Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Purcom PDF
Purcom PDF
Uploaded by
Mary Grace Dela ConcepcionOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Purcom PDF
Purcom PDF
Uploaded by
Mary Grace Dela ConcepcionCopyright:
Available Formats
PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION REVIEWER Advantages of oral com.
• facilitates close contact & promotes
COMMUNICATION mutual exchange of thoughts &
information.
• symbolic interaction with 2 of more people • allows the superior to make rapid
that influence other people behavior. evaluation of subordinates evaluation.
• p rocess of meaning-making • helps in bringing a responsive and
• inevitable (cannot remove) supportive moral among employee and
• transmission of knowledge organization.
EXTRA LINGUISTIC COMMUNICATION
communicares to share ideas in common
commoners (common)
Types of verbal communication PA
RA
NG
LANGUAGE MODES
LIN
•Verbal communication - face to face, GU I
IST GN
spoken/written
IC SI
WRITING &
•Non-verbal - action, facial expression, READING
METALINGUISTIC
gestures S
LI PEE
TIC ST C
IS EN H &
STATEMENT N GU IN
N -LI G
• the ability to communicate effectively NO
through speaking & writing is highly valued
and demand in our society. LINGUISTIC
• this include the following, attitude of
DIFFERENT LEVEL OF COMMUNICATION voice that accompany the words we say.
•Intrapersonal • can affect and change the meaning of the
•Interpersonal word.
•Group Attributes of voice
•Mass • vocal quality • pitch
Setting • tempo • juncture
•informal - colocial, gay lengu METALINGUISTIC
•formal - have rules to follow ~ abstract element that takes place into
Speech mind of the communicators.
- considered as the most miraculous ~ enables the language user to think about
- produce civilization language independently of his/her
- essential to growth of human personality. comprehension.
EXTRA LINGUISTIC
~ aspect does not uses words but may
3 fundamental objectives
enhance or change the linguistic code.
1. We speak for self expression
NON LINGUISTIC
2. We speak to communicate.
~ devices used in conveying message
3. control human behavior without entirely relying on the speech he
language.
Oral communication NON LINGUISTIC CATEGORIES
-process by which thoughts are transferred 1. Kinesics ~ language of the body
with one another through the use of words. 2. Proxemics ~ space
(spoken) 3. Oculetics ~ study of eye contact
• requires oral skills 4. Haptics ~ touch
• oral skills - foundation literacy, able to 5. Chronemics ~ time
speak & listen. 6. Olfactics ~ smell
7. Artifactual ~ object
MODES OF COMMUNICATION
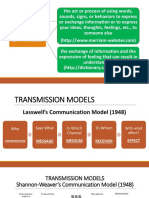
• linear Harold D. Lasswell (1948)
~ Aristotle (300 B.C) • also known as action model or one way
~ Lasswell (1948) model of communication.
~ Berlo (1960) • one of the most influential com. model
• Transactional 5 components of Lasswell model
~ Shannon & Weaver model (1948) • Who (sender) ~ source of info, control
•Interactive • analysis
~ Schramm's model (1940) • says what (message) ~ content analysis
• channel (medium) ~ media use
~ Frank dance, Hellical Dance model (1967)
• To whom receiver) ~ audience analysis
• Effect (feedback) ~ the effect
COMPONENT OF LINEAR
• Sender. • channel
CRITICISM
• Encoding • receiver
• Decoding • noise • does not have feedback & ignore noise
• message • model is general/very simple
• more focus on the outcome and
Aristotle model of communication (300 BC) generally use for media pursuation.
~ first & earliest communication
~ one way process TRANSACTIONAL MODEL
~ most important element (speaker) • without verbal response the sender
~ most common model cannot be sure that the receiver got the
Criticism message as intended.
•no feedback / no concept • exchange of message and receive where
•one way (speaker to audience) in each take turns to receive.
David Berlo Model (1960) SMCR CRITICISM
• SMCR (source, message, channel, • feedback is less important
received) • applicable for interpersonal/mass com.
• simultaneous
• describe the factor affecting the
individual component in the
Shannon & Weaver model (1948)
communication.
