Professional Documents
Culture Documents
10.soil Recent
Uploaded by
vsurender reddyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
10.soil Recent
Uploaded by
vsurender reddyCopyright:
Available Formats
10.
Soil Pollution
1. Define soil pollution.
A. Persistent toxic compounds, chemicals, salts, radioactive materials or disease
causing agents which have adverse effects on soil, to change the texture of soil and
effect on the quality of soil. This is called soil pollution or land pollution.
2. What is a medical waste? Why it is called hazardous waste? What is the safe
way to dispose medical waste?
A. (1) Medical waste is generally defined as solid waste which is released from
hospitals, clinics, research labs and biological productions.
(2) Medical waste which is corrosive, poison or flammable is called hazardous waste.
(3) Laboratory cultures and stocks, pathology waste, blood and items that possess
sharp points — such as needles and syringes require special handling and treatments.
(4) Exposure of infectious agents has been instances where discarded radioactivity
sources such as cobalt used in cancer treatment.
(5) Medical waste creates many problems and leads many ecological problems.
(6) They may have dangerous pathogens within them besides dangerous medicines
and injections.
(7) Treatment of medical waste constitutes disposal in land filling or other solid waste
sites.
(8) Treatment techniques such as incineration, sterilization chemical disinfection and
microwave, well as other methods.
(9) Recycling of radioactive sources which are used in cancer treatment into the commun; with
devasting effects.
3. Briefly describe soil pollution, its causes and methods of control.
A. (1) Soil pollution is caused by xenobiotic factors (manmade) chemicals or other alternation;
the natural soil environment.
(2) It is typically caused by industrial activity, agricultural chemicals or improper dispose| of
waste.
Causes:
(1) Application of pesticides and fertilizers indiscriminately.
(2) Over mining and tilling of soil.
(3) Oil and fuel dumping.
(4) Disposal of coal ash into the soil.
(5) Leaching from the landfills.
(6) Drainage of contaminants into the soil and water resources.
(7) Discharge of urine and faeces into the open areas.
Methods of control:
(1) Excavate soil and take it to a disposal sites away from ready pathways for human or
sensitive ecosystem contact.
(2) Aeration of soil at the contaminated sites.
(3) Thermal remediation by introduction of heat to raise sub surface temperatures sufficiently
high to volatile chemical contaminants out of the soil.
(4) Microbial decomposition of organic matter.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 1
(5) Decomposing of heavy metals by using plants called phyto remediation.
4. What are the three main physical properties of soil? What effects do this have
on the plants?
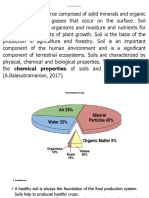
A. (1) Soil composition consist of minerals, organic matter, water and air.
(2) These components influences soil physical properties soil texture, structure and porosity.
(3) These properties regulate the air and water movement in the soil and thus soil ability to
function.
(4) Organic matter consists of nutrients which are necessary for plant growth.
(5) It improves water in filtration, decreases evaporation and increases water holding capacity:
(6) Soil microbes present in the organic matter helps to convert nutrients, create crumb, ideal for
cultivation.
(7) These microbes used for the balancing of natural state of soil.
(8) All of these properties closely associated with the properties of plant growth and crop
production.
5. What is pH? What is its range? What are the negative impacts if the pH of soil is too
low or too high?
A. (1) pH concentration of hydrogen ions present in the medium is known as pH.
(2) pH is used to indicate level of acidity or alkalinity of a soil.
(3) pH value of good soil lies from 5.5 to 7.5 below pH 7 termed as acidic soil and above pH 7
alkaline soil.
(4) Soil pH too low that soil is acidic in nature as result degradation of various substances
producing various acids in soil.
(5) Plant nutrients availability is strongly tied to the pH in soil.
(6) Availability of nutrients like N, K, Ca, Mg and S tends to decrease with acidity of soil and also
decrease the microbial activity.
(7) Soil pH ranges are higher than the normal ratio is called alkaline soil. It has high
concentration of soil solutions.
(8) This decreases absorption of nutrients; it leads to stunted growth of plant.
(9) If sodium is absorbed by plants in excess. It shows toxic effects. Chloride salts of alkaline
causes the death of plants.
