Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theme B: Coasts Cheat Sheet: by Via
Uploaded by
Annaglory NkayalaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theme B: Coasts Cheat Sheet: by Via
Uploaded by
Annaglory NkayalaCopyright:
Available Formats
Theme B: Coasts Cheat Sheet
by etait4502 via cheatography.com/81287/cs/19482/
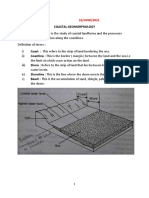
Coastal Processes & Features Coastal Processes - C.A.S.H (cont)
(H) i.e. power of the sea. Can physically wash away soft
Hydraulic rocks like boulder clay; hundreds of tonnes of seawater
Waves Action can hit coast under storm conditions. Air can also be
Waves are caused by wind blowing over a stretch of water. trapped in small cracks within cliffs when waves break
against it. Compressed air can widen cracks leading to
Energy is transferred from wind to water and causes the water to
sections of cliffs breaking away.
begin to move in a circular motion. This wave of pure energy keeps
going across the ocean until it meets a coastline. The distance of
Transportation - Long Shore Drift
unbroken ocean over which a wave has gathered up energy is
known as the 'fetch'. The larger the fetch the longer the wave. Waves approaching at an angle will rush up the beach in the
At the coast line the wave begins to slow down due to friction with the direction of the wave crest, but roll down the beach by gravity. This
land and to fall forward into a breaking wave. It then goes up the means that little by little material is moved sideways on the beach.
beach as swash and rolls back down the beach as backwash. It is This is called long shore drift.
the strength of the swash compared to the backwash that determines
whether a coast will erode or not. Diagram of Longshore Drift
If the wave is long and low with a strong swash then the wave will be
constructive
If the wave is short and steep with a strong backwash then the wave
will be destructive
Coastlines are dynamic - always changing. Some coastlines erode
whilst others are being built up. This is due to the changing energy of
the waves (due to fetch and wind speed) and the material the coast is
made from. Deposition
Coastal Processes - C.A.S.H
(C) When wind hits the coast it throws sand and pebbles
Corrasion against the cliff face; these knock off small parts of the
cliff and cause undercutting, also known as abrasion.
(A) Particles being transported by sea hit against one
Attrition another, reducing their size and making them more
rounded - just like in rivers.
(S) Seawater can dissolve away the rocks from the seabed
Solution or cliffs. This process is especially effective on limestone
coasts and can create spectacular caves. Also known Erosion Landforms
as corrosion.
Cliffs & Wave Cut Platforms Caves, Arches & Stacks
By etait4502 Published 28th April, 2019. Sponsored by Readable.com
cheatography.com/etait4502/ Last updated 28th April, 2019. Measure your website readability!
Page 1 of 4. https://readable.com
Theme B: Coasts Cheat Sheet
by etait4502 via cheatography.com/81287/cs/19482/
Erosion Landforms (cont) Diagram of a Cliff & Wave Cut Platform
Cliffs are shaped through erosion and Caves, arches, stacks and
weathering. Soft rock erodes quickly stumps are erosional
and forms gentle sloping cliffs, features that are commonly
whereas hard rock is more resistant found on a headland.
and forms steep cliffs. A wave-cut
platform is a wide gently-sloping Diagram of Caves, Arches & Stacks
surface found at the foot of a cliff.
- The process repeats. The cliff They form when the
continues to retreat. following happens:
A wave cut platform forms when the - Cracks are widened in the
following occurs: headland through the
erosional processes of Deposition Landforms
hydraulic action and
Beaches Spits
abrasion.
A beach is a coastal landform A spit is a beach that extend out
- The sea attacks the base of the cliff - As the waves continue to
created by deposition. from the mainland into the sea.
between the high and low water grind away at the crack, it
They are a coastal landform
mark. begins to open up to form a
formed by deposition.
cave.
Constructive waves form Spits require a constant supply of
- A wave-cut notch is formed by - The cave becomes larger
beaches as they deposit sand (or other material from
erosional processes such as abrasion and eventually breaks
materials. erosion further up the coast),
and hydraulic action - this is a dent in through the headland to
longshore drift operating most of
the cliff usually at the level of high form an arch.
the time, a coastline with a sudden
tide.
change in direction to leave a
- As the notch increases in size, the - The base of the arch sheltered bay area and quite
cliff becomes unstable and collapses, continually becomes wider shallow sea to form.
leading to the retreat of the cliff face. through further erosion, until
Shingle beaches are much A spit forms when waves hit the
its roof becomes too heavy
steeper than sandy beaches shore at an angle, moving material
and collapses into the sea.
as the energy of a wave is along the beach due to LSD. This
This leaves a stack (an
reduced because the large happens because although the
isolated column of rock).
particle size allows percol‐ sand goes up the beach at an
- The backwash carries away the - The stack is undercut at ation, therefore the backwash angle in the swash, it moves
eroded material, leaving a wave-cut the base until it collapses to is not very powerful and a straight back down the beach in
platform. form a stump. steep beach is created. the backwash.