• the concept of "noise"
• focuses on encoding & decoding
• Telephone model
Criticism • also called information theory
• both people must be similar according to • mechanical & mathematical model
all factor mentioned. • mother of all model
• no feedback, the effect I not considered
• no concept of noise or any barrier INTERACTIVE MODEL
•Schramm'ss model
~ view communication as a process
• Hellical model
~ dynamic process (cylinder or cone)
LANGUAGE OF COMMUNICATION
Language 3. Message ~ meaning, ideas, feelings,
~ most effective medium obf that sent by verb or non-verbal
communication. 4. Channel ~ means accessing the
~ a tool used in expressing ideas & feelings, messages related if it is visual or
auditory channel.
to achieve understanding.
• 2 types
a. visual channel ~ light mass
PROPERTIES OF LANGUAGE
(nonverbal)
1. SYSTEMATIC ~ highly organized system
b. auditory channel ~ sounds mass
2. ARBITARY ~ no necessary connection (verbal)
between the sound & object c. semantic noise (unintentional)
3. DUAL STRUCTURE ~ meaning (syntax) d. mechanical noise ~ use of technology
sounds (chronology) 5. Noise/interference ~ the distraction
4. RULE GOVERNED ~ grammar of the 6. Feedback ~ signifies verbal or non-
language verbal response of messages.
5. GENERATIVE ~ speakers ability to
understand and produce any number of 9 PRINCIPLES OF EFFECTIVE
sentences. COMMUNICATION
6. SOCIALLY LEARNED BEHAVIOR ~ 1. Clarity ~ language is understandable
culturally transmitted 2. Concreteness ~ supported by facts
7. SOCIAL INTERACTIVE TOOL ~ more (research data, statistics etc)
reason to interact to other people 3. Courtesy ~ being polite, manner
4. Correctness ~ grammar must be
When we communicate we use correct
93 % (non-verbal) 5. Consideration ~ consider receivers
ability
(38% ~ tone & infection, 55% ~ facial
6. Creativity ~ able to add elements
expressions)
7. Conciseness ~ simplicity & directness
7% (verbal)
8. Cultural sensitivity ~ background,
Elements of Communication
lifestyle of others
1. Participants 9. Captivity ~ make messages interesting
~ sender (encodes) receiver ~ (decodes) (attention & response)
2. Context ~ interrelated conditions of
communication
•Factors
ETHNICS OF COMMUNICATION
a. Physical Milieu ~
surroundings/environments branch of philosophy that focuses on
b. Social milieu ~ nature of relationship right or wrong
among true communication. ~ characteristic of ethical communicator
c. Cultural milieu ~ beliefs, values, or • respect audience
norms • Consider the result of com.
d. Historical milieu ~ communication is • Accept the result
affected by history. • Value TRUTH
• use information correctly
• Do not falsify information.
COMMUNICATION & COMMUNICATION &
GLOBALIZATION CULTURE
CULTURE is a code we learn and share
Globalization and learning and sharing required
~ communication & assimilation communication .
among individuals, ethnicities, races, & ~communication is an element of
institutions . culture.
~ about improvement Intercultural communication
~ no globalization without ~ first used by Eaward Haul
communication ~ communication between persons
••ethnicities - globally - different with different culture .
culture ~ another meaning :talking to a person
~ international trade with same culture.
Technology World culture
~ serve as help /guide ~ idea that us traditional barriers
~ make our life easier among peope with different people
break down, emphasizing the
communication needs.
CULTURAL BARRIERS
diffusion
1. cultural relativism
~ the process by which 2 cultures
2. Lack of other culture
learn and adopt maternal and adopt
3. Discrimination & harassments
prop practices from other .
4. Languadifferencences 3 forms of Intercultural
• Interracial communication (races)
KRIZAN (STRATEGIES) GLOBAL communicating people with different
COMMUNICATOR races
• review communication principles interethnic communication ( ethnics )
• analyze the message received interacting people with different
• be open to an accepting others culture ethnic group
• learn about culture & apply what is • International (nation)
learned communication between people with
• consider language need. diff. resprentative from different
nation .
• Intracultural com.
interacting with same culture ( co-
culture )
2 communication style
LOW context com .
- system that works straight forward
comm
HIGH context com
~ tradition linked communication
system which adheres strongly to
being indirect.-
LANGUAGE REGISTER
Language register
ENCULTURATION ~ level and style of your writing .
~ socialization process you go through ~ It should be appropmate for the situation
to adopt to your society . you are In .
~ determines the vocabulary structures in
2 types of Enculturation
your writing .
• Frontage culture 3 types of Language Register
~ cultural information that you are Formal ~ professional writing
willing to share with others . Informal ~ casual, conventional
• Backstage culture neutral ~ non emotional , sticks to the facts.
