Professional Documents
Culture Documents
(MCQ) - Coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
padmaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
(MCQ) - Coordinate Geometry
Uploaded by
padmaCopyright:
Available Formats
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
The essence of mathematics is not to make simple things complicated,
but to make complicated things simple.
By O.P. GUPTA Math Mentor
INDIRA AWARD WINNER
For detailed solutions, check YouTube Channel.
YouTube.com/MathematiciaByOPGupta
Multiple Choice Questions, with only one correct option.
Q01. P is a point on x-axis at a distance of 3 units from y-axis to its left. The coordinates of P are:
(a) (3, 0) (b) (0, 3) (c) (–3, 0) (d) (0, –3)
x y
Q02. The coordinates of the point where the line 7 intersects y-axis are:
a b
(a) (a, 0) (b) (0, b) (c) (0, 7b) (d) (7a, 0)
Q03. The area of the triangle OAB, the coordinates of the points A(4, 0), B(0, –7) and O is origin, is:
(a) 11 sq.units (b) 18 sq.units (c) 28 sq.units (d) None of these
x y
Q04. The line 1 intersects the axes at P and Q, the coordinates of the midpoint of PQ are:
2 4
(a) (1, 2) (b) (2, 0) (c) (0, 4) (d) (2, 1)
Q05. The distance between the lines 2x 4 0 and x 5 0 , is:
(a) 9 units (b) 1 unit (c) 5 units (d) 7 units
Q06. The distance between the points 5cos 35o , 0 and 0, 5 cos 55o is:
(a) 10 units (b) 1 unit (c) 5 units (d) 2 units
Q07. If ‘a’ is any positive integer such that the distance between the points P(a, 2) and Q(3, –6) is 10
units, then the value of ‘a’ is:
(a) –3 (b) 6 (c) 9 (d) 3
Q08. The perimeter of triangle formed by the points (0, 0), (2, 0) and (0, 2) is:
(a) 4 units (b) 6 units (c) 6 2 units (d) 4 2 2 units
Q09. The points (1, 2), (–5, 6) and (a, –2) are collinear only if a ______.
(a) –3 (b) 7 (c) 2 (d) 5
Q10. The two points of line segment are (a, b) and (–a, –b), then the length of the line is:
2 2
(a) a 2 b 2 (b) 2 a 2 b 2 (c) a b2 (d) None of these
3
Q11. If the points (a, 0), (0, b) and (1, 1) are collinear, then:
(a) a 2 b 2 ab (b) a b ab (c) a b a 2 b 2 (d) a 2 b 2 0
Q12. The point on the x-axis which is equidistant from (2, –5) and (–2, 9) is:
(a) (–7, 0) (b) (–5, 0) (c) (–6, 0) (d) (–7, 1)
MATHEMATICIA By O.P. GUPTA : MCQ in Mathematics (Class 10) 1
MATHEMATICIA for Class 10 By O.P. GUPTA (INDIRA Award Winner)
Q13. The coordinate of a general point on x-axis is of the form:
(a) (x, 0) (b) (0, x) (c) (x, y) (d) None of these
Q14. If the points A(6, 1), B(8, 2), C(9, 4) and D(p, 3) are vertices of a parallelogram, taken in order,
then the value of p is:
(a) 7 (b) 9 (c) 5 (d) 8
Q15. In what ratio is the segment joining the points A(6, 3) and B(–2, –5) divided by the x-axis?
