Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phylum Arthropoda Transes
Uploaded by
Maribel Ramos InterinoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phylum Arthropoda Transes
Uploaded by
Maribel Ramos InterinoCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYLUM ARTHROPODA -Hemocoel- where the blood is not enclosed in
the blood vessels, but is pumped into a cavity.
RESPIRATION
-Joint legs animals -process of breathing in oxygen and breathing
-Arthropods are the first Phylum animals that out carbon dioxide.
have voluntary muscles. Tracheary system- is a tiny tubes that permit
-Greek word “Arthron”, which means “foot” or passage of gases into the interior of the body.
“leg” which collectively means jointed leg Spiracle- are the openings of surface of some
-Largest Phylum of the animal kingdom. animals, usually lead to respiratory system.
-The body consist of three divisions: Aquatic vs Terrestrial
a segmented body, an exoskeleton (made up of Arthropods Respiration
chitin) and jointed appendages.
AQUATIC- they have gills that absorb oxygen
from water
CHARACTERISTICS
TERRESTIAL- they have book lungs to breath
-Exoskeleton containing chitin
BOOK LUNGS- are made up of stacks of
-They are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic,
folded tissue.
coelomate animals.
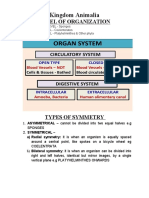
-The circulatory system is open and consists of a
REPRODUCTION
heart, arteries, and the open spaces of the
hemocoel. -most of arthropods reproduce sexually
-They contain colorless blood called
(haemolymph). Internal fertilization
- Arthropods are dioecious and have paired -it occurs in exoskeletons arthropods
reproductive organs (ovaries, testes). -oviparity
- Have sensory organs like antennae, eyes External fertilization
(compound and simple), statocysts, or -occurs in aquatic arthropods like crabs and
balancing organs. lobster
- Undergo internal fertilization in other group TWO STAGES OF DEVELOPMENT
MORPHOLOGY DIRECT DEVELOPMENT- Do not develop
- They are Bilateral Symmetry sex organs and they do not have wings.
- right and left sides of the body are exactly the (E.G) spiders
mirror image of each other. INDIRECT DEVELOPMENT- involves larval
- They have segmented body stages like mosquitoes
-head and thorax are fused together into an egg is a larva that comes from the larvae-
cephalothorax pupil and to the adult.
- They have joint appendages.
-They have Exoskeleton or outside skeleton. CLASSES OF ARTHROPODA
- also known as Arthropod Armor, and made CRUSTACEAN- known as marine life
up of chitin (e.g) prawns and crabs
Crusta- derived from the word shell.
- Molting – process of shedding an outgrown -both aquatic and terrestrial.
skeleton divided into two parts: Cephalothorax and
Abdomen
OPEN CIRCULATORY SYSTEM - The Respiration is Branchial through gills.
The absence of vessels to contain the - The excretion is by green glands.
blood and it flows freely through the cavities of
the body. ARACHNIDA- - is a large and diverse group
that belong to a subphylum.
- known as Chelicerata.
(e.g) scorpions and spider
Arachne- spider
divided into two parts: Cephalothorax and
Abdomen
- Terrestial preadators
- The main types of excretory organs occur in
aracnids are coxal glands and malphigian
tubules.
CHILOPODA AND DIPLODA
-belongs to the sub-strain Myriapoda.
Chilopoda- commonly referred to as a
centipedes.
-can be 4 to 5 inches long.
Diplopoda-commonly referred to as a
millipedes.
-can be 1 to 8 inches long.
They are terrestrial arthropods.
- The excretion occurs through Malpighian
tubules.
- When it comes to their sexual reproduction,
The male Chilopoda deposits bundles of sperm
in the environment known as spermatophores;
they are devoured by female Chilopoda while in
Diplopoda by mating.
HEXAPODA
-commonly known Insecta
- considered as the largest group arthropods
- have chitinous exoskeleton
- The body is divided into 3 body parts; head,
thorax, and abdomen
- - The main excretory organ of the insect is the
Malpighian tubule.
MEROSTOMATA
- Also known as horseshoe crab
-That belongs to subphylum of Chelicerata.
