Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre Cal Reviewer
Uploaded by
Zelian ShcwienOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre Cal Reviewer
Uploaded by
Zelian ShcwienCopyright:
Available Formats
Where the (h, k) are the coordinates of the
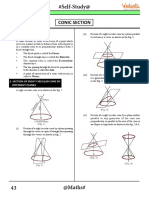
THE CONIC SECTIONS circle and r as the radius. While the x and
The graph of an equation formed by a y are the variables of the equation of the
second degree order or also called circle.
Quadratic Equation, The General Form of Circle
Ax2 + Bxy + Cy2 +Dx + Ey + F = 0.
From the simplification of the circle’s
This equation is graphically represented standard form, we can obtain the general
by a curve or most popularly known as equation of the circle which expressed in a
Conic such as Circle, Ellipse, Parabola form of
and Hyperbola.
A Conic section is defined as a set of
curves formed from dividing or cutting a
right circular cone of two nappes with a
plane where the Ax2 and Cy2 are the quadratic
terms : A and C are always equal. While
the Dx and Ey are the linear term and the
F is any constant.
If the value of radius isn’t given, apply the
DISTANCE FORMULA
CIRCLE
- is a set of all points that are equidistant PARABOLA
from a fixed point called “center”
- is a set of all points that are equidistant
The fixed point is called Center which is from a fixed point called focus and from a
located inside the circle, while the fixed fixed line called directrix
distance is the radius.
Equations:
To clarify, we will have the coordinates of 1. x^2 = 4ay
the center as (h, k) and the points 2. (x-h)^2 = 4a (y-k)
coordinates are (x, y). 3. y^2 = 4ay
The standard form of a circle is 4. (y-k)^2 = 4a (x-h)
expressed by the equation,
PARTS OF A PARABOLA
1. Vertex (V) - It is the main point of the
parabola which lies at the middle portion
of the curve. It is also the midpoint of the
fixed point of the curve and the given line.
2. Focus (F) - It is another important point
of the parabola that is located inside of the
curve. The focus is also known as the
fixed point of the parabola.
3. Focal Distance (a) - This is the length
of space from the focus to the vertex. It is
also the distance between the directrix line
OPENING OF A PARABOLA
and the vertex.
If x^2 is present ;
4. Directrix line (D.L) -It is a line which is
– upward (+)4a
outside and parallel to the parabola curve.
– downward (-)4a
5. Latus Rectum (LR) - This is a chord
If y^2 is present ;
that is parallel to the directrix line and
– to the right (+)4a
intersecting the parabola at the point of
– to the left (-)4a
focus. The end points of the latus rectum
are defined as R1 and R2. The length of
the latus rectum is always twice of the
focal distance. The half of the latus rectum
is called the semilatus rectum.
ELLIPSES
6. Axis of Parabola - It is also known as
It is a conic section whose 1 < e < 0.
axis of symmetry because it is the line that
Ellipse is formed by a locus of points
divides the parabola into two equal parts.
whose sum of the distance from the two
The axis of the parabola passes through
fixed points is constant (2a).
the points of Vertex and Focus; and this
line is perpendicular to the diretrix and the This is the second type of conic section;
latus rectum. unlike the parabola ellipse is a closed
figure. Circle is a special type of ellipse,
7. Eccentricity (e) - This is the ratio of the
with eccentricity value closer to zero. The
distances from a fixed point to one of the
shape of the ellipse is elongated sphere
points of the curve and from this point to
similar to the shape of the orbit of the
the directrix line. Eccentricity value
earth in the solar system.
expresses the degree of roundness of the
given curve. For a parabola, eccentricity
value is always equal to 1.
PARTS OF AN ELLIPSE
1. Center - It is the midpoint inside of the
ellipse curve and denoted by the symbol
C.
2. Vertices - These are the main points of 4.The sum of the distances from any point
the curve expressed by the symbols V. on the ellipse to focus is constant and
equal to the length of the major axis.
3. Foci - These are the fixed points of the
Ellipse and it is the plural form of focus.
This point is located between the center
and the vertices. They are represented by
the symbols F1 and F2.
4. Directrix lines - They are also called
directrices. These are the lines which are
located outside of the ellipse.
5. Minor Axis - It divides the curve into
two symmetrical parts. The end points of
this axis are called intercepts. The length
of the minor axis is 2b.