(a) 3:2 (b) 3:5 (c) 2:3 (d) 2:5
Q16. The distance between the points (3, 7) and (8, 9) is:
(a) 11 units (b) 12 units (c) 29 units (d) Can’t be found
Q17. The distance between ( tan , 0) and (0, 1) is:
(a) sec 2 (b) cot 2 (c) sec (d) cot
Q18. The ratio in which the line joining the points (5, 3) and (–1, 6) is divided by y-axis is:
(a) 5:3 (b) 2:3 (c) 4:5 (d) 5:1
Q19. The centroid of a triangle with two vertices (3, –10), (–1, –9) is (2, –4). The coordinates of the
third vertex are:
(a) (–4, –7) (b) (4, –7) (c) (4, 7) (d) (7, 4)
Q20. The distance of the point (2, 3) from the x-axis is:
(a) 2 units (b) 3 units (c) 4 units (d) 5 units
Q21. The distance of (–6, 8) from the origin is:
(a) 8 units (b) 27 units (c) 10 units (d) 6 units
Q22. AOBC is a rectangle whose three vertices are A(0, 3), O(0, 0) and B(5, 0). Square of the length of
its diagonal is:
(a) 5 (b) 3 (c) 34 (d) 4
Q23. The perimeter of a triangle with vertices (0, 4), (0, 0) and (3, 0) is:
(a) 5 units (b) 12 units (c) 11 units (d) 10 units
Q24. The points (–4, 0), (4, 0) and (0, 3) are the vertices of a:
(a) Right triangle (b) Isosceles triangle
(c) Equilateral triangle (d) Scalene triangle
Q25. Which of the following is a point on x-axis?
(a) (1, 0) (b) (0, 1) (c) (–1, 1) (d) (1, 1)
Q26. If the points (1, x), (5, 2) and (9, 5) are collinear, then value of x is:
5 5
(a) (b) (c) –1 (d) 1
2 2
Q27. The end points of diameter of circle are (2, 4) and (–3, –1). Its radius is:
5 2 5 2
(a) units (b) 5 2 units (c) 3 2 units (d) units
2 2
Q28. The ratio in which x-axis divides the line segment joining the points (5, 4) and (2, –3) is:
(a) 5:2 (b) 3:4 (c) 2:5 (d) 4:3
Q29. The point which divides the line segment joining the points (7, –6) and (3, 4) in ratio 1:2
internally lies in the:
(a) I quadrant (b) II quadrant (c) III quadrant (d) IV quadrant
2 MATHEMATICIA By O.P. GUPTA : MCQ in Mathematics (Class 10)
For all the Math-Gyan, visit at THEOPGUPTA.COM WhatsApp @ +919650350480
Q30. The point which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the line joining the points (–2, –5) and (2, 5)
is given by:
(a) (0, 0) (b) (0, 2) (c) (2, 0) (d) (–2, 0)
Q31. The fourth vertex D of a parallelogram ABCD whose three vertices are A(–2, 3), B(6, 7) and C(8,
3) is:
(a) (0, 1) (b) (0, –1) (c) (–1, 0) (d) (1, 0)
Q32. If the point P(6, 3) divides the line joining A(4, 2) and B(8, 4), then:
1 1
(a) AP AB (b) AP PB (c) PB AB (d) AP AB
3 3
Q33. What type of triangle do the points (3, 2), (–2, –3) and (2, 3) form?
(a) right triangle (b) equilateral triangle (c) isosceles triangle (d) None of these
Q34. The values of y for which the distance between the points P(2, –3) and Q(10, y) is 10 units, is:
(a) –9, 5 (b) –9, 3 (c) –9, 2 (d) –9, 6
Q35. The area of the triangle whose vertices are (1, –1), (–4, 6) and (–3, –5), is
(a) 26 sq.units (b) 34 sq.units (c) 24 sq.units (d) 28 sq.units
Q36. In which quadrant does the point (2, –5) lie?
(a) 1st (b) 2nd (c) 3rd (d) 4th
Q37. The distance between the points A(b, 0) and B(0, a) is:
(a) a 2 b2 (b) a 2 b 2 (c) ab (d) ab
Q38. Two of the vertices of a ABC are A(–1, 4) and B(5, 2) and its centroid is (0, –3).
The coordinates of the vertex C are:
(a) (4, 3) (b) (4, 15) (c) (–4, –15) (d) (–15, –4)
Q39. The equation of a line parallel to x-axis at a distance of 5 units below x-axis is:
(a) x 5 (b) x 5 (c) y 5 (d) y 5x
Q40. Three villages A, B and C are situated in such a way that they form a scalene triangle on flat land
(see the figure below). A well needs to be constructed on the same flat land in such a way that it is
equidistant from the three villages.
