Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Water Cycle E160
The Water Cycle E160
Uploaded by
Memo RedavicOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Water Cycle E160
The Water Cycle E160
Uploaded by
Memo RedavicCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 1
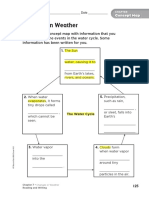
The Water Cycle
Water in the Atmosphere
Key Concept
• How does water cycle
What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide through the atmosphere?
whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before
column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After
you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements to see if you have
changed your mind.
Before Statement After
Water vapor is visible as steam.
Clouds are made of tiny drops of water or
ice crystals.
Mark the Text
Where is water on Earth? Building Vocabulary As
you read, underline the
Earth is often called the blue planet because so much of its words and phrases that you
surface is covered with water. If you look at a photo of Earth do not understand. When
taken from space, you can see that water covers much more of you finish reading, discuss
Earth than land does. Water is also in clouds, the air around these words and phrases
you, beneath your feet, and in you and other living things. with another student or
your teacher.
Water is distributed unevenly on Earth. The distribution of
Academic Vocabulary
water on Earth depends on interactions among Earth systems.
Earth itself is one large system. It is broken into smaller
distribution
(noun) the way that
subsystems, including the atmosphere, the biosphere, the
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
something is divided or
geosphere, and the hydrosphere. Water moves within the spread out
hydrosphere and into other Earth systems. Water is not just a
liquid. Sometimes it changes state and becomes solid ice or a Academic Vocabulary
gas called water vapor. As water flows or changes state, it moves interaction
(noun) the act of things
thermal energy among Earth’s systems.
coming together and having
an effect on each other
What influences why and how quickly
Scientific Vocabulary
water “disappears?” geosphere
After a morning storm, you might notice puddles on the (noun) the solid part of
sidewalk. Later that afternoon, the puddles are gone. In the Earth
same way, water in clouds seems to vanish in the air. What Scientific Vocabulary
makes water seem to disappear? hydrosphere
(noun) all water on Earth
Reading Essentials The Water Cycle 1
THIS MATERIAL IS PROVIDED FOR INDIVIDUAL EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND MAY NOT BE DOWNLOADED OR FURTHER DISTRIBUTED.
Physical Science Connection Water does not actually
disappear from a puddle or a cloud. It evaporates. Evaporation is
the process by which a liquid, such as water, changes into a gas.
Scientific Vocabulary Evaporation can occur when the Sun shines on an ocean.
absorb Water near the surface absorbs thermal energy and becomes
(verb) to take in or warmer. As a molecule of water absorbs thermal energy, it
soak up begins to vibrate faster.
When a molecule of water has enough energy, it breaks away
Scientific Vocabulary from other water molecules in the ocean. It rises into the
atmosphere atmosphere as a particle of gas called water vapor. Water vapor,
(noun) the mixture of like other gases in the atmosphere, is invisible.
gases that surrounds Earth
How else can water enter the
atmosphere?
Oceans hold most of Earth’s water. So oceans are major
sources of water vapor. But water also evaporates from features
such as rivers and lakes, or even puddles and soil. These
sources, along with oceans, make up 90 percent of the water
that enters the atmosphere. Where might the remaining
10 percent come from?
Scientific Vocabulary Life Science Connection Most of the remaining 10 percent
biosphere comes from the biosphere. All living things rely on freshwater. In
(noun) all living things on most plants, water travels from the roots up through the stems
Earth and into the leaves. When plants have enough water or when air
temperatures increase, they transpire. Transpiration is the
Scientific Vocabulary process by which plants release water vapor into the
freshwater atmosphere. Transpiration usually occurs through the leaves.
(noun) water that contains
less than 0.2 percent Some water vapor also comes from organisms through
dissolved salts cellular respiration. Cellular respiration takes place in many
cells. Water and carbon dioxide are produced during cellular
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
respiration. When animals breathe out, they release carbon
dioxide and water vapor from their lungs into the atmosphere.
Plants release these materials through openings in their leaves.
Water is also stored in the tissues of plants and animals. The
water is released back to the environment when organisms die
and decompose.
How can you get water to “reappear?”
How can you make water vapor, an invisible gas in the air,
become liquid water again? Think about how grass is sometimes
wet with dew in the morning, even though it did not rain the
night before. Water vapor becomes liquid water as it cools.
2 The Water Cycle Reading Essentials
THIS MATERIAL IS PROVIDED FOR INDIVIDUAL EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND MAY NOT BE DOWNLOADED OR FURTHER DISTRIBUTED.
When you exhale outside on a cold winter day, the water
vapor in your breath cools and changes into tiny water droplets.
