Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10 Mathematics Ncert ch04 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.3 Ans Ejf PDF
Uploaded by
Shruti ShettyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10 Mathematics Ncert ch04 Quadratic Equations Ex 4.3 Ans Ejf PDF
Uploaded by
Shruti ShettyCopyright:
Available Formats
NCERT Solutions
CLASS – X Mathematics
Chapter-04 Quadratic Equations (Exercise 4.3)
Answers:
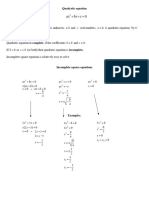
1. (i) 2x2 − 7x + 3 = 0
First we divide equation by 2 to make coefficient of x2 equal to 1,
7 3
x2 − x + = 0
2 2
7 1 7
We divide middle term of the equation by 2x, we get x × =
2 2x 4
7 7 3
We add and subtract square of from the equation x 2 − x + = 0 ,
4 2 2
2 2
7 3 7 7
x − x+ + − = 0
2
2 2 4 4
2 2
7 7 3 7
⇒ x + − x + + − = 0
2
{(a − b)2 = a2 + b2 − 2ab}
4 2 2 4
24 − 49 49 − 24
2 2
7 7
⇒ x− + =0 ⇒ x− =
4 16 4 16
Taking Square root on both sides,
7 5
⇒ x− =±
4 4
5 7 12 5 7 2 1
⇒ x = + = = 3 and x = − + = =
4 4 4 4 4 4 2
1
Therefore, x = ,3
2
(ii) 2
2x + x – 4 = 0
Dividing equation by 2,
x
x2 + − 2 = 0
2
Following procedure of completing square,
2 2
x 1 1
x + −2+ − = 0
2
2 4 4
2
x 1 1
⇒ x + + −2− = 0
2
{(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab}
2 4 16
2 2
1 33 1 33
⇒ x+ − =0 ⇒ x+ =
4 16 4 16
Taking square root on both sides,
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
1 33
⇒ x+ =±
4 4
33 1 33 − 1 33 1 − 33 − 1
⇒ x= − = and x = − − =
4 4 4 4 4 4
33 − 1 − 33 − 1
Therefore, x = ,
4 4
(iii) 4 x 2 + 4 3x + 3 = 0
Dividing equation by 4,
3
x 2 + 3x + = 0
4
Following the procedure of completing square,
2 2
3 3 3
⇒ x + 3 x + +
2
− =0
4 2 2
2
3
⇒ x +
2
+ 3x + 3 − 3 = 0 {(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab}
2 4 4
2
3 3
⇒ x+ 3 =0 ⇒ x + x + = 0
2 2 2
Taking square root on both sides,
3 3 3 3
⇒ x+ = 0, x + =0 ⇒ x=− ,−
2 2 2 2
(iv) 2x2 + x + 4 = 0
Dividing equation by 2,
x
x2 + + 2 = 0
2
Following the procedure of completing square,
2 2
x 1 1
⇒ x + +2+ − = 0
2
2 4 4
2 2
1 x 1
⇒ x + + + 2− = 0
2
{(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab}
4 2 4
1 − 32
2 2
1 1 1 1
⇒ x + + 2− =0 ⇒ x+ = −2=
4 16 4 16 16
Taking square root on both sides
Right hand side does not exist because square root of negative number does
not exist.
Therefore, there is no solution for quadratic equation 2x2+x+4=0
2. (i) 2x2 − 7x + 3 = 0
Comparing quadratic equation 2x2 − 7x + 3 = 0 with general form ax2 + bx + c =
0, we get a = 2, b = -7 and c = 3
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Putting these values in quadratic formula x =
2a
7 ± (−7) 2 − 4(2)(3) 7 ± 49 − 24
x= ⇒ x=
2×2 4
7±5 7+5 7−5
⇒ x= ⇒ x= ,
4 4 4
⇒ x = 3, ½
(ii) 2x2 + x – 4 = 0
Comparing quadratic equation 2x2 + x – 4 = 0 with the general form ax2 + bx + c
= 0, we get a = 2, b = 1 and c = −4
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Putting these values in quadratic formula x =
2a
− 1 ± (1) 2 − 4( 2)( −4) − 1 ± 33
x= ⇒ x=
2× 2 4
− 1 + 33 − 1 − 33
⇒ x= ,
4 4
(iii) 4 x + 4 3x + 3 = 0
2
Comparing quadratic equation 4 x 2 + 4 3 x + 3 = 0 with the general form ax2 +
bx + c = 0, we get a = 4, b = 4 3 and c = 3
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Putting these values in quadratic formula x =
2a
− 4 3 ± (4 3 ) 2 − 4(4)(3) −4 3± 0
x= ⇒ x=
2× 4 8
− 3
⇒ x=
2
A quadratic equation has two roots. Here, both the roots are equal.
