Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDF
Uploaded by
Rudzi UdziOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4.1 One Pager Eye - MEMO PDF
Uploaded by
Rudzi UdziCopyright:
Available Formats
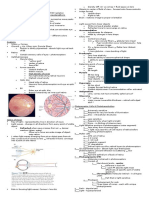
THE EYE Concave lenses
See nearby Surgery
Conjunctiva K objects clearly
A Sclera Convex lenses
Function: Protective function – protects the Functions:
See distant
objects clearly
eye from dust and infection-causing Surgery
• Protects the eye against damage
microorganisms
Bi-focal lenses
(continuation of sclera) Cornea J • Gives shape to the eyeball
Surgery
Function: Responsible for the refraction
Adaptation: Surgery (replace lens
(bending) of light rays
• It’s a tough membrane with synthetic lens)
Adaptation/s:
• Convex in shape – allows refraction
• Transparent – allows light to pass through
Adaptation B Choroid
Yellow SPOT Functions:
Iris I - Area containing lots of cones • Supply the eye with nutrients and oxygen
Function -Best image formed here
Controls the amount of light entering the
• eye / Changes the size of the pupil • Prevents (reduces) internal reflection of light
Aqueous
humour
---------Vitreous humour------------- Adaptation:
Pupil H
Blind SPOT • A dark coloured layer, rich in blood vessels
Function:Allows light to enter the eye
-No image forms here… No rods C Retina
Lens G
and cones are found here Function:
Function: Changes shape for near and
distant vision/Refract light to fall on the retina -Optic nerve leaves the eye at • Converts light stimuli into verve impulses
Adaptations: j the blind spot Adaptation: Contains the light-sensitive receptor cells,
• Bi-convex – Refracts light i.e. the rods (black and white) and cones (colour vision)
• Transparent membrane-allows light through D Optic nerve ( sensory neuron)
Suspensory ligaments F Function:
Function: Holds the lens in position Transmit impulses from the retina
Binocular vision: The ability to maintain visual focus on
Adaptation It is elastic to the cerebrum
an object with both eyes open
Ciliary muscle E Explain the consequences if this neuron is damaged
Function: Contracts and relax to change the Optic nerve won’t be able to transmit impulses to the
Importance of Binocular vision: It allows a person to •
shape (curvature) of the lens cerebrum, to be interpreted
judge distance and depth (enables 3D vision)
• Person won’t be able to see
ACCOMODATION: the adjustment (changing) of the
shape of the lens to see near of far objects clearly
Bright Dim (low light intensity)
Near vision Far/distant vision
-Circularl muscles -Radial muscles of
1. Ciliary muscle contract 1. Ciliary muscle relaxes of the iris relax the iris contract
3. Tension on the lens decrease 3. Tension on the lens increase -Radial muscles -Circular muscles of
4. Lens becomes more curved/convex 4. Lens becomes les convex / flatter of the iris contracts the iris relax
2. Suspensory ligaments slackens 2. Suspensory ligaments tighten -Pupil constricts - Pupil dilates
(becomes taut) Less light enters the eye More light enters eye
You might also like
- Practical Examination Marking Guideline Grade 12 Physical Science 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesPractical Examination Marking Guideline Grade 12 Physical Science 2019 PDFWonder Bee Nzama100% (1)
- 6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMODocument1 page6.1 One Pager Nervous System - MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Document1 page7.1 Human Endocrine System - MEMO - ONE PAGER 2020Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Geography Mapwork Learner BookDocument46 pagesGrade 12 Geography Mapwork Learner BookLamiya BalochNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Poetry 2023 Annotated PoemsDocument13 pagesGrade 12 Poetry 2023 Annotated PoemsCristina Ruela100% (4)
- Gr11 ACC P2 (ENG) June 2022 Question PaperDocument11 pagesGr11 ACC P2 (ENG) June 2022 Question Paperora masha100% (1)
- Tsotsi ElementsDocument7 pagesTsotsi ElementsChanelle RoartyNo ratings yet
- AVBOB STEP 12 English Paper #2 DigitalDocument76 pagesAVBOB STEP 12 English Paper #2 Digitalhopemandi25No ratings yet
- The Slave Dealer - MemoDocument2 pagesThe Slave Dealer - Memowaldo strydomNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Geog p2 n16 Memo EngDocument10 pagesGr11 Geog p2 n16 Memo EngThato MotlhabaneNo ratings yet
- Afr HT SCMP - Gedigte-2023-Afrikaans-Hl - Konsep 2 (2022!10!18)Document123 pagesAfr HT SCMP - Gedigte-2023-Afrikaans-Hl - Konsep 2 (2022!10!18)crizelwilken98No ratings yet
- English Fal Poetry 2024Document87 pagesEnglish Fal Poetry 2024mabelenglehlohonolo3100% (1)
- Maths Literacy GR 12 April 2021 QP and Memo 2Document19 pagesMaths Literacy GR 12 April 2021 QP and Memo 2Mkhululi Khumalo100% (1)