The droplets form a foggy cloud in front of your face. This also
happens when warm air containing water vapor cools as it rises Word Origin
in the atmosphere. Temperatures in the lower atmosphere atmosphere
decrease with increasing altitude. So, as water vapor rises from Greek atmos-, means
through the atmosphere, it becomes cooler. Eventually it loses so “vapor”; and Greek
spharia, means “sphere”
much thermal energy that it returns to the liquid state.
Physical Science Connection The process by which a gas
changes to a liquid is condensation. Water vapor condenses on Academic Vocabulary
small particles in the air and forms droplets. Sometimes water process
droplets in the atmosphere lose so much thermal energy that (noun) a group of actions
tiny ice crystals form. The process by which a liquid turns into a that end in a certain result
crystalline solid is called crystallization. Recall that energy is
absorbed during evaporation. When water changes from a gas to
a liquid, energy is released. Energy is also released when water
changes from a liquid to a solid.
When small water droplets or ice crystals in the atmosphere
are surrounded by thousands of other droplets or ice crystals, Science Use v. Common Use
they block and reflect light. This makes them visible as clouds reflect
or fog. Science Use to return light,
heat, sound, and so on,
after it strikes a surface
Reread the statements at the beginning of the lesson. Fill in Common Use to think
quietly and calmly
the After column with an A if you agree with the statement or a
D if you disagree. Did you change your mind?
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
Reading Essentials The Water Cycle 3
THIS MATERIAL IS PROVIDED FOR INDIVIDUAL EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND MAY NOT BE DOWNLOADED OR FURTHER DISTRIBUTED.
LESSON 2
The Water Cycle
Water on Earth’s Surface
Key Concept
• How does water cycle on
Earth’s surface? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide
whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before
column if you agree with the statement or a D if you disagree. After
you’ve read this lesson, reread the statements to see if you have
changed your mind.
Before Statement After
The water cycle begins in the ocean.
Groundwater is found under the ground.
Mark the Text
Identify Main Ideas As you
read, underline the main
Why do some clouds rain?
ideas under each heading. Energy from the Sun causes water at Earth’s surface to
After you finish reading, evaporate into the atmosphere. Water vapor in the air cools as it
review the main ideas that rises. Then it condenses or crystallizes and forms clouds.
you have underlined. Moisture that falls from clouds to Earth’s surface is precipitation.
Scientific Vocabulary Liquid water falls to the ground as rain. Frozen water falls as
moisture snow, sleet, or hail. But why does precipitation fall from some
(noun) an amount of clouds and not from others? The water droplets that make up
liquid (water) in clouds are pulled toward Earth’s surface by gravity. Some
something droplets move through warm layers of air and they evaporate
before they fall as precipitation. Some droplets move through
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
Scientific Vocabulary
moist layers of air and they join together and grow bigger till
gravity they fall to Earth as precipitation.
(noun) an attractive force
that exists between all Water moves from Earth’s surface to the atmosphere and
objects that have mass back again in the water cycle. The amount of water on Earth
does not change. It is stable. However, changes in Earth’s global
Academic Vocabulary temperature can affect how water is cycled. As the lower
affect atmosphere becomes warmer, rates of evaporation increase. This
(verb) to cause a change increases the amount of moisture in the air. When the lower
in something
atmosphere has more moisture, more intense precipitation
occurs. In other areas, warmer temperatures may lead to drier
Academic Vocabulary
conditions.
intense
(adjective) very strong
4 The Water Cycle Reading Essentials
THIS MATERIAL IS PROVIDED FOR INDIVIDUAL EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND MAY NOT BE DOWNLOADED OR FURTHER DISTRIBUTED.
Where does all the rain go?
The Sun and gravity are the two main factors driving the
water cycle. Energy from the Sun causes water at Earth’s surface
to evaporate. Gravity causes the water to fall back to Earth as Word Origin
precipitation. More than 75 percent of precipitation falls into the precipitation
ocean. The rest falls onto land. Some of this water evaporates from Latin praecipitationem,
and goes back into the atmosphere. Some flows into lakes or means “act or fact of falling
headlong”
streams, which join together and flow back into the ocean.
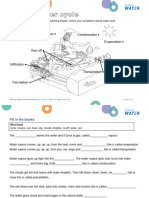
Where is water stored?
On Earth’s surface, gravity moves water from higher to lower
areas. The water can enter rivers and streams, and eventually
reaches lakes or oceans. Water is constantly moving through the
water cycle. But most water remains in certain storage areas for
relatively long periods of time. A storage area is called a
reservoir. Reservoirs can be oceans, lakes, glaciers and ice caps,
and groundwater.