− 3 − 3
Therefore, x = ,
2 2
(iv) 2x2 + x + 4 = 0
Comparing quadratic equation 2x2 + x + 4 = 0 with the general form ax2 + bx + c
= 0, we get a = 2, b = 1 and c = 4
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Putting these values in quadratic formula x =
2a
− 1 ± (1) 2 − 4(2)(4) − 1 ± − 31
x= ⇒ x=
2× 2 4
But, square root of negative number is not defined.
Therefore, Quadratic Equation 2x2 + x + 4 = 0 has no solution.
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
1
3. (i) x− = 3 where x ≠ 0
x
x2 −1
⇒ =3 ⇒ x2 – 1 = 3x
x
⇒ x2 − 3x – 1 = 0
Comparing equation x2 − 3x – 1 = 0 with general form ax2 + bx + c = 0,
We get a = 1, b = −3 and c = −1
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Using quadratic formula x = to solve equation,
2a
3 ± (3) 2 − 4(1)(−1) 3 ± 13
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
3 + 13 3 − 13
⇒ x= ,
2 2
1 1 11
(ii) − = where x ≠ −4,7
x + 4 x − 7 30
( x − 7) − ( x + 4) 11 − 11 11
⇒ = ⇒ =
( x − 4) ( x − 7 ) 30 ( x − 4)( x − 7 ) 30
⇒ 2
−30 = x − 7x + 4x – 28 ⇒ x2 − 3x + 2 = 0
Comparing equation x − 3x + 2 = 0 with general form ax2 + bx + c = 0,
2
We get a = 1, b = −3 and c = 2
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Using quadratic formula x = to solve equation,
2a
3 ± (3) 2 − 4(1)(2) 3± 1
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
3+ 1 3− 1
⇒ x= , ⇒ x = 2, 1
2 2
4. Let present age of Rehman = x years
Age of Rehman 3 years ago = (x − 3) years.
Age of Rehman after 5 years = (x + 5) years
According to the given condition:
1 1 1 ( x + 5) + ( x − 3) 1
+ = ⇒ =
x−3 x+5 3 (x − 3)(x + 5) 3
⇒ 3 (2x + 2) = (x − 3) (x + 5) ⇒ 6x + 6 = x2 − 3x + 5x − 15
⇒ 2
x − 4x – 15 – 6 = 0 ⇒ x2 − 4x – 21 = 0
Comparing quadratic equation x2 − 4x – 21 = 0 with general form ax2 + bx + c = 0,
We get a = 1, b = −4 and c = −21
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Using quadratic formula x =
2a
4 ± ( 4) 2 − 4(1)( −21) 4 ± 16 + 84
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
4 ± 100 4 ± 10 4 + 10 4 − 10
⇒ x= = ⇒ x= ,
2 2 2 2
⇒ x = 7, −3
We discard x=−3. Since age cannot be in negative.
Therefore, present age of Rehman is 7 years.