6. Principal Axis - It is another
symmetrical axis in the ellipse but always
longer in length compare to minor axis.
The endpoints of the Principal or major
axis are the vertices. The length of this
axis is 2a.
7. Focal Distance - This is the distance
between the one of the focus to the
Center. It is denoted by the symbol c.
8. Latera Recta - it is the plural form of
the latus rectum. The length of the lateral
rectum is 2b^2/a
9. Eccentricity - This is the ratio of the
distances from the fixed point to the point
P and from point P to the directrix line.
The value of the eccentricity can be
obtained from the formula of c/a
PROPERTY OF AN ELLIPSE
1.It has closed and symmetrical figure.
2.It has two sets of foci, directrices, latus
recta and symmetrical axes.
3.It has two vertices and two co-vertices.
axes and the asymptotic line of hyperbola
intersects.
2. Vertex (V) – It is the main point of the
hyperbola. There are two vertices in this
curve. This point is located nearer to the
center of the curve than to the foci.
3. Foci (F) – These are the points located
inside of the hyperbola. The foci are
located next to the vertices .
4. Transverse Axis – It is the line that
joining the two vertices and passes
through the center and foci. This is the
counter part of the major axis in the ellipse
and it length measures as 2a.
5. Conjugate Axis – This is a shorter line
that connects the points b1 and b2. It also
passes through the center of the
hyperbola.
6. Directrix lines - These are the lines
that is drawn in between of the curves of
the hyperbola and parallel to the curves.
7. Asymptotes lines - These are the two
lines that intersect the center of the
hyperbola and they are asymptotic to the
two curves.
8. Latera Recta – These are chords that
HYPERBOLA pass through the foci.
This is the last type of conic section. It is
defined as a locus of points such that the
difference of the distances from any points GRAPH OF HYPERBOLA
of the curve to the fixed points is constant.
Hyperbola is composed of pairs of
parabolas whose openings are in opposite
direction and its shape is dependent on
the value of eccentricity which is always
greater than one (e> 1).
PARTS OF HYPERBOLA
1. Center (C) – It is the point in the middle
of the hyperbola. This is where the two
You might also like
- 11 Maths Notes 11 Conic SectionsDocument3 pages11 Maths Notes 11 Conic SectionsamitNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENT TYPES of Conics Mark - pptx01.Pptx123456Document9 pagesDIFFERENT TYPES of Conics Mark - pptx01.Pptx123456Mark Bryan TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Maths ProjectDocument31 pagesMaths ProjectKushagra VermaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Revision Notes Chapter-11 Conic SectionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Revision Notes Chapter-11 Conic SectionsmgfNo ratings yet
- Terminologies in PRE CALCULUSDocument4 pagesTerminologies in PRE CALCULUSRehel AlegreNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument1 pagePre CalDavis PasuquinNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project Math ProjectDocument28 pagesInvestigatory Project Math ProjectYesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal Reviewer in CTDocument3 pagesPre Cal Reviewer in CTGysel BalingitNo ratings yet
- Precal HO4Document6 pagesPrecal HO4eloiza garciaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections PDFDocument95 pagesConic Sections PDFManoj Baishya100% (1)
- Conic SectionsDocument11 pagesConic SectionsSamantha Marie DiabocoNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument5 pagesPre CalculusEd JayNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument2 pagesPre CalculusVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Conic SectionsDocument16 pages5.1 Conic Sectionsapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Intro To ConicsDocument8 pagesIntro To ConicsJoshua Andrew Po BatonghinogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 37 - ConicsDocument49 pagesLesson 37 - ConicsShaineNo ratings yet
- ELLIPSEDocument29 pagesELLIPSEgachaacc335No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Conic Section and Its ApplicationDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Conic Section and Its ApplicationSean Yares100% (1)
- Lecture 3 Conic Section Part 2Document32 pagesLecture 3 Conic Section Part 2Jerwin OliverosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sections and CirclesJanexx DioNo ratings yet