6. What is soil fertility? What are the sources of soil fertility?
(1) Soil with good proportion of minerals, decomposed organic matter, air and water with good
microbial activity, associated with soil properties is called 'soil fertility’.
(2) Soil is the most important nutrient reservoir. Soil organisms transfer the nutrients from
organic matter to mineral stage of plants from the soil.
(3) Soil microbial biomass is composed of fungi. The fungi Mycorrhizae symbiosis with about
90% of all plant roots.
(4) The fungus explores the soil and brings back water as well as nutrients available to plants.
(5) It enlarges rooting zone of plants and improving soil structure.
(6) Soil organisms also contribute to build up of soil organic matter, including humus and make
the soil porous. .
(7) Soil fertility management is very important for successful crop production and farming.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 2
7. What is solid waste? Explain best practices for solid waste management.
(1) Waste materials which cannot be easily degraded into the soil is called solid waste.
(2) The waste consists of household waste, construction and demolition debris, sanitation
residues from’ Municipalities.
(3) Radioactive waste, metallic waste, plastic, glass, industrial and hospital wastes which
consists of toxic substances are hazardous waste.
(4) Other infectious wastes are produced from the human activities are harmful to the survival of
plants, animals and humans.
(5) Solid waste management involves in collection, transfer and transport to suitable sites and
safe disposal of waste.
(6) Industrial waste should be treated physically, chemically and biologically until they are less
hazardous.
(7) Strong acidic or basic wastes should be neutralize before disposal, insoluble materials
should be allowed to degrade under controlled conditions.
(8) Follow the advanced techniques to treat the waste such as incineration, sterilization,
chemical disinfection and microwave.
(9) Radioactive components should be recycled.
(10) Environmental and aesthetic considerations must be taken into considerations before
selecting the dumping sites.
8. What is bioremediation? How it helps in controlling soil pollution?
1. Bioremediation is a biological method which is used in the cleaning process of
contaminated natural resources such as water, land and air.
(2) Microorganisms play a major role in bioremediation process to treat environmental
Problems
(3) Plants also been used to assist bio remediation process. This is called phyto
remediation,
(4) Bioremediation process have been used for the treatment of some inorganic
substances like metals. Low radioactive components and organic contaminants. |
(5) Materials such as plastic things, bags, bottles, glassware and clothes etc should be
reuse, whenever possible.
(6) Recycling and recovery of materials helps in the conservation of natural resources,
9. Describe an environmental friendly method to profitably dispose off human
waste and cattle waste.
(1) Solid waste management follows the methods involves collection, transfer and
transport to suitable sites.
(2) Safe disposal of solid waste consists of methods which are environmentally
compatible.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 3
(3) Decomposition of bio-degradable human waste and cattle waste organic manure
which add good nutrients to the soil.
(4) Decomposition of cattle waste releases the gases like methane should be processed
to produce gobar gas, which is used for domestic usage.
(5) Soil micro-organisms involves in the decomposition process. They convert complex
organic material into simple substances.
(6) These substances enrich the soil without any harmful effect on the environment.
(7) Excrements of earthworm is known as vermi compost which contains 5 times more
nitrogen, 7 times more phosphate, 11 times more potash and 2 times more manganese
and calcium.
(8) Earthworms accelerate the decomposition of plant materials on the soil surface and
prepare the vermi compost.
(9) Dung beetle also helps in the improving of soil fertility by decomposing of animal or
cattle dung.
10. Chemical fertilizers are useful to crops. In which way they cause
environmental pollution?
(1) Chemical fertilizers consist of essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and
potassium which are required for the crop growth.
(2) They are always ready for immediate supply of nutrients to plants.
(3) Chemical fertilizers contaminate the soil with impurities, which come from the raw
material’ of their manufacture.
(4) Lead and cadmium elements present in the rock phosphate accumulate in the soil
through" fertilizers.
(5) These metal substances are not degraded into the soil. Their accumulation in the
soil show the toxic effect on the crop.
(6) Over usage of chemical fertilizers reduces carbohydrate and protein quality in the
grains.
(7) Excess potassium content in the soil decreases vitamin C and carotene content in
the vegetables and fruits.
(8) Excessive usage of chemical fertilizers turns the fertile soil into unfertile. They change the
soil texture and soil structure.
