Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure & Density
Uploaded by
Yoga PratamaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure & Density
Uploaded by
Yoga PratamaCopyright:
Available Formats
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.
com
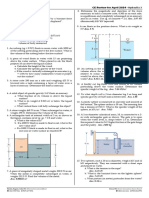
Pressure & Density June 05
7. The hydrostatic pressure p at a depth h in a liquid of density ρ is
given by the formula p = hρ g.
May 02 Which equation, or principle of physics, is used in the derivation of
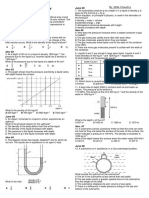
1. A cylindrical block of wood has a cross-sectional area A and this formula?
weight W. It is totally immersed in water with its axis vertical. The A density = mass ÷ volume
block experiences pressures pt and pb at its top and bottom B potential energy = mgh
surfaces respectively. Which of the following expressions is C atmospheric pressure decreases with height
equal to the upthrust on the block? D density increases with depth
Nov 05
8. Why does the pressure increase when a sealed container of gas
is heated?
2. A mass of a liquid of density ρ is thoroughly mixed with an A The gas molecules collide more often with each other.
equal mass of another liquid of density 2ρ. No change of the B The gas molecules expand when they are heated.
total volume occurs. What is the density of the liquid mixture? C The gas molecules travel faster and hit the walls of the container
more often.
D There are more gas molecules present to collide with the walls of
the container.
Nov 02
–3
3. At a depth of 20 cm in a liquid of density 1800 kgm , the 9. Liquids X and Y are stored in large open tanks. Liquids X and Y
–3 –3
pressure due to the liquid is p. Another liquid has a density of have densities of 800 kg m and 1200 kg m respectively.
1200 kgm .
–3 At what depths are the pressures equal?
What is the pressure due to this liquid at a depth of 60 cm?
Nov 03
4. The graph shows how the pressure exerted by a liquid varies
with depth below the surface.
Nov 06
10. Which force is caused by a pressure difference?
A friction B upthrust C viscous force D weight
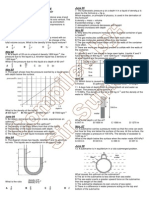
11. A bore hole of depth 2000 m contains both oil and water as
shown. The pressure at the bottom is
–3
17.5 MPa. The density of the oil is 830 kg m and the density of the
–3
water is 1000 kg m .
What is the density of the liquid?
–3 –3 –3 –3
A 600 kgm B 760 kgm C 5900 kgm D 7500 kgm
June 04
5. An object, immersed in a liquid in a tank, experiences an
What is the depth x of the oil?
upthrust.
A 907 m B 1000 m C 1090 m D 1270 m
What is the physical reason for this upthrust?
A The density of the body differs from that of the liquid. Nov. 07
B The density of the liquid increases with depth. 12. A submarine carries a pressure meter so that the crew can work
C The pressure in the liquid increases with depth. out how far they are below the surface of the sea. At the surface, the
D The value of g in the liquid increases with depth. meter indicates a pressure of 100 kPa. The density of seawater is
–3
1030 kg m .
Nov 04 What is the depth below the surface when the meter reads 450 kPa?
6. The diagram shows two liquids, labelled P and Q, which do A 34.6 m B 44.5 m C 340 m D 437 m
not mix. The liquids are in equilibrium in an open U-tube.
June 08
13. A submarine is in equilibrium in a fully submerged position.
What causes the upthrust on the submarine?
A The air in the submarine is less dense than sea water.
B The sea water exerts a greater upward force on the submarine
What is the ratio than the weight of the steel.
C The submarine displaces its own volume of sea water.
D There is a difference in water pressure acting on the top and
bottom of the submarine
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
Nov 08 19. A rectangular metal bar exerts a pressure of 15 200 Pa on the
14. Why does an ideal gas exert pressure on its container? horizontal surface on which it rests.
A The molecules of the gas collide continually with each other. If the height of the metal bar is 80 cm, what is the density of the
B The molecules of the gas collide continually with the walls of metal?
–3 –3
the container. A 190 kg m B 1900 kg m
–3 –3
C The molecules of the gas collide inelastically with the walls of C 19 000 kg m D 190 000 kg m
the container.
D The weight of the molecules exerts a force on the walls of the June 10
container. 20. An object, immersed in a liquid in a tank, experiences an
upthrust.
June 07 What is the physical reason for this upthrust?
3 –3
15. The density of mercury is 13.6 × 10 kg m . A The density of the body differs from that of the liquid.
The pressure difference between the bottom and the top of a B The density of the liquid increases with depth.
column of mercury is 100 kPa. C The pressure in the liquid increases with depth.
