Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist: The Physical Environment
Uploaded by
Jones JonnyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist: The Physical Environment
Uploaded by
Jones JonnyCopyright:
Available Formats
Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist
The Physical Environment
This check list contains the following units:
1 – The Changing Landscape of the UK
Choice of 2 from 1A, 1B & 1C
1A – Coastal Landscapes & Processes
1B – River Landscapes & Processes
1C – Glaciated Upland Landscapes and Processes
2 – Weather Hazards & Climate Change
3 - Ecosystems, Biodiversity & Management
This Symbol Indicates a case study you This Symbol Indicates a skills you may be
will need to know. expected to apply in the exam.
1. The Changing Landscapes of the UK
Types of Rocks Human Activity on UK Distinctive Landscapes
Characteristics & Distribution Advantages and disadvantages of:
Sedimentary (Chalk, Limestone) Agriculture on the South Downs
Igneous (Basalt, Granite) Forestry on the South Downs
Metamorphic (Schists, Slates) Spring-line Settlements on the South Downs
The Role of Geology & Past Tectonic Processes The Role of Geology & Past Tectonic Processes
Upland (Igneous & Metamorphic Rocks) Upland (Igneous & Metamorphic Rocks)
Lowland (Sedimentary Rocks) Lowland (Sedimentary Rocks)
Distinctive Upland & Lowland Landscapes Skills
Dartmoor I can read a Geological Map.
Joints I can identify a geological cross section to show
Freeze thaw weathering the relationship between geology and relief.
Tors I can locate key physical features such as
Clitter slopes uplands, lowland basins and rivers on UK
Malham Cove outline maps.
Limestone Pavements I can identify physical and human Geography
Grykes features on OS maps.
Clints
North & South Downs
Cretaceous Period
Scarp Slope
Dip Slope
1A. Coastal Landscapes and Processes
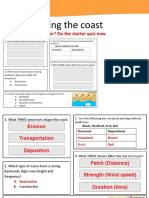
The Coastal Zone & Coastal Influence of waves & geology on The causes and effects of Managing Coastal erosion & flood
Processes the coastal landscape coastal erosion risk
Processes of Coastal Erosion Waves Rates of coastal erosion Shoreline Management Plans
Hydraulic Action Wind strength (or speed) No Intevention
Abrasion Wind duration
Natural Causes Hold the line
Solution Fetch
Rising sea level Managed realignment
Attrition Swash Storms & Storm surges Advance the line
Backwash
Weathering Processes Destructive waves
Human Causes Advantages & disadvantages of coastal
Mechanical (freeze thaw) Constructive waves Groynes management
Chemical (acid rain)
Dredging
Biological (roots & Geological Structure Building coastal defences Soft engineering
burrowing & nesting) Discordant Coasts
Beach Nourishment
Swanage
Effects of Erosion Sand dune regeneration
Mass movement Bay Settlements
Rock Falls Headland
Tourism
Slumping Concordant Coasts
Infrastructure Hard Engineering
Sliding Lulworth Cove
Agriculture Sea Walls
Bay
Groynes
Transportation Rip rap
Traction Landforms of coastal Deposition
Saltation Longshore Drift
Suspension Prevailing Wind Case Study – Dawlish Warren sand spit
Solution Beaches
Profile (Storm beach & Physical factors changing the spit
Deposition berm) Human factors changing the spit
Spit Dawlish Warren Beach management scheme
Landforms of coastal Erosion Saltmarsh Environmental Impact
Cliff Bar Adaptation & resilience
Wave cut notch Lagoon
Wave cut platform Skills
Caves
Arch I can read a geological map to link coastal form to geology.
Stack I can identify coastal landforms on OS maps.
Stump I can use an OS map to investigate the impact of human intervention.
1B. River Landscapes and Processes
Drainage basins and river River processes form distinct Storm Hydrographs Managing Flood Risk
processes landscapes Hydrograph Advantages and disadvantages of
Drainage basin Interlocking Spurs Rising Limb flood defences
Watershed Waterfalls & Gorges Falling Limb
Source Meanders Lag time Hard Engineering
Tributary Oxbow lakes Peak discharge Embankments (levees)
Confluence Flood plains Channelisation
Mouth Levees Land-use Management Flood Relief Channels
Afforestation Dams & Reservoirs
Processes of River Erosion Causes and effects of flooding in Managing
Hydraulic Action the UK Farmland Soft Engineering
Abrasion Physical Causes of Flooding Managing drainage Washlands
Solution Intense rainfall in urban areas River restoration
Attrition During of rainfall Flood-plain Zoning
Snow melt
Weathering Processes Rock Type Reduce the Impact of Flooding
Mechanical (freeze thaw) Relief Flood waring & strategies for the home
Chemical (acid rain)
Biological (plant roots) Human causes of Flooding Case Study – The River Dee
Deforestation The Long Profile
Mass movement Urbanisation Characteristics of the River Dee (Bradshaw’s Model)
Soil creep Human factors changing the river
Sliding Climate Change Physical factors changing the river
Flows Predicting the risk of flooding in the Dee catchment
Effects on People & the
Transportation Environment Examples Skills
Traction Somerset 2014 I can read a geological map to link coastal form to geology.