~ concealed from outsider ( technical writing )
ACCULTURATION
RULES IN FORMAL
~ process of adjusting and adapting to a
• do not use contraction
new culture . • spell out numbers less than 100
ETHNOCENTRISM • use third person point of view
~ belief that you own cultural • avoid to much passive voice
background . • avoid abbreviation & acronym
~ encoding values , beliefs , language , • do not start sentences with words like and,
but, also.
in verbal and non verbal is correct .
• always write in a complex sentence
neutral ~ ( non emotional topics ) Dear sir:
~ propose to deliver facts (ex reviews.)
varieties of English
~ world English
language variety " lect "
~ general term of any language, dialect, diff
kinds of register, jargon
~ connected with the word " dialect "
~ refers to any over lapping sub categories.
dialect - regional/social variety
distinguish by grammar , pronounuation or
vocabulary.
register -the way the language speaker use
jargon ~ specialized of professional
occupational group .
Types Of lect
• regional - spoken in particular o region
• sociolect ~ socio economic ex. jejemon
• ethnolect ~ open by specific ethnic group
• idiolect - spoken by each individual .
SPEECH VARIETY
~ concept of domain
DOMAIN
~ social institutions
~ implementation of the rights and duties for
that relationship.
You might also like
- English 1 Purposive CommunicationDocument174 pagesEnglish 1 Purposive CommunicationDennis Niño Ancheta50% (2)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Englis1Document17 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Englis1Shierah Sheen100% (2)
- MKT FinalDocument327 pagesMKT FinalHira ParachaNo ratings yet
- CT 201 1st & 2nd MODULEDocument34 pagesCT 201 1st & 2nd MODULENase Boy100% (1)
- Language, Culture and Society: Sherry Mae M. Mingo InstructorDocument31 pagesLanguage, Culture and Society: Sherry Mae M. Mingo InstructorSHERRY MAE MINGONo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis: An Approach To Language Research: Speaker: Zesa S. Mino, PH.DDocument46 pagesDiscourse Analysis: An Approach To Language Research: Speaker: Zesa S. Mino, PH.DZesa MinoNo ratings yet
- Rutas y Rubricas Ingles Primer y Segundo PeriodosDocument16 pagesRutas y Rubricas Ingles Primer y Segundo PeriodosPATTY SANDOVALNo ratings yet
- Speech Oralcom REVIEWER 1Document20 pagesSpeech Oralcom REVIEWER 1Whatever WhatwhoNo ratings yet
- Language and CommunicationDocument20 pagesLanguage and CommunicationSTREAM EPIPHANYNo ratings yet
- PurCom ReviewerDocument3 pagesPurCom Reviewerlucerocatapanggwen.03No ratings yet
- Xurposivj Moccueimbtioe Rjvijwjr: Bmmouetbemy (Xbcbetbsbe Ef Auefsol Ef Cbyeiab)Document7 pagesXurposivj Moccueimbtioe Rjvijwjr: Bmmouetbemy (Xbcbetbsbe Ef Auefsol Ef Cbyeiab)mark vincent santiagoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Non Verbal CommunicationDocument7 pagesChapter 7 - Non Verbal CommunicationCarolyn NacesNo ratings yet
- Nonverb Al: Communic AtionDocument48 pagesNonverb Al: Communic AtionDung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Purp CommDocument5 pagesPurp CommKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- cs202 Final NotesDocument35 pagescs202 Final NotesTee ThayaNo ratings yet
- L1 - As4 Eng 103Document13 pagesL1 - As4 Eng 103gt211No ratings yet
- Unit I Natural Language Basics Foundations of Natural Language ProcessingDocument14 pagesUnit I Natural Language Basics Foundations of Natural Language ProcessingI yr IT 10-Cherisha SNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesOral Com Reviewer 2nd QuarterJhuriz BassigNo ratings yet
- Leon Guinto Memorial College, Inc.: Course Title Course Number School Year & Term FacultyDocument21 pagesLeon Guinto Memorial College, Inc.: Course Title Course Number School Year & Term FacultyZarahJoyceSegoviaNo ratings yet
- From Cognitive Linguistics To Cultural Linguistics: Which Comes First, Culture or Language?Document5 pagesFrom Cognitive Linguistics To Cultural Linguistics: Which Comes First, Culture or Language?Felix GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Language and Communication 2023 03Document41 pagesUnit 1 Language and Communication 2023 03Rezelle Mae TrongcoNo ratings yet
- Discourse Analysis: e T e G 0 P eDocument9 pagesDiscourse Analysis: e T e G 0 P eAngel Grace TiempoNo ratings yet
