Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled Document 3
Uploaded by
tiffany0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
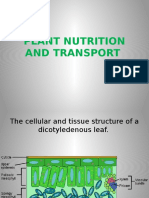
7 views1 pageTranspiration is the process by which water evaporates from the stomata of leaves and diffuses into the atmosphere, creating a transpiration pull that draws water up from the roots through the xylem. Leaves are adapted for transpiration through thin blades that shorten diffusion distance, more stomata on the lower epidermis, and a cuticle that prevents excessive water loss. Roots absorb water and minerals through osmosis and active transport, lowering their water potential and drawing water in through osmotic pressure. Roots are adapted for water absorption with many root hairs that increase surface area, a highly branched structure, and lack of a cuticle.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled document 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTranspiration is the process by which water evaporates from the stomata of leaves and diffuses into the atmosphere, creating a transpiration pull that draws water up from the roots through the xylem. Leaves are adapted for transpiration through thin blades that shorten diffusion distance, more stomata on the lower epidermis, and a cuticle that prevents excessive water loss. Roots absorb water and minerals through osmosis and active transport, lowering their water potential and drawing water in through osmotic pressure. Roots are adapted for water absorption with many root hairs that increase surface area, a highly branched structure, and lack of a cuticle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageUntitled Document 3
Uploaded by
tiffanyTranspiration is the process by which water evaporates from the stomata of leaves and diffuses into the atmosphere, creating a transpiration pull that draws water up from the roots through the xylem. Leaves are adapted for transpiration through thin blades that shorten diffusion distance, more stomata on the lower epidermis, and a cuticle that prevents excessive water loss. Roots absorb water and minerals through osmosis and active transport, lowering their water potential and drawing water in through osmotic pressure. Roots are adapted for water absorption with many root hairs that increase surface area, a highly branched structure, and lack of a cuticle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
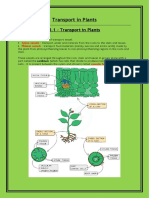
Transpiration : water from the water film on the cells near the stomata evaporates and
diffuses down the concentration gradient to the atmosphere
Transpiration pull : water moves out of the cells near the stomata to replenish water lost from
the water film in transpiration so the water potential of these cells decreases . Water then
moves into these cells by osmosis from the neighbouring cells . This creates a water
potential gradient across a layer of cells until it reaches the cells near the xylem . Water is
then drawn directly from the xylem to replenish the water lost from the leaf cells .
Adaptive features for transpiration :
1. Thin leaf blade : shorten diffusion distance
2. More stomata on the lower epidermis + little on the upper epidermis : prevent
excessive water loss by transpiration
3. Cuticle on the epidermis : prevent water loss
Water absorption through roots
1. The roots absorb minerals from the soil water by diffusion + active transport——>
lowers water potential of the root cells
2. Water moves into the root cells by osmosis through the cell and vacuole
membranes / diffusion through diffusion
Adaptive features of the root
1. Many fine root hairs —> increase surface area for water absorption + contact area
between the soil particles
2. Highly branched roots —-> increases surface area for water absorption
3. Roots are not covered by cuticle ——> allows water and minerals to pass through
easily
Apical meristem / vascular cambium : cells that actively undergo mitotic cell division ——>
for growth and repair
——> found at the root tips +in vascular bundles
You might also like
- 8.0 Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages8.0 Transport in Plantskhenso sitholeNo ratings yet
- The Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDocument40 pagesThe Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDeanne Saz100% (1)
- 06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Document24 pages06 Plant Transport Biology Notes IGCSE 2014Saurabh ShivakumarNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants HandoutDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants HandoutAsawni McDowellNo ratings yet
- Hydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeFrom EverandHydroponic Gardening: A Beginner Guide to Learn How to Design and Build Your Own Sustainable Hydroponics System, for Growing Plants and Vegetables at HomeNo ratings yet
- Core CH 10 TranspirationDocument12 pagesCore CH 10 TranspirationommpNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument34 pagesTransport in PlantsYagna LallNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - The Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsDocument32 pagesTopic 5 - The Uptake and Transport of Water and MineralsAshley BedassieNo ratings yet
- 5090 - Topic6 - Bio - Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument32 pages5090 - Topic6 - Bio - Transport in Flowering PlantsMaryam ShahidNo ratings yet
- Transport in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesTransport in Flowering PlantsChic BoosterNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in PlantstiffanyNo ratings yet
- 8.1 - Transport in PlantsDocument9 pages8.1 - Transport in PlantsAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- Resource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants: Campbell and ReeceDocument94 pagesResource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants: Campbell and ReeceJezterE.BalladosItsujiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Transport in PlantDocument15 pagesUnit 2 - Transport in PlantAbdelrahman GhanimNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants: The Vascular BundleDocument3 pagesTransport in Plants: The Vascular BundleAvyay TopraniNo ratings yet
- CH10 Transpiration, Transport and Support in PlantsDocument38 pagesCH10 Transpiration, Transport and Support in PlantsKwok JackieNo ratings yet
- KLB Biology F3 NoteDocument49 pagesKLB Biology F3 NoteSocdal Abdi100% (1)