The well should be built at:
(a) the incentre of ABC (b) the centroid of ABC
(c) the circumcentre of ABC (d) the orthocenter of ABC
MATHEMATICIA By O.P. GUPTA : MCQ in Mathematics (Class 10) 3
MATHEMATICIA for Class 10 By O.P. GUPTA (INDIRA Award Winner)
ANSWERS KEY
Q01. c Q02. c Q03. d Q04. a Q05. d Q06. c Q07. c
Q08. d Q09. b Q10. b Q11. b Q12. a Q13. a Q14. a
Q15. b Q16. c Q17. c Q18. d Q19. c Q20. b Q21. c
Q22. c Q23. b Q24. b Q25. a Q26. c Q27. a Q28. d
Q29. d Q30. a Q31. b Q32. b Q33. a Q34. b Q35. c
Q36. d Q37. a Q38. c Q39. c Q40. c
# Dear math scholars,
We have taken utmost care while preparing this draft. Still chances of human error can’t be ruled out.
Please inform us about any Typing error / mistake in this document.
This will help many future learners of Mathematics.
Email ID - iMathematicia@gmail.com
WhatsApp @ +91 9650350480 (only message)
O.P. GUPTA, Math Mentor
[Maths (Hons.), E & C Engg., Indira Award Winner]
Follow us on Twitter @theopgupta
Follow us on Instagram @theopgupta
Official Website : www.theOPGupta.com
YouTube.com/MathematiciaByOPGupta
Buy our Books, Test Papers and Sample Papers at theopgupta.com
4 MATHEMATICIA By O.P. GUPTA : MCQ in Mathematics (Class 10)
You might also like
- Coordinate Geometry MCQDocument8 pagesCoordinate Geometry MCQVVS. G.S1074No ratings yet
- Determinants QnsDocument11 pagesDeterminants QnsLokesh Kumar100% (3)
- Mathematics Quadratic Equation MCQDocument7 pagesMathematics Quadratic Equation MCQSoniyaKanwalGNo ratings yet
- COIMBATORE SAHODAYA SCHOOLS COMPLEX & MADURAI SAHODAYA SCHOOLS COMPLEX AISSE/AISSCE COMMON MOCK EXAMDocument8 pagesCOIMBATORE SAHODAYA SCHOOLS COMPLEX & MADURAI SAHODAYA SCHOOLS COMPLEX AISSE/AISSCE COMMON MOCK EXAMXB 02 Gurusaran.VNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 6 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 6 For Board Exam 2024ydprince111No ratings yet
- Mathematic Question Paper Set ADocument4 pagesMathematic Question Paper Set AADITHYA SUJINo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry QnsDocument8 pages3D Geometry QnsLokesh Kumar100% (4)
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 14 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument15 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 14 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersndhrtdNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper-6 With SolutionDocument15 pagesSample Paper-6 With Solutionshubham AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Math Preboards BangaloreDocument6 pagesMath Preboards Bangalorekarun.senthil.kumar.25No ratings yet
- Circle and Straight Line PDFDocument16 pagesCircle and Straight Line PDFprateek amrawanshiNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines Assignment from Bal Bharti Public SchoolDocument2 pagesStraight Lines Assignment from Bal Bharti Public SchoolJEE enius PrepNo ratings yet
- Polynomials MCQDocument6 pagesPolynomials MCQDeebha Anil100% (1)
- Trigonometry - Grade X - MCQDocument3 pagesTrigonometry - Grade X - MCQHadi Zakariya0% (1)
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024suiiironaldo255No ratings yet
- 10th Probability Test Paper-1Document1 page10th Probability Test Paper-1yeatesh009No ratings yet
- M15 Probability 2Document4 pagesM15 Probability 2Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- MATRICES & Determinants HOME WORKDocument25 pagesMATRICES & Determinants HOME WORKSk mNo ratings yet
- Final Maths Q P SET 3Document8 pagesFinal Maths Q P SET 3Tanish MehtaNo ratings yet
