Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cell Cycle and Mitosis DNA Review
Uploaded by
Mazon, Dinah Melisse P.0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the cell cycle and mitosis. It describes that mitosis follows interphase and results in two daughter cells. There are four phases of mitosis - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm, resulting in two individual cells. Cancer occurs when cells divide uncontrollably and form tumors. Cancer therapy uses radiation, chemotherapy, or other methods to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
Original Description:
Original Title
THE CELL CYCLE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the cell cycle and mitosis. It describes that mitosis follows interphase and results in two daughter cells. There are four phases of mitosis - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm, resulting in two individual cells. Cancer occurs when cells divide uncontrollably and form tumors. Cancer therapy uses radiation, chemotherapy, or other methods to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesCell Cycle and Mitosis DNA Review
Uploaded by
Mazon, Dinah Melisse P.The document summarizes the cell cycle and mitosis. It describes that mitosis follows interphase and results in two daughter cells. There are four phases of mitosis - prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis then divides the cytoplasm, resulting in two individual cells. Cancer occurs when cells divide uncontrollably and form tumors. Cancer therapy uses radiation, chemotherapy, or other methods to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
THE CELL CYCLE MITOSIS
DNA REVIEW Mitosis follows interphase.
During mitosis, one parent cell divides into
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) contains the two daughter cells.
information for life – all the instructions needed All somatic cells ( cells that are not sex cells
to make proteins (including enzymes) that make eggs & sperm) undergo mitosis.
A segment of DNA that controls the production There are FOUR phases of Mitosis (PMAT):
of a protein is called a gene. Hundreds of genes - Prophase
together make up a chromosome. - Metaphase
DNA → Gene → Chromosome - Anaphase
DNA is a polymer made up of a chain of - Telophase
nucleotides
Each nucleotide has three parts: PROPHASE
simple sugar (deoxyribose)
1st and longest phase in mitosis
phosphate group
Chromosomes in the cell condenses
Nitrogen base (adenine, guanine, thymine,
Nuclear envelope disappears.
or cytosine)
Centrioles (organelle that produces spindle
THE CELL CYCLE fibers) have separated and move to opposite
ends of the cell.
We have learned that the basic unit of life is Spindle fibers form and radiate toward the
the cell. center of the cell.
Like all living things, the cell goes through a
cycle of growth and reproduction.
The sequence of growth and division of a cell is
METAPHASE
called the Cell Cycle.
Most of the cell’s life is spent in in the growth Shortest phase of mitosis
phase known as interphase. Chromosomes line up across the middle of the
- Made up of three phases: G1, S, and G2 cell.
The shortest phase in the cycle is the cell Spindle fibers connect the centromere of each
division phase known as mitosis and sister chromatid to the poles of the cell.
cytokinesis. Sister chromatids are pulled to the middle of
the cell and line up on the midline.
IMPORTANCE OF CELL SIZE
One sister chromatid from each pair points to
Once a cell becomes a certain size, it will divide one pole while the other points to the opposite
into two cells pole.
The larger a cell grows
ANAPHASE
- The more demands on the cell’s DNA
- Proteins and other substances are not Centromeres that join the sister chromatids
produced quick enough for a large cell split.
to maintain. Sister chromatids separate becoming
- The more demands on the cell’s membrane individuals’ chromosomes.
- Nutrients and wastes have a hard time Separated chromatids move to opposite poles
crossing the membrane because of the of the cell.
lack of surface area.
TELOPHASE
Last phase of mitosis TUMORS
Chromosomes (each consisting of a single
Mass of cancer cells= tumor
chromatid) uncoil.
Benign Tumor- abnormal mass of cells stays at
A nuclear envelope forms around the
original site.
chromosomes at each pole of the cell.
Malignant Tumor- abnormal cells that break
Spindle fibers break down and dissolve.
off, enter the blood and lymph systems and
Cytokinesis begins.
invade other organs and form new tumors.
CYTOKINESIS A tumor grows from a single cancer cell, Cancer
Cells invade neighboring tissue, Cancer Cells
Cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm into spread through lymph and blood vessels too
two individual cells. other parts of the body
Each new cell has its own nucleus and
organelles CANCER THERAPY
Different process in animal and plant cells:
Radiation Therapy- uses radiation to kill cancer
In animals: the cell membrane forms a cleavage
cells and shrink tumors
furrow that will pinch into two cells.