The end of a spit has a
hooked/curved end due to waves
changing direction. This is called a
headland. A salt marsh may also
form.
By etait4502 Published 28th April, 2019. Sponsored by Readable.com
cheatography.com/etait4502/ Last updated 28th April, 2019. Measure your website readability!
Page 2 of 4. https://readable.com
Theme B: Coasts Cheat Sheet
by etait4502 via cheatography.com/81287/cs/19482/
Sustainable Management of Coasts Coastal Management Strategies
Seawalls
Description Look like tall concrete walls built at the back of
Coastal Land Use
beaches, may have curved shape to deflect erosive
Climate Change energy.
Making need for coastal defences pressing issue. Needed for Advantages Can be economically acceptable, protects many
example because the world bank estimates a 1m rise in sea levels people, can reflect wave energy
would flood half of Bangladesh's rice fields and force the migration of
Disadv‐ Expensive to build (£10mil per km), need constant
millions of people.
antages maintainence, need very deep foundation, cause
Tourism erosion elsewhere.
60% of Majora's gross national product comes from tourism centred Gabions
around beaches. In Dubai they have gone as far as creating more
Description Metal cage measuring 1m by 1m, built on site from 6
beach front space by building an artificial island off the coastline like
metal sides that are filled with local rocks.
Palm Islands.
Advantages Low cost, wave energy absorbed, deflects sea energy
Fishing
Disadv‐ Not long term; rust quickly and can be damaged by
The fishing industry is important in both MEDCs and LEDCs. The
antages storms, eyesore.
FAO estimates that over 100 million tonnes of fish are caught from
Gryones
the wild each year and provide for 10-12% of the world's population.
90% of those employed in fisheries are working in small scale Description Made of wood and look like low fences stretching
operations in developing countries. seawards out on beaches at intervals
Industry/Ports Advantages Tourist attraction, slow down LSD, saves beaches
Coastal areas suitable for locating a port. Ports are important today Disadv‐ Reduce public access, can cause extra erosion,
as ever due to the increase in global trade. Large container ships antages unattractive, expensive: £5000 per m, wooden ones
cross the world carrying up to 19,000 standard containers. In 2015 erode quickly
the world's largest container ship, made in China, the 'CSCL Globe' Beach Nourishment
docked in the port of Felixstowe, UK. Description Sand is dredged from seabed and added to eroded
beach
Why do we need to protect coasts?
Advantages Cheaper than groynes, receives significant economic
Just over half the worlds population, around 3.2 billion, live within returns (tourism), softer (supports beach)
20km of the sea. The use of shoreline has a direct and significant
Disadv‐ Needs regular maintenance, erode faster, still
impact on coastal waters. These areas are vulnerable to rising sea
antages expensive, short term, £1mil per mile.
levels or coastal erosion, large numbers of people inhabit these
areas and are thus at risk. By 2025 it is estimated that 6 billion will
live in coastal areas.
By etait4502 Published 28th April, 2019. Sponsored by Readable.com
cheatography.com/etait4502/ Last updated 28th April, 2019. Measure your website readability!
Page 3 of 4. https://readable.com
Theme B: Coasts Cheat Sheet
by etait4502 via cheatography.com/81287/cs/19482/
Case Study - Newcastle, Co. Down Keywords
Sustainable means meeting the needs of today without compro‐ Sustainable
mising the needs of future generations. Sustainable development at Sustainable Coast
the coast means implementing hard and soft engineering methods to
Wave
protect local areas.
Longshore Drift
Newcastle is located in County Down, in the South East of Northern
Corrasion (abrasion)
Ireland. It is a coastal town, one hour away from the Capital, Belfast.
Attrition
The sand from the 8km of beach originally came from the last ice
age, carried by glaciers from Dundrum, 15,000 years ago. This Solution
means there is no ways of replacing a sand, a finite source and no Hydraulic Action
new sand can make management hard.