- Relation between determinants, matrices, and system of equationsDocument10 pagesRelation between determinants, matrices, and system of equationsLakshmi100% (1)
- CLASS-X (MATH) Standard Paper QuestionsDocument4 pagesCLASS-X (MATH) Standard Paper QuestionsAnkurNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023Priyanshu KasanaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Denji KunNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Test 10 Maths SolutionsDocument6 pagesSample Paper Test 10 Maths SolutionsKashvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Sample paper test 01 for board exam (2022-23Document6 pagesSample paper test 01 for board exam (2022-23K Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- DPP-TEST MATH Determinant and Linear EquationsDocument5 pagesDPP-TEST MATH Determinant and Linear EquationsYash PatilNo ratings yet
- Solving Math Problems Rapidly With Practice QuestionsDocument17 pagesSolving Math Problems Rapidly With Practice QuestionsChinmay SwainNo ratings yet
- Theory of Equations DPP-1Document6 pagesTheory of Equations DPP-1SaήjaγKsNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024ravindramaithul124421No ratings yet
- Maths Sample Question Paper AnalysisDocument10 pagesMaths Sample Question Paper AnalysisAsad farukiNo ratings yet
- 10 Math Eng PP 2023 24 2Document7 pages10 Math Eng PP 2023 24 2aniketyadav122311No ratings yet
- VectorsDocument88 pagesVectorsHimanshu Gupta100% (1)
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument17 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersPriyanshu KasanaNo ratings yet
- X Maths KS Sample PaperDocument6 pagesX Maths KS Sample PaperMukul SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths Sample Question Paper Class IxDocument17 pagesMaths Sample Question Paper Class Ixshahreenimaad123100% (3)
- Worksheet On Wavy Curve MethodDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Wavy Curve MethodAvinandan DuttaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2020 Set 65-1-1Document12 pagesCBSE Class 12 Maths Question Paper Solution 2020 Set 65-1-1SA EED100% (1)
- Maths-Class-X - Paper - 6Document6 pagesMaths-Class-X - Paper - 6Prabha sharmaNo ratings yet
- 9th Math CH Triangle Test PaperDocument1 page9th Math CH Triangle Test PaperJanardan SunilNo ratings yet
- Standard Sample Paper XyzDocument7 pagesStandard Sample Paper XyzMaurya Sachin100% (1)
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 04 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument15 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 04 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersMohanalakshmi ManoharNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 AnswersDocument16 pagesClass Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023 Answersshubham Awasthi100% (1)
- Xii - Mock Test - 1Document6 pagesXii - Mock Test - 1Kartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ARGON-SAMPLE-PAPER 10th PDFDocument22 pagesARGON-SAMPLE-PAPER 10th PDFsapna kain100% (1)
- 10 Maths PB (23.1.23) Standard FinalDocument8 pages10 Maths PB (23.1.23) Standard Finalpick assNo ratings yet
- Maths-Class-X - Paper - 3 PDFDocument7 pagesMaths-Class-X - Paper - 3 PDFPrabha sharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Triangles Important Questions 2023-24Document49 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Triangles Important Questions 2023-24rajNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 ObjectiveDocument4 pagesUnit 1 ObjectiveTharun konda100% (1)
