Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Micro P Terms
Micro P Terms
Uploaded by
Jensen SengsonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Micro P Terms
Micro P Terms
Uploaded by
Jensen SengsonCopyright:
Available Formats
Registers – are a type of computer memory used to quickly accept store and transfer data and instructions that
are
being used immediately by the CPU.
Segment Register – holds the addresses of instructions and data in memory which are used by the processor
access memory locations.
AX & Dx - ?????
BX – instructions where we need to specify in a general purpose register the 16 bit effective address of a memory
location.
CX – is always used in loop instructions, it is always the implied counter.
Flags – are modified kind of register that record the condition of a microprocessor’s calculation.
Status flag – reflect the result of executing an instruction. Cannot be set directly. (There are 6 SF)
Control flag – enable or disable Certain CPU operations. (There are 3 control Flags)
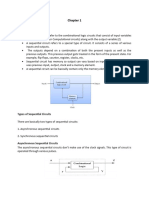
Sequential Logic Circuit – have a inherent memory built in
Event driven – Asynchronized circuit that changes immediately when available.
Clock Driven – Synchronized to clock signal.
Pulse Driven – Responds to trigger pulses.
SR FLIP FLOP – a one bity memory bistable device that has two inputs S for set and R for reset or 1 or 0.
A flag is set if its 1.
Directional Flag – affects the direction of moving data blocks by such instructions as MOVS CMPS and SCAS
Interrupt Flag – Dictates whether system interrupts can occur.
Interrupts – are actions initiated by hardware block such as input devices that will interrupt normal
execution of programs.
Trap Flag – determines whether the CPU is halted after the execution of each instruction.
Carry Flag – is set when the result of an unsigned arithmetic operation is too large to fit in the destination register.
Overflow Flag – determines whether the arithmetic operation is too large to fit in the destination register.
Overflow can occur when adding two numbers with the same sign.
Sign Flag – is set when the sign of arithmetic or logic operation is negative.
Zero Flag – is set when the result is equal to zero. A value of 1 means the result is 0 a value of zero means its value
is not 0
Auxiliary carry Flag - is set when an operation causes a carry from bit 3 to bit 4 ( or a borrow from bit 4 to bit 3 ) of
an operand. A value of 1 = carry a value of 0 = no carry
Parity Flag – reflects the number of 1s in the result of an operation.
You might also like
- PLC NotesDocument170 pagesPLC NotesBikasita Talukdar100% (2)
- Preliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960From EverandPreliminary Specifications: Programmed Data Processor Model Three (PDP-3) October, 1960No ratings yet
- Assembly Language (Lab Manual)Document13 pagesAssembly Language (Lab Manual)Nurfaizah Hasanah Sahimi100% (2)
- SAP Report Group 2Document14 pagesSAP Report Group 2Chanel Hooper0% (1)
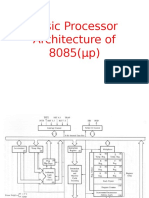
- Architechture or Functional Block Diagram of 8085Document15 pagesArchitechture or Functional Block Diagram of 8085Rawat RajatNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Assembly Language: Lecture 2 - x86 Processor ArchitectureDocument23 pagesComputer Organization and Assembly Language: Lecture 2 - x86 Processor ArchitectureNosreffejDelRosarioNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Org of MicroprocessorsDocument31 pagesLec 2 - Org of Microprocessorsapi-237335979No ratings yet
- Computer 1 File Final-1Document36 pagesComputer 1 File Final-1Priyanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3 Architecture of 8086Document25 pages3 Architecture of 8086Sudeeksha GanguliNo ratings yet
- 1-Architecture of 8085Document34 pages1-Architecture of 8085Pinki KumariNo ratings yet
- Coal Lab Exeersice-1Document4 pagesCoal Lab Exeersice-1Maham FatimaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 CoaDocument17 pagesUnit-4 CoaArun KrishNo ratings yet
- Microprocessors & Microcontrollers Most Important Questions SolutionsDocument34 pagesMicroprocessors & Microcontrollers Most Important Questions SolutionsSrijal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Micro 2Document6 pagesMicro 2Zuhaib AyazNo ratings yet
- Unit 3: Machine InstructionsDocument16 pagesUnit 3: Machine Instructionsshreya ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Cep 1Document8 pagesCep 1ShivamNo ratings yet
- Architecture Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument4 pagesArchitecture Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorbhatiaharryjassiNo ratings yet
