0% found this document useful (0 votes)
715 views8 pagesSteel Design Lecture
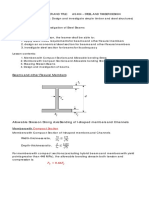
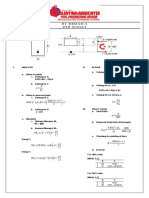
This document provides examples of calculating effective areas and design strengths for steel tension members with bolt holes.
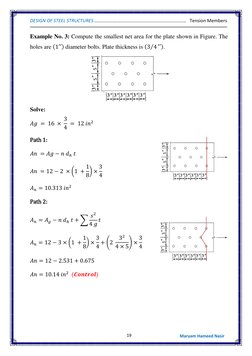
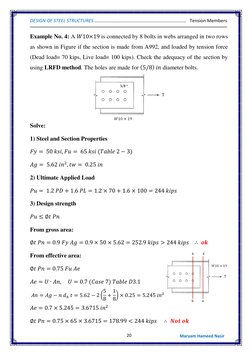
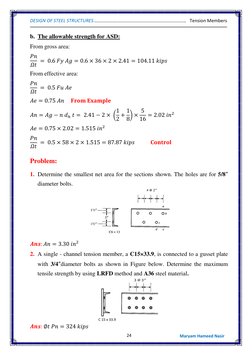
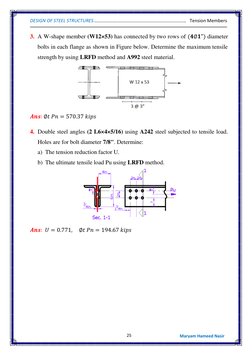
Example 1 shows determining the effective area of a single angle section with bolt holes. Example 2 calculates the smallest net area of a plate with bolt holes. Example 3 checks the adequacy of a W-shape section connected by bolts using LRFD.
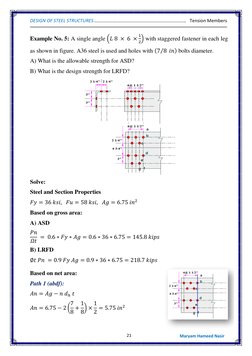
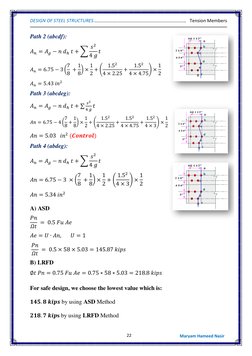
Example 4 calculates the allowable strength and design strength of a single angle section using ASD and LRFD methods. Example 5 determines the effective area and design strengths of a double angle shape. Example 6 provides the design tensile strength and allowable strength for a problem involving a double angle section.
Uploaded by
Dad MeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
715 views8 pagesSteel Design Lecture
This document provides examples of calculating effective areas and design strengths for steel tension members with bolt holes.
Example 1 shows determining the effective area of a single angle section with bolt holes. Example 2 calculates the smallest net area of a plate with bolt holes. Example 3 checks the adequacy of a W-shape section connected by bolts using LRFD.
Example 4 calculates the allowable strength and design strength of a single angle section using ASD and LRFD methods. Example 5 determines the effective area and design strengths of a double angle shape. Example 6 provides the design tensile strength and allowable strength for a problem involving a double angle section.
Uploaded by
Dad MeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Example No. 2
- Example No. 3
- Example No. 4
- Example No. 5
- Example No. 6
- Problem 1
- Problem 2