Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
DarkstalkerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 11
Uploaded by
DarkstalkerCopyright:
Available Formats
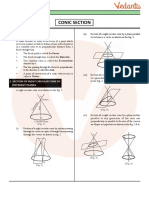
Mind map : learning made simple Chapter - 11
• An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane, the sum of whose distances from •A parabola is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a
two fixed points in the plane is constant. fixed line and a fixed point in the plane. Fixed line is called ‘directrix’ of
• The two fixed points are called the ‘foci’ of the ellipse. parabola. Fixed point F is called the ‘focus’. A line through focus &
• The midpoint of line segment joining foci is called the ‘centre’ of the ellipse. perpendicular to directrix is called ‘axis’. Point of intersection of parabola
• The line segment through the foci of the ellipse is called’ major axis’. with axis is called ‘vertex’.
• The line segment through centre & perpendicular to major axis is called •The equation of parabola with focus at (a, 0), a > 0 and directrix
minor axis. x= −a is y2=4ax, where 4a is the length of the latus rectum
• The end point of the major axis are called the vertices of the ellipse. Eg: Find the equation of the parabola with vertex at (0, 0) and focus at (0, 2).
• The equation of ellipse with ‘foci’ on the x-axis is xa + yb = 1.
2 2
2 2 Sol: Since, vertex is at (0, 0) and focus is at (0, 2) which lies on y-axis, the
• Length of the latus rectum of the ellipse xa + yb = 1 is 2ba
2 2
2 y-axis is the axis of parabola. Therefore, equation of the parabola is of
Ellipse
2 2
the form x2 = 4ay. Thus we have x2 = 4(2)y
• The eccentricity of an ellipse is the ratio of distances fromc centre of ellipse to i.e., x2 = 8y
one of foci and to one of the vertices of ellipse i.e., e=
a
Hyp
erbol
a Conic Sections Circles, ellipses, parabolas and hyperbolas are known as conic sections
because they can be obtained as intersections of plane with a double
napped right circular cone.
• A hyperbola is the set of all points in a plane, the difference of whose
distances from two fixed points in the plane is a constant.
• x2 y2
The equation of a hyperbola with foci on the x-axis is 2 − 2 = 1
a b
• The two fixed points are called the ‘foci’ of the hyperbola. A circle is a set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from
• The mid-point of the line segment joining the foci is called the ‘centre’ of a fixed point in the plane. The fixed point is called the ‘centre’ of the
the hyperbola. circle and the distance from the centre to a point on the circle is called
• The line through the foci is called ‘transverse axis’. the ‘radius’ of the circle.
• Line through centre and perpendicular to transverse axis is called The equation of a circle with centre (h, k) and the radius r is
‘conjugate axis’.
(x − h) + ( y − k )
2 2
= r2
• Points at which hyperbola intersects transversex axisyare called2b‘vertices’.
2 2 2
Eg: Find the equation of the circle with centre (−3, 2) and radius 4.
• Length of the latus rectum of the hyperbola : a − b = 1 is a
2 2 Sol: Here, h = − 3, k = 2 and r = 4
• The eccentricity of a hyperbola is the ratio of the distances from the centre Therefore, the equation of the required circle is ( x + 3 )2 + ( y − 2 )2 = 16
of the hyperbola to one of the foci and to one of the vertices of the hyperbola.
You might also like
- 5.1 Conic SectionsDocument16 pages5.1 Conic Sectionsapi-26570979No ratings yet
- Lesson 2.4-Ellipse PDFDocument28 pagesLesson 2.4-Ellipse PDFChelsea RoqueNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document14 pagesGroup 4alethuaNo ratings yet
- Intro to Conic Sections and CirclesDocument7 pagesIntro to Conic Sections and Circlesha hakdogNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.5-HyperbolaDocument15 pagesLesson 2.5-HyperbolaChelsea RoqueNo ratings yet
- Pre-Cal Reviewer Conic Sections (Conics) Properties of A CircleDocument3 pagesPre-Cal Reviewer Conic Sections (Conics) Properties of A CircleHSeuji LspONo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument16 pagesHYPERBOLAJenie SoncioNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections NotesDocument7 pagesConic Sections Notesbavithaprasanthi27No ratings yet
- PRECAL_LESSON 1Document6 pagesPRECAL_LESSON 1alayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument51 pagesLesson1 Introduction To Conic SectionsKrissa Mae PenalosaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PrecalDocument3 pagesReviewer PrecalErwin Ranel ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Kalkulus 2_Pertemuan ke 7Document71 pagesKalkulus 2_Pertemuan ke 7muhammadsyarifgtg47No ratings yet
- Different Types of Polar CurvesDocument17 pagesDifferent Types of Polar CurvesJade ConsolacionNo ratings yet
- CH 10. Conic Section (Math +1)Document51 pagesCH 10. Conic Section (Math +1)Dinesh BabuNo ratings yet