-The body is divided into two parts;
cephalothorax and abdomen
- The respiration is book gills.
You might also like
- FG ODjl TZF I0 OJXxron 9 CDocument5 pagesFG ODjl TZF I0 OJXxron 9 Ctensazangestuiit24No ratings yet
- Zoology (Plathy - Echano) NotesDocument7 pagesZoology (Plathy - Echano) NotesJanani RajeshNo ratings yet
- Zoology 1 Year Part BDocument58 pagesZoology 1 Year Part BPankaj KewratNo ratings yet
- Samuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarreroDocument15 pagesSamuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarrerosamuelNo ratings yet
- Samuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarreroDocument15 pagesSamuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarrerosamuelNo ratings yet
- Samuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarreroDocument15 pagesSamuel Sanchez, Samuel Garzon & Juan Jose BarrerosamuelNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch04 Animal KingdomDocument5 pages11 Biology Notes Ch04 Animal KingdomTushar RajNo ratings yet
- What Is Morphology?Document26 pagesWhat Is Morphology?Michael Vincent P.No ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch04 Animal KingdomDocument8 pages11 Biology Notes Ch04 Animal KingdomPriyanshu BhadanaNo ratings yet
- Boi 115 - AssignmentDocument9 pagesBoi 115 - Assignmentmiominzy09No ratings yet
- ARTHOPODA1Document23 pagesARTHOPODA1Kritika LohaniNo ratings yet
- Insectsphysiologyppt 170801053717Document54 pagesInsectsphysiologyppt 170801053717kdicolanoNo ratings yet
- Basic Health BiologyDocument18 pagesBasic Health BiologyJohn BasseyNo ratings yet
- Phylum Echinodermata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Echinodermata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument35 pagesAnimal KingdomSuresh KuppananNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdompdfDocument9 pagesAnimal KingdompdfAkshay G SNo ratings yet
- XI 4 Animal KingdomDocument58 pagesXI 4 Animal KingdomDeepti KashyapNo ratings yet
- Ciclatory Systems of Different OrganismsDocument5 pagesCiclatory Systems of Different OrganismsSekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- 4 Animal KingdomDocument8 pages4 Animal KingdomPHANI KUMAR A.V.SNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument16 pagesAnimal Kingdomaravind kishanNo ratings yet
- Class Notes Animal KingdomDocument6 pagesClass Notes Animal Kingdomdevu sinhaNo ratings yet
- ArthropodaDocument3 pagesArthropodaLêð VëlåscõNo ratings yet
- ČlánkonožceDocument21 pagesČlánkonožcecircovaesterkaNo ratings yet
- Assboi115 2Document11 pagesAssboi115 2NORHIDAYATI BINTI MD GHAZALI MoeNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Focuspoints NVSDocument8 pagesAnimal Kingdom Focuspoints NVSAyush Gupta; 11-Science; 4402No ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument152 pagesKingdom AnimaliaS SNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument7 pagesAnimal Kingdomsivarigil0610No ratings yet
- Ento ReviewerDocument8 pagesEnto ReviewerGray Odyssey M.No ratings yet
- Bio Animal KingdomDocument2 pagesBio Animal KingdomradhirajchemNo ratings yet
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocument22 pagesKingdom AnimaliaPrarthanaSudeepNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Animl KingdomDocument12 pagesCHAPTER 4 Animl KingdomAnushka MishraNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata: C O P C NDocument8 pagesPhylum Chordata: C O P C NBaikuntha SabarNo ratings yet
- Class - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4 HandoutDocument4 pagesClass - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4 HandoutNewcomerNo ratings yet
- Animal KigdomDocument17 pagesAnimal KigdomKAMESH .GNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ImportantDocument7 pagesAnimal Kingdom Importants.sameera9fgs110u0007No ratings yet
- Summary Practical ScienceDocument8 pagesSummary Practical ScienceFaiq Nur AqliNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera - : Sycon, Spongilla, EuspongiaDocument8 pagesPhylum Porifera - : Sycon, Spongilla, EuspongiaCrazy about JunglesNo ratings yet
- Protochordates-WPS OfficeDocument6 pagesProtochordates-WPS OfficeOgualu FavourNo ratings yet