5. Let Shefali's marks in Mathematics = x
Let Shefali's marks in English = 30 − x
If, she had got 2 marks more in Mathematics, her marks would be = x + 2
If, she had got 3 marks less in English, her marks in English would be = 30 – x − 3 = 27 − x
According to given condition:
(x + 2) (27 − x) = 210
⇒ 27x − x2 + 54 − 2x = 210 ⇒ x2 − 25x + 156 = 0
Comparing quadratic equation x − 25x + 156 = 0 with general form ax2 + bx + c = 0,
2
We get a = 1, b = −25 and c = 156
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Applying Quadratic Formula x =
2a
25 ± ( 25) 2 − 4(1)(156)
x=
2 ×1
25 ± 625 − 624 25 ± 1
⇒ x= ⇒ x=
2 2
25 + 1 25 − 1
⇒ x= , ⇒ x = 13, 12
2 2
Therefore, Shefali's marks in Mathematics = 13 or 12
Shefali's marks in English = 30 – x = 30 – 13 = 17
Or Shefali's marks in English = 30 – x = 30 – 12 = 18
Therefore her marks in Mathematics and English are (13, 17) or (12, 18).
6. Let shorter side of rectangle = x metres
Let diagonal of rectangle = (x + 60) metres
Let longer side of rectangle = (x + 30) metres
According to pythagoras theorem,
(x + 60)2 = (x + 30)2 + x2 ⇒ x2 + 3600 + 120x = x2 + 900 + 60x + x2
⇒ x2 − 60x – 2700 = 0
Comparing equation x2 − 60x – 2700 = 0 with standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0,
We get a = 1, b = −60 and c = −2700
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Applying quadratic formula x =
2a
60 ± (60) 2 − 4(1)(−2700) 60 ± 3600 + 10800
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
60 ± 14400 60 ± 120 60 + 120 60 − 120
⇒ x= = ⇒ x= ,
2 2 2 2
⇒ x = 90, –30
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
We ignore –30. Since length cannot be in negative.
Therefore x = 90 which means length of shorter side = 90 metres
And length of longer side = x + 30 = 90 + 30 = 120 metres
Therefore, length of sides are 90 and 120 in metres.
7. Let smaller number = x and let larger number = y
According to condition:
y2 − x2 = 180 … (1)
Also, we are given that square of smaller number is 8 times the larger number.
⇒ x2 = 8y … (2)
Putting equation (2) in (1), we get
y2 − 8y = 180 ⇒ y2 − 8y – 180 = 0
Comparing equation y2 − 8y – 180 = 0 with general form ay2 + by + c = 0,
We get a = 1, b = −8 and c = −180
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Using quadratic formula y =
2a
8 ± (−8) 2 − 4(1)(−180) 8 ± 64 + 720
y= ⇒ y=
2 ×1 2
8 ± 784 8 ± 28 8 + 28 8 − 28
⇒ y= = ⇒ y= ,
2 2 2 2
⇒ y = 18, −10
Using equation (2) to find smaller number:
x2 = 8y
⇒ x2 = 8y = 8 × 18 = 144 ⇒ x = ±12
2
And, x = 8y = 8 × −10 = −80 {No real solution for x}
Therefore two numbers are (12, 18) or (−12, 18)
8. Let the speed of the train = x km/hr
If, speed had been 5 km/hr more, train would have taken 1 hour less.
So, according to this condition
360 360 1 1
= +1 ⇒ 360 − =1
x x+5 x x+5
x+5− x
⇒ 360 = 1 ⇒ 360 × 5 = x2 + 5x
x ( x + 5)
⇒ x2 + 5x – 1800 = 0
Comparing equation x2 + 5x – 1800 = 0 with general equation ax2 + bx + c = 0,
We get a = 1, b = 5 and c = −1800
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Applying quadratic formula x =
2a
− 5 ± (5) 2 − 4(1)(−1800) − 5 ± 25 + 7200
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
− 5 ± 7225 − 5 ± 85 − 5 + 85 − 5 − 85
⇒ x= = ⇒ x= ,
2 2 2 2
⇒ x = 40, −45
Since speed of train cannot be in negative. Therefore, we discard x = −45
Therefore, speed of train = 40 km/hr
9. Let time taken by tap of smaller diameter to fill the tank = x hours
Let time taken by tap of larger diameter to fill the tank = (x – 10) hours
th
1
It means that tap of smaller diameter fills part of tank in 1 hour. … (1)
x
th
1
And, tap of larger diameter fills part of tank in 1 hour. … (2)
x − 10
When two taps are used together, they fill tank in 758 hours.