- EllipseDocument2 pagesEllipsetishvill18No ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document1 pageChapter 11DarkstalkerNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal 1st Semester (Midterm) - ReviewerDocument5 pagesPre Cal 1st Semester (Midterm) - ReviewerFrancine Chalcy CanlasNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review in Pre CalDocument3 pagesPointers To Review in Pre CalKristine Valerie UpodNo ratings yet
- Math9 2012 05 13 File3Document42 pagesMath9 2012 05 13 File3HARSHIT sharmaNo ratings yet
- Analytic GeometryDocument10 pagesAnalytic GeometryWengie Kay San InfelisNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus Week 1 Learning MaterialDocument6 pagesPre Calculus Week 1 Learning MaterialPrince Josel Ezekiel MonteroNo ratings yet
- Chapter ViDocument23 pagesChapter Vilj6244866No ratings yet
- Conic Section - WikipediaDocument24 pagesConic Section - WikipediaAustin ZilkerNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument14 pagesParabolaMary Jane Asuncion PascualNo ratings yet
- Ellipse 1Document31 pagesEllipse 1REBY ARANZONo ratings yet
- What Is Circle? What Is Circle?Document2 pagesWhat Is Circle? What Is Circle?Alexa Jill MirandaNo ratings yet
- Advance Write UpDocument15 pagesAdvance Write UpQuenlay KP WangchukkNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal Reviewer Conic Sections (Conics) Properties of A CircleDocument3 pagesPre-Cal Reviewer Conic Sections (Conics) Properties of A CircleHSeuji LspONo ratings yet
- Learners Packet in Precalculus: Prepared By: Ma. Cecilia A. Andrada Trece Martires City Senior High SchoolDocument14 pagesLearners Packet in Precalculus: Prepared By: Ma. Cecilia A. Andrada Trece Martires City Senior High SchoolKyro KlinxNo ratings yet
- MathDocument16 pagesMathPATRICIA NICOLE DIZONNo ratings yet
- Conic Section: MATH-002 Dr. Farhana ShaheenDocument30 pagesConic Section: MATH-002 Dr. Farhana ShaheensivabathyNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus: Lesson 1: Knowing The Conic SectionsDocument33 pagesPre Calculus: Lesson 1: Knowing The Conic SectionsGENEEN LOUISE F. GELVOLEONo ratings yet
- Eloisa Marie R. Valiente STEM 11 - Hypatia: Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument7 pagesEloisa Marie R. Valiente STEM 11 - Hypatia: Introduction To Conic SectionsAuoei Thoth SjvourNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola - WikipediaDocument115 pagesHyperbola - WikipediaRishabNo ratings yet
- Ellipse (Definition, Equation, Properties, Eccentricity, Formulas)Document10 pagesEllipse (Definition, Equation, Properties, Eccentricity, Formulas)Anwar AftabNo ratings yet
- PRE-CALCULUS - MODULE - Week 3Document16 pagesPRE-CALCULUS - MODULE - Week 3Azur LaneNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections NotesDocument7 pagesConic Sections Notesbavithaprasanthi27No ratings yet
- Theorems of Central Angles, Arcs and Chords Distance Between Two Points Midpoint FormulaDocument3 pagesTheorems of Central Angles, Arcs and Chords Distance Between Two Points Midpoint FormulaShella VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4-5 Curve-1Document28 pagesLecture-4-5 Curve-1nameNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument38 pagesHyperbolaMarineth MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Glass 15 Car Photes Part ThrityDocument30 pagesGlass 15 Car Photes Part ThrityAbcNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionRiza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionJohn Anthony Bersabe ChavezNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesConic SectionsAldrin PabloNo ratings yet
- Conic-Sections Ellipse Group1 Malaguit (Edited)Document29 pagesConic-Sections Ellipse Group1 Malaguit (Edited)Jhoana Marie EugenioNo ratings yet
- Parabola (Theory)Document8 pagesParabola (Theory)The Champion100% (1)
- Calculus IIDocument51 pagesCalculus IIJessy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Torres-PT1-Module-Pre - CalculusDocument38 pagesTorres-PT1-Module-Pre - CalculusKing TorresNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument20 pagesCoordinate GeometryMaisah BhaNo ratings yet
- Ellipse 1Document24 pagesEllipse 1REBY ARANZONo ratings yet