- Bansal Bulls Eye Test PaperDocument19 pagesBansal Bulls Eye Test PaperDevesh AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Basic Inequalities: Time: 90 Mins Part-ADocument2 pagesMathematics Basic Inequalities: Time: 90 Mins Part-AAshwani Kumar Singh100% (2)
- Maths Term 1 - QPs 1,2,3Document12 pagesMaths Term 1 - QPs 1,2,3subhaseduNo ratings yet
- Straight Lines QnsDocument8 pagesStraight Lines QnsLokesh Kumar100% (3)
- Maths Class Xi Sample Paper Test 03 For Annual Exam 2022 23Document5 pagesMaths Class Xi Sample Paper Test 03 For Annual Exam 2022 23RudraNo ratings yet
- Apex Entrance Exam Test PaperDocument12 pagesApex Entrance Exam Test PaperApex Institute100% (1)
- Maths (Standard) Class - X - SET-1 (English Version)Document7 pagesMaths (Standard) Class - X - SET-1 (English Version)shanmugan rajNo ratings yet
- KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI SAMPLE PAPER TEST 11 FOR BOARD EXAM 2023 MATHEMATICSDocument6 pagesKENDRIYA VIDYALAYA GACHIBOWLI SAMPLE PAPER TEST 11 FOR BOARD EXAM 2023 MATHEMATICSShivam RajNo ratings yet
- Maths MCQDocument16 pagesMaths MCQmadhuNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Question Bank 109 122Document14 pagesMaths Class X Question Bank 109 122DARKLORDNo ratings yet
- 10th - Coordinate Geometry PDFDocument5 pages10th - Coordinate Geometry PDFhaloNo ratings yet
- Linear-Quadratic_SystemsDocument11 pagesLinear-Quadratic_SystemspadmaNo ratings yet
- Dividing rational expressionsDocument2 pagesDividing rational expressionspadmaNo ratings yet
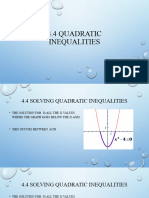
- 4.4_Solving_Qudratic_InequalitiesDocument7 pages4.4_Solving_Qudratic_InequalitiespadmaNo ratings yet
- Factors 1Document2 pagesFactors 1padmaNo ratings yet
- Graphing_Polynomial_FunctionsDocument16 pagesGraphing_Polynomial_FunctionspadmaNo ratings yet
- Composite functionsDocument7 pagesComposite functionspadmaNo ratings yet
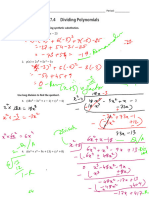
- 7.4_Factor TheoremDocument2 pages7.4_Factor TheorempadmaNo ratings yet
- Factors 1Document2 pagesFactors 1padmaNo ratings yet
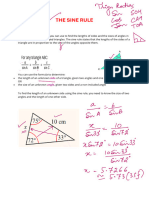
- THE SINE RULEDocument3 pagesTHE SINE RULEpadmaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TrigonometryDocument6 pagesIntroduction To TrigonometrySaumyaNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Maths Paper Solving StrategyDocument2 pagesClass 10 Maths Paper Solving StrategypadmaNo ratings yet
- (MCQ) - Applications of Trigo.Document4 pages(MCQ) - Applications of Trigo.padmaNo ratings yet
- CirclesDocument3 pagesCirclespadmaNo ratings yet
- MCQ TrianglesDocument6 pagesMCQ TrianglesSharulathaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument5 pagesQuadratic EquationsGIRIDHARAN MURUGANNo ratings yet
- Polinomlar 6Document6 pagesPolinomlar 6emrecan yıldırımNo ratings yet
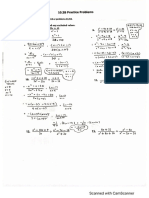
- Solution of Practice Paper 2Document20 pagesSolution of Practice Paper 2padmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 6Document10 pagesPractice Paper 6padmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 1 PDFDocument11 pagesPractice Paper 1 PDFpadmaNo ratings yet
- Science Practice Paper SolutionsDocument11 pagesScience Practice Paper SolutionspadmaNo ratings yet
- 45 Days Plan PDFDocument18 pages45 Days Plan PDFpadmaNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 5Document12 pagesPractice Paper 5padmaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE in MATH 9 QUADRILATERAL and SIMILARITY 2022 2023Document73 pagesLECTURE in MATH 9 QUADRILATERAL and SIMILARITY 2022 2023Vittorio ApidosNo ratings yet