- Absorption of WaterDocument43 pagesAbsorption of WaterOGAANSHO TUBENo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants Part 1Document12 pagesTransport in Plants Part 1Andre MorrisonNo ratings yet
- A, Level Transport by MR Li - 1Document107 pagesA, Level Transport by MR Li - 1asadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Transport in Multicellular Plants: SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 10: Transport in Multicellular Plants: SummaryMerimaNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Water Absorption: Lecture - 3Document32 pagesMechanism of Water Absorption: Lecture - 3Santhosh SanthoshNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Transport System in PlantsDocument18 pagesForm 3 Transport System in PlantsachikgaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Term 2 Support and Transport Systems in Plants 5Document22 pagesGrade 10 Term 2 Support and Transport Systems in Plants 5Abdulah.AbisolaNo ratings yet
- CHP .5.2Document2 pagesCHP .5.2laracassar22No ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantsDocument31 pagesTransportation in PlantssamskruthamanabroluNo ratings yet
- ch7 NotesDocument6 pagesch7 Notesisabella cucumberNo ratings yet
- Absorption of WaterDocument17 pagesAbsorption of WaterMuqadas Zahra lNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument24 pagesTransport in PlantsAreebNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDocument49 pagesBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsPeter Osundwa Kiteki100% (3)
- Biology Form 2 NotesDocument80 pagesBiology Form 2 NotesLutern RayNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition and TransportDocument41 pagesPlant Nutrition and TransportKomalesh TheeranNo ratings yet
- Independent Notes Plant TransportDocument3 pagesIndependent Notes Plant TransportIqbal WahyuNo ratings yet
- Absorption by Roots - Summary NotesDocument5 pagesAbsorption by Roots - Summary NotesSanjayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - Transport in PlantsDocument8 pagesLecture 12 - Transport in PlantsAmmar RizwanNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecDocument24 pagesTRANSPORT IN PLANTS Updated ZimsecnatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- Topic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqDocument6 pagesTopic:: Submitted To: Prof. Hina TariqZubair BalouchNo ratings yet
- 3 Transport in Plants Bio NotesDocument8 pages3 Transport in Plants Bio NotesContactkeaneNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument20 pagesTransport in PlantsForthtNo ratings yet
- Identify Root Hair Cells, As Seen Under The Light Microscope, and Describe Their FunctionsDocument16 pagesIdentify Root Hair Cells, As Seen Under The Light Microscope, and Describe Their FunctionsMandla RebirthNo ratings yet
- How Minerals Are Transported in PlantsDocument2 pagesHow Minerals Are Transported in PlantsMariam KidwaiNo ratings yet
- مذكرة بيولوجي للصف الثاني الاعدادي الترم الاولDocument116 pagesمذكرة بيولوجي للصف الثاني الاعدادي الترم الاولLolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document3 pagesChapter 11Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- Absorption by Roots - The Processes InvolvedDocument6 pagesAbsorption by Roots - The Processes InvolvedRahulNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants and Transpiration NotesDocument7 pagesTransport in Plants and Transpiration NotesAshleigh JarrettNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in PlantsKekeletsoNo ratings yet
- 13.7 Movement of Water Through RootsDocument31 pages13.7 Movement of Water Through RootsgereseNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants 2Document7 pagesTransport in Plants 2Pankaj PatelNo ratings yet
- Transport System in PlantDocument16 pagesTransport System in PlantAbu-Omar50% (4)
- Transport in Plant SDADocument5 pagesTransport in Plant SDAkmakabe78No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Topic 8 Transport in Plants PresentationDocument28 pagesIGCSE Biology Topic 8 Transport in Plants PresentationhannahhishamNo ratings yet
- Transport Xylem and Phloem 2015 PDFDocument46 pagesTransport Xylem and Phloem 2015 PDFjuanNo ratings yet
- Y10 Plant Transport Lesson 1Document27 pagesY10 Plant Transport Lesson 1Sherry LeeNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument15 pagesTransport in PlantsUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- Transport in Flowering Plants Final VersionDocument9 pagesTransport in Flowering Plants Final VersionJohn MoyoNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument7 pagesTransport in PlantsMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- Factores Affecting The Rate of TranspirationDocument77 pagesFactores Affecting The Rate of TranspirationtasawerNo ratings yet
- Topic 9Document7 pagesTopic 9Talia Elan VickeryNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Untitled Document 4Document1 pageUntitled Document 4tiffanyNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument1 pageUntitled DocumenttiffanyNo ratings yet
- Comp 6 (Brainstorming)Document2 pagesComp 6 (Brainstorming)tiffanyNo ratings yet
- Production Economics NotesDocument2 pagesProduction Economics NotestiffanyNo ratings yet
- Compositions (Argumentative Essay)Document1 pageCompositions (Argumentative Essay)tiffanyNo ratings yet
- Vocab Ex 2Document2 pagesVocab Ex 2tiffanyNo ratings yet
- Transport in HumansDocument3 pagesTransport in HumanstiffanyNo ratings yet
- Function of MoneyDocument1 pageFunction of MoneytiffanyNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumenttiffanyNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument2 pagesReproduction in PlantstiffanyNo ratings yet
- LS ConceptsDocument4 pagesLS ConceptstiffanyNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 05-13-2020 08.35.46Document2 pagesCamScanner 05-13-2020 08.35.46tiffanyNo ratings yet
- DSE Revision-S4 Term2aDocument15 pagesDSE Revision-S4 Term2atiffanyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Revision NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry Revision NotestiffanyNo ratings yet
- Econ MC Answers (By Topics)Document7 pagesEcon MC Answers (By Topics)tiffanyNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesTransport in PlantstiffanyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Self-Learning Unit3 2Document41 pagesChemistry Self-Learning Unit3 2tiffanyNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem (Measurement of Biodiversity)Document2 pagesEcosystem (Measurement of Biodiversity)tiffanyNo ratings yet
- MacroeconomicsDocument206 pagesMacroeconomicstiffanyNo ratings yet