Saltation Boscastle 2004 I can use UK weather and climate data
Suspension Tewkesbury 2007 I can draw a simple storm hydrograph using rainfall and
Solution North Wales 2012 discharge data.
I can identify river landforms on OS maps.
Deposition I can use an OS map to investigate the impact of human
intervention.
1C. Glaciated Upland Landscapes and Processes
Glaciers
Landforms of glacial erosion Case Study – Changes to the glaciated uplands of Snowdonia
Types of Glaciers
Corries Changing physical landscape of Snowdonia
Ice sheet
Tarn Geology of Snowdonia
Valley glacier
Arête Settlement living in Snowdonia
Pyramidal peak Farming & Forestry
The glacial system
Glacial trough (U-shaped valley) Human impacts on natural processes
Zone of accumulation
Truncated spurs
Zone of ablation
Hanging valleys Development in the glaciated uplands of Snowdonia
Calving
Misfit stream Water storage & supply
Ribbon lake Quarrying & mining
Glacial Budget
Roche moutinnee Renewable energy (Hydro-electric power)
Seasonality
Many years/ Centuries Recreation, tourism & conservation
Landforms of glacial
transportation & deposition The impact of development in Snowdonia
Glacial and post-glacial processes
Glacial Erosion
Moraine Advantages & disadvantages of development in Snowdonia
Ground Moriane Managing development in Snowdonia
Abrasion
Lateral Moriane
Plucking
Medial Moriane The impact of climate change on development in Snowdonia
Terminal Moriane Pros and cons of Farming
Glacial Movement &
Recessional Moriane Pros and cons of recreation and tourism
Transportation
Basal sliding
Drumlins
Rotational slip Skills
Moraine
Carg and tail I can use UK weather and climate data
Deposition I can identify glaciated upland landforms on OS maps.
Bulldozing I can use an OS map to investigate the impact of human
intervention.
Post-glacial processes
Mechanical weathering
(freeze thaw)
Rock falls
Soil movement
2. Weather Hazards & Climate Change
Global Climate The UK climate Case Study – Hurricane Sandy, USA (2012) [developed country]
Atmospheric Circulation UK climate over change over Social Impacts
Coriolis effect time Economic Impacts
Jet streams Environmental Impacts
Oceanic Circulation Significance of the UK’s location on Responses to the disaster
climate
Global Climate Change Maritime influence Case Study – Typhoon Haiyan, Philippines (2013) [emerging]
Natural Causes of climate Prevailing wind Social Impacts
change North Atlantic Drift Economic Impacts
Eccentricity Circulation cells Environmental Impacts
Axial tilt Altitude Responses to the disaster
Precession
Solar Variation Tropical cyclones Drought Case Study – Drought in
Volcanism Formation of cyclones Natural causes of drought California, USA (2012-
Surface impact Movement of cyclones Meteorological present)
Greenhouse effect Location of cyclones Hydrological Location
Frequency of cyclones Causes
Human causes of climate Human causes of drought Key effects
change Impacts of Tropical Cyclones Dams Key responses
Enhanced greenhouse High winds Deforestation
effect Intense rainfall Agriculture Case Study – Drought in
Industry Storm surges Ethiopia (1983-present)
Transport Coastal flooding Impacts of drought Location
Energy Landslides Social Impacts Causes
Farming Economic Impacts Key effects
Effects on People & the Environmental Impacts Key responses
Negative Impact of Climate Environment Examples
Somerset 2014
Change Skills
Food Production Boscastle 2004 I can interpret line graphs/ bar charts showing climate
Sea level rise: Maldives Tewkesbury 2007
change.
Retreating glaciers & North Wales 2012 I can use maps to track the movement of tropical cyclones.