Hard Engineering
Gryones
Gryone
(+) Wooden gryones cheaper, (-) Have decayed.
Gabion
Gabions
Seawall
(+) More sustainable than sea wall and rock armour, slowly dissipate
Rock Armour
energy, replaced in 2006. (-) Not sustainable, first set badly
Soft Engineering
decayed, cheaper.
Rock Armour
(+) Effective and environmentally friendly (-) Unsustainable, reduces
sediment supply for Murlough Bay
Sea Walls
(+) £10mil per kilometre, effective, curved meaning wave will return
design. (-) Severe storm in 2002 washed old sea wall away, was
rebuilt and extended by 1m for £4mil. Increased erosion North of
Shima River.
Beach nourishment and new gryones are being considered for the
future of Newcastle's coast.
The methods currently employed at Newcastle are not sustainable
as it is no longer a naturally fuctioning beach. Professor Derek
Jackson notes that sea walls that reflect waves will gradually erode
away once stable beaches. Comments on lack of sustainability in
Northern Ireland given background of sea level rises made.
By etait4502 Published 28th April, 2019. Sponsored by Readable.com
cheatography.com/etait4502/ Last updated 28th April, 2019. Measure your website readability!
Page 4 of 4. https://readable.com
You might also like
- Coastal ProcessesDocument44 pagesCoastal Processesamabelle sibugNo ratings yet
- Coasts g10 GeoDocument9 pagesCoasts g10 Geowabwire fredNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Topic 5 Coastal Change and ConflictDocument11 pagesPaper 1 Topic 5 Coastal Change and ConflictteeeNo ratings yet
- Coasts Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Document20 pagesCoasts Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Georgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- The Coastal Zone Revision Booklet-4jy8Document24 pagesThe Coastal Zone Revision Booklet-4jy8minnie20050912sNo ratings yet
- Destructive Waves V/s Constructive Waves Constructive (Or Depositional) Waves. 1. Destructive Waves Have A Number of Important CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDestructive Waves V/s Constructive Waves Constructive (Or Depositional) Waves. 1. Destructive Waves Have A Number of Important CharacteristicsRavi MothoorNo ratings yet
- Coasts g10 Geo NotesDocument9 pagesCoasts g10 Geo Noteswabwire fredNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandformsDocument60 pagesCoastal Landformsrileyjalon7No ratings yet
- Coasts - Revision GuideDocument2 pagesCoasts - Revision GuidectxkdtmyvpeqeNo ratings yet
- Coasts SummaryDocument2 pagesCoasts SummaryFlora ForresterNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 8Document8 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2 - Module 8benes salamancaNo ratings yet
- The UKs Physical Landscape Coastal Change and Conflict EQ2Document19 pagesThe UKs Physical Landscape Coastal Change and Conflict EQ2Huseyn HuseynovNo ratings yet
- Geo Csec ToppicsDocument26 pagesGeo Csec ToppicsThierry PierreNo ratings yet
- Coasts Notes The Coast Is A Zone Where Land and Sea Meet and Interact. The Coast Can Be Made Up of Many Landforms and It Ever Changing. KeywordsDocument15 pagesCoasts Notes The Coast Is A Zone Where Land and Sea Meet and Interact. The Coast Can Be Made Up of Many Landforms and It Ever Changing. KeywordsLiu Yi JiaNo ratings yet
- Coastal Features - Erosion ProcessesDocument21 pagesCoastal Features - Erosion Processes3alliumcourt100% (2)
- All of Geography Broad TopicsDocument22 pagesAll of Geography Broad TopicsNICHOLAS HENRYNo ratings yet
- Geography Sba Submission)Document17 pagesGeography Sba Submission)shellyNo ratings yet
- Igcse Geography CoastsDocument24 pagesIgcse Geography CoastsMunir LakhaNo ratings yet
- What Factors Lead To The Differences and Dynamism of Coastal Environments?Document4 pagesWhat Factors Lead To The Differences and Dynamism of Coastal Environments?Nethra SasikumarNo ratings yet
- Coastal Geomorphology NotesDocument33 pagesCoastal Geomorphology NoteswhytedafoxNo ratings yet