What is the height of the column? D The value of g in the liquid increases with depth.
A 0.75 m B 1.3 m C 7.4 m D 72 m
21. Atmospheric pressure at sea level has a value of 100 kPa.
–3
June 09 The density of sea water is 1020 kg m .
16. The diagram represents a sphere under water. P, Q, R, and At what depth in the sea would the total pressure be 110 kPa?
S are forces acting on the sphere, due to the pressure of the A 1.0m B 9.8 m C 10 m D 11 m
water.
Answers
1 c 16 a
2 a 17 d
3 c 18 d
4 b 19 b
5 c 20 c
6 a 21 a
7 a
8 c
9 c
Each force acts perpendicularly to the sphere’s surface. P and R
act in opposite directions vertically. Q and S act in opposite 10 b
directions horizontally. 11 d
Which information about the magnitudes of the forces is correct? 12 a
AP<R;S=Q BP>R;S=Q
CP=R;S=Q DP=R=S=Q 13 d
14 b
17. The diagram shows a flask connected to a U-tube containing 15 a
liquid. The flask contains air at atmospheric pressure.
The flask is now gently heated and the liquid level in the right-
hand side of the U-tube rises through a distance h. The density
of the liquid is ρ.
What is the increase in pressure of the heated air in the flask?
A hρ B ½ hρg C hρg D 2hρg
Nov 09
18. In the kinetic model of gases, what is pressure equal to?
A the number of atoms hitting and rebounding from a surface of
the gas container
B the number of atoms hitting and rebounding from a unit area
of the gas container surface
C the force exerted by the atoms hitting and rebounding from a
surface of the gas container
D the force exerted by the atoms hitting and rebounding from a
unit area of the gas container surface
You might also like
- Pressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910From EverandPressure, Resistance, and Stability of Earth American Society of Civil Engineers: Transactions, Paper No. 1174, Volume LXX, December 1910No ratings yet
- Pressure & DensityDocument2 pagesPressure & DensityIffi AkramNo ratings yet
- Pressure AnsDocument2 pagesPressure AnsHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- CQZ1 Solutions ExplanationsDocument11 pagesCQZ1 Solutions Explanationsricardo lopezNo ratings yet
- X GLzee CVu 9 S TBLmamwbxDocument8 pagesX GLzee CVu 9 S TBLmamwbxaavaathebestNo ratings yet
- 9702 p1 Properties of Matter All PDFDocument8 pages9702 p1 Properties of Matter All PDFkwon jiyongNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Understanding Pressure in LiquidsDocument14 pages3.2 Understanding Pressure in LiquidsArif KhanNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsjunquelalaNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Pressure in LiquidDocument12 pages3.2 Pressure in LiquidNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- GP1 - Q2M5 Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesGP1 - Q2M5 Lecture NotesROMER NYLIM DE GUZMANNo ratings yet
- Physics Work Sheet 2Document6 pagesPhysics Work Sheet 2Debela mendaraNo ratings yet
- Pressure Liquids +pressure Gas OnlineDocument14 pagesPressure Liquids +pressure Gas OnlineayydenNo ratings yet
- Hyd 3Document1 pageHyd 3Jocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- Fluids PhysicsDocument24 pagesFluids PhysicsNtobeko MjiyakoNo ratings yet
- Physics Test Prep: States of MatterDocument4 pagesPhysics Test Prep: States of MattervaraprasadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pressure Quiz 2019Document2 pagesFluid Pressure Quiz 2019Hermy E. Feliciano0% (1)
- Worksheet V: Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesWorksheet V: Fluid MechanicsAeriel May PliegoNo ratings yet
- M Y9 YBpl IHKLqou 25 GyabDocument8 pagesM Y9 YBpl IHKLqou 25 GyabaavaathebestNo ratings yet
- Phy 061 Chapter 7 Fluid MechanicsDocument5 pagesPhy 061 Chapter 7 Fluid MechanicsAngel Lou LiwagonNo ratings yet
- PHYS 101 - Lecture 6Document23 pagesPHYS 101 - Lecture 6ShahadNo ratings yet
- FluidMechanicsI HW02Document1 pageFluidMechanicsI HW02AzlNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 3Document5 pagesPhysics Form 4 Chapter 3YanHo100% (1)
- ProblemsDocument3 pagesProblemsimPERFECTme09No ratings yet