- Damages the cell’s DNA so that it cannot
In plants: the cell plate forms midway the cell
divide.
wall of the plant cell. Between the divided
- Usually localized so it won’t kill healthy cells.
nuclei, which gradually develops into a
Chemotherapy- uses drugs to kill actively
separating membrane
dividing cells and healthy cells.
CYTOKINESIS IN ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS - Travels throughout the entire body
•Animal cells – cell membrane starts to pinch CELL DEATH
around middle of cell (forms a cleavage furrow)
Apoptosis
until it completely separates 2 new cells
- programmed cell death
•Plant cells – cell wall starts to lay down pieces of
- Internal or external signals produce self-
cell wall between 2 new cells (called cell plate) until
destructive enzyme
it is completed
Ex.
Cell membrane and wall then forms around
each new cell - Human embryos have webbing between their
fingers and toes.
MITOSIS OUT OF CONTROL
- Before birth, these cells go through apoptosis
Cancer cells are an example of cells that do not so that the webbing disappears.
listen to the cell’s control system.
Cancer cells keep dividing even though they
may be closely packed together, or no growth
factor is present.
Cancer begins as a single cell.
This cell is normally found and destroyed by the
body’s immune system. If not, this cell could
divide into a mass of identical daughter cancer
cells.
You might also like
- BIOL-1110 - Unit 3 - Study GuideDocument3 pagesBIOL-1110 - Unit 3 - Study GuideOmarNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell DivisionDocument5 pages1.6 Cell DivisionmariamNo ratings yet
- Mitosis - DiscussionDocument30 pagesMitosis - DiscussionTRISTAN KENT SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Izat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmDocument18 pagesIzat Ezatte Binti Musa 4 UtmSuhailina Mohd IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Division Reviewer PDFDocument16 pagesCellular Division Reviewer PDFBrylle Angelo PolintanNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument27 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsYecid Rojas-MolinaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument21 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsCristina MariaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Cell Division: Stages and RoleDocument7 pagesGrade 10 Cell Division: Stages and RoleKaylaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionDocument36 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Cell DivisionHeart VidalNo ratings yet
- Relab Term 3Document57 pagesRelab Term 3Nqobile NjokoNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle N Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell Cycle N Cell DivisionDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis OnlyDocument56 pagesCell Division Discussion - Cell Cycle and Mitosis Onlymarimay.lumabanNo ratings yet
- MF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2Document29 pagesMF009 4B Nuclear Division James L2PikuNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: DNA Replication and Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesThe Cell Cycle: DNA Replication and Cell DivisionThatcher RortvedtNo ratings yet
- (W3) Cell CycleDocument6 pages(W3) Cell CycleRednaxela Mejico TarucNo ratings yet
- LAS 36 MitosisDocument27 pagesLAS 36 MitosisAls Centre A OpolNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PowerpointDocument28 pagesMitosis PowerpointShairah LozanoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument23 pagesCell DivisionLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsDocument27 pagesCell Division-Mitosis Notes: 2 New CellsMARY ANN PANGANNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument56 pagesMitosisAlexine CartinNo ratings yet
- Cell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleDocument43 pagesCell Division - Mitosis and The Cell CycleJomar CarabotNo ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument3 pagesMitosis WorksheetHipster48No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument28 pagesMeiosisPari ValechaNo ratings yet
- Cell Diviosin For CCDocument27 pagesCell Diviosin For CCmiss HalaNo ratings yet
- Gr.10 Remote Learning Workbook Term 3Document58 pagesGr.10 Remote Learning Workbook Term 3ffalchemyNo ratings yet
- 1.3 - Mitosis-1Document27 pages1.3 - Mitosis-1sophiewayman07No ratings yet