- And Ass Essm Ent Isten Ing Skill SDocument42 pagesAnd Ass Essm Ent Isten Ing Skill SFe CanoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in CommunicationDocument4 pagesBasic Concepts in CommunicationsecreNo ratings yet
- The Universality of Human Language: PsycholiinguisticsDocument10 pagesThe Universality of Human Language: PsycholiinguisticsRicky WijayaNo ratings yet
- Cultural Iceberg, Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication BehaviorDocument19 pagesCultural Iceberg, Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication BehaviorBelinda EspirituNo ratings yet
- D 1.3 Use & Properties of LanguageDocument23 pagesD 1.3 Use & Properties of LanguageYuvaneswari ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Branches of Linguistics: Prof. K.T.KhaderDocument50 pagesBranches of Linguistics: Prof. K.T.KhaderHani QarmootNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Speech and Stage ArtsDocument3 pagesSyllabus Speech and Stage ArtsCollegesecond semNo ratings yet
- Communicative CompetenceDocument36 pagesCommunicative CompetenceAnnisa Ratna Purwanti100% (1)
- Chapter 1language, Learning, and Teaching2Document38 pagesChapter 1language, Learning, and Teaching2Endar SukadiNo ratings yet
- Mindful Intercultural Verbal Communication: Human Language: A Coherent SystemDocument34 pagesMindful Intercultural Verbal Communication: Human Language: A Coherent SystemTran Thanh Binh B2005100No ratings yet
- Stefano Piantino - Diffusion Studies - Language Borrowing in JapaneseDocument14 pagesStefano Piantino - Diffusion Studies - Language Borrowing in JapaneseSealNo ratings yet
- Cultural Iceberg, Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication BehaviorDocument19 pagesCultural Iceberg, Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication BehaviorBelinda EspirituNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.2Document16 pagesUnit 1.2Iffat BasirNo ratings yet
- PurCom MidtermsDocument5 pagesPurCom MidtermshaneenamaedediosNo ratings yet
- Z00260010120174028Introduction To Communication Science-Session 9 & 10Document25 pagesZ00260010120174028Introduction To Communication Science-Session 9 & 10daesha putriNo ratings yet
- Oc CM Week 3Document19 pagesOc CM Week 3Zasha Denise LunarNo ratings yet
- Purc111 Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurc111 Prelim ReviewerJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- OralCom ReviewerDocument3 pagesOralCom ReviewerImogen SantosNo ratings yet
- CMAP English 9Document14 pagesCMAP English 9Maranatha A. CarabeoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Linguistics '23Document7 pagesModule 1 Linguistics '23Zyrel Joy Santos MirandaNo ratings yet
- LING2Document19 pagesLING2John Troy LabadanNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Communication SkillsDocument19 pagesUnit-4 Communication SkillsSuzan DahitNo ratings yet
- OralCom Reviewer11Document3 pagesOralCom Reviewer11Imogen SantosNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts in Language Learning and Language EducationDocument9 pagesKey Concepts in Language Learning and Language EducationEduardo AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Human Communication Disorders An Introduction 8 e 8th Edition 0137061331Document29 pagesSolution Manual For Human Communication Disorders An Introduction 8 e 8th Edition 0137061331turncoattrews7bla100% (14)
- Lang 121 W5-6 3Document29 pagesLang 121 W5-6 3DaisyADenialNo ratings yet
- SAA - Resuello, Charles G - Task 1Document3 pagesSAA - Resuello, Charles G - Task 1Charles ResuelloNo ratings yet
- Text and DiscourseDocument20 pagesText and DiscourseDian Nuzulia AreraNo ratings yet
- Nonverbal: IntonationDocument2 pagesNonverbal: IntonationKrisha Anne ChanNo ratings yet
- Project SSLDocument27 pagesProject SSLAyesha Iqbal SulehryNo ratings yet
- Cross Cultural Comm N NegotiationDocument26 pagesCross Cultural Comm N NegotiationzabrinadevaNo ratings yet
- The Interactional Approaches To LanguageDocument18 pagesThe Interactional Approaches To LanguageEugenio A. SebastiaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 PowerPointDocument20 pagesChapter 1 PowerPointAaliyah.AdonisNo ratings yet
- Interpersonal CommunicationDocument11 pagesInterpersonal CommunicationBea Hannah FarrenNo ratings yet