Water Under Your Feet Generally, water that lies below
ground is called groundwater. If you have ever been inside a Academic Vocabulary
cave, you might have seen groundwater. The water seeping immense
down the sides of the cave is groundwater seeping through rock. (adjective) very great in
Groundwater can stay underground for long periods of time. It size or amount
can remain there for thousands or millions of years.
Scientific Vocabulary
An immense amount of water below our feet is found in
permeable
aquifers. Aquifers are areas of permeable sediment or rock that
(adjective) allowing water,
hold significant amounts of water. The water seeps through soil oil, or gas to pass through it
and into tiny pores, or spaces, between sediment and rock.
Land surface
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
Water table
Unsaturated zone
Sand Broken rock
Saturated zone
Level of
Surface water water table
Aquifer
All openings below
the water table are
full of groundwater.
Reading Essentials The Water Cycle 5
THIS MATERIAL IS PROVIDED FOR INDIVIDUAL EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND MAY NOT BE DOWNLOADED OR FURTHER DISTRIBUTED.
Groundwater Flow Because of gravity, groundwater flows
from higher areas to lower areas. Eventually, it reaches the
ocean. In some areas, groundwater is very close to the surface. It
Scientific Vocabulary keeps the soil wet. In other areas, such as deserts and other dry
surface climates, groundwater is hundreds of meters below the surface.
(noun) the outer face or
In low-lying areas at Earth’s surface, groundwater might
area of a thing
eventually seep out of the ground and into a stream, a lake, or a
wetland. In this way, groundwater can become surface water.
When surface water seeps into the ground, it becomes
groundwater. Groundwater is replenished by surface water.
Scientific Vocabulary Water in Glaciers and Ice Sheets Water on Earth can also be
glacier stored as solid ice, such as glaciers and ice sheets. How does
(noun) a large mass of ice this occur?
that moves slowly over
land Imagine what happens when snow falls but doesn’t melt.
Year after year layers of snow pile up. The top layers of snow
press down on the lower layers of snow. This turns the lower
Scientific Vocabulary
layers of snow into ice. Over time, the mass of ice and snow gets
ice sheet very heavy. Gravity then causes it to flow downhill like a slow-
(noun) a glacier that
moving river of ice. For most glaciers, this process takes over
spreads out over land in
all directions 100 years.
Reread the statements at the beginning of the lesson. Fill in
the After column with an A if you agree with the statement or a
D if you disagree. Did you change your mind?
Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education. Permission is granted to reproduce for classroom use.
6 The Water Cycle Reading Essentials
THIS MATERIAL IS PROVIDED FOR INDIVIDUAL EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND MAY NOT BE DOWNLOADED OR FURTHER DISTRIBUTED.
You might also like
- Comic StripDocument5 pagesComic StripIraila Mora MartinezNo ratings yet
- Product Infotmation Grotanol 3025Document2 pagesProduct Infotmation Grotanol 3025Luis David Rincon RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lesson 2Document9 pagesChapter 3 Lesson 2karinaderalonNo ratings yet
- Unit BDocument15 pagesUnit Bdanielrajas2No ratings yet
- A Teaching Unit For Years 3 - 6 ChildrenDocument35 pagesA Teaching Unit For Years 3 - 6 ChildrenKhalip HamzahNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Science Digital Learners Book 7 - Cambridge GODocument1 pageCambridge Lower Secondary Science Digital Learners Book 7 - Cambridge GOkhanhlinh27072012No ratings yet
- G5 - LSR - 2Y - 5.07 Earths WaterDocument14 pagesG5 - LSR - 2Y - 5.07 Earths WaterJohn DavissonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Changing Earth S SurfaceDocument7 pagesLesson 4 Changing Earth S SurfaceRias GremorNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plankareen balladNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan WATER CYCLEDocument8 pagesLesson Plan WATER CYCLENoreenzel Joy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1Document2 pagesSheet 1Demiana MagdyNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IVJulie Ann Ocumen - AustriaNo ratings yet
- Water Cycle and States of MatterDocument14 pagesWater Cycle and States of MatterSong MinyingNo ratings yet
- Science4 Water CycleDocument8 pagesScience4 Water CycleJoy PartozaNo ratings yet
