Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Body
Uploaded by
LeticiaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Body
Uploaded by
LeticiaCopyright:
Available Formats
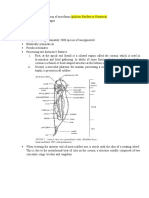
The human body is the structure of a human being.
It is composed of many different types of
cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis
and the viability of the human body. It comprises a head, hair, neck, trunk (which includes the
thorax and abdomen), arms and hands, legs and feet. The study of the human body involves
anatomy, physiology, histology and embryology. The body varies anatomically in known
ways. Physiology focuses on the systems and organs of the human body and their functions.
Many systems and mechanisms interact in order to maintain homeostasis, with safe levels of
substances such as sugar and oxygen in the blood. The body is studied by health
professionals, physiologists, anatomists, and by artists to assist them in their work.
The human body is composed of elements including hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, calcium and
[1]
phosphorus. These elements reside in trillions of cells and non-cellular components of the
body.
The adult male body is about 60% water for a total water content of some 42 litres (9.2 imp
gal; 11 US gal). This is made up of about 19 litres (4.2 imp gal; 5.0 US gal) of extracellular fluid
including about 3.2 litres (0.70 imp gal; 0.85 US gal) of blood plasma and about 8.4 litres (1.8
imp gal; 2.2 US gal) of interstitial fluid, and about 23 litres (5.1 imp gal; 6.1 US gal) of fluid
[2]
inside cells. The content, acidity and composition of the water inside and outside cells is
carefully maintained. The main electrolytes in body water outside cells are sodium and
[3]
chloride, whereas within cells it is potassium and other phosphates.
The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or extant). Clades
are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect
evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed They are
an important food source for predators and part of the food web dynamics of many of the world's
ecosystems. The skin is semi-permeable, making them susceptible to dehydration, so they either
live in moist places or have special adaptations to deal with dry habitats. Frogs produce a wide
range of vocalizations, particularly in their breeding season, and exhibit many different kinds of
complex behaviors to attract mates, to fend off predators and to generally survive.
Credits: Wikipedia
You might also like
- Hair Cutting Power PointDocument34 pagesHair Cutting Power Pointbarbershop ali100% (1)
- Biodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesDocument8 pagesBiodiversity and Conservation A Level NotesNaseer SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Course TDocument5 pagesCourse TBOBO GamingNo ratings yet
- Activity Animal KingdomDocument8 pagesActivity Animal KingdomGerald Agacid BangeroNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Chapter IDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology - Chapter IG.k. Vinnan Rao100% (2)
- Muscle Strength and Muscle ActionDocument54 pagesMuscle Strength and Muscle ActionFarrukh Shahzad100% (6)
- Biology and EcologyDocument5 pagesBiology and EcologykarennNo ratings yet
- Work Out ProgramDocument3 pagesWork Out ProgramNathanNo ratings yet
- 01 - NOA - E.D.S MCQsDocument21 pages01 - NOA - E.D.S MCQsAwais BhattiNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Status Consolidation Form - AutomatedDocument4 pagesNutritional Status Consolidation Form - AutomatedXhan JieNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Reproductive SystemDocument32 pagesScience 10 - Reproductive SystemHanabi Scarlet ShadowNo ratings yet
- Arnold WorkoutDocument2 pagesArnold Workoutjavitejano100% (1)
- SkeletalDocument29 pagesSkeletalROMNICK NILMAO100% (1)
- (The Natural History of The Crustacea) Les Watling, Martin Thiel (Eds.) - Functional Morphology and Diversity. 1-Oxford University Press (2013)Document515 pages(The Natural History of The Crustacea) Les Watling, Martin Thiel (Eds.) - Functional Morphology and Diversity. 1-Oxford University Press (2013)Yamaly Barragán MarínNo ratings yet
- Kolisko, Twelve Groups of AnimalsDocument13 pagesKolisko, Twelve Groups of AnimalsBruno Morin50% (2)
- Grade 9 Science ModuleDocument27 pagesGrade 9 Science Modulegrace cordita0% (2)
- Slow and Steady - A Comprehensive Guide To SnailsDocument8 pagesSlow and Steady - A Comprehensive Guide To SnailsDavid EliasNo ratings yet
- Arthropoda Characteristics: Circulatory SystemDocument15 pagesArthropoda Characteristics: Circulatory SystemBello AjetayoNo ratings yet