- Direct File Topic DownloadDocument24 pagesDirect File Topic DownloadJass SidhuNo ratings yet
- Eapp Reviewer 1stquarterDocument20 pagesEapp Reviewer 1stquarterTrsha MirandaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm 2ND ReviewerDocument3 pagesOral Comm 2ND ReviewerJamie Kayle N. LavitoriaNo ratings yet
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-٠٢-٠٤ في ٣.٥٤.١١ مDocument48 pagesلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٣-٠٢-٠٤ في ٣.٥٤.١١ مHaliyah A. HurubiNo ratings yet
- Speech Oralcom REVIEWERDocument16 pagesSpeech Oralcom REVIEWERWhatever WhatwhoNo ratings yet
- Lcs RevieverDocument6 pagesLcs Revievererikakimperez7No ratings yet
- How Much Information Do People With Aphasia Convey Via Gesture?Document15 pagesHow Much Information Do People With Aphasia Convey Via Gesture?Luis.fernando. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sign Language of the Deaf: Psychological, Linguistic, and Sociological PerspectivesFrom EverandSign Language of the Deaf: Psychological, Linguistic, and Sociological PerspectivesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- COM295r3 Communication Process WorksheetDocument2 pagesCOM295r3 Communication Process Worksheetfa1therrNo ratings yet
- Interactive EnglishDocument145 pagesInteractive EnglishMark Juliah NaveraNo ratings yet
- CORE - MIL Q3 Week1 7Document39 pagesCORE - MIL Q3 Week1 7Torzy TubeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 001Document18 pagesChapter 001uthayaNo ratings yet
- BBDM1013 Business Communication: Chapter 1 - 1Document33 pagesBBDM1013 Business Communication: Chapter 1 - 1蓝政No ratings yet
- ORAL COMMUNICATION Page PDFDocument93 pagesORAL COMMUNICATION Page PDFEizle Ellevera0% (1)
- LESSON 2 Q1 Oral Com G11Document2 pagesLESSON 2 Q1 Oral Com G11Joshua Lander Soquita CadayonaNo ratings yet
- Quizzes in OralDocument82 pagesQuizzes in OralMarissa Urnos100% (6)
- Business Communication For Success 1622152607Document1,109 pagesBusiness Communication For Success 1622152607LaVida LocaNo ratings yet
- West Bay College: CS1: Oral Communication in ContextDocument15 pagesWest Bay College: CS1: Oral Communication in ContextMA. KRISTINA BLANCAFLORNo ratings yet
- D2 Models of CommunicationDocument32 pagesD2 Models of CommunicationNeko CommsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Interpersonal Communication: Chapter GoalsDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Interpersonal Communication: Chapter GoalsSeptiana wulandariNo ratings yet
- Westley and Maclean Model of CommunicationDocument4 pagesWestley and Maclean Model of Communicationjohnleegiba09No ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: "Communication Process With Customers: A Study On AB Bank Limited"Document31 pagesAcknowledgement: "Communication Process With Customers: A Study On AB Bank Limited"SAMIUL HOSSAINNo ratings yet
- COM101 Session 2 Communication Models-1-1Document22 pagesCOM101 Session 2 Communication Models-1-1Hênry Stanley NkhuwaNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document35 pagesModule 1Marielle GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Communication, Media, Information, and Technology LiteracyDocument12 pagesCommunication, Media, Information, and Technology LiteracyAgustin RonnNo ratings yet
- Complete Module On MarketingDocument41 pagesComplete Module On MarketingElvie VigaNo ratings yet
- Mms With PressDocument74 pagesMms With PressJude JohnNo ratings yet
- Group 5 SHANNON-WEAVER COMMUNICATION METHODDocument8 pagesGroup 5 SHANNON-WEAVER COMMUNICATION METHODRirin Panca AstutiNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1Document2 pagesQuiz No. 1Ronaliza CerdenolaNo ratings yet
- Communicating Across CulturesDocument17 pagesCommunicating Across CulturesSneha SahaNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication AssignmentDocument5 pagesModels of Communication AssignmentJustine Ann Gonzales0% (1)
- Chapter 3: Verbal Communication SkillsDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Verbal Communication SkillsFares EL DeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter One Oral CommunicationDocument21 pagesChapter One Oral CommunicationJason SebastianNo ratings yet
- M. Course Outline (January 2019)Document6 pagesM. Course Outline (January 2019)joseph.kabaso96No ratings yet