melting ice sheets
3. Ecosystems, Biodiversity & Management
The World’s ecosystems The Nutrient Cycle Tropical Rainforests Deciduous Woodland
Distribution of ecosystems Gersmel’s Model Tropical rainforest Deciduous characteristics
Temperature Soil characteristics Biotic factors
Convection cell Litter Biotic factors Abiotic factors
Biomas Abiotic factors Food Webs
Tilt of the Earth
Biodiversity in the TRF Deciduous Biodiversity
Inter-Tropical Convergence
Biotic Components Goods & Services
Zone (ITCZ) Abiotic components Importance of the TRF
Interior of continents Goods & services Threats to ecosystem
High mountains The UK’s Ecosystems Climate change Climate change – Milder
Terrestrial (land) ecosystems Changes to TRF structure winters
Characteristics & Vegetation Woodland Changes to TRF function Climate change – Fire
of biomes Moorland Changes to TRF biodiversity Climate change – drought
Tropical rainforest Wetlands Biodiversity
Tropical grasslands Heathland Deforestation in the TRF
Deserts Deforestation in the Deforestation
Marine Ecosystems Madagascan TRF Deforestation vs coniferous
Temperate grasslands
Inshore habitats Tavy & Deforestaion Economic causes
Temperate forest
Offshore habitats Population growth & Social causes
Boreal forest deforestation
Tundra Benefits of Marine Ecosystems Logging & deforestation Case Study – The New Forest:
Mountain Tourism Sustainable Deciduous woodland
Mediterranean Fishing Case Study – Sustainable management
Energy: oil rainforest management in Purpose of New Forest
Local factors affecting Energy: offshore wind farms Madagascar Woodland management
distribution Government Policies Sustainable use of New
Altitude (Height) Human activities that damage marine Ecotourism Forest
Soils ecosystems Rainforest services
Humans Overfishing Sustainable agriculture Skills
Eutrophication Social benefits I can use a world map to
Construction of deep-water ports Problems locate global biomes
The Biosphere Coastline economic development Example – Analamazaotra I can compare climate graphs
Resources of the Biosphere Offshore wind farms reserve I can use and interpret
Food nutrient cycle & food web
Medicine Skills diagrams.
Fuel I can interpret line graphs showing the range of future global population I can use GIS to identify the
Building materials projections and the likely impact to resources. pattern of forest loss.
Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist
The Human Environment
This check list contains the following units:
4 – Changing Cities
5 – Global Development
6 – Resource Management
Choice between one of the following:
6A – Energy Resource Management
6B – Water Resource Management
This Symbol Indicates a case study you This Symbol Indicates a skills you may be
will need to know. expected to apply in the exam.
Case Study – Birmingham: A Case Study – Mumbai/
4. Changing Cities major UK city Mexico City: A major city in
The Site and situation of an emerging country
Urbanisation is a global Degree of Urbanisation varies
Birmingham The Site and situation of
process across the UK
Trends of population living The Structure of Birmingham city
Physical Factors
Tees-exe line The Structure of the city
in urban areas
Urbanisation Mountains/Steep slopes The changing city
Counter-urbanisation Urbanisation (18th & 19th Reasons for variable
(North)
Re-urbanisation Thin soils (North) Centuries) population growth
Shanty towns Low and flat land (South) Suburbanisation (1920s & Rural-to-urban migration
Rich Soils (South) 1930s) Rates of natural increase
Counter-urbanisation (1970s) Economic investment &
Why are cities in emerging &
Re-urbanisation (after 1990) Growth
developing countries growing Historical Factors
so fast? Industrial Revolution
Natural increase Industrial Centres Migration Causes & Impact of
Migration Conurbations National Migration Migration
Push factors International Migration National Migration
Pull factors Impact of Migration International Migration
Recent Economic Factors
Megacities Focus on tertiary industries Impact of Migration
Focus on quaternary Population Characteristics
Population
Degree of Urbanisation varies industries
Industries in London Causes of De-industrialisation Characteristics
across the UK
Globalisation
UK population distribution
De-centralisation Effects of rapid growth
Population density Political Factors (London)
Centre of UK Government Technological advances Housing
Relationship with the EU Transport developments Informal & Under –
World-class financial centre Impacts of de-industrialisation employment
Pollution
Skills Changes and Impacts
I can interpret line graphs and calculate rate of population Inequality in Birmingham Changes and Impacts
growth. Quality of life in Birmingham Inequality in the city
I can use satellite images to identify land use zones and urban Changes in retailing in Quality of life in the city
patterns. Birmingham Sustainable urban living
I can use and interpret population pyramids & choropleth maps. Sustainable urban living Bottom-up strategies
I can use GIS/satellite images, historic images and maps to Top-down strategies
investigate spatial growth.