- Week 20 MAT C Cycle Test-1Document8 pagesWeek 20 MAT C Cycle Test-1hansdermann269No ratings yet
- Dr. Srikanth Pai Inmo Training Camp 2023 KarDocument19 pagesDr. Srikanth Pai Inmo Training Camp 2023 KarHimansu MookherjeeNo ratings yet
- Q3 Math 8 Module 3Document19 pagesQ3 Math 8 Module 3Joris Jandayan100% (1)
- 05 - Properties and Solution of TrianglesDocument8 pages05 - Properties and Solution of TrianglesRekha BhasinNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry H D Sot MR Statistics Relation 1590398170Document28 pagesTrigonometry H D Sot MR Statistics Relation 1590398170Jijo SagaiNo ratings yet
- Area of TriangleDocument21 pagesArea of TriangleAdarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Mat435 Chapter 1 Trigonometric IntegralsDocument6 pagesMat435 Chapter 1 Trigonometric IntegralsNabil MahadzirNo ratings yet
- Methods of Trigonometry by J E HebbornDocument45 pagesMethods of Trigonometry by J E HebbornTenson Chikumba100% (1)
- Trigonometry Assignment 4Document5 pagesTrigonometry Assignment 4Ayush PatwardhanNo ratings yet
- MT144 Problems and FormulasDocument20 pagesMT144 Problems and FormulasJoshua Guerrero CaloyongNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument16 pagesTrigonometrystella vellandaNo ratings yet
- Triangle roof applications and geometryDocument18 pagesTriangle roof applications and geometrymica valerioNo ratings yet
- Class Ix Revision Worksheet Subject: Mathematics Topic: Congruency of TrianglesDocument4 pagesClass Ix Revision Worksheet Subject: Mathematics Topic: Congruency of TrianglesMr TacoNo ratings yet
- Trig Chapter 03: Angles, Ratios & IdentitiesDocument46 pagesTrig Chapter 03: Angles, Ratios & IdentitiesReemmoq 12No ratings yet
- GRE Geometry - by Greenlight Test PrepDocument193 pagesGRE Geometry - by Greenlight Test PrepRamuNo ratings yet
- Sam4b Tab4bDocument6 pagesSam4b Tab4bBeloved DhinaNo ratings yet
- 2 Complex Numbers Part 2 of 3Document5 pages2 Complex Numbers Part 2 of 3Sandeep ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Unit CircleDocument7 pagesUnit CircleAileen OrbinaNo ratings yet
- 10 Maths Chapter 11Document6 pages10 Maths Chapter 11Santhosh Kavya Santhu JeevaNo ratings yet
- Review - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringDocument11 pagesReview - Mathematics, Surveying and Transportation EngineeringPaulyne TuganoNo ratings yet
- SSC CHSL Tier 1 (Quantitative Aptitude) Feb 7, 2016Document7 pagesSSC CHSL Tier 1 (Quantitative Aptitude) Feb 7, 2016hareesh babuNo ratings yet
- 8 Unit7Document45 pages8 Unit7HEXAGON ProductionNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 5.1A: Area of A Triangle 2 1Document41 pagesWorksheet 5.1A: Area of A Triangle 2 1g8f27w5ywgNo ratings yet
- Straight Line and CircleDocument32 pagesStraight Line and CircleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning PlanDocument8 pagesWeekly Learning PlanBrendaNo ratings yet
- Circle ExerciseDocument58 pagesCircle Exerciselakshit singhalNo ratings yet
- Introduction to TrianglesDocument16 pagesIntroduction to TrianglesShruti PatelNo ratings yet
- Geomtery II AssignmentDocument20 pagesGeomtery II AssignmentHimanshu Chahar100% (1)
- Constructions PDFDocument6 pagesConstructions PDFRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Fluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldFrom EverandFluent in 3 Months: How Anyone at Any Age Can Learn to Speak Any Language from Anywhere in the WorldRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (79)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet