterogeneous Panel DataDocument26 pagesThe Relationship Between Health Expenditure, CO Emissions, and Economic Growth in G7: Evidence From Heterogeneous Panel DataHuy Lê ThanhNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Gas: ConstituentsDocument25 pagesGreenhouse Gas: ConstituentsKarl GustavNo ratings yet
- Carbon Imprints and Their Significance in Climate Change MitigationDocument15 pagesCarbon Imprints and Their Significance in Climate Change Mitigationdelacruzjr.enrique.bsceNo ratings yet
- Guidelines EDocument25 pagesGuidelines Eshahid latifNo ratings yet
- Sustainability 14 17054Document18 pagesSustainability 14 17054Syed DanishNo ratings yet
- The Carbon EconomyDocument35 pagesThe Carbon EconomyBrenda Nicolls JaramilloNo ratings yet
- The Effect of National GDP Growth On Indonesia's CO2 Emissions Per CapitaDocument3 pagesThe Effect of National GDP Growth On Indonesia's CO2 Emissions Per CapitaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Proyeksi Emisi Gas Rumah Kaca Tahun 2012 2030: ResearchDocument8 pagesProyeksi Emisi Gas Rumah Kaca Tahun 2012 2030: ResearchIzzu FaturNo ratings yet
- spf00003012Document12 pagesspf00003012JC PeraltaNo ratings yet
- EmissionsDocument20 pagesEmissionsBahy ElkolalyNo ratings yet
- Articulo 1Document41 pagesArticulo 1estebanNo ratings yet
- Sustainability and Climate ChangeDocument51 pagesSustainability and Climate ChangeKirish Inc.No ratings yet
- How Green Growth Affects Carbon Emissions in China - The Role of Green FinanceDocument23 pagesHow Green Growth Affects Carbon Emissions in China - The Role of Green FinanceMubashir ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Energy & Climate Change - Lect-5 (23.09.2021)Document13 pagesEnergy & Climate Change - Lect-5 (23.09.2021)humza abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Relative Humidity Temperature MDocument13 pagesRelative Humidity Temperature Mmelaku tadeleNo ratings yet
- PBL 2020 Trends in Global Co2 and Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2019 Report 4068Document70 pagesPBL 2020 Trends in Global Co2 and Total Greenhouse Gas Emissions 2019 Report 4068thuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive and Synthetic Dataset For GlobalDocument40 pagesA Comprehensive and Synthetic Dataset For GlobalRoxy Estefania MonserrateNo ratings yet
- Environmental Design Studio - II: Identification of Environemental Problems and Its Causes in HyderabadDocument9 pagesEnvironmental Design Studio - II: Identification of Environemental Problems and Its Causes in HyderabadHaritha NemoNo ratings yet
- Pathways of Human Development and Carbon EmissionsDocument6 pagesPathways of Human Development and Carbon EmissionsAlyaa SallamNo ratings yet
- Energies: Process Integration of Green Hydrogen: Decarbonization of Chemical IndustriesDocument16 pagesEnergies: Process Integration of Green Hydrogen: Decarbonization of Chemical IndustriesMayur TapadiaNo ratings yet
- Impact On Air Quality of The COVID-19 Lockdown in The Urban Area of Palermo (Italy)Document12 pagesImpact On Air Quality of The COVID-19 Lockdown in The Urban Area of Palermo (Italy)Concetta PizzichettaNo ratings yet
- Sample of Writing - The Correlation of Meteorological Parameters and Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in The North of JordanDocument11 pagesSample of Writing - The Correlation of Meteorological Parameters and Atmospheric CO2 Concentration in The North of JordanFares RababaNo ratings yet
- Seminar LikhithaDocument18 pagesSeminar LikhithaPrajwal KRNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study On Black CarbonDocument26 pagesA Comprehensive Study On Black CarbonNikhil RastogiNo ratings yet
- Vietnam AseanDocument24 pagesVietnam AseanAnh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Tài Liệu Lý ThuyếtDocument12 pagesTài Liệu Lý ThuyếtAnh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Conferences pg.61) : Planning and Agenda SettingDocument2 pagesConferences pg.61) : Planning and Agenda SettingAnh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Nguyen Thi Ngoc Anh r4Document5 pagesNguyen Thi Ngoc Anh r4Anh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- Joe and Sue CarterDocument2 pagesJoe and Sue CarterAnh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- 195160528Document1 page195160528Anh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet
- The Global Financial Crisis and Its Impact On Renewable Energy Finance-20091016Document143 pagesThe Global Financial Crisis and Its Impact On Renewable Energy Finance-20091016Anh Nguyễn Thị NgọcNo ratings yet