5 Global Development
Factors comprising Factors affecting Uneven development International strategies to Types of Aid
Quality of Life development Location of countries of high and reduce uneven development International Aid
Economic Economic factors low GDP. Foreign Direct investment Government Aid
Income Average wealth/ Income (FDI) Multilateral Aid
Job Security Growth rate of an As countries and regions Fair Trade Bilateral Aid
Standard of Living economy develop: International Aid Voluntary Aid
Trade surplus/deficit Infant mortality falls Debt relief Short-term
Social Unemployment rate Total fertility rate declines Remittances emergency aid
Family & Friends Cost of living Life expectancy rises Top-down development Long-term
Education % of the pop. Living in urban e.g. HS2, England emergency aid
Health Social factors areas increases. Bottom-up development
Housing e.g. Water aid, Mali or Case Study – Positive
Physical Education Measuring inequality within SPARC, India & negative impacts of
Diet/Nutrition Health countries rapid development in
Water Supply Equity Gini Coefficient Case Study – How India, an India
Climate Opportunities for leisure Gross Disposable Household emerging country is Air Pollution
Water Pollution
Environmental & recreation Income (GDHI) developing
India’s Location & Context Deforestation
quality/ hazards
Desertification
Technological factors Causes of global inequalities in the World
Greenhouse gases
Psychological Electrification Physical environment Environmental Contrasts
Climate change
Happiness Internet access Demography Social & religious
Managing growth
Security Efficiency gains in Political & Economic Policies composition
Freedom farming & industry History (Colonialism) Internal Boundaries
Skills
Social Investment The Indian diaspora I can compare
How development is Cultural factors rankings of countries
measured Happiness Impact of uneven development Uneven Development using development
Democratisation Regional Contrasts indicators
Gross Domestic Access to housing I can use proportional
Product (GDP) Balance between Health Economic Core regions flow line maps to
Human Development traditional & imported Education (Mumbai) visualize trade
Index (HDI) cultures Employment Periphery (Bihar) patterns & flows
Life expectancy Work-life balance I can interpret
Technology & Appropriate
Mean schooling Changing Economic Sectors population pyramids.
Expected years of
technology I can use socio-
Food & water security Food & water security Trade, aid and investment economic data to
schooling Availability of food Demographic Change calculate data to
Gross National Income
Access to food Skills Changing social factors calculate the
(GNI) Geopolitics difference from the
Corruption perceptions Consumption of food I can interpret population pyramids
I can interpret choropleth maps Technology & Connectivity mean, for the core and
index Water security periphery regions.
I can use numerical economic data
6. Resource 6A. Energy Resource Management 6B. Water Resource Management
Management
Types of Energy Resources Development of renewable Global variation of fresh Meeting the demand
Classifying resources Pros & Cons energy resources water supply for water
Abiotic resources Non-renewable (Finite) Wind energy e.g. London Array Distribution of countries Desalination
Biotic resources Fossil Fuels Hydro-electric Power (HEP) in: Management
Non-renewable Coal e.g. Itaipu HEP plant, Brazil & Water Surplus disputes
resources Oil Paraguay Water deficit Las Vegas Water
Renewable resources Natural Gas Solar Power e.g. Mojave Problems
Nuclear (Renewable Desert, USA Causes of water stress
How is exploitation
changing environments? energy from a finite Population growth How stakeholders can
Deforestation in resource) Development of non-renewable Climate change manage energy
Cameroon energy resources Level of Development resources
Oil extraction in Renewable energy Oil reserves e.g. Athabasca tar Differences in Water Individuals
Ecuador Wind sands, Canada consumption Organisations
Overfishing in the Hydro-electric Power Natural Gas – Fracking Agriculture (Irrigation of Governments
North Sea (HEP) Nuclear Energy - Uranium crops)
Solar Industry (Cooling Case Study –
Distribution of natural Tidal & Wave Disputes over energy resources machinery, washing Sustainable water
resources on a global and Geothermal Fracking (Pros & Cons in USA) Management, UK
products)
national scale Increase water use
Biofuels Should the UK introduce Washing (Drinking &
Global variety & Build Reservoirs
distribution fracking (Pros & Cons) Washing) Extract more water
Minerals & fossil fuels UK’s Energy Mix (2014) Recycle Water
Agriculture & forestry Gas 34.1% How stakeholders can manage Change in supply & Decrease water use
Natural resources in Oil 34% energy resources Demand for water in Water Meters
the UK Coal 16.4% Individuals (Carbon footprint) Las Vegas Cut use by farmers
Nuclear 7.1% Organisations Education to use less
Consumption of resources Bioenergy 5.5% Governments Water Supply problems in
Global patterns of Wind & Hydro 1.9% Case Study – Sustainable
the UK
consumption Case Study – Sustainable energy water Management, China
Imports 0.9% Rainfall imbalance
Global energy Management, China (Emerging) Hard engineering
Seasonal imbalance South-North Water
consumption China’s Energy Mix
Global food Reasons for variations in HEP – Three Gorges Dam Ageing Infrastructure Transfer scheme
global energy mix Management Plan
consumption Solar Power – Gobi Desert Effective Monitoring
Global fresh water Population Water Supply problems in
Water Irrigation
Income & wealth Case Study – Sustainable energy emerging & developing Environmental
Skills Availability of energy Management, Germany(Developed) Countries protection of freshwater
I can use and interpret UK Germany’s Energy Mix Unsafe Water Agriculture
supplies
and World maps showing
Wind – Norsee Ost farm Pollution of water courses Cities & Industry
Growth of industry
distribution of resources.
Solar Power – Bavaria Solarpark Low annual rainfall: The
Technological Advances Sahel
Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist
Fieldwork & UK Challenges
This check list contains the following units:
7 – Geographical Investigation – Fieldwork
You must choose between
7A Physical – River or Coastal landscapes
7B Human – Rural or Urban environments
8 – Geographical Investigations – UK Challenges
This Symbol Indicates a skills you may be
expected to apply in the exam.