- Activity 2 Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesActivity 2 Cell DivisionJL Masangcay DayagNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument20 pagesMitosisResego lentsweNo ratings yet
- THE CELL - Basic Unit of Life: Mrs - Lakshmi Priya Thyagarajan, (PH.D) LBT GCTDocument68 pagesTHE CELL - Basic Unit of Life: Mrs - Lakshmi Priya Thyagarajan, (PH.D) LBT GCTAnonymous GhQ1eIyxunNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Chromosome ReplicationDocument5 pagesCell Division and Chromosome Replicationkami gourgaemNo ratings yet
- Cell Division and Mitosis ExplainedDocument29 pagesCell Division and Mitosis ExplainedEL PEPENo ratings yet
- 4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)Document58 pages4 Science 2 RPK - Chap 5 Cell Division (Part 1)zanayanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: The Great Divide Cell Cycle TidbitsDocument4 pagesMitosis: The Great Divide Cell Cycle TidbitsPhoebe Gay VillarealNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument24 pagesMitosisapi-202349222No ratings yet
- Cell Division: Growth, Replication and DistributionDocument3 pagesCell Division: Growth, Replication and DistributionMohnish MNo ratings yet
- Mitosis & Meiosis SheetDocument4 pagesMitosis & Meiosis SheetJoly Ann GesmanNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Life Science Remote Learning BookletDocument57 pagesTerm 3 Life Science Remote Learning BookletAgrarianNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument8 pagesMitosisMilongy JavierNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell Divisionfefaw93458No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Document42 pagesChapter 9 Cell Cycle Chromosome and Mitosis 2018Nehjoy GerangueNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument11 pagesCell DivisionDr Nicholas AdeNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: The Process That Keeps Us AliveDocument49 pagesCell Division: The Process That Keeps Us AlivePROJECTS SKNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle ExplainedDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle ExplainedFatimah AfzalNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument12 pagesMitosisCrystal Janelle TabsingNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis 1225581257073362 9Document50 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis 1225581257073362 9Defriel TaripeNo ratings yet
- Bio Rev 2Document3 pagesBio Rev 2mailforprinting101No ratings yet
- 3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument46 pages3.2 Mitosis and MeiosisAhmed AimanNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceDocument11 pagesMitotic Cell Cycle + InheritanceNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis PowerpointDocument31 pagesMitosis PowerpointLeenfranzen MagadiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document4 pagesLesson 6Thea MillanesNo ratings yet
- Corrina Pledger - hssb0502s - ReinforceDocument1 pageCorrina Pledger - hssb0502s - ReinforceCorrina PledgerNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- BIO 101 Chapter 8Document13 pagesBIO 101 Chapter 8mkmanNo ratings yet
- Prometaphase: Somatic Cells Somatic CellsDocument4 pagesPrometaphase: Somatic Cells Somatic CellsMica CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Cell Division: Understanding Mitosis and MeiosisDocument50 pagesCell Division: Understanding Mitosis and MeiosisLyca GunayNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis Meiosis 1225581257073362 9Document50 pagesCell Division Mitosis Meiosis 1225581257073362 9PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 MitosisDocument36 pagesLesson 7 MitosisMobileLegends SbNo ratings yet
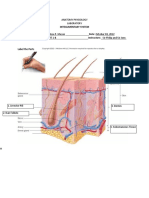
- Mazon - Prelims Histology Week 1Document2 pagesMazon - Prelims Histology Week 1Mazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Pfit MidtermsDocument6 pagesPfit MidtermsMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Mazon - Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesMazon - Integumentary SystemMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- The Integumentary System MazonDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System MazonMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Muscular System OverviewDocument5 pagesMuscular System OverviewMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- MICROSCOPE Types and PartsDocument2 pagesMICROSCOPE Types and PartsMazon, Dinah Melisse P.100% (1)
