Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nagornov Task2
Nagornov Task2
Uploaded by
Snag0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document contains questions and answers about electrical relays and protections. It discusses:
1) The operating principle of relays using electromagnets and contacts to open and close circuits.
2) Key requirements for protection systems like selectivity, speed, sensitivity, reliability and simplicity.
3) The need for protections to prevent equipment failures and service interruptions.
4) How to select the pickup value of a relay based on load and fault current levels.
5) How relay operating times are set to ensure backup relays operate after primary relays during a fault.
Original Description:
Original Title
Nagornov_task2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains questions and answers about electrical relays and protections. It discusses:
1) The operating principle of relays using electromagnets and contacts to open and close circuits.
2) Key requirements for protection systems like selectivity, speed, sensitivity, reliability and simplicity.
3) The need for protections to prevent equipment failures and service interruptions.
4) How to select the pickup value of a relay based on load and fault current levels.
5) How relay operating times are set to ensure backup relays operate after primary relays during a fault.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesNagornov Task2
Nagornov Task2
Uploaded by
SnagThe document contains questions and answers about electrical relays and protections. It discusses:
1) The operating principle of relays using electromagnets and contacts to open and close circuits.
2) Key requirements for protection systems like selectivity, speed, sensitivity, reliability and simplicity.
3) The need for protections to prevent equipment failures and service interruptions.
4) How to select the pickup value of a relay based on load and fault current levels.
5) How relay operating times are set to ensure backup relays operate after primary relays during a fault.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Individual task 2
Questions:
1. What is the operation principle of relay?
2. What requirements for protections do you know?
3. Why do we need protection?
4. How to select the pickup value of a relay?
5. How to set the operating time of a relay?
6. What the selectivity is?
7. How relays are connected in the power system?
8. What is time relay?
Answers:
1. Electromechanical relays transfer signals between its contact through a
mechanical motion. It consists of two sections: the fƠiƠrst is the
electromagnet section and the other is the armature and mechanical
contacts section. The electromagnet section consists of a set of coil
wound over a magnetic core.
When an input voltage (almost equal to the rated voltage of the coil) is
applied to the coil, it gets magnetized and attracts the armature. The
mechanical contacts are attached to the armature. Hence, when the
armature is pulled towards the electromagnet, the contact closes. When
the input voltage applied to the coil is removed, the armature is brought
back to its original position by the spring release.
2.
1. Selectivity
2. Speed
3. Sensitivity
4. Reliability
5. Simplicity
6. Economy
3. Electrical equipment failures would cause intolerable outages. There
must be additional provisions to minimize damage to equipment and
interruptions to the service when failures occur.
4. The relay should allow normal load as well as a certain degree of
overload to be supplied. So the pickup value of the relay should be more
than maximum load. At the same time, the relay should be sensitive
enough to respond to the smallest fault. So, pickup value should be less
than the smallest fault current.
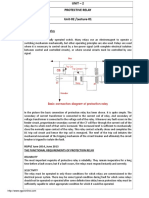
5. Naturally when a fault occurs it is sensed by both the primary and
backup protection. As the operating time of primary relay is less than
that of the backup relay, it will operate fƠiƠrst. There will be an overshoot
time (due to moment of inertia of moving relay system).
6. It is the ability of the protective system to select correctly that part of
the system in trouble and disconnect the faulty part without disturbing
the rest of the system.
7. The relays are connected to the power system through the current
transformer (CT) or potential transformer (PT).
8. Time relay is a type of device that can control power fƠlƠow in a
circuit by
using an electromagnet. The device includes a coil of wire that is
wrapped around an iron core. When power fƠlƠows through the circuit, it
creates a magnetic fƠiƠeld in the electromagnet.
This magnetic fƠiƠeld can attract or repel another magnet attached to a
timer relay switch inside the device. The time relay will allow you to
control when this happens by controlling how long the current fƠlƠows
through its coils before stopping.