7 Geographical Investigations 8 Geographical Investigations – UK Challenges
Stages of the Enquiry Process Resource Consumption & Sustainability UK Landscape Challenges
1. The Enquiry Question & Location of study Changes to the UK Population Sustainable development in UK National Parks
2. Methodology – Range of techniques and Pressure on UK Ecosystems Conservation Apprentices
methods used in fieldwork Agribusiness Change transport habits
3. Data Presentation – Processing and presenting Greenfield sites Encourage local businesses to use
fieldwork data Brownfield sites renewable energy sources
4. Analysing and explaining fieldwork data Green Belt Create more employment in national parks
5. Conclusion Addressing the issue of consumption Funding & investments to small businesses.
6. Evaluation and critical reflection of fieldwork
data, methods used, conclusions drawn and Sustainable Transport Options in the UK River Flood Risk in the UK
knowledge gained. Public Transport Systems Flooding resulting from
Cycle Hire & Routes Increasing population
Skills Car Sharing Changes in land use
I can identify questions or issues for Zero/low emission transport Climate change
investigation. Congestion Charge Somerset Levels 2013/2014
I can develop a hypothesis and/or key Hard & soft engineering to manage
questions. Settlement, population & Economic flooding.
I can consider appropriate sampling techniques Challenges
(Systematic vs random vs stratified). The ‘two speed economy’ The UK coastal challenges
I can consider health & safety and undertake Solutions Storm Surges (December 2013)
risk assessment. High Speed Rail 2 (HS2) Addressing coastal flood risk
I can select data collection methods and Transport across Northern UK Hard & soft engineering to manage
equipment to ensure accuracy and reliability. Improve Northern Airport flooding.
The UK’s climate change challenges
I can present my data using ICT and hand drawn connections Changes to average temperatures
methods. Pros & Cons of Brownfield & Changes to average precipitation
I can write descriptively, analytically and Greenfield
critically about my findings. Impacts
I can write well evidences and informed Migration and the UK Risk of drought
conclusions. Patterns of migration change Water deficits
Reasons for migration Ecosystems
Migrants Food supply (Local & global)
Emigrant
Immigrant Responses on an individual, local, national &
Net Migration international scales.
Views of different groups (Businesses,
local government)
You might also like
- KO Physical Landscapes in The UKDocument4 pagesKO Physical Landscapes in The UKianbradley3No ratings yet
- Introduction To Coastal Processes and LandformsDocument1 pageIntroduction To Coastal Processes and Landformslyana1234100% (1)
- Coastal Planning Management Lesson1-OverviewDocument57 pagesCoastal Planning Management Lesson1-OverviewshirleyNo ratings yet
- Shallow-Water Environments and Their Sediments: Shelf SeasDocument31 pagesShallow-Water Environments and Their Sediments: Shelf SeasanibalNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction, Types of Structures & The Coastal EnvironmentDocument16 pages01 Introduction, Types of Structures & The Coastal Environmentcherry viernesNo ratings yet
- Coastal Structures and Their ImpactsDocument48 pagesCoastal Structures and Their Impactsshirley100% (2)
- L8 Defending The CoastDocument27 pagesL8 Defending The CoastRahma AbdullahiNo ratings yet
- 1a Coastal Landscapes Role of Geology High Low Energy Littoral Zone Coast As A System Sediment Supply Classifying CoastsDocument19 pages1a Coastal Landscapes Role of Geology High Low Energy Littoral Zone Coast As A System Sediment Supply Classifying Coastsapi-373301029No ratings yet
- Coasts SummaryDocument2 pagesCoasts SummaryFlora ForresterNo ratings yet
- Geomorphic Processes and Resulting LandformsDocument51 pagesGeomorphic Processes and Resulting LandformsSwati TomarNo ratings yet
- Balino ABE34 Journal-ArticleDocument16 pagesBalino ABE34 Journal-ArticleRaymond BalinoNo ratings yet
- Coasts - OverviewDocument1 pageCoasts - OverviewKatieNo ratings yet
- Geological Reservoir CharecterizationDocument265 pagesGeological Reservoir CharecterizationShahnawaz MustafaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Revision Teams 2023Document53 pagesPaper 1 Revision Teams 2023alfiepetersdenisonNo ratings yet
- Coasts Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Document20 pagesCoasts Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Georgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- Oceans Day Pamphlet - ReducedDocument2 pagesOceans Day Pamphlet - ReducedOmer ErgeanNo ratings yet