- B.sc. I Detailed ClassificationDocument9 pagesB.sc. I Detailed ClassificationSuchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Organ System LevelDocument16 pagesAnimal Kingdom: Cellular Level Tissue Level Organ Level Organ System LevelRahul RavteNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument5 pagesAnimal KingdomArthav KumarNo ratings yet
- Diversity in AnimalsDocument10 pagesDiversity in AnimalsGhalib khattakNo ratings yet
- Biol 1002 Exam2 NotesDocument21 pagesBiol 1002 Exam2 NotesJashayla GillespieNo ratings yet
- Organ System: Kingdom AnimaliaDocument18 pagesOrgan System: Kingdom AnimaliaTanishq AroraNo ratings yet
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocument31 pagesDiversity in Living OrganismsAnand MohanNo ratings yet
- Amphibi: (Esm Zoology For School)Document19 pagesAmphibi: (Esm Zoology For School)CokroNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom ClassificationDocument11 pagesAnimal Kingdom ClassificationcharminemarideNo ratings yet
- Iv Unit BiodasDocument14 pagesIv Unit BiodasCokroNo ratings yet
- Animals NoteDocument23 pagesAnimals NoteMike LuchNo ratings yet
- Phylums of Animal KiingdomDocument44 pagesPhylums of Animal Kiingdomkiran kombeNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 - Animal Kingdom (Notes)Document8 pagesCh.4 - Animal Kingdom (Notes)ketakiNo ratings yet
- Class - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4Document20 pagesClass - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4Anshu RajNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom BSTDocument20 pagesAnimal Kingdom BSTRBSNo ratings yet
- Animals 1Document2 pagesAnimals 1alxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- RevisedinvertebratesdocDocument6 pagesRevisedinvertebratesdocapi-250255513No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom-Class 11Document6 pagesAnimal Kingdom-Class 11ICSE BOARDNo ratings yet
- Hemi ChordatesDocument17 pagesHemi ChordatesMUHAMMAD ILYASNo ratings yet
- Simion Ana-MariaDocument8 pagesSimion Ana-MariaAna-Maria SimionNo ratings yet
- Phylum ChordataDocument25 pagesPhylum ChordataNicole100% (1)
- Mathematics 8 - Tos - Quarter 1 2Document4 pagesMathematics 8 - Tos - Quarter 1 2Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Parent ConsentDocument1 pageParent ConsentMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 MAPEH Assessment Tool FINALDocument8 pagesGrade 10 MAPEH Assessment Tool FINALAldrin BagasinaNo ratings yet
- G8DLL Q2W9 LC38Document10 pagesG8DLL Q2W9 LC38Jena Rose Gane GanancialNo ratings yet
- WaiverDocument1 pageWaiverMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Work Immersion Parental ConsentDocument1 pageWork Immersion Parental ConsentMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Parent ConsentDocument2 pagesParent ConsentMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Table of Specifications: Third Periodic Test in Mathematics 10Document4 pagesTable of Specifications: Third Periodic Test in Mathematics 10Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- G8DLL Q1W1 LC01Document10 pagesG8DLL Q1W1 LC01Jonathan CanonigoNo ratings yet
- SHS-School-Program-1st Sem 2022-2023Document3 pagesSHS-School-Program-1st Sem 2022-2023Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Gen, Math - DLL WK 1Document11 pagesGen, Math - DLL WK 1Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- CLASS PROGRAM SHS 2022-2023 RegularDocument11 pagesCLASS PROGRAM SHS 2022-2023 RegularMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Table 1.1: Status of Ways Forward For The Previous Quarter: 3Rd Quarter Issues/Concerns/ Needs/GapsDocument23 pagesTable 1.1: Status of Ways Forward For The Previous Quarter: 3Rd Quarter Issues/Concerns/ Needs/GapsMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- 3RD Quarter Examination G10Document4 pages3RD Quarter Examination G10Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Gen Math Q2 W7 QADocument20 pagesGen Math Q2 W7 QAMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Enterp 4Document4 pagesEnterp 4Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- TEMPLATE For HISTORICAL SOURCES 1Document11 pagesTEMPLATE For HISTORICAL SOURCES 1Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- G8DLL Q2W10 LC39Document14 pagesG8DLL Q2W10 LC39Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Enterp 2Document5 pagesEnterp 2Maribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Phylum Chordata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Chordata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Phylum Echinodermata TransesDocument2 pagesPhylum Echinodermata TransesMaribel Ramos InterinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6: at The End of The Lesson The Students Should Be Able ToDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6: at The End of The Lesson The Students Should Be Able ToGrace Music100% (9)