- Animal: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia For Other Uses, See - "Animalia" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeDocument4 pagesAnimal: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia For Other Uses, See - "Animalia" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, SeeGeorgeNo ratings yet
- How Plant and Animal Adapt To Aquatic HabitatDocument16 pagesHow Plant and Animal Adapt To Aquatic HabitatCharles Amaechi100% (2)
- Study QuestionDocument24 pagesStudy QuestionEbookslatinosEbookslatinosNo ratings yet
- Lecture12 AnimalDiversity p1Document34 pagesLecture12 AnimalDiversity p1Jacky RodriguezNo ratings yet
- An Introductionto MammalsDocument10 pagesAn Introductionto MammalsRIZKI MAHESA IPBNo ratings yet
- CordovillaMark King Joseph P - MODULE8 - ZOOLOGYDocument2 pagesCordovillaMark King Joseph P - MODULE8 - ZOOLOGYMark king Joseph CordovillaNo ratings yet
- Arthropods: Arthropods Are Invertebrate Animals Having An Exoskeleton, A Segmented Body, and PairedDocument10 pagesArthropods: Arthropods Are Invertebrate Animals Having An Exoskeleton, A Segmented Body, and Pairedpkkalai112No ratings yet
- An Introductionto MammalsDocument10 pagesAn Introductionto MammalsRizza PearlNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2565-04-25 at 09.03.21Document34 pagesScreenshot 2565-04-25 at 09.03.21min nbNo ratings yet
- ZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionDocument32 pagesZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionAdwale oluwatobi festusNo ratings yet
- Ls1 Final Study GuideDocument7 pagesLs1 Final Study GuideMinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- Animal Diversity NOTE - 111104Document5 pagesAnimal Diversity NOTE - 111104Mohammed KasimNo ratings yet
- Animal: OrganismDocument22 pagesAnimal: OrganismWraith WrathNo ratings yet
- Definition and Classification, Exemplification Text, Arado, BrettniaDocument5 pagesDefinition and Classification, Exemplification Text, Arado, BrettniaShiela JoyNo ratings yet
- Ciclatory Systems of Different OrganismsDocument5 pagesCiclatory Systems of Different OrganismsSekhar ReddyNo ratings yet
- ZoologyDocument7 pagesZoologySandra Nicole RiveraNo ratings yet
- Animals Kinds and ClassificationsDocument2 pagesAnimals Kinds and ClassificationsleslieayzNo ratings yet
- BZ Lab 5Document8 pagesBZ Lab 5Alexa Jean D. HonrejasNo ratings yet
- Unit:1 Kingdom Protista General Characters and Classification Upto Classes Locomotory Organelles and Locomotion in ProtozoaDocument34 pagesUnit:1 Kingdom Protista General Characters and Classification Upto Classes Locomotory Organelles and Locomotion in ProtozoaEgga AndiniNo ratings yet
- Animals - Use As Example OnlyDocument4 pagesAnimals - Use As Example OnlyKiana DouglasNo ratings yet
- Final Notes of ZoologyDocument63 pagesFinal Notes of ZoologyASIF KHANNo ratings yet
- Platyhelminthes and MolluscaDocument7 pagesPlatyhelminthes and MolluscaIsnaeni RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- MasteringBio Exercise-NotesDocument10 pagesMasteringBio Exercise-Notesavuong3No ratings yet
- Writing AssignmentDocument6 pagesWriting Assignmentapi-241828006100% (1)
- Unit 7 Activities - Animals Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesUnit 7 Activities - Animals Structure and FunctionOriana RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes 1Document9 pagesZoology Notes 1Alvarez, Chesna LoiseNo ratings yet
- AnimalsDocument11 pagesAnimalsAneesvk VkNo ratings yet
- Simion Ana-MariaDocument8 pagesSimion Ana-MariaAna-Maria SimionNo ratings yet
- Pyhylum Chordata: "An Overview of Chordates"Document10 pagesPyhylum Chordata: "An Overview of Chordates"shriyans4269No ratings yet
- BOL 2006 Biology NotesDocument35 pagesBOL 2006 Biology NotesSteven XuNo ratings yet
- By: Raymund RieglDocument22 pagesBy: Raymund RieglAl-ameen OlawunmiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Animals-2Document23 pagesCharacteristics of Animals-2api-297087367No ratings yet
- Rotifera 2Document5 pagesRotifera 2YAN TINGNo ratings yet
- Aquarium ClassificationDocument10 pagesAquarium ClassificationPrincess DarishanaNo ratings yet
- Main Menu: Create Account Log inDocument39 pagesMain Menu: Create Account Log inKESATRIA JAKARTANo ratings yet
- ANATOMI HEWAN VERTEBRATA - AmaliaDocument13 pagesANATOMI HEWAN VERTEBRATA - AmaliaDodi SaputraNo ratings yet
- SZL 201Document182 pagesSZL 201Charity100% (1)
- Can Axolotls Go On LandDocument5 pagesCan Axolotls Go On LandJavad AhmadiNo ratings yet
- COL3Document11 pagesCOL3Clefford CorporalNo ratings yet