11. Rank the negative impact practices in your area in the order in which you think they
should be eliminated?
(1) Indiscriminate usage of chemical fertilizers to improve the soil fertility but they shows the
negative impact on the soil.
(2) Prolonged usage of chemical fertilizers changes the soil structure and decrease the soil
fertility.
(3) Indiscriminate use of insecticides, pesticides and herbicides the pathogens develops the -
10.Soil Pollution Page No 4
resistance against to these chemical compounds.
(4) They show their impact on other animals and birds they damage the ecosystem and leads to
environmental imbalance.
(5) Prolonged cultivation of single type of crop variety leads to decrease in the specific type of
soil nutrients, attacking of different types of diseases and pests.
(6) Usage of organic manure, biofertilizers, vermi compost etc., instead of chemical fertilizers
enriches the soil.
(7) To eradicate diseases and pest by following biological methods reduce the usage of
insecticides, pesticides and herbicides.
(8) Through these methods protect the ecosystem without any harmful effects on other
organisms.
(9) Crop rotation method, cultivation of mixed crops cultivation of green manure crops enrich the
soil nutrients and soil health.
12. What is organic matter? Why it is important to plants?
(1) Decaying and decomposed matter produced from the plants and humans as waste
substances are called organic matter.
(2) It gives good nutrients to the soil and makes the soil fertile.
(3) This organic matter enriches the soil nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorous and potassium etc,
(4) Organic matter improves quality of humus, water holding capacity and porosity of soil.
13. What are the factors affecting organic matter levels in the soil? How this level of
organic matter can be increased?
i) The top most layer of the soil consists of mostly organic matter and biological activity.
ii) Plant material, green manure, animal manure, compost, straw etc are affects the Organic
matter of the soil.
iii) Rocks and minerals being broken down to smaller pieces. Soil organic matter Provide
structure, to the soil, prevents compaction and increase in the root growth.
iv) Soil microbes decompose the organic matter and mixed into the soil.
v) Green manure provide food for soil, plant debrices, animal manure, and compost are the
organic matter which increase the soil organic matter.
14. What steps can be taken into reduce pollution due to particulate matter from the
industries?
i) Waste materials released from the industries are dangerous to environment.
ii) These should be treated physically, chemically and biologically until they are less hazardous,
iii) Microbial digestion of certain organic chemicals and other techniques like land farming,
biostimulation and bio augmentation are used to clean up the hazardous waste.
iv) Extraction of ground water with an active electro mechanical system with subsequent
stripping of the contaminants from the extract.
v) Phyto remediation or plants are used to remove heavy metals such as lead, cadmium and
mercury from the atmosphere.
vi) Excavate soil and take it to a disposal site away from human and sensitive ecosystem.
vii)Reutilization of radioactive materials which are released from the industries.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 5
viii) Sewage water released from the industries should be treated physically, chemically until
less then released into the environment.
15. How would soil texture affect the nutrients in soil? What would be its impacts
on crop production?
A. i) Soil fertility is closely associated with the properties of the soil.
ii) Soil is made up of minerals, decomposed organic matter, air and ‘water. These components
influence the soil texture, structure and porosity.
iii) Soil consists of nutrients which are necessary for plant growth such as nitrogen,
phosphorous and potassium.
iv) Soil microbes feed on plant and animal residues burrow the soil and help in aeration and
percolation of water.
(v) These microbes convert organic form of elements into inorganic form. They influence the
nutrient cycles in all major ecosystems.
(vi) Nutrients availability in the soil is influenced by soil pH, acidity or alkalinity ot soul.
(vii) Soil fertility management is important thing for successful crop production and
farming.
(viii) Crop quality directly depends on the soil texture. |
(ix) Soil with texture, composition and nutrients, gives good crop yielding.
16. Why soil conservation is important to us? What will happen if no preventive
measures would be taken?
(i) Several ways are possible for soil conservation that can be achieved through
agricultural practices.
(ii) Soil conservation prevents the soil erosion, rooting of trees deeper into the soil and
spread into the layers of the soil.
(iii) Deep tilling and some other farm practices can lead to the rapid loss of organic
matter and death of soil born micro-organisms.
