Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reporting Bio2
Uploaded by
Ajeay Pamintuan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
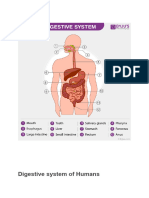
7 views2 pagesThe digestive system breaks down food and liquid into nutrients that the body can use. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Accessory organs that help with digestion include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary glands. Food is ingested, broken down mechanically and chemically, absorbed, and waste is eliminated.
Original Description:
Original Title
reporting_bio2.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe digestive system breaks down food and liquid into nutrients that the body can use. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Accessory organs that help with digestion include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary glands. Food is ingested, broken down mechanically and chemically, absorbed, and waste is eliminated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesReporting Bio2
Uploaded by
Ajeay PamintuanThe digestive system breaks down food and liquid into nutrients that the body can use. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus. Accessory organs that help with digestion include the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and salivary glands. Food is ingested, broken down mechanically and chemically, absorbed, and waste is eliminated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
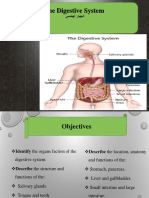
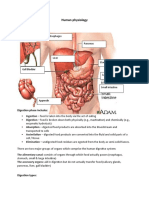
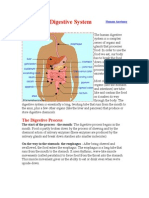
WHAT IS DIGESTIVE SYSTEM?
The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract—also called the GI tract or digestive
tract. The GI tract is a series of hollow organs joined in a long, twisting tube from the mouth to
the anus.
PARTS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Alimentary Tract
1) Mouth - The mouth is an oval-shaped cavity inside the skull. The two main functions of
the mouth are eating and speaking. Parts of the mouth include the lips, vestibule, mouth
cavity, gums, teeth, hard and soft palate, tongue and salivary glands. The mouth is also
known as the oral cavity or the buccal cavity.
2) Pharynx - The pharynx, commonly called the throat, is a passageway that extends from
the base of the skull to the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
3) Esophagus - The esophagus is the hollow, muscular tube that passes food and liquid from
your throat to your stomach.
4) Stomach - The stomach is a J-shaped organ that digests food. It produces enzymes
(substances that create chemical reactions) and acids (digestive juices). This mix of
enzymes and digestive juices breaks down food so it can pass to your small intestine.
5) Small intestine - A long tube-like organ that connects the stomach and the large intestine.
It is about 20 feet long and folds many times to fit inside the abdomen. The small
intestine has three parts: the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. It helps to further digest
food coming from the stomach.
6) Large intestine - The long, tube-like organ that is connected to the small intestine at one
end and the anus at the other. The large intestine has four parts: cecum, colon, rectum,
and anal canal. Partly digested food moves through the cecum into the colon, where water
and some nutrients and electrolytes are removed.
7) Rectum - The last several inches of the large intestine closest to the anus.
8) Anus - The anus is the opening at the far end of the digestive tract through which stool
leaves the body.
Associated with the alimentary tract are the following accessory organs:
1) Salivary glands - make saliva, which aids in digestion, keeps your mouth moist and
supports healthy teeth. You have three pairs of major salivary glands under and behind
your jaw. parotid, sublingual and submandibular.
Parotid - located below and in front of each ear.
Sublingual - located under your tongue.
Submandibular – located under your jaw.
2) Liver - The liver is the largest solid organ in the body. It removes toxins from the body's
blood supply, maintains healthy blood sugar levels, regulates blood clotting, and
performs hundreds of other vital functions.
3) Gallbladder - is a small, pear-shaped organ on the right side of your abdomen, just
beneath your liver. The gallbladder holds a digestive fluid called bile that's released into
your small intestine.
4) Pancreas - A glandular organ located in the abdomen. It makes pancreatic juices, which
contain enzymes that aid in digestion, and it produces several hormones, including
insulin. The pancreas is surrounded by the stomach, intestines, and other organs.