You might also like
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionFrom EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Plant ProtectionDocument0 pagesPower Plant ProtectionSHIVAJI CHOUDHURY100% (7)
- Simulation Report of Over Current RelayDocument8 pagesSimulation Report of Over Current RelayAbdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectric Actuators: Vector Control Method: Basic, Modeling and Mechatronic Design of Ultrasonic DevicesFrom EverandPiezoelectric Actuators: Vector Control Method: Basic, Modeling and Mechatronic Design of Ultrasonic DevicesNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Induction MotorsDocument18 pagesMultiple Choice Question (MCQ) of Induction Motorskibrom atsbha75% (4)
- Electric Motor ReportDocument23 pagesElectric Motor ReportAnfield Faithful67% (3)
- Switchgear and Protection: CH Hari PrasadDocument54 pagesSwitchgear and Protection: CH Hari PrasadPardha Saradhi JNo ratings yet
- Protection System in Power SystemDocument12 pagesProtection System in Power SystemHero Cordova de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Bee053 P&S NotesDocument60 pagesBee053 P&S NotesADDIS JOHNNo ratings yet
- Power System ComponentsDocument9 pagesPower System ComponentsLiezl Jeane TejamoNo ratings yet
- Ee8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Document30 pagesEe8602 PSG Notes - New - Unit2Vairaperumal KNo ratings yet
- SGP 6Document7 pagesSGP 6Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- Electrical BEE VIII Power System Protection EE 48E2 6Document37 pagesElectrical BEE VIII Power System Protection EE 48E2 6Usman deoNo ratings yet
- Protective RelaysDocument33 pagesProtective RelaysThotakura Nsc SekharNo ratings yet
- Nagornov Task4Document4 pagesNagornov Task4SnagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Det50083 PTSBDocument12 pagesChapter 4 Det50083 PTSBNUR RABBIATUL ADAWIYAH MOHAMMADNo ratings yet
- International University of Business Agriculture & TechnologyDocument13 pagesInternational University of Business Agriculture & TechnologyMd Hasibur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Power System ProtectionDocument46 pagesPower System ProtectionRatul MollickNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Nitesh Hatankar (I-48) Title: Objective: AbstractKkNo ratings yet
- Working Principle of Distance or Impedance RelayDocument16 pagesWorking Principle of Distance or Impedance Relayrobertovm2002No ratings yet
- Overcurrent RelayDocument11 pagesOvercurrent RelayChandana K R 4UB20EE010No ratings yet
- Study About Relay & Meter Function & ReadingDocument44 pagesStudy About Relay & Meter Function & ReadingAnand SundaramNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PSP - CH1Document52 pagesIntroduction To PSP - CH1engidawabelNo ratings yet
- Types of Relays: Protection-Relays-Or-Protective-RelaysDocument2 pagesTypes of Relays: Protection-Relays-Or-Protective-Relayspoonam yadavNo ratings yet
- Notes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Document32 pagesNotes Switchgear and Protection Unit 2Pratik SinghNo ratings yet
- Circuit Breaker SGPDocument34 pagesCircuit Breaker SGPSamuel BhukyaNo ratings yet
- Ee2402 Protection and SwitchgearDocument12 pagesEe2402 Protection and SwitchgearVasudha SinghNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysDocument29 pagesPower System Protection (Control System) : Protective RelaysBagirath SwaminathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment of System Protection Eeg 806Document24 pagesAssignment of System Protection Eeg 806emechetasamuel27No ratings yet
- RelaysDocument30 pagesRelaysujjwalNo ratings yet
- EE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedDocument12 pagesEE1302 Protection and Switchgear-SignedarivurpNo ratings yet
- PSP MidDocument3 pagesPSP MidMarupakaNo ratings yet
- قسم الوقاية - الجزء الثانيDocument14 pagesقسم الوقاية - الجزء الثانيوليد موسىNo ratings yet