(iv) Continuous cultivation of same crop for several years leads to the imbalance in the
soil nutrients.
(v) Acidic or basic pollutants and acid rains show adverse effect on the soil pH. It is
essential for the conservation of soil.
(vi) Salinity of soil causes death and improper growth and functioning of crop. It is one
of the indirect way to conserve the soil.
(vii) Over stimulation of soil by excessive amount of organic matter leads to decrease in
the soil fertility.
(viii) Application of more than needed chemical fertilizers also stimulates the soil
microbes and decreases the soil fertility.
17. What farm practices impact soil? Do they impact in a positive or negative
way?
(i) Cultivation of land in agricultural purposes is known as farm practices.
(ii) Roots of trees spread and penetrate into the deep layers of soil. They prevent the
soil erosion.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 6
(iii) Terrace forming prevents rapid surface run off of water and slowing the easy
washing down of the soil and helps in the percolation of water into the soil.
(iv) Tilling of soil mixes the organic fertilizers into the soil and creates the aeration to the
soil.
(v) Crop rotation method improves the soil fertility and structure.
(vi) Tilling of soil can leads compaction of soil, loss of organic matter in the soil and
death of organisms in the soil.
(vii) It leads to reduce in the nitrogen fixation, increase in the aerodibility.
(viii) This type of farming reduces the crop yield, imbalance in soil fauna and flora.
18. Name 5 living things that live in soil. What do these things affect the soil?
Living organism Functions that effect the soil
1. Rhizobium leguminosarum The bacteria which leads symbiotic life
with root nodules of fabaceae family
plants. It involves in the nitrogen fixation
into the soil.
2. Mycorrhiza The fungus which leads symbiotic life with
plant roots. It explore the soil it bring back
water nutrients which are not easily
available to the plant.
3. Algae Lead symbiotic life with other organisms
and are involved in the nitrogen fixation
and absorption of harmful gases,
4. Nematodes These are the worms which improves soil
porosity and facilitates the availability of
macro nutrients in the soil.
5. Earthworms Aeration of soil, enhance the availability of
soil macronutrients and enhance the
porosity of soil.
6. Insectivore insects They eat the soil born micro-organisms
and larvae of other insects and pest to
control the plant diseases.
7. Dung beetle Decomposition of organic matter like cattle
dung and other animal’s excreta.
8. Gophers Make burrows and helps in the aeration
and percolation of water.
9. Azo sporillum Bacteria It is used for decomposing of dead and
decayed substances.
10. Azolla It controls excess nitrogen compounds and
absorbs toxic substances in the field.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 7
11. Nitrobacter It is used for the conversion of Nitrites into
Nitrates.
12. Denitrifying bacteria It converts solid nitrates into gaseous
nitrogen to maintain ecological balance
19. Why are plastic bags a big environmental nuisance?
A. (1) Conventional plastic have been associated with reproductive problems in both wild life
and humans.
(2) Decline in human sperm count and quality, genetal abnormalities and arise in the incidence
of breast cancer in female.
(3) Dioxin is highly carcinogenic and toxic by product released from manufacturing process of
plastic and in burning of plastic.
(4) Careless disposal of plastic bags, chokes drains, blocks the porosity of soil leads to the
problem for ground water recharge.
(5) Plastic materials disturb the soil microbial activity.
(6) Plastic bags can also contaminate food stuffs. It may leads to many health problems.
(7) It causes extensive damage to the environment and it become a big environmental
nuisance,
20. What ‘soil problems « do you find 4 in n your area?”Prepare a list of those problems
and suggest a method for each of them to control those problems?
Ans:
(1) In our region the soil type is black soil, it is suitable for some types of crops only.
(2) Farmers use chemical fertilizers indiscriminately. It leads to several problems like soil
become infertile, increase in pest attack and other crop diseases.
(3) To control the diseases they use insecticides and pesticides frequently. Insects and pests
develop the resistance against to the insecticides and pesticides.
(4) These chemical substances show their effects on soil born microorganisms which are useful
to the crop are die.
(5) Other animals and insects which helps in the eradication of insects and pests like
insectivores, birds and pollinating agents are may also die due to the effect of these strong
chemicals.
(6) Farmers should know the importance of soil health, soil structure, composition and
properties.