- Final Coastal GeomorphologyDocument34 pagesFinal Coastal GeomorphologyTadiwa MawereNo ratings yet
- Coastal GeomorphologyDocument35 pagesCoastal GeomorphologyJasonNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandformsDocument46 pagesCoastal LandformsShreya YugalNo ratings yet
- 9042 Coastal EngineeringDocument56 pages9042 Coastal Engineeringcheukhin ngNo ratings yet
- COASTDocument40 pagesCOASTtiyaresti31No ratings yet
- Coast, Coastal Process, Land Form and ManagementDocument6 pagesCoast, Coastal Process, Land Form and ManagementLeon ElblingNo ratings yet
- OceansDocument54 pagesOceansKhoirulhaqNo ratings yet
- Geo Report ExplainDocument6 pagesGeo Report Explainirinacuevas123No ratings yet
- Coastline NotesDocument12 pagesCoastline NotesDacia BarrettNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandscapesDocument7 pagesCoastal LandscapesKirk InocianNo ratings yet
- CoastDocument5 pagesCoastRahemah 拉希马 AlliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: CoastsDocument84 pagesChapter 12: CoastsM. Kate Green100% (1)
- Coastal LandformsDocument2 pagesCoastal LandformsJovie StoreyNo ratings yet
- WS C2 U6 Eng AnsDocument7 pagesWS C2 U6 Eng AnsyanaaNo ratings yet
- Intro Notes - CoastsDocument4 pagesIntro Notes - CoastsVictoria KairooNo ratings yet
- Edexceligcsegeographychapter 2Document31 pagesEdexceligcsegeographychapter 2api-265424071No ratings yet
- Theme 1 - Rivers and Coasts Revision NotesDocument26 pagesTheme 1 - Rivers and Coasts Revision NotesZantaye ThomasNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Identify Landscapes Terminology Table ActivityDocument6 pages1.0 Identify Landscapes Terminology Table Activityrishitharaju.1207No ratings yet
- Coasts Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesCoasts Knowledge OrganiserAbdellahNo ratings yet
- s5 Geog1 (Coastal Geomorphology)Document47 pagess5 Geog1 (Coastal Geomorphology)Batisibwa WyclifiousNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandformDocument4 pagesCoastal Landformrooey21No ratings yet
- Presentation and Analysis of DataDocument8 pagesPresentation and Analysis of DatashellyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Formation of Coastal LandformsDocument55 pagesCharacteristics and Formation of Coastal Landformsamabelle sibugNo ratings yet
- IgcsecoastsrevisionDocument18 pagesIgcsecoastsrevisionapi-232441790100% (2)
- ProsPan 2018 01Document23 pagesProsPan 2018 01guedbryalNo ratings yet
- Erosional Landforms: Headlands and BaysDocument5 pagesErosional Landforms: Headlands and BaysJesse RamroopNo ratings yet
- Coastal Erosion ProcessesDocument48 pagesCoastal Erosion ProcessesMalia Damit100% (1)
- Coastal ProcessesDocument10 pagesCoastal ProcessesMegyes VivienNo ratings yet
- Coastal ErosionDocument46 pagesCoastal Erosionali karboub100% (1)
- Chemistry FoundationDocument7 pagesChemistry Foundationkhalison khalidNo ratings yet
- Effects of Waves On Land Form Development in East AfricaDocument4 pagesEffects of Waves On Land Form Development in East Africakalule elvis100% (1)
- GHL Coastal Landforms 2 COVIDDocument32 pagesGHL Coastal Landforms 2 COVIDiGotheInfoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Sea Features of Erosion and DepositionDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Sea Features of Erosion and DepositionGracia OmariNo ratings yet
- Csec GeographyDocument26 pagesCsec GeographyAmelia PitterNo ratings yet
- 6 Coastal Geology and Geomorphology - 094202Document26 pages6 Coastal Geology and Geomorphology - 094202Von Genevieve LoquiasNo ratings yet
- Geography Revision AidDocument2 pagesGeography Revision AidRandy RiddleNo ratings yet
- AQA Geography - The Coastal Zone Revision NotesDocument3 pagesAQA Geography - The Coastal Zone Revision NotesEsther CheongNo ratings yet
- Landforms of Coastal Erosion and Deposition: Erosional Features Teacher: Mrs. A. Reid-AllenDocument49 pagesLandforms of Coastal Erosion and Deposition: Erosional Features Teacher: Mrs. A. Reid-AllenRuksi CocoNo ratings yet