8
th 1 8
In 1 hour, they fill part of tank = … (3)
75 75 75
8
From (1), (2) and (3),
1 1 8 x − 10 + x 8
+ = ⇒ =
x x − 10 75 x( x − 10) 75
⇒ 75 (2x − 10) = 8 (x2 − 10x) ⇒ 150x – 750 = 8x2 − 80x
⇒ 8x2 − 80x − 150x + 750 = 0 ⇒ 4x2 − 115x + 375 = 0
Comparing equation 4x − 115x + 375 = 0 with general equation ax2 + bx + c = 0,
2
We get a = 4, b = −115 and c = 375
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Applying quadratic formula x =
2a
115 ± ( −115) 2 − 4( 4)(375) 115 ± 13225 − 6000
x= ⇒ x=
2× 4 8
115 ± 7225 115 ± 85
⇒ x= ⇒ x=
8 8
115 + 85 115 − 85
⇒ x= , ⇒ x = 25, 3.75
8 8
Time taken by larger tap = x – 10 = 3.75 – 10 = −6.25 hours
Time cannot be in negative. Therefore, we ignore this value.
Time taken by larger tap = x – 10 = 25 – 10 = 15 hours
Therefore, time taken by larger tap is 15 hours and time taken by smaller tap
is 25 hours.
10. Let average speed of passenger train = x km/h
Let average speed of express train = (x + 11) km/h
132
Time taken by passenger train to cover 132 km = hours
x
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
132
Time taken by express train to cover 132 km = hours
x +11
According to the given condition,
132 132 1 1
= +1 ⇒ 132 − =1
x x + 11 x x + 11
x + 11 − x
⇒ 132 = 1 ⇒ 132 (11) = x (x + 11)
x( x + 11)
⇒ 1452 = x2 + 11x ⇒ x2 + 11x – 1452 = 0
Comparing equation x2 + 11x – 1452 = 0 with general quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c =
0, we get a = 1, b = 11 and c = −1452
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Applying Quadratic Formula x =
2a
− 11 ± (11) 2 − 4(1)(−1452) − 11 ± 121 + 5808
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
− 11 ± 5929 − 11± 77
⇒ x= ⇒ x=
2 2
− 11 + 77 − 11 − 77
⇒ x= , ⇒ x = 33, −44
2 2
As speed cannot be in negative. Therefore, speed of passenger train = 33 km/h
And, speed of express train = x + 11 = 33 + 11 = 44 km/h
11. Let perimeter of first square = x metres
Let perimeter of second square = (x + 24) metres
x
Length of side of first square = metres {Perimeter of square = 4 × length of side}
4
x + 24
Length of side of second square = metres
4
x x x2 2
Area of first square = side × side = × = m
4 4 16
x + 24 2
2
Area of second square = m
4
According to given condition:
x 2 x + 24 x 2 x 2 + 576 + 48 x
2
+ = 468 ⇒ + = 468
16 4 16 16
x 2 + x 2 + 576 + 48 x
⇒ = 468 ⇒ 2x2 + 576 + 48x = 468 × 16
16
⇒ 2x2 + 48x + 576 = 7488 ⇒ 2x2 + 48x – 6912 = 0
⇒ x2 + 24x – 3456 = 0
Comparing equation x2 + 24x – 3456 = 0 with standard form ax2 + bx + c = 0,
We get a = 1, b =24 and c = −3456
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
NCERT Solutions
− b ± b 2 − 4ac
Applying Quadratic Formula x =
2a
− 24 ± (24) 2 − 4(1)(−3456) − 24 ± 576 + 13824
x= ⇒ x=
2 ×1 2
− 24 ± 14400 − 24 ± 120 − 24 + 120 − 24 − 120
⇒ x= = ⇒ x= ,
2 2 2 2
⇒ x = 48, −72
Perimeter of square cannot be in negative. Therefore, we discard x=−72.