(7) Farmers should follow the biological and ecofriendly methods which are helpful to increase
the soil fertility.
(8) Farmers should use biofertilizers, vermi compost and organic manure instead of chemical
fertilizers.
(9) In the agricultural practices they follow the crop rotation methods and growing of mixed
crops in increases soil fertility.
(10) To eradicate the insects and pests should follow the biological methods instead of chemical
insecticides and pesticides.
(11) These methods decrease the cost of agriculture and benefit to the farmer as well as soil.
10.Soil Pollution Page No 8
21. Look at the following symbol what does it means?
Ans.
(1) Removal of pollutants from the environment by using micro-organisms
and other biological methods is known as bioremediation.
(2) Bioremediation involves treating the contaminated materials at the site or
to treat elsewhere.
(3) Phyto remediation is useful to remove toxins and strong metals.
(4) Plants are able to bio accumulate these toxins in their above ground parts.
(5) Elimination of wide range of pollutants and waste from the environment protects the
ecosystem and improves the environmental conditions.
22. Ravi said soil health is important. How can you support him?
Ans:
(1) Soil is one of the major natural resources; It is made up of minerals, decomposed
organic matter air and water.
2) Soil is a good habitat for fungi, bacteria, algae, protozoans and other organisms.
3) Soil health directly proportional to the soil fertility, soil fertility management is very
important for successful crop production.
4) Healthy soil is fundamental to the quality of food it produces and the health of
organisms those who eat it.
Choose the Correct Answer:
1) The organism which acts as farmer's friend : [ ]
(A) cockroach (B) spider (C) fungus (D) earthworm
2) It is the prevention of soil erosion caused by wind : [ ]
(A) Growth of grasslands (B) Addition of microorganisms
(C) Watering the soil (D) Reforestation
3) The process of cultivation takes place in the hilly region by levelling of
cultivated soil is : [ ]
(A) Terraces (B) No till farming
(C) Contour ploughing (D) Crop rotation
4) In India approximately ............ ..... Of plastic waste is recycled: [ ]
(A) 50 - 60% (B) 60 - 80%
(C) 70 - 90% (D) 40 - 60%
5) A dung beetle can bury the dung it is .............. Times more than its own weight:
[ ]
(A) 150 (B) 250 (C) 350 (D) 450
6) Excrements of earth worm affects on soil to ............... : [ ]
(A) decrease organic matter (B) decrease porosity of soil
(C) improve organic matter (D) improve soil salinity
7) Combustion of waste in the absence of oxygen is known as ................ : [ ]
(A) pyrolysis (B) paralysis
(C) thermostat (D) incineration
8. Decomposition of wet garbage in presence of micro organisms converts into
10.Soil Pollution Page No 9
harmless organic matter is called: [ ]
(A) organic manure (B) illuviation
(C) Bioaccumulation (D) bioremediation
9. Normal pH of good soil is: [ ]
(A) 5.5 - 7.5 (B) 3.2 - 5.8 (C) 7.5 - 8.6 (D) 4.5 - 7.9
10. Conversion of organic compounds into inorganic form and other elements is
known as ……….. [ ]
A) carbonization (B) fertilization (C) decomposition (D) mineralization
11) ………………. is the foundation for the life on earth: [ ]
(A) Regolith (B) Humus (C) Core (D) Mantle
12. Main gases in the soil atmosphere are ............ [ ]
(A)02,N2,S2 (B)O2,S2,CO2 (C)O2,CO2,N2 (D) O2,S2, Cl2
10.Soil Pollution Page No 10
You might also like
- Soil Pollution SwarDocument13 pagesSoil Pollution SwarSwar VatareNo ratings yet
- Land Pollution PDFDocument9 pagesLand Pollution PDFkapilNo ratings yet
- Soil Pollution SudeeptaDocument13 pagesSoil Pollution SudeeptaSanthilal S PillaiNo ratings yet
- Land Pollution: An OverviewDocument25 pagesLand Pollution: An OverviewSaujanya PaswanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 6 PDFsandeep shahaNo ratings yet
- SoilPollutionMMCDocument5 pagesSoilPollutionMMCibrahim Alfrkahi100% (1)
