Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer Sheet For Activity 1 Lab Group 3
Uploaded by
Xheena SarabiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer Sheet For Activity 1 Lab Group 3
Uploaded by
Xheena SarabiaCopyright:
Available Formats
ADGE 102
GENERAL CHEMISTRY (ORGANIC)
Bachelor of Science in Criminology
Prof: Susan E. Montebon
Subject Teacher
Activity 4
Construct the graphs and answer the following questions. Take picture of the graph and paste them on
the last pages
A. Atomic Radius
1. What are the elements found at the peak
of the curve?
2. Are they members of the same family?
Name the family.
3. What are the elements at the lowest point Ar and H
of every downward swing of the curve?
Ar is a noble gas, and H is a alkali metal, s
4. Are they members of the same family? basically they don’t belong to the same
Name the family. group.
5. Give a brief explanation for this trend as As we go down, atomic size increases
you go from top to bottom of a group in because we add shells.
the periodic table.
6. Describe the change in the atomic radius
of elements in
Atomic radius increases from Li to Ne.
a. Period 2 (Li to Ne)
Atomic radius decreases from (Na to Ar)
b. Period 3 (Na to Ar)
7. Give a brief explanation for this trend as As we go to the right, atomic radius
you go from left to right of the period in decreases because we are moving within a
the periodic table. shell and each element to the right has one
more proton in the nucleus than the last so
there is this stronger electromagnetic
attraction felt by the electrons and the radius
shrinks.
B. Ionization Energy
1. What are the elements at the peak of the Noble gases of Group 18 have the highest
curve? ionization energy in their respective periods.
2. What are their positions in the periodic Group 18.
table?
3. What are the elements at the lowest point Cesium,Francium.
of every downward swing of the curve?
4. What are their positions in the periodic The first ionization energy varies in a
table? predictable way across the periodic table. The
ionization energy decreases from top to
bottom in groups, and increases from left to
right across a period. Thus, helium has the
largest first ionization energy, while francium
has one of the lowest.
5. How does ionization energy vary across a As you move across a period, the atomic
period? radius decreases, that is, the atom is smaller.
The outer electrons are closer to the nucleus
and more strongly attracted to the center.
6. How does ionization energy vary within a Ionization energy decreases down the
family/group? family/group.
7. How does ionization energy change as the As atomic size decreases, ionization energy
atomic size decreases? also decreases.
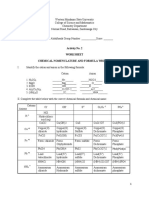
Part B – Nomenclature, Formula Writing and Classification of Inorganic Compounds
I- Identify the cation and anion in the following formula:
Cation Anion
1. H2CO3 H+ HCO3
2. MgO +2 -2
3. KOH K+ OH-
4. Al2(Cr2O7)3 A12(+) CrO(3-)
5. (NH4)2S NH4(+) S(2-)
II. Complete the table below with the correct chemical formula and chemical name.
Anions
Cl- S-2 OH- Cr2O7 -2 PO4-3
Cations
HCl H2S H(OH) H2 (Cr207) H3(PO4)
H+
Hydrochloric Hydrogen Holmium Hydrogen Phosphoric
acid (aq) Sulfide Hydroxide Dichromate Acid
ZnC12 Zn2s2 Zn(OH)2 Zn2(Cr207)2 Zn3(PO4)2
Zn+2
Zinc Zinc Zinc Dichromate Zinc
Chloride Sulfide Hydroxide Phosphate
FeC13 Fe2S3 Fe(OH)3 Fe2(Cr207)3 Fe3(P04)3
Fe+3
Iron(III) Iron(3+) Iron(III) Iron(III) Iron(III)
Chloride Sulfide Oxide- Dichromate Phosphate
Hydroxide
PbC14 Pb2S4 Pb(OH)4 Pb2(CR207)4 Pb3(PO4)4
Pb+4
Lead Lead(IV) Lead(IV) Lead Iron
Tetrachloride Sulfide Hydroxide Chromium Polonium
Oxygen
(NH4) CI (NH4)2S (NH4)OH (NH4)2Cr207 (NH4)3PO4
NH4 +
Ammonium Ammonium Ammonium Ammonium Ammonium
Chloride Sulfide Hydroxide Dichromate Phosphate
III. Complete the table with the chemical name, chemical formula and what the type of compounds
these substances belong.