- Conics: Top of FormDocument13 pagesConics: Top of FormRichard Canar PerezNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument13 pagesHyperbolaSyed MuzammilNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Project On Conic Sections by DivyaDocument39 pagesMathematics Project On Conic Sections by DivyaDivya72% (25)
- Cell Division: MitosisDocument52 pagesCell Division: MitosisZelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Term Paper: UcspolDocument10 pagesTerm Paper: UcspolZelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis 29Document52 pagesCell Division Mitosis 29Zelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Reviewer SHS Pe2Document2 pagesReviewer SHS Pe2Zelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Research ReviewerDocument8 pagesResearch ReviewerZelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Trig MsDocument33 pagesTrig MsHappybabyNo ratings yet
- Conics and ConvexityDocument7 pagesConics and ConvexityTim PenNo ratings yet
- 2003 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 5-7Document24 pages2003 KS3 Maths - Paper 1 - Level 5-7Wong Kah Kei JoyceNo ratings yet
- Csec Mathematics MC January 2020 P1 SolutionsDocument15 pagesCsec Mathematics MC January 2020 P1 SolutionsDAndre WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 Bee20303 QuestionDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 Bee20303 Questionnikhaziqhazimi5080No ratings yet
- 3rd Quarterly Exam in MATH 8Document3 pages3rd Quarterly Exam in MATH 8NORMAN BARDELASNo ratings yet
- Xii Maths Activity File (Term-1) 2023-24 CRPF School, Rohini, DelhiDocument15 pagesXii Maths Activity File (Term-1) 2023-24 CRPF School, Rohini, Delhivatitara64No ratings yet
- Properties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Let's Check Your Understanding! Grade 5 MathematicsDocument28 pagesProperties of Triangles and Quadrilaterals: Let's Check Your Understanding! Grade 5 MathematicsAnggia PramithasariNo ratings yet
- AIME Problem SetDocument3 pagesAIME Problem SetEugene ChenNo ratings yet
- Geometry Regents ReviewDocument15 pagesGeometry Regents Reviewapi-277841659No ratings yet
- Kami Export - TestBooklet PDFDocument5 pagesKami Export - TestBooklet PDFJen Harng LawNo ratings yet
- DatasufficiencyDocument62 pagesDatasufficiencyrajatNo ratings yet
- Gcse Equivalent Foundation Mathematics Calculator Paper: Equivalency TestingDocument28 pagesGcse Equivalent Foundation Mathematics Calculator Paper: Equivalency TestingSmita NagNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper - TRIGONOMETRYDocument5 pagesLesson Proper - TRIGONOMETRYMontenegro Roi Vincent100% (1)
- Evaluation ExamDocument3 pagesEvaluation ExamEmileandro Perito QuindiaganNo ratings yet
- Proportions With Perimeters, Areas and VolumesDocument4 pagesProportions With Perimeters, Areas and VolumesJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Areas Related To Circles PDFDocument40 pagesChapter 12 Areas Related To Circles PDFDeepakNo ratings yet
- Junior Inter Mathematics Model PaperDocument4 pagesJunior Inter Mathematics Model Paperkk11091079No ratings yet
- Centre of Gravity of A QuadrilateralDocument2 pagesCentre of Gravity of A Quadrilateraltim penttilaNo ratings yet
- Aptitude Question and Answers PDFDocument10 pagesAptitude Question and Answers PDFNth NgNo ratings yet
- Complex No. ArihantDocument21 pagesComplex No. Arihantrahul0% (1)
- Vectors (Add Math) Unsolved PDFDocument14 pagesVectors (Add Math) Unsolved PDFSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Geometry Handout #6 Answers and SolutionsDocument9 pagesGeometry Handout #6 Answers and SolutionsWalker KroubalkianNo ratings yet
- 1 7+Card+Sort+Answer+KeyDocument4 pages1 7+Card+Sort+Answer+Keyfeng yanNo ratings yet
- VolumeDocument28 pagesVolumeDhianNurulIstiqomahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Limit of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument5 pagesLesson 2 Limit of Trigonometric FunctionsJunior LifeNo ratings yet
- The Contest Problem Book VII American Mathematics Competitions 1995 2000Document199 pagesThe Contest Problem Book VII American Mathematics Competitions 1995 2000kodalidhana100% (16)
- Inscribed Angles and Intercepted ArcsDocument6 pagesInscribed Angles and Intercepted ArcsReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- Pre Half Yearly STD X MathsDocument6 pagesPre Half Yearly STD X MathsnaeblahblahNo ratings yet
- Curve SimpleDocument10 pagesCurve SimpleBrian Rey L. AbingNo ratings yet