- BIO3119-Marine & Coastal Ecology: Lecture 6: Coastal Processes Lecturer: Mark RamDocument43 pagesBIO3119-Marine & Coastal Ecology: Lecture 6: Coastal Processes Lecturer: Mark RamNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Beach Profilegeography CourseworkDocument8 pagesBeach Profilegeography Courseworkafjwoovfsmmgff100% (2)
- Marine & Coastal Processes and Their EffectsDocument34 pagesMarine & Coastal Processes and Their EffectsHarriette Wyne Aguado Lapuz0% (1)
- Coasts g10 Geo NotesDocument9 pagesCoasts g10 Geo Noteswabwire fredNo ratings yet
- The Role of Government - : Profile 3 QuestionsDocument11 pagesThe Role of Government - : Profile 3 QuestionsAngel LawsonNo ratings yet
- UNIT-5 Harbour EngineeringDocument20 pagesUNIT-5 Harbour EngineeringsuryaNo ratings yet
- Matthew Marajh Geography EssayDocument6 pagesMatthew Marajh Geography Essaymatthew marajhNo ratings yet
- Final Coastal GeomorphologyDocument34 pagesFinal Coastal GeomorphologyTadiwa MawereNo ratings yet
- Answers For Past Papers On Coasts Up To June 2010Document16 pagesAnswers For Past Papers On Coasts Up To June 2010teeeNo ratings yet
- 0460 w13 Ms 22 PDFDocument6 pages0460 w13 Ms 22 PDFLuciano Sánchez AramburuNo ratings yet
- A 12-04-019 Direct Testimony of Larry M Hampson MPWMD PDFDocument12 pagesA 12-04-019 Direct Testimony of Larry M Hampson MPWMD PDFL. A. PatersonNo ratings yet
- Coastal Landforms Caused by Deposition and ErosionDocument19 pagesCoastal Landforms Caused by Deposition and Erosionesteban duranNo ratings yet
- Prevention & Mitigation of The Impact of Coastal Processes, Land Development & Waste DisposalDocument20 pagesPrevention & Mitigation of The Impact of Coastal Processes, Land Development & Waste DisposalVieyah Angela VicenteNo ratings yet
- Coastal Engineering: Environmental Issues, Coastal ProblemsDocument4 pagesCoastal Engineering: Environmental Issues, Coastal ProblemsCole Jade Dayo0% (1)
- Settling VelocityDocument10 pagesSettling VelocityMunhu Wakanaka100% (1)
- Alongshore Sediment Transport R A T E: by J. William Kamphuis, Member, ASCEDocument17 pagesAlongshore Sediment Transport R A T E: by J. William Kamphuis, Member, ASCEdodoNo ratings yet
- Problems PDFDocument9 pagesProblems PDFEduarGelvezNo ratings yet
- Coastal Features - Erosion ProcessesDocument21 pagesCoastal Features - Erosion Processes3alliumcourt100% (2)
- Rivers YtjDocument1 pageRivers YtjS.L.L.CNo ratings yet
- Sedimentary Geology: Boyan K. Vakarelov, R. Bruce Ainsworth, James A. MaceachernDocument19 pagesSedimentary Geology: Boyan K. Vakarelov, R. Bruce Ainsworth, James A. Maceachernc_b_umashankarNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Geographical Investigation AdditionalDocument24 pages4.2 Geographical Investigation AdditionalTheRealDanNo ratings yet
- Hydrological Fluvial Coastal Limestone EnvironmentsDocument52 pagesHydrological Fluvial Coastal Limestone EnvironmentsDharam Jagroop100% (1)
- Glossary of Geographical TermsDocument33 pagesGlossary of Geographical Termscleophil_yontingNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist: The Physical EnvironmentDocument13 pagesEdexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist: The Physical EnvironmentJones Jonny100% (1)
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 12Document5 pagesDETAILED LESSON PLAN Earth and Life Sciences Grade 11 Week 12Austin Capal Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Coastal Regulation Zone Notification 2011Document5 pagesCoastal Regulation Zone Notification 2011AayshaNo ratings yet
- Design and Performance of Artificial Beaches For The Kuwait Waterfront ProjectDocument14 pagesDesign and Performance of Artificial Beaches For The Kuwait Waterfront ProjectSujanNepalNo ratings yet
- Agents of GradationDocument4 pagesAgents of Gradationsarayoo50% (2)
- Coasts Knowledge Organiser IGCSEDocument2 pagesCoasts Knowledge Organiser IGCSEQWERTYNo ratings yet
- Bahan Referensi Tugas 3 RPPDocument5 pagesBahan Referensi Tugas 3 RPPhafizhizzan zaldiNo ratings yet
- Coastal LandformsDocument42 pagesCoastal LandformsJeronNo ratings yet