Type of Compound
Formula Chemical Name Binary or Ionic or Acid/base/
Ternary Molecular salt/hydrate
1) Mg(NO3)2 Magnesium Nitrate Ternary Ionic Salt
2) Al2O3 Aluminium Oxide Binary Ionic Base/Acid
3) P2O5 Diphosphorus Pentoxide Binary Molecular Acidic
4) NH4OH Ammonium Hydroxide Ternary Ionic Base
5) O3PbS Plumbic Sulfite Ternary Molecular Acidic
6) NaHCO3 Sodium Bicarbonate Ternary Ionic Salt
7) Cr2O3 Chromium (III) Oxide Binary Ionic Salt
8) HNO3 (gas) Nitric Acid Binary Ionic Acid
9) HBr(aq) Hydrobromic acid (aq) Binary Molecular Hydrate
10) KMnO4 Potassium Manganate Ternary Ionic Salt
11) H2CrO4 (aq) Chromic Acid Ternary Molecular Acid
12) Ba(OH)2 Barium Hydroxide Ternary Ionic Base
13) Cu(OH)2 Copper (II) Hydroxide Ternary Molecular Acid/Base
14) N2O5 Dinitrogen Pentoxide Binary Molecular Salt
15) CaCl2. 2H2O Calcium Chloride Binary Ionic Hydrate
Dihydrate
You might also like
- Maya Smith - Isotopes Gizmos Activity - 9065228Document5 pagesMaya Smith - Isotopes Gizmos Activity - 9065228MAYA SMITH0% (2)
- 16 Naming Ionic Compounds S PDFDocument6 pages16 Naming Ionic Compounds S PDFGideon CavidaNo ratings yet
- Alien Periodic TableDocument4 pagesAlien Periodic TableAsif Ali Jafery100% (2)
- 3 Periodic TableDocument14 pages3 Periodic TableCas AndersNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Document27 pagesChemical Nomenclature: Experiment #3Ayi PunsalanNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesCHEMISTRYXyiee ViorNo ratings yet
- Etymology: Electrostatic Potential Nitrate Ion N ODocument7 pagesEtymology: Electrostatic Potential Nitrate Ion N ORigioGerryNo ratings yet
- Writing Chemical Formula Week 2Document81 pagesWriting Chemical Formula Week 2tupasrowen65No ratings yet
- 12TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperDocument22 pages12TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperMugal HanzalaNo ratings yet
- Language of ChemistryDocument12 pagesLanguage of ChemistryVenkatNo ratings yet
- chemistry-ELEMENTS AND CHEMICAL BONDINGDocument20 pageschemistry-ELEMENTS AND CHEMICAL BONDINGfelixmatchumbuza041No ratings yet
- AP Summer AssignmentDocument14 pagesAP Summer AssignmentNaleen EshuchiNo ratings yet
- Sarah Compound Dice ActivityDocument3 pagesSarah Compound Dice ActivityAnaria ManojNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Part II 5 6Document109 pagesGeneral Chemistry Part II 5 6LUH EKA YANTHINo ratings yet
- MANTARA - Docx ACTIVITY#5 PART BDocument3 pagesMANTARA - Docx ACTIVITY#5 PART BFarks Mantara0% (1)
- Study GuideDocument2 pagesStudy Guidebiaobarros2005No ratings yet
- Metals With Only One ChargeDocument6 pagesMetals With Only One ChargejohnenzNo ratings yet
- The Value of X Represents The Least Oxidation Number. 3. Balance The Charge 4. It Forms Ionic Bond. 5. The Oxidation Number of All Metals Are Positive While Non-Metals Are NegativeDocument7 pagesThe Value of X Represents The Least Oxidation Number. 3. Balance The Charge 4. It Forms Ionic Bond. 5. The Oxidation Number of All Metals Are Positive While Non-Metals Are NegativeCupcake Swirl NNo ratings yet
- Naming and Formula WritingDocument15 pagesNaming and Formula WritingMeggy CaparasNo ratings yet
- BES111 LAB Act.2 Worksheet On Chemical Nomenclature 1Document2 pagesBES111 LAB Act.2 Worksheet On Chemical Nomenclature 1Ahmed Dhempsey Hali AbdulbasikNo ratings yet
- Ionic Compounds and Formula WorksheetDocument4 pagesIonic Compounds and Formula WorksheetKemoy FrancisNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1. Ionic CompoundsDocument4 pagesLesson 1. Ionic CompoundsJamelle SilvestreNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Lecture Series 2Document13 pagesInorganic Lecture Series 2Ajayi DemiladeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2, Inorganic Chemistry (2.11-2.15) Study GuideDocument22 pagesChemistry Unit 2, Inorganic Chemistry (2.11-2.15) Study Guidemannm26No ratings yet
- Complete NomenclatureDocument10 pagesComplete NomenclaturezainalexanderaliNo ratings yet
- Before Getting Started, Spend One Minute of Silence For Opening PrayerDocument47 pagesBefore Getting Started, Spend One Minute of Silence For Opening PrayerFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- Formula and Equations - NotesDocument5 pagesFormula and Equations - Notesshrikant19829No ratings yet
- ACTIVITY NO. 2 (CHEMISTRY LABORATORY) - Chemistry For EngineersDocument2 pagesACTIVITY NO. 2 (CHEMISTRY LABORATORY) - Chemistry For EngineersArvhenn BarcelonaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form4 Chapter 4Document10 pagesChemistry Form4 Chapter 4Yi WenNo ratings yet