- EVS - Module - 7.3 - Pollution - SoilDocument3 pagesEVS - Module - 7.3 - Pollution - SoilSudheer KottaNo ratings yet
- Soil PollutionDocument2 pagesSoil PollutionferdiantoNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 SPM Chapter 9Document19 pagesBiology Form 4 SPM Chapter 9Lim SuyingNo ratings yet
- Wepik Examining The Causes Impacts and Mitigation Strategies of Soil Pollution A Comprehensive Analysis 20230713162237oSKd PDFDocument9 pagesWepik Examining The Causes Impacts and Mitigation Strategies of Soil Pollution A Comprehensive Analysis 20230713162237oSKd PDFsumayahmittalNo ratings yet
- Soil Pollution Diaconu Vasile Grupa 7401Document7 pagesSoil Pollution Diaconu Vasile Grupa 7401Adelina GeorgianaNo ratings yet
- HEAVY METAL POLLUTION IN NEPAL'S AGRICULTURAL SOILS AND VEGETABLESDocument8 pagesHEAVY METAL POLLUTION IN NEPAL'S AGRICULTURAL SOILS AND VEGETABLESSurendra KarkiNo ratings yet
- Soil PollutionDocument6 pagesSoil PollutionBipinNo ratings yet
- Soil Contamination or Soil Pollution Is Caused by The Presence of Xenobiotic (Human-Made)Document8 pagesSoil Contamination or Soil Pollution Is Caused by The Presence of Xenobiotic (Human-Made)Prem KumarNo ratings yet
- Pollution and Its TypeDocument22 pagesPollution and Its TypeSehrawat SurenderNo ratings yet
- Soil Pollution Control Management Techniques and Methods: Available Online ADocument9 pagesSoil Pollution Control Management Techniques and Methods: Available Online ANatalia DonțuNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument13 pages4 PDFbah mamadouNo ratings yet
- Soil Organic Matter: Composition, Importance and Maintenance (35 charactersDocument9 pagesSoil Organic Matter: Composition, Importance and Maintenance (35 charactersEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- 수리수문학 Intro PDFDocument17 pages수리수문학 Intro PDF주성현No ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Soil ColloidsDocument11 pagesChemical Properties of Soil Colloidsgurpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Waste Management-IDocument9 pagesWaste Management-ICricketer OPNo ratings yet
- Land PollutionDocument3 pagesLand Pollutioneristretto04No ratings yet
- Environment & SustainableDocument9 pagesEnvironment & SustainableSamim MallickNo ratings yet
- My Ph.D. Presentation - 09.04.2019Document43 pagesMy Ph.D. Presentation - 09.04.2019Sunil RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- 3 - Review of LiteratureDocument26 pages3 - Review of LiteratureVinoth Kumar78% (23)
- 2) Issues On Environmental EngineeringDocument95 pages2) Issues On Environmental EngineeringNur FatehaNo ratings yet
- Lec 20 EE DR - NoamanDocument22 pagesLec 20 EE DR - NoamanHadia SAULATNo ratings yet
- Importance of Vermicomposting at Industrial and Domestic LevelDocument6 pagesImportance of Vermicomposting at Industrial and Domestic LevelMiddle East Journal of Applied Science & TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 5-Role of Plant in Waste Management REVISEDDocument10 pages5-Role of Plant in Waste Management REVISEDommimishra0No ratings yet
- Soil Sience - Awoke E.Document77 pagesSoil Sience - Awoke E.awokeNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument8 pagesJurnalAdella OktaviaNo ratings yet
- National Seminar On Impact of Toxic MetalDocument3 pagesNational Seminar On Impact of Toxic Metal20011 harsh sharma SvnitNo ratings yet
- C05061518 PDFDocument4 pagesC05061518 PDFinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- UNIT-2,3,4,5Document44 pagesUNIT-2,3,4,5kartikaysinghco20b446No ratings yet
- Heavy Metals Pollution Of Soil; Toxicity And Phytoremediation TechniquesDocument13 pagesHeavy Metals Pollution Of Soil; Toxicity And Phytoremediation TechniquesAlcides Cordova MateoNo ratings yet
- Negative Impacts of Human Activities To EcosystemsDocument23 pagesNegative Impacts of Human Activities To EcosystemsLouNo ratings yet
- 1st Mid PartDocument13 pages1st Mid PartAbdullah Al Mamun100% (1)