- ArthropodDocument15 pagesArthropodVidhyaNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Function of Animal Cells and Cell ModificationDocument47 pagesBio1 Function of Animal Cells and Cell Modificationdanzkietanaleon10No ratings yet
- Crustacean As BioindicatorDocument34 pagesCrustacean As BioindicatorOrmphipod WongkamhaengNo ratings yet
- Diversity and General Characteristics of Animals UpdatedDocument8 pagesDiversity and General Characteristics of Animals UpdatedDavid AsuquoNo ratings yet
- AdrwaDocument19 pagesAdrwasnoopyboyNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document5 pagesSession 3KESHAVA MURTHY M VNo ratings yet
- Module Q.2 Els 2Document3 pagesModule Q.2 Els 2altheaveniceholanda02No ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University IslamabadDocument16 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University IslamabadAbdullah NagraNo ratings yet
- REVIEW Year 6 1st T PDFDocument25 pagesREVIEW Year 6 1st T PDFizaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: BiologyDocument9 pagesAnimal Kingdom: BiologyHarsh SarafNo ratings yet
- CH 7.2 Plant Kingdom Diversities 1 3Document16 pagesCH 7.2 Plant Kingdom Diversities 1 3Shreyash Mitra Educational PurposeNo ratings yet
- Science: 3. Ecology - (FromDocument4 pagesScience: 3. Ecology - (From[AP-STUDENT] Leona Charlize De ChavezNo ratings yet
- SovietDocument1 pageSovietLeticiaNo ratings yet
- Security CouncilDocument1 pageSecurity CouncilLeticiaNo ratings yet
- Bantan BTSDocument1 pageBantan BTSLeticiaNo ratings yet
- AnacardiaceaeDocument1 pageAnacardiaceaeLeticiaNo ratings yet
- Mango TreeDocument1 pageMango TreeLeticiaNo ratings yet
- HairDocument1 pageHairLeticiaNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument1 pageCellsLeticiaNo ratings yet
- FrogDocument1 pageFrogLeticiaNo ratings yet
- Mammals GroupDocument1 pageMammals GroupLeticiaNo ratings yet
- SubarticDocument1 pageSubarticLeticiaNo ratings yet
- CladeDocument1 pageCladeLeticiaNo ratings yet
- CarnivoreDocument2 pagesCarnivoreLeticiaNo ratings yet
- Caplan, Michael J-Reference Module in Biomedical Research-Elsevier (2014)Document17 pagesCaplan, Michael J-Reference Module in Biomedical Research-Elsevier (2014)Muhammad IkbarNo ratings yet
- Week1. Reflectionon VMGO: Week 4-6 Project Plan For Pajama ShirtDocument4 pagesWeek1. Reflectionon VMGO: Week 4-6 Project Plan For Pajama ShirtVINCYL JANE QUINESNo ratings yet
- Voluntary Muscle: Muscle We Can Control It: The Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesVoluntary Muscle: Muscle We Can Control It: The Muscular SystemAbrar HussamNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 ECG BiopacDocument6 pagesLesson 5 ECG BiopacJavier VeintimillaNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Major Organs of The BodyDocument3 pagesHuman Anatomy Major Organs of The BodyKert trocioNo ratings yet
- Science Examination NotesDocument2 pagesScience Examination NotesGilda Genive AriolaNo ratings yet
- Science of Human MovementDocument2 pagesScience of Human MovementSweso KunNo ratings yet
- Body Fat Percentage Chart For ChildrenDocument3 pagesBody Fat Percentage Chart For ChildrenLouis RoderosNo ratings yet
- Psychological Elements in YogaDocument156 pagesPsychological Elements in YogaomersonNo ratings yet
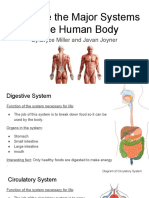
- Javan and Bryces Human Body ProjectDocument9 pagesJavan and Bryces Human Body Projectapi-347432027No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Mcas Review Question SetDocument13 pagesGrade 8 Mcas Review Question Setapi-294483847No ratings yet
- Mass Update Shipping Info Mdhbrother 04-09-2020 1599153621714Document131 pagesMass Update Shipping Info Mdhbrother 04-09-2020 1599153621714MDH BrotherNo ratings yet
- Mark Pretorius - Meta Assessment of Music Tones (Kybalion On Vibration)Document9 pagesMark Pretorius - Meta Assessment of Music Tones (Kybalion On Vibration)WalkinLANo ratings yet
- PR Brand Email List Sheet1Document4 pagesPR Brand Email List Sheet196cmpwrgrrNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W2Document10 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W2Sheena Claire dela Pe?No ratings yet
- 1.introduction, The General Description of OsteologyDocument47 pages1.introduction, The General Description of OsteologyRioNo ratings yet
- 10A 1 Units 2,3Document35 pages10A 1 Units 2,3Hưng LêNo ratings yet
- What Is HemmingDocument4 pagesWhat Is Hemmingsureshparekh023No ratings yet
- American Fashion Through The DecadesDocument7 pagesAmerican Fashion Through The DecadesVanessa Bolotaolo OperianoNo ratings yet
- Cells Are The Starting PointDocument2 pagesCells Are The Starting PointDONABEL ESPANONo ratings yet