- Protective RelayDocument17 pagesProtective RelayAmit ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Natural Mode of Synchronous Operation. It Implies ThatDocument20 pagesNatural Mode of Synchronous Operation. It Implies ThatTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Switchgear and Protection 1st ClassDocument24 pagesSwitchgear and Protection 1st ClassBayezid khan100% (1)
- Switchgear & Protection Government College of Engineering Karad (Electrical Engineering Department) Prof - Uma S.PatilDocument162 pagesSwitchgear & Protection Government College of Engineering Karad (Electrical Engineering Department) Prof - Uma S.Patilgameging35No ratings yet
- Ee2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit IDocument38 pagesEe2402 - Protection and Switchgear Seventh Semester Two Marks Question &answers Unit INavneethNo ratings yet
- Rellay Protection: Before Reading This Text, Answer These QuestionDocument6 pagesRellay Protection: Before Reading This Text, Answer These QuestionPandu Wahyu UtomoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Slides 2023Document52 pagesUnit 4 Slides 2023Theko LeroyatvarsityNo ratings yet
- Relay Protection - Discussioin-KEADocument43 pagesRelay Protection - Discussioin-KEAShirajul IslamNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Fundamentals of Power System Protection: Objectives in This LectureDocument17 pagesModule 1: Fundamentals of Power System Protection: Objectives in This LectureXero KrossingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 RelaysDocument47 pagesLecture 4 RelaysnakkasrinuNo ratings yet
- Ee1302 Protection and SwitchgearDocument12 pagesEe1302 Protection and SwitchgearMukesh Kumar0% (1)
- Protection and Switchgear Important QuestionsDocument38 pagesProtection and Switchgear Important QuestionsAkhil Surya0% (1)
- Electrical Drive 2015 RegularDocument64 pagesElectrical Drive 2015 Regularkabtamu mamoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Electromagnetic & Static Relays PDFDocument94 pagesUnit 3 - Electromagnetic & Static Relays PDFAkula VeerrajuNo ratings yet
- PSP ImpDocument36 pagesPSP ImpHarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- NPTEL - Curso de Proteção de SistemasDocument321 pagesNPTEL - Curso de Proteção de SistemasGianey Fernandes da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection (EE-523) Lecture-01: Samiya Zafar Assistant Professor, EED NEDUET M.Engg Fall Semester 2017Document47 pagesPower System Protection (EE-523) Lecture-01: Samiya Zafar Assistant Professor, EED NEDUET M.Engg Fall Semester 2017JaleesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document26 pagesUnit 1chintuchetan123No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Mosab SalamaNo ratings yet
- Switch GearDocument46 pagesSwitch GearDUE DATENo ratings yet
- JURNAL2 - Fachrul Rozi Ramadhan - 201971039 - B - B1Document12 pagesJURNAL2 - Fachrul Rozi Ramadhan - 201971039 - B - B1Fachrul rozi ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Differential Relay Reliability Impliment Enhancement of Power TransformerDocument7 pagesDifferential Relay Reliability Impliment Enhancement of Power TransformerAde SafitriNo ratings yet
- Relays - Open ElectricalDocument5 pagesRelays - Open Electricalstalin63No ratings yet
- Electrical Protection System 1 To 150Document95 pagesElectrical Protection System 1 To 150Anirban Bandyopadhyay50% (2)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 4: Electromagnetic CompatibilityFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 4: Electromagnetic CompatibilityNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet
- Nagornov Task4Document4 pagesNagornov Task4SnagNo ratings yet
- Nagornov Task5Document1 pageNagornov Task5SnagNo ratings yet
- Nagornov Task1Document1 pageNagornov Task1SnagNo ratings yet
- Nagornov Task3Document1 pageNagornov Task3SnagNo ratings yet