- Cornell Notes - Classification of Living Things Filled in VersionDocument4 pagesCornell Notes - Classification of Living Things Filled in Versionapi-307861748No ratings yet
- Animal EvolutionDocument6 pagesAnimal EvolutionYsabella PolanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Test: Food Chains/Food WebsDocument5 pagesUnit 5 Test: Food Chains/Food Websapi-428677890No ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument1 pageAnimal Kingdommaishakk512No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: Organ Level of OrganisationDocument24 pagesAnimal Kingdom: Organ Level of Organisationshaunasweeney5144No ratings yet
- Spelling BEE 2021Document42 pagesSpelling BEE 2021harryNo ratings yet
- Polifera JurnalDocument14 pagesPolifera JurnalPuri RahmaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: (Non-Chordates and Chordates)Document19 pagesAnimal Kingdom: (Non-Chordates and Chordates)Raj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Exit Mcqs.-1Document180 pagesExit Mcqs.-1Muhammad Yasin Sabir0% (1)
- 1108 Principles of Biology Syllabus FatsyDocument5 pages1108 Principles of Biology Syllabus Fatsyapi-293162935No ratings yet
- Science 6 - Q2 - PT - NewDocument8 pagesScience 6 - Q2 - PT - NewAlvin AbordeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15: Diversity of AnimalsDocument2 pagesChapter 15: Diversity of AnimalsFatima BjaijihNo ratings yet
- Ivri 11Document403 pagesIvri 11danutaNo ratings yet
- Word by Word Picture DictionaryDocument126 pagesWord by Word Picture DictionaryMuthu Raman ChinnaduraiNo ratings yet
- 9 Major Animal Phyla PresentationDocument27 pages9 Major Animal Phyla PresentationSamil UdinNo ratings yet
- Classification IGCSEDocument55 pagesClassification IGCSEelizabethNo ratings yet
- Vertebrates and Invertebrates: VertebraeDocument7 pagesVertebrates and Invertebrates: VertebraeFaraiNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom (Non-Chordata) PDFDocument71 pagesAnimal Kingdom (Non-Chordata) PDFasima rath75% (4)
- Key 2544424 2023-10-1520043A093A31202B0000 PDFDocument24 pagesKey 2544424 2023-10-1520043A093A31202B0000 PDFrohit19loharNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Animals - FinalDocument7 pagesVertebrate Animals - FinalAlyzza Ann EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Animal DiversityDocument87 pagesAnimal DiversityharshitaNo ratings yet
- (D) AV2.End.181 PDFDocument2 pages(D) AV2.End.181 PDFBảo Nguyễn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAanchal Pandey100% (2)
- Dodington 2018 Companion Species WantedDocument3 pagesDodington 2018 Companion Species WantedAnna ConrickNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Life Assessment MsDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Life Assessment Msapi-375761980No ratings yet
- Architectural Pattern of An AnimalDocument26 pagesArchitectural Pattern of An AnimalMSSM EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Science Chapter 3Document23 pagesForm 2 Science Chapter 3qq23592% (25)
- Science 218: (C) 2012 Dorling Kindersley. All Rights ReservedDocument1 pageScience 218: (C) 2012 Dorling Kindersley. All Rights ReservedJohn ArredondoNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 1 The Living World ExamplerDocument6 pagesClass 11 Biology NCERT Textbook Chapter 1 The Living World ExamplerTitan 2000No ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (516)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- The Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightFrom EverandThe Invention of Tomorrow: A Natural History of ForesightRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (215)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)