- Poetry Pack 1 GR 11 FAL 2020Document104 pagesPoetry Pack 1 GR 11 FAL 2020salmarigroenewaldNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences P1 Feb-March 2014 Memo Afr & EngDocument20 pagesPhysical Sciences P1 Feb-March 2014 Memo Afr & Engbennie07No ratings yet
- EFAL POETRY QuestionsDocument20 pagesEFAL POETRY QuestionsLethukuthula MbathaNo ratings yet
- Setswana HL PoetryDocument77 pagesSetswana HL PoetryTshidy LekweneNo ratings yet
- Enghl p2 Gr11 QP Nov2020 DDocument21 pagesEnghl p2 Gr11 QP Nov2020 DRebecca GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Mapwork Techniques Term 1 2023 Practical Task PDFDocument94 pagesMapwork Techniques Term 1 2023 Practical Task PDFMoagi LekakaNo ratings yet
- English Fal 18 April 2023Document41 pagesEnglish Fal 18 April 2023thabileshab08No ratings yet
- Eye PDFDocument11 pagesEye PDFManas kumarNo ratings yet
- Science 11Document10 pagesScience 11ranjitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteDocument13 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World NoteJay MakiNo ratings yet
- Eg9 TB Sci Chap2Document22 pagesEg9 TB Sci Chap2JAYDEN JANSZNo ratings yet
- The Colourful WorldDocument9 pagesThe Colourful WorldShalom LogosNo ratings yet
- Optics and RefractionDocument1 pageOptics and RefractionAurel FeodoraNo ratings yet
- 400-750 NM AccommodationDocument2 pages400-750 NM AccommodationTeves AdrianNo ratings yet
- Eye and Colourful WorldDocument11 pagesEye and Colourful WorldutsavpihuNo ratings yet
- Light Human EyeDocument33 pagesLight Human EyeDevika ManiNo ratings yet
- The Human Eye - StructureDocument8 pagesThe Human Eye - Structuremarealyn.hermida.camachoNo ratings yet
- 1.6 The Sense of SightDocument18 pages1.6 The Sense of SightNasiruddin KutatNo ratings yet
- Bio Experiment 4Document3 pagesBio Experiment 4Vinushree SanthoshkumarNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EyeDocument18 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EyeMargaretha AdhiningrumNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear - 2019Document3 pagesEye and Ear - 2019Mr. RWord100% (1)
- Chapter 14 Animal Receptor Organ (The Eye) - Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesChapter 14 Animal Receptor Organ (The Eye) - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (2)
- CH 11 Human EyeDocument4 pagesCH 11 Human EyekniFe VisualzNo ratings yet
- Eye and Ear 2.1 Human EyeDocument12 pagesEye and Ear 2.1 Human Eyechakshana kannangaraNo ratings yet
- The Human EyeDocument15 pagesThe Human EyeAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Error of RefractionDocument3 pagesError of RefractionMargot SanchezNo ratings yet
- SB2h The Eye UpdatedDocument32 pagesSB2h The Eye Updated6c4xmbykfvNo ratings yet
- Our Sense of Sight and LightDocument6 pagesOur Sense of Sight and LightnorafaizalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5Anjali GoelNo ratings yet
- Science NotesDocument9 pagesScience NotesClaire MaeNo ratings yet
- Sci Quiz 4 q2Document11 pagesSci Quiz 4 q2eslNo ratings yet
- Human EyeDocument3 pagesHuman Eyeupadhyayula srikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Opto Reviewe2Document8 pagesOpto Reviewe2isseylimboNo ratings yet
- Human Visual SystemDocument6 pagesHuman Visual SystemNagarajan V ANo ratings yet
- Week 7 - Assessment of The EyeDocument7 pagesWeek 7 - Assessment of The EyeBLOCK 20 - EULER PABILLONo ratings yet
- Eye StructureDocument15 pagesEye StructurekathyNo ratings yet
- Eyes and Camera (Autosaved)Document15 pagesEyes and Camera (Autosaved)Larisha Frixie M. DanlagNo ratings yet
- TR Special Senses Intensive TransDocument7 pagesTR Special Senses Intensive TransAngelica AlayonNo ratings yet
- Eye StructureDocument15 pagesEye StructurekathyNo ratings yet
- ATENGCO - Activity11 The Sense OrgansDocument8 pagesATENGCO - Activity11 The Sense OrgansJoann Mae PudaderaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Plane MirrorDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Plane MirrorJazelle PaciaNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Looking Aftera Retinoscope and Trial Lens SetDocument2 pagesUnderstanding and Looking Aftera Retinoscope and Trial Lens SetAurel FeodoraNo ratings yet
- MCB Lab ReviewerDocument5 pagesMCB Lab ReviewerJhoanna Mae MinionNo ratings yet
- Class01 - 08 Visual Optics IntroductionDocument13 pagesClass01 - 08 Visual Optics IntroductioncehborrotoNo ratings yet
- 10science EyesDocument36 pages10science EyesChuNie TangNo ratings yet