- Hyperbola (Theory) Module-3Document9 pagesHyperbola (Theory) Module-3Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Project Math ProjectDocument28 pagesInvestigatory Project Math ProjectYesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections PDFDocument95 pagesConic Sections PDFManoj Baishya100% (1)
- Glass 15 Car Photes Part ThrityDocument30 pagesGlass 15 Car Photes Part ThrityAbcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Conic Section and Its ApplicationDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Conic Section and Its ApplicationSean Yares100% (1)
- Four conic sections explainedDocument20 pagesFour conic sections explainedWendell ReyesNo ratings yet
- Conic-Sections Ellipse Group1 Malaguit (Edited)Document29 pagesConic-Sections Ellipse Group1 Malaguit (Edited)Jhoana Marie EugenioNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLADocument10 pagesHYPERBOLAChazz RensNo ratings yet
- Parabola PDF SK GOYAL - CompressedDocument97 pagesParabola PDF SK GOYAL - CompressedDarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Week 1: Analytic Geometry and Conic SectionsDocument49 pagesWeek 1: Analytic Geometry and Conic SectionsPerfect BeanNo ratings yet
- Simple CurveDocument2 pagesSimple CurvefillosheenaNo ratings yet
- 1004 753-762 PDFDocument10 pages1004 753-762 PDFGenivie EnesandoNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal ReviewerDocument5 pagesPre Cal ReviewerZelian ShcwienNo ratings yet
- Conic Section - WikipediaDocument24 pagesConic Section - WikipediaAustin ZilkerNo ratings yet
- SPLM Analytic Geometry Part 2Document85 pagesSPLM Analytic Geometry Part 2Joey TelinNo ratings yet
- TMK2023chap7 1Document19 pagesTMK2023chap7 1Miu MakriNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11Document5 pagesCONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument38 pagesHyperbolaMarineth MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Equation of Ellipse: Loci of Circle, Ellipse, Parabola and HyperbolaDocument17 pagesEquation of Ellipse: Loci of Circle, Ellipse, Parabola and HyperbolaIrene ChingNo ratings yet
- 14 Analytic Geometry (Conics)Document44 pages14 Analytic Geometry (Conics)Anonymous 5aPb088W100% (1)
- Introduction to Conic Sections - Parabolas, Hyperbolas, Ellipses, Circles, and MoreDocument7 pagesIntroduction to Conic Sections - Parabolas, Hyperbolas, Ellipses, Circles, and MoreAuoei Thoth SjvourNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionRiza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionJohn Anthony Bersabe ChavezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1a. Standard Equation of A CircleDocument5 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1a. Standard Equation of A CircleJarkos BarrilNo ratings yet
- HyperbolaDocument32 pagesHyperbolaDiane Mendez100% (1)
- Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sections and CirclesJanexx DioNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsDocument6 pagesA Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsPat ChuNo ratings yet
- MathDocument16 pagesMathPATRICIA NICOLE DIZONNo ratings yet
- 11 Maths Notes 11 Conic SectionsDocument3 pages11 Maths Notes 11 Conic SectionsamitNo ratings yet
- Feb 4 - 2Document10 pagesFeb 4 - 2MJ HidalgoNo ratings yet
- Conic Section - CircleDocument8 pagesConic Section - CircleAPngnbnNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument16 pagesConic SectionLovish GargNo ratings yet
- Intro To ConicsDocument8 pagesIntro To ConicsJoshua Andrew Po BatonghinogNo ratings yet
- Conic Section DefinitionDocument5 pagesConic Section DefinitionElyssamae PonceNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - STEM Pre-Calculus: Prepared By: Nikko Jay R. SenopeDocument27 pagesGrade 11 - STEM Pre-Calculus: Prepared By: Nikko Jay R. SenopeRalph obenaNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus EllipseDocument24 pagesPre Calculus EllipseKarl OliverosNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Revision Notes Chapter-11 Conic SectionsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Revision Notes Chapter-11 Conic SectionsmgfNo ratings yet
- PC Reviewer Q1Document4 pagesPC Reviewer Q1Tricia BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Ch 11. Conic SectionDocument7 pagesHsslive-Ch 11. Conic SectionRose martinNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections GuideDocument3 pagesConic Sections GuideGysel BalingitNo ratings yet
- Group 2 (Parabola)Document33 pagesGroup 2 (Parabola)krisgil ronquilloNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument58 pagesConic SectionNailah Sakinah100% (1)
- Conic Sections Equations and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesConic Sections Equations and ApplicationsDeniece RonquilloNo ratings yet
- HYPERBOLA L-V and VIDocument28 pagesHYPERBOLA L-V and VIShashwat PalNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus: Lesson 1.4: HyperbolasDocument21 pagesPre-Calculus: Lesson 1.4: HyperbolasSept Apple Lafuente-ZantuaNo ratings yet