Therefore, perimeter of first square = 48 metres
And, Perimeter of second square = x + 24 = 48 + 24 = 72 metres
Perimeter 48
⇒ Side of First square = = = 12 m
4 4
Perimeter 72
And, Side of second Square = = = 18 m
4 4
Material downloaded from http://myCBSEguide.com and http://onlineteachers.co.in
Portal for CBSE Notes, Test Papers, Sample Papers, Tips and Tricks
You might also like
- MTH101 Practice Qs Solutions Lectures 1 To 22 PDFDocument50 pagesMTH101 Practice Qs Solutions Lectures 1 To 22 PDFRubab Babar75% (4)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Kalman Decomposition PDFDocument5 pagesThe Kalman Decomposition PDFJose H. Vivas100% (2)
- Ecuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesoDocument3 pagesEcuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesokkkkkNo ratings yet
- F4 Textbook Answer C2 (ENG)Document45 pagesF4 Textbook Answer C2 (ENG)Hui Ern SeeNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Formula and Discriminant NOtesDocument4 pagesQuadratic Formula and Discriminant NOtesGabbriel Emmanuel Y. CabagnotNo ratings yet
- 5 17 44 418Document17 pages5 17 44 418kesharNo ratings yet
- Algebra 101 DDocument7 pagesAlgebra 101 DjohannyNo ratings yet
- Maths Lessons 1 To 5Document49 pagesMaths Lessons 1 To 5selar7347No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Quadratic EquationsDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Quadratic EquationsDøomNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using The Quadratic FormulaDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Solving Quadratic Equations by Using The Quadratic FormulaJowelyn MaderalNo ratings yet
- 10th Quadratic Equations Solved Problems - 1.compressedDocument7 pages10th Quadratic Equations Solved Problems - 1.compressedS Balagopal SivaprakasamNo ratings yet
- 1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic EquationDocument8 pages1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic Equationkhrr7brbpcNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Grade 9 Week 1 Topic: Quadratic Equations Sub Topic: Illustrating Quadratic EquationsDocument13 pagesMathematics - Grade 9 Week 1 Topic: Quadratic Equations Sub Topic: Illustrating Quadratic EquationsCleo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- SDLP - Completing The SquareDocument5 pagesSDLP - Completing The Squarekylene.abante.sNo ratings yet
- Completing The Square (A 1)Document6 pagesCompleting The Square (A 1)Alexander BautistaNo ratings yet
- Equations and Inequalities, Mixed Exercise 3: B B Ac X ADocument6 pagesEquations and Inequalities, Mixed Exercise 3: B B Ac X ASaiyara KhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 5 Mathematics (Chapter 4)Document7 pagesLecture No. 5 Mathematics (Chapter 4)Taha SheikhNo ratings yet
- 4A02 ExerciseDocument35 pages4A02 ExerciseHarryNo ratings yet
- LESSON 4 Quadratic EquationsDocument7 pagesLESSON 4 Quadratic EquationsMa RiaNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Cuadráticas Incompletas - Gurpo 6Document7 pagesEcuaciones Cuadráticas Incompletas - Gurpo 6daviany pomar zabalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaDocument9 pagesLesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaflyleafNo ratings yet
- SampleDocument5 pagesSampleJuan Carlos SandomingoNo ratings yet
- How To Factorize The Quadratic Equation E CientlyDocument2 pagesHow To Factorize The Quadratic Equation E CientlyNikola Pacek-VetnićNo ratings yet
- Solutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsDocument12 pagesSolutionbank: Edexcel AS and A Level Modular MathematicsMaruf_007No ratings yet
- BBB 2023 Final Review Set 1 (Solution Manual)Document12 pagesBBB 2023 Final Review Set 1 (Solution Manual)Gil Deon BasaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Notes Gr.11Document59 pagesMathematics Notes Gr.11iyermagsNo ratings yet