- Morphological CausesDocument6 pagesMorphological CausesSudipto RoyNo ratings yet
- 02 Coastal Processes, Winds and CurrentsDocument17 pages02 Coastal Processes, Winds and CurrentsAnton MNo ratings yet
- Development Impacts Disaster - Coastal Town - PallabiDocument32 pagesDevelopment Impacts Disaster - Coastal Town - PallabiPallabi BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Coastal Erosion Problems and SolutionsDocument10 pagesCoastal Erosion Problems and SolutionsAzwani AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Beach: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument33 pagesBeach: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAsma HussainNo ratings yet
- RIVER ENGINEERING: KEY PROCESSES AND LANDFORMSDocument69 pagesRIVER ENGINEERING: KEY PROCESSES AND LANDFORMSAdiatma SaputraNo ratings yet
- Coastal Managemtn Holderness 2Document5 pagesCoastal Managemtn Holderness 2Grand OverallNo ratings yet
- Identifying The Hazards Caused by Geological Processes: Geologic Event Hazards They Cause EarthquakeDocument7 pagesIdentifying The Hazards Caused by Geological Processes: Geologic Event Hazards They Cause Earthquakejzeaska damianNo ratings yet
- Coastal Mapping Infographic 508Document2 pagesCoastal Mapping Infographic 508WashingtonCunhaNo ratings yet
- UK Coastal Landscapes and Management StrategiesDocument2 pagesUK Coastal Landscapes and Management StrategieschemphycombNo ratings yet
- Coastal Vulnerability Mapping: R S MahendraDocument12 pagesCoastal Vulnerability Mapping: R S Mahendrabenito jayadasNo ratings yet
- 0101SED16 17intro TextDocument32 pages0101SED16 17intro TextAdrian GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Coastal Vulnerability Mapping and Analysis Training CourseDocument25 pagesCoastal Vulnerability Mapping and Analysis Training CourseDiego Acevedo FernandezNo ratings yet
- 2 Karakteristik DPIDocument24 pages2 Karakteristik DPISudi DidiNo ratings yet
- Geo HazardsDocument50 pagesGeo Hazardsعلي عبيداتNo ratings yet
- The Interaction Between Coastal Sediment Dynamics and Coastal Sea Defences at Christchurch, Dorset, EnglandDocument5 pagesThe Interaction Between Coastal Sediment Dynamics and Coastal Sea Defences at Christchurch, Dorset, EnglandInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Constructive and Destructive Forces Shape Earth's SurfaceDocument24 pagesConstructive and Destructive Forces Shape Earth's SurfaceDecereen Pineda RodriguezaNo ratings yet
- Geoindicadoes (BUSH, 1999)Document24 pagesGeoindicadoes (BUSH, 1999)Luan MartinsNo ratings yet
- Coasts: Earth: Our HomeDocument32 pagesCoasts: Earth: Our HomeVernon100% (1)
- Lecture 10 - Natural Terrain Landslide Risk Management (19 Nov 2020) FinalDocument99 pagesLecture 10 - Natural Terrain Landslide Risk Management (19 Nov 2020) FinalYUK LAM WONGNo ratings yet
- Coastal GeomorphologyDocument61 pagesCoastal GeomorphologyYolo YoloNo ratings yet
- L4 Coastal Erosion LandformsDocument22 pagesL4 Coastal Erosion Landformsxofah81094No ratings yet
- CP Against Wave EnergyDocument19 pagesCP Against Wave EnergyHafiz_Murni_4791No ratings yet
- Formation Problem Challenges SolutionDocument21 pagesFormation Problem Challenges Solutionphares khaledNo ratings yet
- Safari - 4 Jan 2021 at 6:38 PM 2Document1 pageSafari - 4 Jan 2021 at 6:38 PM 2Joseph MawacNo ratings yet
- Groyne Field Design For No. 63 BeachDocument26 pagesGroyne Field Design For No. 63 BeachJonathanNo ratings yet
- Geomorphic ProcessesDocument51 pagesGeomorphic ProcessesAnonymous 8enaNCTaedNo ratings yet
- Shallow-marine Sandstone Reservoirs, Depositional Environments, Stratigraphic Characteristics and Facies Model: A Review Numair Ahmed Siddiqui, Abdul Hadi A. Rahman, Chow Weng Sum, Wan Ismail Wan Yusoff and Mohammad Suhaili bin Ismail Department of Geoscience, Faculty of Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Perak, MalaysiaDocument27 pagesShallow-marine Sandstone Reservoirs, Depositional Environments, Stratigraphic Characteristics and Facies Model: A Review Numair Ahmed Siddiqui, Abdul Hadi A. Rahman, Chow Weng Sum, Wan Ismail Wan Yusoff and Mohammad Suhaili bin Ismail Department of Geoscience, Faculty of Geoscience and Petroleum Engineering, Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS, Perak, MalaysiaCris TinaNo ratings yet
- 1200-Article Text-3855-1-10-20220110Document12 pages1200-Article Text-3855-1-10-20220110Ibtihaj ChairulNo ratings yet
- Title (View Menu/View Master To Edit)Document28 pagesTitle (View Menu/View Master To Edit)dsanchez89No ratings yet
- IPG-CH-16-Landforms Made by Waves and WindDocument32 pagesIPG-CH-16-Landforms Made by Waves and WindLakshay MehtaNo ratings yet