- σcosθ ρgd σ = surface tension in N/m θ = wetting angle, 0 for water d = diameter of tube in m ρ = density of fluidDocument1 pageσcosθ ρgd σ = surface tension in N/m θ = wetting angle, 0 for water d = diameter of tube in m ρ = density of fluidJustine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Physical MeasurementsDocument3 pagesPhysical MeasurementsDisha MehtaNo ratings yet
- Fluida (English)Document56 pagesFluida (English)aliNo ratings yet
- (01-25) Hydraulics 3Document2 pages(01-25) Hydraulics 3Ram CaniculaNo ratings yet
- Ejersicios Cap2Document14 pagesEjersicios Cap2Jaime AguilarNo ratings yet
- Properties of FluidsDocument21 pagesProperties of FluidsJhay-Pee QueliopeNo ratings yet
- Working For Behavioral and Academic Excellence! 0118353382/0113484199/0922730929Document2 pagesWorking For Behavioral and Academic Excellence! 0118353382/0113484199/0922730929samuel zelaelmNo ratings yet
- 3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012Document12 pages3 2 Liquid Pressure 2012ZaoiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04 Fluid MechanicsDocument30 pagesLesson 04 Fluid MechanicsMona fabrigarNo ratings yet
- Exercise Pressure in LiquidDocument3 pagesExercise Pressure in LiquidArezly HarunNo ratings yet
- Practice Fluids - 3Document7 pagesPractice Fluids - 3jayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9: Water Retention in Soil: EART3339 Land RehabilitationDocument38 pagesLecture 9: Water Retention in Soil: EART3339 Land RehabilitationMayaraCarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics EngineeringDocument3 pagesHydraulics EngineeringRon Christian Pardilla RicohermosoNo ratings yet
- Which of The Following Is The Correct Equation For The Net Force Acting On A Submerged ObjectDocument2 pagesWhich of The Following Is The Correct Equation For The Net Force Acting On A Submerged ObjectWaleed El ShirbeenyNo ratings yet
- The Velocity of Water Hammer WavesDocument9 pagesThe Velocity of Water Hammer WavesNana LiuNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Ms Nasuha 18.03.2024Document14 pagesForm 5 Physics Ms Nasuha 18.03.2024SITI AISYAH SOFEA BINTI MOHD ROZEE MoeNo ratings yet
- SafariDocument9 pagesSafariPuteri ElianiNo ratings yet
- 3 Forces and Pressure 3 1 UnderstandingDocument24 pages3 Forces and Pressure 3 1 UnderstandingLance ShahNo ratings yet
- Problems On PressureDocument4 pagesProblems On Pressurevinod kumarNo ratings yet
- regPofM PDFDocument59 pagesregPofM PDFSakshi SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Notes in HydraulicsDocument4 pagesNotes in HydraulicsMichael Angelo FernandezNo ratings yet
- Phys 1011-Chapter 3Document49 pagesPhys 1011-Chapter 3melaku zegeyeNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument30 pagesFluid MechanicsChrismar ZalsosNo ratings yet
- Notes 7.2 Pressure in LiquidsDocument2 pagesNotes 7.2 Pressure in Liquidselty TanNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Unit 2Document14 pagesPressure: Unit 2Sumit ShahNo ratings yet
- G10 - Solids and FluidsDocument46 pagesG10 - Solids and FluidsOliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument91 pagesPhysicsnu837157No ratings yet
- FloatationDocument6 pagesFloatationMollel TajiriNo ratings yet
- Usman Public School System: Pressure WorksheetDocument2 pagesUsman Public School System: Pressure Worksheetmarium khanNo ratings yet
- Physics PDFDocument97 pagesPhysics PDFJacob AyoolaNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument7 pagesArchimedes PrincipleRoselle Tura75% (8)
- Quiz 11Document2 pagesQuiz 11Mel VilNo ratings yet
- Archemids PrincipleDocument10 pagesArchemids PrincipleMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- EVALUATION 2 SolutionsDocument17 pagesEVALUATION 2 SolutionsHubert Jay Fedalino YubatNo ratings yet
- UP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024Document9 pagesUP Paper1 S1 SECOND TERM 2024erumriaz.1995No ratings yet