- Valency and Formulae-HandoutDocument3 pagesValency and Formulae-HandoutABHAVYA RAJNo ratings yet
- Module 4. Periodic TableDocument5 pagesModule 4. Periodic TableBiancaQuitasolNo ratings yet
- ApsummerDocument5 pagesApsummerLayleeNo ratings yet
- Chemical Nomenclature Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesChemical Nomenclature Chemical Reactionslexter john lopezNo ratings yet
- Naming Ionic CompoundsDocument6 pagesNaming Ionic CompoundsMary Jane YepesNo ratings yet
- TRANSISIDocument61 pagesTRANSISIAlanNo ratings yet
- Lecture04c - Main-Group - Elements-PART3 - PenDocument48 pagesLecture04c - Main-Group - Elements-PART3 - PenAaf AbdRashidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheets Class 8 On Chapter 4 Materials Metals and Non Metals With Answers Set 1Document5 pagesChemistry Worksheets Class 8 On Chapter 4 Materials Metals and Non Metals With Answers Set 1Amirthan ArulNo ratings yet
- NomenclatureDocument3 pagesNomenclatureDean Joyce AlborotoNo ratings yet
- Activity 9 - Properties of MetalDocument30 pagesActivity 9 - Properties of MetalAbbey Frosty'Knight Dawn MortaleNo ratings yet
- Summer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021Document5 pagesSummer Assignment For AP Chemistry Class 2020-2021shelly zhangNo ratings yet
- Learn PracticallyDocument55 pagesLearn Practicallyprincethakan9No ratings yet
- 01 NomenclaturesDocument6 pages01 NomenclaturesKarolina DoskoczNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersDocument4 pagesChemistry - Review On Chemical Formulas With AnswersAbdullah HassanNo ratings yet
- NamingDocument8 pagesNamingMADAYAG, RUTH L.No ratings yet
- Answers of Exercise 1 (A)Document6 pagesAnswers of Exercise 1 (A)Lisa SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Names and Formulas: Ionic CompoundsDocument66 pagesChemical Names and Formulas: Ionic CompoundsKiao CODMNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes PT 3 4Document53 pagesChemistry Notes PT 3 4Eunice Kyla MapisaNo ratings yet
- Transition Elements PDFDocument18 pagesTransition Elements PDFArslanAliNo ratings yet
- Work On Naming FormulaDocument11 pagesWork On Naming FormulamilonaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 NomenclatureDocument90 pagesCH 3 Nomenclaturemarc.breslerNo ratings yet
- Naming of Compounds-General ChemistryDocument14 pagesNaming of Compounds-General Chemistry7assan1300No ratings yet
- GCI Topics PDFDocument4 pagesGCI Topics PDFMuhammad QaisarNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023-24 Revision Notes On P-Block Elements - Free PDF DownloadDocument10 pagesJEE Main 2023-24 Revision Notes On P-Block Elements - Free PDF Downloadharshad.vikramNo ratings yet
- 2009-10-F3-CHEM First Term Exam Paper ReviewDocument70 pages2009-10-F3-CHEM First Term Exam Paper Review2E (04) Ho Hong Tat AdamNo ratings yet
- Tai Lieu AV2 2023Document56 pagesTai Lieu AV2 2023truongnhu0211No ratings yet
- Chemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Document30 pagesChemical Formula, Naming & Writing Compound: General Chemistry 1Synne Mae BorneaNo ratings yet
- Ions and MoleculesDocument25 pagesIons and MoleculescelinekateannNo ratings yet
- Nutrient General Chemistry and Plant FunctionDocument80 pagesNutrient General Chemistry and Plant Functionjames reidNo ratings yet
- Chemo AssignmentDocument6 pagesChemo AssignmentYamlak NegashNo ratings yet
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972From EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverNo ratings yet
- Genchem Lec Act1Document5 pagesGenchem Lec Act1Xheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- GEN CHEM ACT 2, SerevoDocument12 pagesGEN CHEM ACT 2, SerevoXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document8 pagesActivity 2Xheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- ReflectionLABPaperOnGenChem - XheenaSarabia IIIDDocument5 pagesReflectionLABPaperOnGenChem - XheenaSarabia IIIDXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Genchem LecDocument2 pagesGenchem LecXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Act 3 J Gen ChemDocument5 pagesAct 3 J Gen ChemXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- GenChem Activity 3Document3 pagesGenChem Activity 3Xheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Abibi Chemlab ProjDocument2 pagesAbibi Chemlab ProjXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Dahdahchemlab ProjDocument3 pagesDahdahchemlab ProjXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Batomalaki, JelynT Activity1Document8 pagesBatomalaki, JelynT Activity1Xheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Technicalwriting ReqsDocument6 pagesTechnicalwriting ReqsXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- AbibibbibibibibibDocument1 pageAbibibbibibibibibXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Excuse LetterDocument1 pageExcuse LetterXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Dictionary of Terms in CriminologyDocument27 pagesDictionary of Terms in CriminologyXheena Sarabia100% (1)
