Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exam 56
Uploaded by
Arthur LeywinOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exam 56
Uploaded by
Arthur LeywinCopyright:
Available Formats
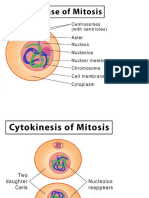
Prophase is the first stage in mitosis, occurring after the conclusion of the G2
portion of interphase. During prophase, the parent cell chromosomes � which were
duplicated during S phase � condense and become thousands of times more compact
than they were during interphase
When prophase is complete, the cell enters prometaphase � the second stage of
mitosis. During prometaphase, phosphorylation of nuclear lamins by M-CDK causes the
nuclear membrane to break down into numerous small vesicles. As a result, the
spindle microtubules now have direct access to the genetic material of the cell.
As prometaphase ends and metaphase begins, the chromosomes align along the cell
equator. Every chromosome has at least two microtubules extending from its
kinetochore � with at least one microtubule connected to each pole.
Metaphase leads to anaphase, during which each chromosome's sister chromatids
separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. Enzymatic breakdown of cohesin �
which linked the sister chromatids together during prophase � causes this
separation to occur.
During telophase, the chromosomes arrive at the cell poles, the mitotic spindle
disassembles, and the vesicles that contain fragments of the original nuclear
membrane assemble around the two sets of chromosomes.
You might also like
- Cell DivisionDocument52 pagesCell DivisionRamachandran Ram100% (1)
- Human Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsFrom EverandHuman Chromosomes: An Illustrated Introduction to Human CytogeneticsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mitosis Cell Division PDFDocument8 pagesMitosis Cell Division PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle NotesDocument12 pagesCell Cycle NotesMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- The Proposed Maharlika Investment Fund PDFDocument2 pagesThe Proposed Maharlika Investment Fund PDFArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Big Picture in Focus: Ulob Metalanguage: Develop Work Breakdown StructureDocument7 pagesBig Picture in Focus: Ulob Metalanguage: Develop Work Breakdown StructureArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument2 pagesCell CycleJeyah FornillosNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument3 pagesMitosisSabina MaharjanNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument3 pagesMitosisLea Mari JavierNo ratings yet
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument7 pagesMitosisRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleSTEINER 97No ratings yet
- Science Project Science 2 ch2Document2 pagesScience Project Science 2 ch2MG VedNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleMoffat KaprezzoNo ratings yet
- CytokinesisDocument15 pagesCytokinesisMar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cell DivisionDocument92 pages1.2 Cell DivisionHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Online Study GuideDocument7 pagesCH 12 Online Study Guideюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument32 pagesCell DivisionRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- InterphaseDocument9 pagesInterphaseJeazel MosendoNo ratings yet
- Burgos, John Adrian Ingco General Biology 1 STEM 12-21Document5 pagesBurgos, John Adrian Ingco General Biology 1 STEM 12-21Lorie Austria DinoNo ratings yet
- Activity 15 - Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction - Mitosis and Meiosis-PERALTADocument11 pagesActivity 15 - Cellular Metabolism and Reproduction - Mitosis and Meiosis-PERALTACogie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Folio Kerja Kursus Biology SPMDocument29 pagesFolio Kerja Kursus Biology SPMzam_ir100% (2)
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceChristian GilbertNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell Cyclewebpixel servicesNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Is The Process by Which A: Aspergillus Nidulans Saccharomyces CerevisiaeDocument7 pagesMitosis Is The Process by Which A: Aspergillus Nidulans Saccharomyces CerevisiaeLeo Paolo LuceroNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document48 pagesModule 1Saalif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Meosis 1Document12 pagesMeosis 1lyraiglesiajaneNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis and MeiosisFrances Isko FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseDocument17 pagesChapter 2: Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: A. G1 PhaseIrish GatpoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cell CycleDocument28 pagesChapter 6 Cell CyclefatimaNo ratings yet
- Degree Assignment SolutionDocument4 pagesDegree Assignment SolutionESTHER MWEEMBANo ratings yet
- Discovery: Cladophora GlomerataDocument8 pagesDiscovery: Cladophora GlomeratamuhammadismailNo ratings yet