- Unit3.5-Soil PollutionDocument3 pagesUnit3.5-Soil PollutionrostamNo ratings yet
- V1I2G4Document7 pagesV1I2G4guddi bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis Paper - HPSDocument8 pagesSynthesis Paper - HPSJayde GalopeNo ratings yet
- Chemical & Biological Properties of The SoilDocument122 pagesChemical & Biological Properties of The SoilJoshua StevenNo ratings yet
- Report On Soil PollutionDocument4 pagesReport On Soil Pollutionaskmee100% (1)
- Ajayi FreshDocument33 pagesAjayi FreshSAMUEL AKANDENo ratings yet
- Lalalia ResearchDocument9 pagesLalalia ResearchLicia BulanadiNo ratings yet
- Elijah TobiDocument39 pagesElijah TobiMarshallNo ratings yet
- Organic Farming NotesDocument46 pagesOrganic Farming NotesNisarga T DaryaNo ratings yet
- Environ Biology Unit III Part IIIDocument36 pagesEnviron Biology Unit III Part IIIrajx2shekharNo ratings yet
- Applied Environmental Health Soil Pollution: Kigongo Eustes Department of Public Health Lira UniversityDocument25 pagesApplied Environmental Health Soil Pollution: Kigongo Eustes Department of Public Health Lira UniversityAYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- Group JDocument3 pagesGroup Jusman abdulkarimNo ratings yet
- The Role Humans in Maintaining The Balance of NatureDocument4 pagesThe Role Humans in Maintaining The Balance of Naturepclim20100% (1)
- Edta PDFDocument14 pagesEdta PDFfesooNo ratings yet
- Plants: Assisting Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals Using Chemical AmendmentsDocument14 pagesPlants: Assisting Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals Using Chemical AmendmentsfesooNo ratings yet
- Soil PollutionDocument11 pagesSoil PollutionAnkesh Shrivastava50% (2)
- Soil Components, Properties and Farming TechniquesDocument3 pagesSoil Components, Properties and Farming TechniquesSawsan ElteebNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation of Heavy MetalsDocument9 pagesBioremediation of Heavy MetalsshwetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document35 pagesChapter 3ARPITA MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Preparation Questions on Water Pollution and Waste ManagementDocument9 pagesFinal Exam Preparation Questions on Water Pollution and Waste ManagementIlhan KlisuraNo ratings yet
- Navigation Search: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 pagesNavigation Search: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPradeep Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- A review of organic and inorganic fertilizersDocument14 pagesA review of organic and inorganic fertilizersJonard Opamen73% (11)
- INSTA June 2023 Static Quiz CompilationDocument54 pagesINSTA June 2023 Static Quiz Compilationvsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- INSTA JUNE 2023 Editorials Quiz CompilationDocument64 pagesINSTA JUNE 2023 Editorials Quiz Compilationvsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- PSIR 1A BookDocument2 pagesPSIR 1A Bookvsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- INSTA June 2023 Current Affairs Quiz Compilation 1Document67 pagesINSTA June 2023 Current Affairs Quiz Compilation 1vsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- Police Constable: SUSC - 2022 Mains Grand Test - 045Document32 pagesPolice Constable: SUSC - 2022 Mains Grand Test - 045vsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- 10th IMP PracticeDocument9 pages10th IMP Practicevsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- SI POLICE EXAMDocument16 pagesSI POLICE EXAMvsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledvsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- Madhubabu - ShadowinHyderabadDocument47 pagesMadhubabu - ShadowinHyderabadvsurender reddy100% (1)
- Chemical Science (A-02-18)Document24 pagesChemical Science (A-02-18)vsurender reddyNo ratings yet