- Part3 DRUGSDocument3 pagesPart3 DRUGSXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- SARABIA, XHEENA - Lesson 15 Properties of GasesDocument3 pagesSARABIA, XHEENA - Lesson 15 Properties of GasesXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Chemlab ProjectDocument2 pagesChemlab ProjectXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- DisputeRes XSDocument2 pagesDisputeRes XSXheena SarabiaNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level: Learning Compentency/ies: Key Concepts/ Understanding To Be DevelopedDocument16 pagesSchool Grade Level: Learning Compentency/ies: Key Concepts/ Understanding To Be DevelopedsandrabuangNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Periodic Table - DPP 1 To 5Document9 pagesAdvanced - Periodic Table - DPP 1 To 5OJAS DwivediNo ratings yet
- CH301 - Infrared Spectros PDFDocument11 pagesCH301 - Infrared Spectros PDFRicky Makini-Purcell80% (5)
- Target: Jee (Advanced) 2019: P H Y S I C SDocument8 pagesTarget: Jee (Advanced) 2019: P H Y S I C SraghavbhatiaNo ratings yet
- ka a a a M:) cos cos sin (= + αDocument5 pageska a a a M:) cos cos sin (= + αFaizan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Instapdf - in 118 Elements List 216Document5 pagesInstapdf - in 118 Elements List 216HARISH UNo ratings yet
- Phy475 Homework 3Document1 pagePhy475 Homework 3ProfAndré GazotoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table (Chemistry)Document25 pagesPeriodic Table (Chemistry)bm OUREMNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 UEC Atoms and MoleculesDocument27 pagesChap 1 UEC Atoms and MoleculesGan Suk LingNo ratings yet
- D and F Block ElementsDocument23 pagesD and F Block Elementsvkn2417No ratings yet
- Pages From 0625 s11 QP 33Document1 pagePages From 0625 s11 QP 33Nicole TNo ratings yet
- Presentation - Atomic Structure and Mass SpecDocument23 pagesPresentation - Atomic Structure and Mass SpecDBXGAMINGNo ratings yet
- Uv Vis & FtirDocument15 pagesUv Vis & FtirVannessa Shallomy100% (2)
- Atomic Models - TheoryDocument109 pagesAtomic Models - TheoryDr-Walid FemtosecondNo ratings yet
- Ch11 1 Transition Metals Absorption SpectraDocument29 pagesCh11 1 Transition Metals Absorption SpectraTapas GhatakNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atoms and IonsDocument34 pagesStructure of Atoms and IonsChristineNo ratings yet
- 核磁共振部分习题及答案 1Document14 pages核磁共振部分习题及答案 1Tariq Rahim MarwatNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - ch117l - Final Lab Report 4Document10 pagesGroup 2 - ch117l - Final Lab Report 4Luis Alfonso DañezNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Unit 3 NotesDocument6 pagesIGCSE Unit 3 NotesmayurbuddyNo ratings yet
- Fluorescence SpectrosDocument36 pagesFluorescence SpectrosRakesh Bijarnia Chaudhary0% (1)
- Week 16Document14 pagesWeek 16Harry Jhonley LabisteNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Metode X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Dan Fourier Transform Infra Red (FTIR) Untuk Analisis Unsur Kalium (K) Dan Kalsium (Ca) Dalam Sagu Asal Luwu TimurDocument2 pagesAplikasi Metode X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) Dan Fourier Transform Infra Red (FTIR) Untuk Analisis Unsur Kalium (K) Dan Kalsium (Ca) Dalam Sagu Asal Luwu TimurKrappionNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Radiation: Visible LightDocument39 pagesElectromagnetic Radiation: Visible LightgeethaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Emission SpectrometryDocument11 pagesAtomic Emission SpectrometrySubhash DhungelNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument28 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureANITA YADAVNo ratings yet
- 2018 G12 Chemistry E Clor PDFDocument403 pages2018 G12 Chemistry E Clor PDFMaximillion AnthonyNo ratings yet
- AAS Lab ManualDocument3 pagesAAS Lab ManualJC100% (1)
- Module 3Document19 pagesModule 3Ratay EvelynNo ratings yet
- OCR Chemistry A: Isotopic AbundanceDocument3 pagesOCR Chemistry A: Isotopic AbundanceMasih KhanNo ratings yet