- SolJul2022 3Document4 pagesSolJul2022 3joshuathepapuNo ratings yet
- Axb C: Chapter 0 Assumed Knowledge: Self-Review Solutions Self-Review 1Document8 pagesAxb C: Chapter 0 Assumed Knowledge: Self-Review Solutions Self-Review 1aNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths June 2015Document24 pagesCsec Add Maths June 2015ValNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations by Completing The Square: ObjectivesBaems AmborNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareDocument3 pages3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The SquareAanya RalhanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic FunctionsDocument37 pagesQuadratic FunctionsHadi Alnaher100% (3)
- Quadratic Formula ProjectDocument6 pagesQuadratic Formula ProjectCameron TomNo ratings yet
- Home School Sub-Maths NotesDocument36 pagesHome School Sub-Maths NotesbeanoderapperrNo ratings yet
- Me N Mine Mathematics PDFDocument186 pagesMe N Mine Mathematics PDFVilva VivithaNo ratings yet
- Ial pm1 Exam Practice SolutionbankDocument4 pagesIal pm1 Exam Practice SolutionbankDiyaNo ratings yet
- Question 3Document5 pagesQuestion 3Amir LukmanNo ratings yet
- Jayson Santis Tarea2Document3 pagesJayson Santis Tarea2Jayson SantisNo ratings yet
- CJC H1 Math SolDocument15 pagesCJC H1 Math SoljunaidahNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Quadratic EquationsDocument8 pagesTopic 2-Quadratic Equations丽娜钱霙No ratings yet
- Math Module 3Document4 pagesMath Module 3Cristina AmantiadNo ratings yet
- Fichas MatemáticasDocument7 pagesFichas MatemáticasmarNo ratings yet
- Module in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityDocument5 pagesModule in Mathematics 9: Department of Education-National Capital Region Schools Division of Pasay CityShein SheilaNo ratings yet
- 0a.review of Pre-Requisite Skills - Ja21 (Answers)Document5 pages0a.review of Pre-Requisite Skills - Ja21 (Answers)tylerchoykwNo ratings yet
- Algebra 1esoDocument3 pagesAlgebra 1esoalberto580ANo ratings yet
- Algebra 01 Test Answer KeyDocument4 pagesAlgebra 01 Test Answer KeySunnyNo ratings yet
- Exam-Style Paper A - Pure 1Document2 pagesExam-Style Paper A - Pure 1Syeda Asra AkhterNo ratings yet
- 2.monomials and PolynomialsDocument6 pages2.monomials and PolynomialsMohamed AlyNo ratings yet
- Csec Add Maths June 2019Document29 pagesCsec Add Maths June 2019Tavar WhyteNo ratings yet
- Exercise No 3 - AnswerDocument4 pagesExercise No 3 - AnswerRabiahNo ratings yet
- Límites (Laboratorio) (Reparado)Document4 pagesLímites (Laboratorio) (Reparado)No Transmisibles Red de Salud OtuzcoNo ratings yet
- Gr9math Q1W1 - LasDocument22 pagesGr9math Q1W1 - LasIvanhoe BalaroteNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Las Week1 S.Y. 2021 2022Document5 pagesMath 9 Las Week1 S.Y. 2021 2022Alleah Fate CunananNo ratings yet
- Jorge RDZ LimitesDocument3 pagesJorge RDZ LimitesoscarNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations MethodsDocument29 pagesQuadratic Equations MethodsPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Eew - ps1 - Sol (Logarithms and Exponents)Document3 pagesEew - ps1 - Sol (Logarithms and Exponents)James WigtonNo ratings yet
- Grade10 - W6 - MathSTE - Additional Activities - PCVRaymundoDocument4 pagesGrade10 - W6 - MathSTE - Additional Activities - PCVRaymundoxander isonNo ratings yet
- SoluciónDocument2 pagesSoluciónKmpos PercyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2019 Set 3Document14 pagesCBSE Class12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2019 Set 3Ankush BNo ratings yet
- Systematic Circuit Analysis: Nodal Analysis Chapter 4 Section 1Document55 pagesSystematic Circuit Analysis: Nodal Analysis Chapter 4 Section 1Marvin - Soriente VILLALUNANo ratings yet