You might also like
- DSE4610 DSE4620 Operators ManualDocument86 pagesDSE4610 DSE4620 Operators ManualJorge Carrasco100% (6)
- Science Project - Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesScience Project - Digestive Systemapi-35222133565% (17)
- Urinary Tract Infection Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Anatomy and PhysiologyPaul Anthony Centeno PimentelNo ratings yet
- Shakila Hamed Report PDFDocument9 pagesShakila Hamed Report PDFShakila HamidNo ratings yet
- Attention: 6R60/6R75/6R80 Installation GuideDocument4 pagesAttention: 6R60/6R75/6R80 Installation GuideEdwinferNo ratings yet
- Gi 2Document38 pagesGi 2وجد عمرNo ratings yet
- Microsoft PowerPoint - Digestive 2011.Document50 pagesMicrosoft PowerPoint - Digestive 2011.LadyseptianiNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Digestive SystemDocument12 pagesFunctions of The Digestive SystemRomeo Penyihir ChrestomancyNo ratings yet
- Handout in Science 8: Biology LESSON 1: Organs of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesHandout in Science 8: Biology LESSON 1: Organs of The Digestive SystemJanna SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesDigestive SystemQueencess Ara TorresNo ratings yet
- A & PDocument2 pagesA & PSahil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument27 pagesDigestive Systemnandhini raguNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy & HistologyDocument7 pagesDigestive System Anatomy & HistologyAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnaPhy - Digestive SystemJan Mark SotoNo ratings yet
- Strategic Intervention Material: Dig Esti Ve Syst emDocument16 pagesStrategic Intervention Material: Dig Esti Ve Syst emKarla Javier PadinNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of Human (Biology)Document35 pagesDigestive System of Human (Biology)liofve X viNo ratings yet
- TomdDocument15 pagesTomdduinnemerriedithcastroNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument47 pagesDigestive SystemKhant Si ThuNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument26 pagesHuman PhysiologyLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology of The Digestive System-PowerpointDocument21 pagesAnatomy & Physiology of The Digestive System-Powerpointlynflores272402100% (2)
- 4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveDocument49 pages4thQ Week1 PPT DigestiveGeronimo SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument18 pagesDigestive System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDNo ratings yet
- DigestiveDocument5 pagesDigestivealayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument32 pagesDigestive SystemHashley CastellyNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive SystemVictoria VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: MouthDocument5 pagesDigestive System: MouthSTEPHEN OTEDANo ratings yet
- Nutrition in Human Beings Class 6Document5 pagesNutrition in Human Beings Class 6Sarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesDigestive SystemJerald CodillaNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology by SalarDocument47 pagesHuman Physiology by SalarAdul basit mughalNo ratings yet
- LP Sistem PencernaanDocument10 pagesLP Sistem Pencernaandiana ratriNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Digestive SystemDocument28 pagesGrade 8 Digestive SystemKryssia Dema-alaNo ratings yet
- Chapter22notes DIGESTIONDocument42 pagesChapter22notes DIGESTIONpancit cantonNo ratings yet
- دمج شباتر البالغين .....Document511 pagesدمج شباتر البالغين .....Abdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesThe Digestive SystemAnonymous X3pqnliPjNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesDigestive SystemHaider CheemaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System of HumansDocument13 pagesDigestive System of HumansNAMISH MAHAKULNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument50 pagesDigestive SystemAlexander VonPatrickNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Human AnatomyDocument42 pagesDigestive System: Human Anatomycristobal melegritoNo ratings yet
- Ingles StudyDocument23 pagesIngles StudyMatiasUrraNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument3 pagesDefinition of TermsJoanne Sianson BucayanNo ratings yet
- BG3-3-The Digestive and Respiratory SystemsDocument36 pagesBG3-3-The Digestive and Respiratory Systemsapa@No ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument25 pagesDigestive Systembazaar9No ratings yet
- I. Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument15 pagesI. Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemPATRICIA KAYE RIO100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument43 pagesDigestive SystemSimply MiniNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesDigestive Systemsikandercheema123No ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument41 pagesThe Digestive Systemkrmgxc8p4fNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Nutrition in Animals Digestion in HumansDocument6 pagesChapter - 2 Nutrition in Animals Digestion in HumansGeeta BhattNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesFunctions of The Digestive SystemPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- What Is The Digestive System?Document9 pagesWhat Is The Digestive System?sri wiqayatul fajariyahNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 9 Digestive SystemDocument187 pagesUNIT - 9 Digestive SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiolog AMOEBIASISDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiolog AMOEBIASISSamer SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Reported By: Debbie Arboleda Cecille Toquero Joshua Duropan Erika PizarroDocument77 pagesDigestive System: Reported By: Debbie Arboleda Cecille Toquero Joshua Duropan Erika PizarroJezreel OrquinaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - Lecture GuideDocument11 pagesDigestive System - Lecture GuideJEFFERSON ANDAYANo ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Digestive SystemHuiTene Sim100% (1)