- Emt318 Cytology Note3 2021Document10 pagesEmt318 Cytology Note3 2021Ehigie promiseNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Interphase Prophase: ChromoDocument12 pagesInterphase Prophase: ChromoNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Bio SemDocument10 pagesBio SemHenin FathimaNo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionCharlotte JalaNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesCell DivisionGenevieve GanubNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKiMii EstebanNo ratings yet
- CycleDocument7 pagesCycleAbbas TalibNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument17 pagesBiologyMuskan ShreeNo ratings yet
- Interphase: Cell Cycle Nucleus Daughter CellsDocument4 pagesInterphase: Cell Cycle Nucleus Daughter CellsKàtrįńá Jøÿ ÅgùśtïńNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle (Mitosis)Document2 pagesThe Cell Cycle (Mitosis)magdalenasilviNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - MitosisDocument3 pagesMODULE 3 - MitosisNicoleBenaguaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Mitosis Tutorial: What Is (And Is Not) Mitosis?Document2 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Mitosis Tutorial: What Is (And Is Not) Mitosis?Sharifa McLeodNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument7 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Divisionzainab.syed017No ratings yet
- 2.5 - Cell DivisionDocument5 pages2.5 - Cell DivisionAlvin JovanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 NotesibtiNo ratings yet
- Cell Div Part 2Document2 pagesCell Div Part 2Rabi SyedNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology NotesDocument21 pagesBiotechnology NotesRommel BauzaNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSISdeepaNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument111 pagesCell Cyclepreyaaa pascuaNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisDocument27 pagesCell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisAngryBird_jinx100% (1)
- C. References Stages-W-Pictures-Flash-Cards/ Levetin & Mcmahon. 2008. Plants and Society 5Document2 pagesC. References Stages-W-Pictures-Flash-Cards/ Levetin & Mcmahon. 2008. Plants and Society 5Brev CandareNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Activity 3Document5 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Activity 3Cobe Christian LascunaNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 3Document11 pagesBZ Lab 3Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Unit Presentation - 6554Document30 pagesCell Division Unit Presentation - 6554M Noaman AkbarNo ratings yet
- Agric QuizDocument3 pagesAgric QuizKelsy SalazarNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument4 pagesMitosisCyra BantilloNo ratings yet
- Science ResearchDocument3 pagesScience ResearchShaira Jea ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Poem)Document1 pagePoem)Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- What Is PowerDocument1 pageWhat Is PowerArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Philo PotaDocument1 pagePhilo PotaArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- TRTDocument1 pageTRTArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- SpeechDocument1 pageSpeechArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Work ImmersionDocument1 pageWork ImmersionArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Work 11Document1 pageWork 11Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Over The Past 30 YearsDocument1 pageOver The Past 30 YearsArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Work 18Document1 pageWork 18Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Work 12Document1 pageWork 12Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Keith Aikeen RDocument1 pageKeith Aikeen RArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- The Proposed Maharlika Investment DadwDocument2 pagesThe Proposed Maharlika Investment DadwArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Genbio Exam 2Document1 pageGenbio Exam 2Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- A Sovereign Wealth FundDocument1 pageA Sovereign Wealth FundArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Genshin Na HackDocument1 pageGenshin Na HackArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- A Sovereign Wealth Fun2Document2 pagesA Sovereign Wealth Fun2Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Keith Aikeen 1Document1 pageKeith Aikeen 1Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Learning ObjectivesDocument35 pagesLearning ObjectivesArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- ExammmmmmmmDocument1 pageExammmmmmmmArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Letter of RequestDocument1 pageLetter of RequestArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Gelo Uge 1Document4 pagesGelo Uge 1Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Gelo Uge 1Document4 pagesGelo Uge 1Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- ADJECTIVEPPTDocument22 pagesADJECTIVEPPTArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Keith Uj23Document3 pagesKeith Uj23Arthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Keith Aikeen CarinDocument3 pagesKeith Aikeen CarinArthur LeywinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Art and Nature of ArtDocument6 pagesChapter 1 - Art and Nature of ArtArthur LeywinNo ratings yet