- Bisare Small Scale Irrigation ProjectDocument72 pagesBisare Small Scale Irrigation ProjectAbiued EjigueNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Warta Rimba E-ISSN: 2579-6287 Volume 8 Nomor 2 Juni 2020 Penggaruh Jenis Skarifikasi Terhadap Perkecambahan Benih SagaDocument6 pagesJurnal Warta Rimba E-ISSN: 2579-6287 Volume 8 Nomor 2 Juni 2020 Penggaruh Jenis Skarifikasi Terhadap Perkecambahan Benih SagaKhxlifx CarakaNo ratings yet
- Red Red WineDocument18 pagesRed Red WineSunnyNo ratings yet
- Organic Farm Questionnaire Response from Benguet, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesOrganic Farm Questionnaire Response from Benguet, PhilippinesCornelio JR BenignoNo ratings yet
- ISCC Self-Declaration For Points of Origin Generating Waste and ResiduesDocument1 pageISCC Self-Declaration For Points of Origin Generating Waste and ResiduesPos PublikNo ratings yet
- Honey Bee Life CycleDocument9 pagesHoney Bee Life CycleBảo Linh Thái ThanhNo ratings yet
- The Role of Road Infrastructure in Agricultural Production: Emmanuel Fungo, Stephan Krygsman and Hannelie NelDocument11 pagesThe Role of Road Infrastructure in Agricultural Production: Emmanuel Fungo, Stephan Krygsman and Hannelie NelDhiraj Kumar.No ratings yet
- Agricultural Engineering: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument8 pagesAgricultural Engineering: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchMichaelNo ratings yet
- Genetic ModificationDocument25 pagesGenetic ModificationMark Jherson LingconNo ratings yet
- Document (1) DDDDDocument9 pagesDocument (1) DDDDMuhammad Fariq Al HusniNo ratings yet
- Modernization of Spate Irrigated AgricultureDocument11 pagesModernization of Spate Irrigated AgricultureAziz Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Shrimp FarmingDocument132 pagesRecent Advances in Shrimp FarmingMeghamala MallickNo ratings yet
- ID Perhitungan Laju Erosi Metode Usle UntukDocument18 pagesID Perhitungan Laju Erosi Metode Usle Untukmiftahul jannah makaohoNo ratings yet
- Agrotextiles - Study Material - 8th Semester BTech - 2023Document27 pagesAgrotextiles - Study Material - 8th Semester BTech - 2023Sanju100% (1)
- 1 - RN Singh Review - NEWDocument7 pages1 - RN Singh Review - NEWSachin TiwaryNo ratings yet
- DAFM - Sustainability in Agriculture, Food Production and Food Technology in The Danube Region - Danube AgriFood MasterDocument2 pagesDAFM - Sustainability in Agriculture, Food Production and Food Technology in The Danube Region - Danube AgriFood MasterNicolás BaqueroNo ratings yet
- SecondDocument149 pagesSecondShankar KalambeNo ratings yet
- 6.session PlanDocument7 pages6.session PlanMerly SalvadorNo ratings yet
- TaylOrganic Farm CSA ContractDocument3 pagesTaylOrganic Farm CSA ContractryezziNo ratings yet
- A Debate About Prohibition ofDocument3 pagesA Debate About Prohibition ofLance Kelly P. ManlangitNo ratings yet
- D85ess P2uDocument1 pageD85ess P2uTyler GoodwinNo ratings yet
- Part VI The Central Plains GEOG 321Document26 pagesPart VI The Central Plains GEOG 321jack stauberNo ratings yet
- Agriboom DPDocument3 pagesAgriboom DPudaya kumarNo ratings yet
- Taishan African Marigold GrowerFactsDocument2 pagesTaishan African Marigold GrowerFactsgheorge alexNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For Agricultural Technologies: 1.11 Okra ProductionDocument56 pagesInstruction Manual For Agricultural Technologies: 1.11 Okra ProductionDamion SuiteNo ratings yet
- Word List For VocabDocument140 pagesWord List For Vocabmuskan sNo ratings yet
- AGRICULTURE NotesDocument3 pagesAGRICULTURE NotesramkrishnapasalaNo ratings yet
- Trees For Gardens, Orchards, and Permaculture (PDFDrive) PDFDocument250 pagesTrees For Gardens, Orchards, and Permaculture (PDFDrive) PDFRaul Lazar100% (1)
- 10 Philippine Herbal Medicines Approved by DohDocument38 pages10 Philippine Herbal Medicines Approved by DohhannahleatanosornNo ratings yet
- Discover Happiness in BhutanDocument2 pagesDiscover Happiness in Bhutantth28288969No ratings yet