- Drainage BasinsDocument18 pagesDrainage BasinsSyeda moosviNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. EarthDocument6 pagesUnit 2. EarthCasajardinmania JaenNo ratings yet
- Teks Eksplanasi Hujan Kelompok 2Document5 pagesTeks Eksplanasi Hujan Kelompok 2Meutia Safira AuliaNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle: Did You Know?Document14 pagesThe Water Cycle: Did You Know?Oliver ChantNo ratings yet
- Matter and Water CycleDocument4 pagesMatter and Water CycleHazel IrisNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science IVFevy Abanag100% (1)
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN in ScienceDocument4 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN in ScienceHannah Shield Carullo100% (2)
- Chapter 12 Air, Water and WeatherDocument10 pagesChapter 12 Air, Water and WeatherPushpa DeviNo ratings yet
- Elicit: What Are The Sources of Water On Earth?Document8 pagesElicit: What Are The Sources of Water On Earth?Panget pangetNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceCherry Queen TuandaNo ratings yet
- The Sun and Water CycleDocument6 pagesThe Sun and Water Cycleapi-368883407No ratings yet
- The Water Cycle WorksheetsDocument4 pagesThe Water Cycle WorksheetsNoprilianiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Water and It's Spatial DistributionDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Water and It's Spatial DistributionKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Science V DLPDocument5 pagesScience V DLPFarah Eva CarpioNo ratings yet
- Geog - LS 1 - Term3Document7 pagesGeog - LS 1 - Term3Muhamma Ibrahim AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Water CycleDocument2 pagesLesson Plan Water Cyclediana bulawitNo ratings yet
- The Water Cycle WorksheetsDocument9 pagesThe Water Cycle Worksheetsafifa.mdatbm00No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IV Water CycleDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Science IV Water CycleninsantocildesNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument5 pagesWater CycleZednanreh NnaojNo ratings yet
- The Water CycleDocument13 pagesThe Water Cycleapi-294782922No ratings yet
- M8 ListeningDocument2 pagesM8 ListeningYunita SariNo ratings yet
- 6e Ag U1lq3Document4 pages6e Ag U1lq3adhrit.mahatoNo ratings yet
- Reading Asssignment 1Document2 pagesReading Asssignment 1KISAKYE ANTHONYNo ratings yet
- The Hydrosphere PDFDocument23 pagesThe Hydrosphere PDFTabada NickyNo ratings yet
- Water CycleDocument6 pagesWater CycleVal Daryl AnhaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Earth SystemsDocument9 pagesLesson 1 Earth SystemsjohnosborneNo ratings yet
- English 8 q2 ST PT w3Document3 pagesEnglish 8 q2 ST PT w3Rechelle SopioNo ratings yet
- Lasgen Chemistry 2 Q3 W2Document3 pagesLasgen Chemistry 2 Q3 W2Franzhean Balais CuachonNo ratings yet
- t3 G 96 The Water Cycle Activity Sheet Ver 3Document2 pagest3 G 96 The Water Cycle Activity Sheet Ver 3Calm SeekNo ratings yet
- t3 G 96 The Water Cycle Activity Sheet - Ver - 3Document2 pagest3 G 96 The Water Cycle Activity Sheet - Ver - 3Nishaleeny Nainar Ayyavo0% (1)
- Objectives: Observe The Picture. What Is The Importance of Tree? Think and TellDocument5 pagesObjectives: Observe The Picture. What Is The Importance of Tree? Think and TellKyvyn EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Earth Sheryn ReanaDocument10 pagesEarth Sheryn ReanaSHERYN REANA A/P KUMARASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Student DiscussionDocument2 pagesStudent DiscussionLiin TPNo ratings yet
- WATER CYCLE GagaDocument6 pagesWATER CYCLE GagacedrickjamesarestaNo ratings yet
- S2 Science August 2023Document29 pagesS2 Science August 2023kirrl6347No ratings yet
- Chap05 0 PDFDocument30 pagesChap05 0 PDFNga Phạm ThanhNo ratings yet
- Step 3 PPT Science Oct 17-24th, 2017Document20 pagesStep 3 PPT Science Oct 17-24th, 2017Isai Jonas50% (4)
- Critical Thinking Activity: The Water Cycle: StatesDocument8 pagesCritical Thinking Activity: The Water Cycle: StatesrrNo ratings yet
- EarthDocument9 pagesEarthSHERYN REANA A/P KUMARASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Science 4-LE-for COT 2Document5 pagesScience 4-LE-for COT 2Nizeth SuarezNo ratings yet
- Water: "No Water, No Life. No Blue, No Green." - Sylvia EarleDocument3 pagesWater: "No Water, No Life. No Blue, No Green." - Sylvia EarleJeslyn MonteNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Grade 8Document10 pagesLesson Plan Grade 8Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in EnglishDocument6 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in EnglishJocelyn Dumlao BeltranoNo ratings yet