- Stepper MotorDocument9 pagesStepper MotorHasan Mahmood100% (1)
- Material Handling Trolley List For Starters and Starter KitsDocument11 pagesMaterial Handling Trolley List For Starters and Starter KitsSaptorshi BagchiNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii Electrical MachinesDocument63 pagesUnit Ii Electrical Machinespriya dharshiniNo ratings yet
- Ee 5703 Module SummaryDocument2 pagesEe 5703 Module SummaryJie RongNo ratings yet
- Brosur Isolasi Trafo CENTRADO Dry TypeDocument1 pageBrosur Isolasi Trafo CENTRADO Dry TypeBudi IriantoNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Characteristic-1Document12 pagesDC Motor Characteristic-1Maysara BalakiNo ratings yet
- AMI UNIT III Presentation 5 04.09.2020Document22 pagesAMI UNIT III Presentation 5 04.09.2020Jayashree SathiyanarayananNo ratings yet
- ZGB102FEE: Dimension (MM)Document1 pageZGB102FEE: Dimension (MM)ahmadmn_scribdNo ratings yet
- Magnetic LevitationDocument26 pagesMagnetic LevitationSalil Sharma100% (1)
- Ac-Dc-Servomotor-Net NotesDocument9 pagesAc-Dc-Servomotor-Net NotesDINESHKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Reverse Power RelayDocument4 pagesReverse Power RelayJadeja KuladipsinhNo ratings yet
- EE8301 Electrical Machines-I Transformers Ms.J.Sumithra, Asp/EeeDocument39 pagesEE8301 Electrical Machines-I Transformers Ms.J.Sumithra, Asp/Eeedaniel alejandro chaparro zipaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SDocument112 pagesChapter-3 Induction Machines: I E M & P SLim Kai XuanNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument53 pagesProject ReportMUDAM ALEKYANo ratings yet
- Per-Unitization and Equivalent Circuits: 1.0 Normalization of Voltage EquationsDocument35 pagesPer-Unitization and Equivalent Circuits: 1.0 Normalization of Voltage EquationsfbhkeNo ratings yet
- Sub Module 3.18 AC MotorsDocument22 pagesSub Module 3.18 AC MotorsInterogator5No ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Permanent Magnet AC Drives, Load-Commutated-Inverter Synchronous Motor Drives, and Synchronous GeneratorsDocument23 pagesSinusoidal Permanent Magnet AC Drives, Load-Commutated-Inverter Synchronous Motor Drives, and Synchronous GeneratorshariNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of High Performance of A BLDC Motor For Electric VehicleDocument4 pagesDesign and Analysis of High Performance of A BLDC Motor For Electric VehicleShubhzsNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument38 pagesDC MotorasuypowerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 TransformerDocument20 pagesChapter 4 Transformershahmi nordinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Alternating Current Motors: Electrical MachineDocument28 pagesChapter 7: Alternating Current Motors: Electrical MachineThe zeroNo ratings yet
- Maglev Presentation FinalDocument26 pagesMaglev Presentation FinalAishwarya ChintaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Lab Experiment #1 Constructional Feature, Transformation Ratio Determination & Polarity Identification of A 1-TransformerDocument3 pagesElectrical Machines Lab Experiment #1 Constructional Feature, Transformation Ratio Determination & Polarity Identification of A 1-TransformerBiks AlebachewNo ratings yet
- 13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesDocument18 pages13C NMR Spectroscopy of Coumarin DerivativesGeorge MoshiashviliNo ratings yet
- Basics of AC Electric Motors and PartsDocument3 pagesBasics of AC Electric Motors and PartsPankaj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- IMSM - Assienment Question - II Sem 2021-22Document2 pagesIMSM - Assienment Question - II Sem 2021-22Leela Krishna MNo ratings yet
- 3ph IM - T-Slip Characteristics - ProblemsDocument22 pages3ph IM - T-Slip Characteristics - Problemskarthikeyan249No ratings yet
- Electric Machinery, 6th EditionDocument5 pagesElectric Machinery, 6th EditionSubha Kumar25% (4)