- Kimia Us AbyanDocument1 pageKimia Us AbyanYoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim Math 040224Document1 pageIbrahim Math 040224Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10Document11 pagesMathematics Grade 10Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 FurtherIntegration - HardDocument13 pages5.1 FurtherIntegration - HardYoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Physics Annual Plan 2022-2023 Grade 11.xlsx - 11Document21 pagesPhysics Annual Plan 2022-2023 Grade 11.xlsx - 11Yoga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Epekto NG Paninigarilyo Sa Kabataan ThesisDocument5 pagesEpekto NG Paninigarilyo Sa Kabataan ThesisWriteMyPaperCollegeWichitaFalls100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Multiple 200 300 PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 2 Multiple 200 300 PDFRajeswari Rajarammurthy R0% (1)
- Quiz Organic 1Document6 pagesQuiz Organic 1ronakgupta332005No ratings yet
- Dr. Ahmed Shafai P6Document13 pagesDr. Ahmed Shafai P6Haya ZayedNo ratings yet
- Seismic InterpretationDocument23 pagesSeismic Interpretationnasir.hdip8468No ratings yet
- He Rit Age Conservationand Adapt Ive Re - Use of Buildings: Shivani Mishra 7 S E M / 4 YearDocument18 pagesHe Rit Age Conservationand Adapt Ive Re - Use of Buildings: Shivani Mishra 7 S E M / 4 YearShivaniNo ratings yet
- English Report EssayDocument3 pagesEnglish Report EssayTen Fatin67% (3)
- SA Steam GenerationDocument6 pagesSA Steam GenerationRajagopalNo ratings yet
- Principles of ChromatographyDocument8 pagesPrinciples of ChromatographylordniklausNo ratings yet
- Nchem2 PosttestDocument4 pagesNchem2 PosttestJessa GuerraNo ratings yet
- "Ergonomic Smart Chair": Carried Out byDocument59 pages"Ergonomic Smart Chair": Carried Out byMohsin ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Comparing and Cross Matching (1.3) EIM NC IIDocument2 pagesComparing and Cross Matching (1.3) EIM NC IIHarvey RamosNo ratings yet
- Arizona Community Foundation 2011 - Arizona Organizing Project Grant ApplicationDocument5 pagesArizona Community Foundation 2011 - Arizona Organizing Project Grant ApplicationElizabeth VenableNo ratings yet
- 1-Global Trends in Opencast Mining HemmDocument46 pages1-Global Trends in Opencast Mining Hemmjimcorbett099No ratings yet
- Covenant On Civil and Political RightsDocument3 pagesCovenant On Civil and Political RightsRainier Rhett ConchaNo ratings yet
- 2011UCMC Trauma Care Q&ADocument2 pages2011UCMC Trauma Care Q&ASam CholkeNo ratings yet
- 5 SS Data Sheet TurboDocument34 pages5 SS Data Sheet TurboYhony Gamarra VargasNo ratings yet
- Sinamics G180: Converters - Compact Units, Cabinet Systems, Cabinet Units Air-Cooled and Liquid-CooledDocument240 pagesSinamics G180: Converters - Compact Units, Cabinet Systems, Cabinet Units Air-Cooled and Liquid-CooledAnonymous PDNToMmNmRNo ratings yet
- Balochistan Province Civil Servants Leave Rules 1981 PDFDocument10 pagesBalochistan Province Civil Servants Leave Rules 1981 PDFAhsan 130% (1)
- In Vivo Bio-Safety Evaluations and Diagnostic/Therapeutic Applications of Chemically Designed Mesoporous Silica NanoparticlesDocument33 pagesIn Vivo Bio-Safety Evaluations and Diagnostic/Therapeutic Applications of Chemically Designed Mesoporous Silica NanoparticlesAFRIZANo ratings yet
- Electrostatic - 1Document3 pagesElectrostatic - 1AnjuNo ratings yet
- Home Page Principles Practitioners Help Yourself Contact: Main NavigationDocument2 pagesHome Page Principles Practitioners Help Yourself Contact: Main NavigationAbdurrahmanUsmanNo ratings yet
- Answering Questions About Wild Wild WeatherDocument2 pagesAnswering Questions About Wild Wild WeatherVivekAnandNo ratings yet
- Tear Cooling Tower Energy Operating Cost SoftwareDocument9 pagesTear Cooling Tower Energy Operating Cost Softwareforevertay2000No ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument3 pages1 PDFSugiThanikaNo ratings yet
- Times Leader 06-04-2013Document32 pagesTimes Leader 06-04-2013The Times LeaderNo ratings yet
- Medi Claim Health InsuranceDocument3 pagesMedi Claim Health InsuranceRupesh VNo ratings yet
- 12 Hvac Design Guide For High Rise Tall BuildingsDocument94 pages12 Hvac Design Guide For High Rise Tall BuildingsjendrikoNo ratings yet
- Kharif Crops Vs Rabi CropsDocument1 pageKharif Crops Vs Rabi CropsAsim MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Inverter TrainerDocument2 pagesInverter TrainerBudhi PrasetiyoNo ratings yet