- Propositional Logic in Artificial Intelligence: ExampleDocument5 pagesPropositional Logic in Artificial Intelligence: Examplerayachoty swathiNo ratings yet
- Name - Discovering TrigDocument3 pagesName - Discovering Trigshirleydavid82No ratings yet
- Polygons Are Used inDocument1 pagePolygons Are Used inSaraah GhoriNo ratings yet
- Topology Uniform ConvergenceDocument16 pagesTopology Uniform ConvergenceANDRES DAVID GUEVARA MENDOZANo ratings yet
- AIMO 2016 Trial G8 PaperDocument7 pagesAIMO 2016 Trial G8 PaperHary PurbowoNo ratings yet
- IGNOU MCA MCS-21 Solved Assignments 2011Document17 pagesIGNOU MCA MCS-21 Solved Assignments 2011Syedkareem_hkgNo ratings yet
- 7UT6 Transformer Differential Protection: Vector Group, Io-Elimination, Io-CorrectionDocument11 pages7UT6 Transformer Differential Protection: Vector Group, Io-Elimination, Io-Correctionpraful varsadaNo ratings yet
- Archibald Fripp Dr. Archibald Fripp is an electrical engineer and materials scientist. He was a senior scientist at NASA and managed many space shuttle experiments. He retired from NASA in 1998 but st.pdfDocument346 pagesArchibald Fripp Dr. Archibald Fripp is an electrical engineer and materials scientist. He was a senior scientist at NASA and managed many space shuttle experiments. He retired from NASA in 1998 but st.pdfprashantnasaNo ratings yet
- A Dynamical Systems Perspective On InteractionDocument43 pagesA Dynamical Systems Perspective On InteractionAnonymous CjcDVK54No ratings yet
- Coloring VertexDocument14 pagesColoring VertexejuneorNo ratings yet
- lecPL PDFDocument161 pageslecPL PDFrafik94No ratings yet
- Chapter3 Elementary FunctionsDocument17 pagesChapter3 Elementary FunctionsEric RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Yr7 AreaPerimeterDocument87 pagesYr7 AreaPerimeterAman SinghNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics - Propositional LogicDocument8 pagesDiscrete Mathematics - Propositional LogicAldrich PanioNo ratings yet
- Integral of SQRT (Tanx)Document1 pageIntegral of SQRT (Tanx)wyrmczarNo ratings yet
- ACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 1Document5 pagesACJC JC 2 H2 Maths 2012 Year End Exam Question Paper 1ofji4oNo ratings yet
- 1 AlgebraDocument48 pages1 AlgebraDiana Perez100% (1)
- L 313 18.+270Document7 pagesL 313 18.+270jpyusiongNo ratings yet
- Linear Time Invariant Systems - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument5 pagesLinear Time Invariant Systems - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook BlogNo ratings yet
- Coordinate SystemDocument14 pagesCoordinate Systemreach_arindomNo ratings yet
- Rate of ConvergenceDocument10 pagesRate of ConvergenceKhalid ShahNo ratings yet
- General Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 01Document2 pagesGeneral Math DLL For SHS - (More DLL at Depedtambayanph - Blogspot.com) Q1, Week 01Jester Guballa de Leon100% (1)
- University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila: Lab Manual No 01 Introduction To MATLABDocument27 pagesUniversity of Engineering and Technology, Taxila: Lab Manual No 01 Introduction To MATLABWaqas Ahmed100% (1)
- Inspire Structures 2018 Training-CH8-SKETCHING-JAN11-2018Document5 pagesInspire Structures 2018 Training-CH8-SKETCHING-JAN11-2018faizfebriantokajenNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Solutions: 2 3 4 K 2 3 K 2 3 K k+1 k+1 k+1 2 3 4 K 2 3 4 K K MDocument9 pagesHomework 1 Solutions: 2 3 4 K 2 3 K 2 3 K k+1 k+1 k+1 2 3 4 K 2 3 4 K K Mhomanho2021No ratings yet
- Fluent 13.0 Lecture05 Solver SettingsDocument32 pagesFluent 13.0 Lecture05 Solver Settingsshraveen1991No ratings yet
- Sukkrivaa Vijayan's Recommendation LetterDocument2 pagesSukkrivaa Vijayan's Recommendation LetterSukkrivaaNo ratings yet
- Practice For 2ND PTDocument3 pagesPractice For 2ND PTCherry CabatbatNo ratings yet