- Digestive System Anatomy PhysiologyDocument20 pagesDigestive System Anatomy PhysiologyKids JangNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument7 pagesDigestion and AbsorptionlalitNo ratings yet
- Visible Body DigestiveDocument8 pagesVisible Body Digestivejellypish269No ratings yet
- Patologi Sistem Pencernaan (Tractus Digestivus) By: Sarah Suzanna, Dr. Farida Gustini, DRGDocument47 pagesPatologi Sistem Pencernaan (Tractus Digestivus) By: Sarah Suzanna, Dr. Farida Gustini, DRGNova Pinte NiateNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 11Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 11Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Main FinalDocument14 pagesMain FinalAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Narrative Final 1Document3 pagesNarrative Final 1Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Contrast EssayDocument1 pageComparison and Contrast EssayAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Contrast EssayDocument2 pagesComparison and Contrast EssayAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- UCSPDocument2 pagesUCSPAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Level of Job Satisfaction Among Registered Nurses - Chapter 1Document4 pagesLevel of Job Satisfaction Among Registered Nurses - Chapter 1Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report Format 1Document1 pageNarrative Report Format 1Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- RRL and RRS (Group 5)Document3 pagesRRL and RRS (Group 5)Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Mental Health AwarenessDocument1 pageMental Health AwarenessAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Group-5Document4 pagesChapter 2-Group-5Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Goodafternoon To All of You!! Thank You For Having Me Today. Shall We Start Sir?Document3 pagesGoodafternoon To All of You!! Thank You For Having Me Today. Shall We Start Sir?Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Transportation Crisis Causing Traffic Problems: Ajeay M. Pamintuan 12-SocratesDocument2 pagesTransportation Crisis Causing Traffic Problems: Ajeay M. Pamintuan 12-SocratesAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Resume Work ImmersionDocument1 pageResume Work ImmersionAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- ANXIETY (Informative Speech) COM 165.Mp3Document2 pagesANXIETY (Informative Speech) COM 165.Mp3Ajeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Podcast ScriptDocument3 pagesPodcast ScriptAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Gas FluctuationDocument11 pagesGas FluctuationAjeay PamintuanNo ratings yet
- (Application Transfer Manual Volume: Be The CadreDocument2 pages(Application Transfer Manual Volume: Be The CadreVishnu MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Techniques of A PN Junction DiodeDocument5 pagesFabrication Techniques of A PN Junction DiodeNida Amber100% (3)
- The Normal DistributionDocument9 pagesThe Normal DistributionElfren BulongNo ratings yet
- 3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)Document6 pages3 - RA-Erecting and Dismantling of Scaffolds (WAH) (Recovered)hsem Al EimaraNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument4 pagesConcept Paperjanet a. silosNo ratings yet
- Internal Audit, Compliance& Ethics and Risk Management: Section 1) 1.1)Document6 pagesInternal Audit, Compliance& Ethics and Risk Management: Section 1) 1.1)Noora Al ShehhiNo ratings yet
- BagbagtoDocument3 pagesBagbagtoJayson Valentin EscobarNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 1st Quarter Poetry Writing WorkshopDocument3 pagesPerformance Task 1st Quarter Poetry Writing WorkshopNicole john ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Sacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsDocument13 pagesSacramento County Compensation Survey Board of SupervisorsCBS13No ratings yet
- Box Transport MechanismDocument36 pagesBox Transport MechanismInzi Gardezi81% (16)
- Monorail Hoist SystemDocument17 pagesMonorail Hoist SystemypatelsNo ratings yet
- GlobalisationDocument8 pagesGlobalisationdummy12345No ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailDocument5 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Mobile No: +917019900128 E-MailJay MNo ratings yet
- 2020 ESIA Guideline Edited AaDocument102 pages2020 ESIA Guideline Edited AaAbeje Zewdie100% (1)
- BVP651 Led530-4s 830 Psu DX10 Alu SRG10 PDFDocument3 pagesBVP651 Led530-4s 830 Psu DX10 Alu SRG10 PDFRiska Putri AmirNo ratings yet
- 1778 3557 1 SM PDFDocument4 pages1778 3557 1 SM PDFjulio simanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Cutting Conics AsDocument3 pagesCutting Conics Asbabe09No ratings yet
- UX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlineDocument7 pagesUX-driven Heuristics For Every Designer: OutlinemuhammadsabirinhadisNo ratings yet
- Determination of Iron in Water - SpectrophotometryDocument4 pagesDetermination of Iron in Water - Spectrophotometryhanif ahmadNo ratings yet
- ASWP Manual - Section 1 - IntroductionDocument17 pagesASWP Manual - Section 1 - Introductionjmvm56No ratings yet
- Productstock 2021-01-18 (Produk Laku & Belum KinwatchDocument32 pagesProductstock 2021-01-18 (Produk Laku & Belum KinwatchKin WatchNo ratings yet
- AAR Safety Fact SheetDocument2 pagesAAR Safety Fact Sheetrogelio mezaNo ratings yet
- DrosteDocument4 pagesDrosteapi-478100074No ratings yet
- Application of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignDocument7 pagesApplication of Geosynthetics in Pavement DesignAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rNo ratings yet
- Microtech Testing & Research Laboratory: Condition of Sample, When Received: SatisfactoryDocument1 pageMicrotech Testing & Research Laboratory: Condition of Sample, When Received: SatisfactoryKumar AbhishekNo ratings yet
- Lazard Levelized Cost of Storage v20Document46 pagesLazard Levelized Cost of Storage v20macNo ratings yet
- CH 11 International TradeDocument20 pagesCH 11 International TradeSANTU GHORAINo ratings yet
- Imamsha Maharaj Na Parcha NewDocument16 pagesImamsha Maharaj Na Parcha NewNARESH R.PATELNo ratings yet