- E 4160 Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument39 pagesE 4160 Introduction To MicroprocessorSyaz ZanaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Purpose of A Register in A CPU and What Are Special Purpose Registers PDFDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Purpose of A Register in A CPU and What Are Special Purpose Registers PDFVishnupriya KashyapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Introduction To Intel 8086 MicroprocessorDocument12 pagesChapter 4 - Introduction To Intel 8086 MicroprocessorNaimur EshanNo ratings yet
- MPC 2Document29 pagesMPC 2rohit sharmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microprocessor Based SystemDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Microprocessor Based SystemkusumgdasNo ratings yet
- Co NotesDocument29 pagesCo NotesLisa FiverNo ratings yet
- Von Neumann Architecture 2019Document74 pagesVon Neumann Architecture 2019CS101No ratings yet
- Unit III CPU Organization PG 1-20Document20 pagesUnit III CPU Organization PG 1-20dhruwchanchal31No ratings yet
- Registers AssignmentDocument7 pagesRegisters AssignmentZohaib AmjadNo ratings yet
- Eec Practical 8085 MicroprocessorDocument8 pagesEec Practical 8085 MicroprocessorinxludezNo ratings yet
- Processor Basics: Nizwa College of Technology Department of IT Computer ArchitectureDocument30 pagesProcessor Basics: Nizwa College of Technology Department of IT Computer Architecturealinma76No ratings yet
- Short NotesDocument14 pagesShort NotesAman Ethio LijNo ratings yet
- Features of 8086 Microprocessor:: 1. EU (Execution Unit)Document6 pagesFeatures of 8086 Microprocessor:: 1. EU (Execution Unit)Md Raton AliNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8086 Functional UnitsDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8086 Functional UnitsShahanasNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1: Software TechnologyDocument4 pagesAssignment-1: Software TechnologySwarnim ShuklaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 MechatronicsDocument38 pagesUNIT 3 MechatronicsMuthuvel M67% (6)
- MPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureDocument17 pagesMPMC - Unit 1 - 8085 ArchitectureWickNo ratings yet
- 10 - Processor Structure and FunctionDocument45 pages10 - Processor Structure and FunctionAbdukadir AbdullahNo ratings yet
- U ProcDocument32 pagesU ProcRohitSrinivasNo ratings yet
- Philippine College of Science and Technology: Assignment 3 Overview of Z8 Microcontroller FamilyDocument4 pagesPhilippine College of Science and Technology: Assignment 3 Overview of Z8 Microcontroller FamilyIvan-Jeff AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Unit - VI DEDocument60 pagesUnit - VI DErahulbixt23No ratings yet
- 8086 Pin Diagram Here Is The Pin Diagram of 8086 MicroprocessorDocument17 pages8086 Pin Diagram Here Is The Pin Diagram of 8086 MicroprocessorRakesh ChaudhuriNo ratings yet
- Chp3.1 MicroarchitectureDocument5 pagesChp3.1 Microarchitectureheyfiez12No ratings yet
- Microprocessor8085 BestDocument145 pagesMicroprocessor8085 BestDebashis TaraiNo ratings yet
- Embedded Microprocessor Lecture 2Document15 pagesEmbedded Microprocessor Lecture 2ojasbhosale07No ratings yet
- Cpre 381 Processor Project 1Document20 pagesCpre 381 Processor Project 1api-272773251No ratings yet
- RemaingDocument4 pagesRemaingshuklchitrankNo ratings yet
- Registri TriDocument4 pagesRegistri TriNenad FemicNo ratings yet
- COA Module 4Document11 pagesCOA Module 4shoaibakthar231No ratings yet
- 8 Ee8551 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument1 page8 Ee8551 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersKeerthana SahadevanNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument20 pages8085 Microprocessorjeravi84No ratings yet
- Microprocessor - 8086 Functional UnitsDocument3 pagesMicroprocessor - 8086 Functional UnitsKavi SanjaiNo ratings yet
- SAP-1 (Simple As Possible-1) Computer ArchitectureDocument8 pagesSAP-1 (Simple As Possible-1) Computer ArchitecturesaikotNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureDocument19 pagesMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureSindhujaSindhuNo ratings yet
- Micro U1Document43 pagesMicro U1Avinash SharmaNo ratings yet
- NMIDocument36 pagesNMIVipan SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 IntroDocument49 pages1.1 IntroKarl Martin AlduesoNo ratings yet
- Lectures Section 3 ModifiedDocument73 pagesLectures Section 3 ModifiedcoventryUkNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic ControllerDocument98 pagesProgrammable Logic Controller126 N.EZHILARASAN EEERNo ratings yet
- CO Unit 1Document43 pagesCO Unit 1Dinkesh JainNo ratings yet
- Processor RegistersDocument6 pagesProcessor Registersirinaasdf12No ratings yet
- An Over View of 8085Document12 pagesAn Over View of 8085nskprasad89No ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Micro Controller Lecture NotesDocument118 pagesMicroprocessor and Micro Controller Lecture NotesSivanesh SK50% (2)