- The Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesThe Muscular SystemMazon, Dinah Melisse P.No ratings yet
- Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research: Narendra P. SinghDocument8 pagesMutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research: Narendra P. SinghAndrea bedoya vasquezNo ratings yet
- Abnormal PueperiumDocument24 pagesAbnormal Pueperiumvvmounika reddy907No ratings yet
- Classification of VirusesDocument39 pagesClassification of VirusesYeyeh Santos100% (3)
- People's Friendship University of Russia: Acute Odontogenic and Hematogenous OsteomyelitisDocument22 pagesPeople's Friendship University of Russia: Acute Odontogenic and Hematogenous OsteomyelitisAyad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- RNA VIRUS MNEMONIC DEVICEDocument2 pagesRNA VIRUS MNEMONIC DEVICEJad Jaffal100% (1)
- Stages of Infection 2Document7 pagesStages of Infection 2Karren Taquiqui PleteNo ratings yet
- Effects of Oleic Acid: Review Article Doi: 10.17546/msd.25609Document8 pagesEffects of Oleic Acid: Review Article Doi: 10.17546/msd.25609Radwan AjoNo ratings yet
- PACHECO - EXERCISE NO.1-The CellDocument3 pagesPACHECO - EXERCISE NO.1-The CellMaria Brooklyn PachecoNo ratings yet
- New Perspectives in Fermented Dairy Products and Their Health RelevanceDocument11 pagesNew Perspectives in Fermented Dairy Products and Their Health RelevanceAndrea Osorio AlturoNo ratings yet
- A Review On Exosomes Application in Clinical Trials Perspective, Questions, and ChallengesDocument13 pagesA Review On Exosomes Application in Clinical Trials Perspective, Questions, and ChallengesEsra YÖNDEMNo ratings yet
- RNADocument21 pagesRNAManoj SigdelNo ratings yet
- 4 5881784375581870090Document6 pages4 5881784375581870090Ahmed noor Ahmed noorNo ratings yet
- Vivas in Surgical Pathology For DM 1: What Is A Neoplasm? Define Neoplasia?Document11 pagesVivas in Surgical Pathology For DM 1: What Is A Neoplasm? Define Neoplasia?Giovanni HenryNo ratings yet
- Biology Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology Exam QuestionsSiddharth PradhanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Course OverviewDocument155 pagesMolecular Biology Course OverviewXiao AlexNo ratings yet
- A Guide To The Application of The WHO Multimodal Hand Hygiene. OMS PDFDocument73 pagesA Guide To The Application of The WHO Multimodal Hand Hygiene. OMS PDFanon_157163700100% (1)
- A Level Homework 5Document4 pagesA Level Homework 5szyzypNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Human Immune Cell Characterization by Flow CytometryDocument5 pagesA Guide To Human Immune Cell Characterization by Flow CytometryLeo TolstoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document29 pagesChapter 10MaskManNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Training and Procedures: Bacteriological TechniquesDocument8 pagesLaboratory Training and Procedures: Bacteriological TechniquesMarco cenabreNo ratings yet
- A Pharmacology-Based Comprehensive Review On Medicinal PlantsDocument14 pagesA Pharmacology-Based Comprehensive Review On Medicinal PlantsissamebenNo ratings yet
- Quiz 9 14 Answers PDFDocument2 pagesQuiz 9 14 Answers PDFюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Whooping CoughDocument22 pagesWhooping CoughAqeel AhmadNo ratings yet
- Product Information Omeprazole Sandoz Iv 40 MG Powder For InjectionDocument13 pagesProduct Information Omeprazole Sandoz Iv 40 MG Powder For Injectionminhmap90_635122804No ratings yet
- Septic Arthritis 97-03Document20 pagesSeptic Arthritis 97-03john michael olivares100% (5)
- Infectious Diseases. Etiology PDFDocument76 pagesInfectious Diseases. Etiology PDFIoana CozmaNo ratings yet
- Proteins and Cell Regulation Vol 02 - Myb Transcription Factors, 1E (2004)Document435 pagesProteins and Cell Regulation Vol 02 - Myb Transcription Factors, 1E (2004)DiahaNo ratings yet
- Postharvest Biology and Technology: SciencedirectDocument9 pagesPostharvest Biology and Technology: SciencedirectErwin Gutama PutraNo ratings yet
- LEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsDocument11 pagesLEUKEMIA, MPDs & MDSsMary Kaye Yvonne OtillaNo ratings yet
- CYP2C19 2, CYP2C19 3, CYP2C19 17 Allele and Genotype Frequencies in Clopidogrel-Treated Patients With Coronary Heart Disease in RussianDocument5 pagesCYP2C19 2, CYP2C19 3, CYP2C19 17 Allele and Genotype Frequencies in Clopidogrel-Treated Patients With Coronary Heart Disease in RussianSabrina JonesNo ratings yet