- Finals - Eyes and EarsDocument4 pagesFinals - Eyes and EarsCrisanta Grace OpondaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Stimuli and Responses in HumansDocument38 pages1.2 Stimuli and Responses in HumansNaveen AlexanderNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument9 pagesMeiosisRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Life Science Needs To KnowDocument3 pagesLife Science Needs To KnowRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMODocument1 page5.1 One Pager Reflex Action - MEMORudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 3.1 One Pager The Ear - MemoDocument1 page3.1 One Pager The Ear - MemoRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Solution Step AheadDocument127 pagesSolution Step AheadRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P1 Revision LiveDocument71 pagesLife Sciences P1 Revision LiveRudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- P1 Diagram Book GR12Document30 pagesP1 Diagram Book GR12Rudzi UdziNo ratings yet
- 404T Opioid Analgesics and AntagonistDocument14 pages404T Opioid Analgesics and AntagonistRaja RajaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology GametogenesisDocument14 pagesDevelopmental Biology Gametogenesispragyamaharjan2No ratings yet
- Functions of The Human Respiratory System: What's inDocument4 pagesFunctions of The Human Respiratory System: What's injoyNo ratings yet
- Neurobiological Theories of ConsciousnessDocument14 pagesNeurobiological Theories of ConsciousnessRodrigo Aguirre BáezNo ratings yet
- Radio Study of Middle EarDocument44 pagesRadio Study of Middle EarDOC AJNo ratings yet
- Muscle Physiology & Its SignificanceDocument25 pagesMuscle Physiology & Its SignificanceTarun Goyal100% (2)
- Study Guide For Bio 101 Final ExamDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Bio 101 Final ExamJinnyCakes100% (1)
- Endoplasmic ReticulumDocument3 pagesEndoplasmic ReticulumHanumat SinghNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Unit 6Document2 pagesDiscussion Forum Unit 6Benses AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Etextbook 978 0323088541 Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease in Adults and Children Pathophysiology The Biologic BasisDocument62 pagesEtextbook 978 0323088541 Pathophysiology The Biologic Basis For Disease in Adults and Children Pathophysiology The Biologic Basiseric.chandler298100% (47)
- Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)Document38 pagesSystemic Acquired Resistance (SAR)Arulsia ANo ratings yet
- Physiology AccommodationDocument109 pagesPhysiology AccommodationAmmar bushraNo ratings yet
- Botany Plant Anatomy SEM II H SEM I GDocument34 pagesBotany Plant Anatomy SEM II H SEM I GMartha-Angella MassaquoiNo ratings yet
- Biology Human Reproduction PDFDocument15 pagesBiology Human Reproduction PDFmbsureshNo ratings yet
- Fascia of Lower LimbDocument16 pagesFascia of Lower LimbAshraf SidrahNo ratings yet
- Gen BioDocument86 pagesGen BioPaul MagbagoNo ratings yet
- Xi. Biology. Revision Work.-Ch.3,4,&5. 3. Plant Kingdom. 1.what Do You Mean by ? 3.why Is Algae Grouped Under Thllophyta? 4. Write TheDocument2 pagesXi. Biology. Revision Work.-Ch.3,4,&5. 3. Plant Kingdom. 1.what Do You Mean by ? 3.why Is Algae Grouped Under Thllophyta? 4. Write TheOwasisNo ratings yet
- The Thermoregulatory Theory of Yawning: What We Know From Over 5 Years of ResearchDocument13 pagesThe Thermoregulatory Theory of Yawning: What We Know From Over 5 Years of ResearchAndré AmorimNo ratings yet
- Module 2: Biology and PsychologyDocument23 pagesModule 2: Biology and Psychologyshain aldovinoNo ratings yet
- 1 Klöppel Vortrag GEP NET The NE System 120217Document32 pages1 Klöppel Vortrag GEP NET The NE System 120217soledad88No ratings yet
- Clonin ModelDocument9 pagesClonin ModelNano AlmukasabyNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolismcalista osdonNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: Structures and Functions in Living Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For Edexcel Biology IGCSEDocument9 pagesTopic 2: Structures and Functions in Living Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For Edexcel Biology IGCSEArfaan WaheedNo ratings yet
- BC Tiempo de Trombina Inserto OWNAG11E05Document6 pagesBC Tiempo de Trombina Inserto OWNAG11E05Isa Mar BCNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BSC (Hons) Agriculture, HNBGU, As Per of 5th Dean Committee From 2020-2021Document58 pagesSyllabus BSC (Hons) Agriculture, HNBGU, As Per of 5th Dean Committee From 2020-2021Ganesh dattaNo ratings yet
- Anti AgingDocument6 pagesAnti AgingZubair Akram JanjuaNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissuesDocument9 pagesMuscle Tissuesangelo beldaNo ratings yet
- Faradic Type CurrentDocument26 pagesFaradic Type CurrentzainabnoorNo ratings yet
- Castor Oil Packs ImmunomodulationDocument6 pagesCastor Oil Packs ImmunomodulationCiprian AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis Part 3Document12 pagesGlycolysis Part 3Rishav BajoriaNo ratings yet