- MGS G06 Na 200Document1 pageMGS G06 Na 200Miranda HandNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 11Document10 pagesExp SC 3 - Chapter 11megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Evaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksFrom EverandEvaporation, Transpiration and Precipitation | Water Cycle for Kids | Children's Water BooksNo ratings yet
- Mineral UsesDocument2 pagesMineral UsesMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Pand AcellsDocument4 pagesPand AcellsMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Human Body SystemDocument3 pagesHuman Body SystemMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Minerals WorksheetDocument21 pagesRocks and Minerals WorksheetMemo Redavic100% (1)
- Skills in YearsDocument1 pageSkills in YearsMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Weathering Erosion or Deposition WorksheetDocument2 pagesWeathering Erosion or Deposition WorksheetMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Learners Profiles in YearsDocument1 pageLearners Profiles in YearsMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Earth's InteriorDocument6 pagesEarth's InteriorMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- Key Concepts in YearsDocument1 pageKey Concepts in YearsMemo RedavicNo ratings yet
- USACOE Permit Withdrawal and Supplemental EIS Request PRDocument3 pagesUSACOE Permit Withdrawal and Supplemental EIS Request PRAlaska's News SourceNo ratings yet
- Clever 2000Document12 pagesClever 2000LudNo ratings yet
- Land, Water & Air LPDocument6 pagesLand, Water & Air LPPrincess De VegaNo ratings yet
- Water Arab World Full-241-256Document16 pagesWater Arab World Full-241-256Moe FoeNo ratings yet
- The Rain For KidsDocument27 pagesThe Rain For KidsValen Valibia100% (1)
- Veritas Vitas NG TondoDocument2 pagesVeritas Vitas NG TondoAkemi ParkNo ratings yet
- HYDROGEOLOGYDocument3 pagesHYDROGEOLOGYimrankhanNo ratings yet
- Flotation EquipmentDocument42 pagesFlotation EquipmentAnn MariyaNo ratings yet
- OQ AVL-ValvesDocument3 pagesOQ AVL-ValvesMDhana SekarNo ratings yet
- Ms Prathmesh Construction ProfileDocument20 pagesMs Prathmesh Construction ProfilePratik KharmateNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: (Formerly Known As Nagarjuna Agrichem Limited)Document6 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: (Formerly Known As Nagarjuna Agrichem Limited)Shagun PathaniaNo ratings yet
- Waukesha Digester GasDocument13 pagesWaukesha Digester GasA2 BhaskarNo ratings yet
- A Study On Reclamation of Open Cast Mines in IndiaDocument20 pagesA Study On Reclamation of Open Cast Mines in IndiaShubh KumarNo ratings yet
- Fish HonorDocument3 pagesFish HonorKIARA B SAMUELNo ratings yet
- Supplier Questionnaire - TAL SA COMPLETDocument22 pagesSupplier Questionnaire - TAL SA COMPLETTal SANo ratings yet
- Condorchem Envitech ENVIDEST MFE3 enDocument2 pagesCondorchem Envitech ENVIDEST MFE3 enpabloNo ratings yet
- Geography HonDocument99 pagesGeography Honshivamsahu890No ratings yet
- Unit 4 BiomassDocument37 pagesUnit 4 BiomassManoj ka Manoj kaNo ratings yet
- ABEN 55 - 1. Introduction Hydrologic CycleDocument13 pagesABEN 55 - 1. Introduction Hydrologic CyclealexontingNo ratings yet
- JXN Water Rate HikeDocument4 pagesJXN Water Rate Hikethe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Bộ Đề 02 - Tham Khảo Avdv Ute 2023Document6 pagesBộ Đề 02 - Tham Khảo Avdv Ute 2023Trân TrầnNo ratings yet
- Piranha 08 110 TDSDocument4 pagesPiranha 08 110 TDSchu42No ratings yet
- Rural-Sanitation ReviewDocument22 pagesRural-Sanitation ReviewAbubakar SadiqNo ratings yet
- Product Handbook 2020Document2,526 pagesProduct Handbook 2020valiuddinNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesBahasa InggrisMauritius BryanNo ratings yet
- Streams As Sensors: Arctic Watersheds As Indicators of ChangeDocument6 pagesStreams As Sensors: Arctic Watersheds As Indicators of ChangeSaanvi Rao EravelliNo ratings yet
- Land, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and WildlifeDocument6 pagesLand, Soil, Water, Natural Vegetation and Wildlifevikas kumarNo ratings yet
- Slide 3 Bunaken National Marine Park: Turtles DolphinsDocument2 pagesSlide 3 Bunaken National Marine Park: Turtles DolphinsCaloumNo ratings yet
- Poutini WaitaikiDocument6 pagesPoutini WaitaikiTroy BrockbankNo ratings yet