- 1 Depositional Environment of SandstonesDocument18 pages1 Depositional Environment of SandstonesAndy HNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology and Hydrology of Lincoln Fok's CourseDocument50 pagesGeomorphology and Hydrology of Lincoln Fok's Coursemichael wongNo ratings yet
- Shoreline Change Assessment of Kerala Coast MappedDocument6 pagesShoreline Change Assessment of Kerala Coast MappedAnonymous 3akQhQFJSLNo ratings yet
- Surface Processes: Mass Wasting Streams Ground WaterDocument45 pagesSurface Processes: Mass Wasting Streams Ground WaterrhaineNo ratings yet
- OceansDocument54 pagesOceansKhoirulhaqNo ratings yet
- 2020 Gec-Fcp Poster Searise 06Document1 page2020 Gec-Fcp Poster Searise 06muiz musaNo ratings yet
- Geol Proc Hazards Fall11 Forpost PDFDocument16 pagesGeol Proc Hazards Fall11 Forpost PDFAnna Kathleen LimNo ratings yet
- Geologic Processes and Hazards ExplainedDocument16 pagesGeologic Processes and Hazards ExplainedAlexa Fatima100% (1)
- LST Report Web1Document47 pagesLST Report Web1aliem sukmaraNo ratings yet
- Bs Geology, MSC Geotech Eng'G, Mba: Eduardo S. TanDocument83 pagesBs Geology, MSC Geotech Eng'G, Mba: Eduardo S. Tanrinsandesu 27No ratings yet
- 6-Sedimentary PPTminimizerDocument25 pages6-Sedimentary PPTminimizerapi-3823621No ratings yet
- Elements of Physical Oceanography: A derivative of the Encyclopedia of Ocean SciencesFrom EverandElements of Physical Oceanography: A derivative of the Encyclopedia of Ocean SciencesNo ratings yet
- Part D - Progress Update & EvaluationDocument2 pagesPart D - Progress Update & EvaluationJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Classical Guitar Sample Booklet 10-19 PDFDocument21 pagesClassical Guitar Sample Booklet 10-19 PDFJones Jonny100% (1)
- What is the Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pagesWhat is the Electromagnetic SpectrumJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - HomeworkDocument9 pagesLesson 5 - HomeworkJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Mass Media and SocietyDocument2 pagesMass Media and SocietyJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- SECTION D GuidanceDocument1 pageSECTION D GuidanceJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Part D: Arts Apprenticeship Feedback Sheet: Name: - DateDocument1 pagePart D: Arts Apprenticeship Feedback Sheet: Name: - DateJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Black Lion Level 3 Winter Open Meet 2019: Licence NoDocument3 pagesBlack Lion Level 3 Winter Open Meet 2019: Licence NoJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- How Do We Use Radio WavesDocument12 pagesHow Do We Use Radio WavesJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- We Run Running Technique A Beginners Guide WWW - We Run - Co - .Uk - PDFDocument34 pagesWe Run Running Technique A Beginners Guide WWW - We Run - Co - .Uk - PDFJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- How Do We Use Radio WavesDocument12 pagesHow Do We Use Radio WavesJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- We Run Running Technique A Beginners Guide WWW - We Run - Co - .Uk - PDFDocument34 pagesWe Run Running Technique A Beginners Guide WWW - We Run - Co - .Uk - PDFJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- What Do We Use EM Waves ForDocument5 pagesWhat Do We Use EM Waves ForJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- How Do We Use Radio WavesDocument12 pagesHow Do We Use Radio WavesJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- What Do We Use EM Waves ForDocument5 pagesWhat Do We Use EM Waves ForJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- What Do We Use EM Waves ForDocument5 pagesWhat Do We Use EM Waves ForJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Exam Topic List - Higher AADocument16 pagesExam Topic List - Higher AAJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Exam Topic List - Higher BDocument14 pagesExam Topic List - Higher BJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Topic ChecklistDocument2 pagesTopic ChecklistJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- What Do We Use EM Waves ForDocument5 pagesWhat Do We Use EM Waves ForJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- What is the Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument13 pagesWhat is the Electromagnetic SpectrumJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Higher Revision ChecklistDocument1 pageHigher Revision ChecklistJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Higher Checklist 2017: Maths DepartmentDocument4 pagesEdexcel Higher Checklist 2017: Maths DepartmentJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Dev Dynamics - RAG Confidence Before & AfterDocument1 pageDev Dynamics - RAG Confidence Before & AfterJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Geography GCSE Edecel-B BOOK PDFDocument58 pagesGeography GCSE Edecel-B BOOK PDFJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Geography GCSE Edecel-B BOOK PDFDocument58 pagesGeography GCSE Edecel-B BOOK PDFJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Best Audios for Money - What is Hi-Fi AudioDocument6 pagesBest Audios for Money - What is Hi-Fi AudioJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Best Audios for Money - What is Hi-Fi AudioDocument6 pagesBest Audios for Money - What is Hi-Fi AudioJones JonnyNo ratings yet
- Edexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist: The Physical EnvironmentDocument13 pagesEdexcel GCSE Geography A Checklist: The Physical EnvironmentJones Jonny100% (1)
- Evs PresentationDocument68 pagesEvs PresentationSHETH DEEPNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 Product - Service DesignDocument12 pages1.3.1 Product - Service DesignMax ClaydonNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1: What Are Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources?Document16 pagesAssignment - 1: What Are Renewable and Non-Renewable Resources?ᏋᏒ ᎴᏋᏋᎮᏗᏦ ᏦᏬᎷᏗᏒ ᏕᎥᏁᎶᏂNo ratings yet
- FomegasDocument3 pagesFomegasSummer pickNo ratings yet
- ENERGY AUDITING & DSM TEXTBOOK GUIDEDocument112 pagesENERGY AUDITING & DSM TEXTBOOK GUIDESA S CNo ratings yet
- CATEGORIZING QUESTIONSDocument14 pagesCATEGORIZING QUESTIONSdecentyNo ratings yet
- Importance of Energy Conservation: EarthDocument3 pagesImportance of Energy Conservation: EarthEinah EinahNo ratings yet
- 7 Environmental Principles ExplainedDocument2 pages7 Environmental Principles ExplainedRosaly BontiaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Solar Electricity in Sri Lanka and Recycling ProcessesDocument29 pagesOverview of Solar Electricity in Sri Lanka and Recycling ProcessesAmal WahidNo ratings yet
- Bioresource Technology: Katarzyna Chojnacka, Konstantinos Moustakas, Anna Witek-Krowiak TDocument11 pagesBioresource Technology: Katarzyna Chojnacka, Konstantinos Moustakas, Anna Witek-Krowiak TamanuelNo ratings yet
- APES Unit 6 Notes FramesDocument14 pagesAPES Unit 6 Notes FramesKIM JEEHEENo ratings yet
- Physical Science 11 q1 Module 11 How Energy Is Produced and Managed 08082020Document31 pagesPhysical Science 11 q1 Module 11 How Energy Is Produced and Managed 0808202010 A Angelic GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Đề cương Anh 10 - Học kỳ IIDocument8 pagesĐề cương Anh 10 - Học kỳ IINguyễn NamNo ratings yet
- Renewable Energy Sources in Libya - EP703Document37 pagesRenewable Energy Sources in Libya - EP703kemoNo ratings yet
- Upp-Int Cumulative Tests A AKsDocument10 pagesUpp-Int Cumulative Tests A AKsТори ПавленкоNo ratings yet
- PBD Chapter 6Document17 pagesPBD Chapter 6Aathirah HashimNo ratings yet
- Renewable vs Nonrenewable Resources and Environmental Policy GuideDocument6 pagesRenewable vs Nonrenewable Resources and Environmental Policy GuideOwen PastorNo ratings yet
- (123doc) Bai Tap Tong Hop Tieng Anh Lop 11 Hkii With KeyDocument46 pages(123doc) Bai Tap Tong Hop Tieng Anh Lop 11 Hkii With KeyLưu Thanh TúNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit 1&2Document25 pagesMCQ Unit 1&2abcd100% (1)
- Bài Tập Thực Hành Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 HKIIDocument26 pagesBài Tập Thực Hành Tiếng Anh Lớp 11 HKIItamarind leavesNo ratings yet
- Coal Persuasive WritingDocument4 pagesCoal Persuasive Writingapi-242785990No ratings yet
- Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesNatural ResourcesCindy YaoNo ratings yet
- VCE Chemistry Unit 4Document311 pagesVCE Chemistry Unit 4Danny GoldstoneNo ratings yet
- Module 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceDocument42 pagesModule 1: Introduction To Energy ScienceNishita Waghmare50% (2)
- Week 1 - Energy Management Lecture - Energy SourcesDocument59 pagesWeek 1 - Energy Management Lecture - Energy SourcesNorbertsanJebaNo ratings yet
- Detailed - Lessonplan-Energy ResourcesDocument11 pagesDetailed - Lessonplan-Energy Resourcesrhealyn jaramillaNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies PPT ModifiedDocument58 pagesEnvironmental Studies PPT ModifiedPradeepkumarKatgi100% (1)
- Unit 7 - No.1 - NCDocument7 pagesUnit 7 - No.1 - NCnguyen ngaNo ratings yet
- Danisco A/S 2009-10 Sustainability ReportDocument112 pagesDanisco A/S 2009-10 Sustainability ReportJeffrey HogueNo ratings yet
- Exploitation of Natural ResourcesDocument3 pagesExploitation of Natural ResourcesMuhammad HabibNo ratings yet