Professional Documents
Culture Documents
THE NEMATODES Notes
Uploaded by
Glaiza BolanoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
THE NEMATODES Notes
Uploaded by
Glaiza BolanoCopyright:
Available Formats
THE NEMATODES
6. Strongyloides stercoralis
1. Enterobius vermicularis
S.stercoralis eggs is smaller than
The specimen of choice is
hookworm eggs
cellophane tape preparation
Well-developed larvae are always
collected from perianal region
contained in S.stercoralis eggs
Most common helminth in US
Diagnostic rhabditiform larvae may
Copulation- mating of select worms
be recovered in fresh stool samples
Gravid- pregnant female worm
and duodenal aspirates
It is believed that E.vermicularis is
Enterotest has proven successful in
responsible for the transmission of
obtaining desired larvae and
D.fragilis
hookworm-like eggs
2. Trichuris trichuria
7. Trichinella spiralis
Male worm possesses an easily
Examination of the affected skeletal
recognizable curled tail
muscle is the method of choice for
Laboratory diagnosis technique for
recovery of the encysted larvae
recovery is zinc floatation method
Resistant to colder regions
Third most common helminth
Known as the great imitator
Symptoms resembles to ulcerative
colitis
8. Dracunculus medinensis
Adult D.medinensis may be
3. Ascaris lumbricoides
recovered in infected ulcers
The egg is usually corticated
Symptoms are associated with
Decorticated: lacking an outer
allergic reactions
mammillated albuminous coating
Guinea worms are suspected as
Largest known intestinal nematode
being “fiery serpents” responsible
Most common intestinal helminth for a plague
in the world
4. Necator americanus
Hook is more pronounced
5. Ancyclostoma duodenale
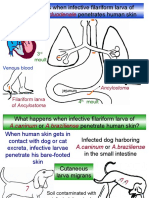
Ancyclostoma braziliense &
Ancyclostoma caninum are
parasites of dogs and cats;
condition is known as cutaneous
larva migrans
You might also like
- Leyte Normal University Science Unit: Lab Activity # 7 NematodaDocument11 pagesLeyte Normal University Science Unit: Lab Activity # 7 NematodaEdward Glenn AbaigarNo ratings yet
- Phylum NematodaDocument11 pagesPhylum NematodaKristine Aranna ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Nematodes Part 2Document21 pagesNematodes Part 2Grazielle Almazan100% (2)
- Para Lab 2Document3 pagesPara Lab 2api-3743217100% (2)
- HelminthsDocument10 pagesHelminthsMaureen Kate DuqueNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9 PARA LABDocument9 pagesExercise 9 PARA LABBishal KunworNo ratings yet
- Exercise 9Document9 pagesExercise 9Bishal KunworNo ratings yet
- Enterobius Vermicularis: Ciulla Chapter 8 - ParasitologyDocument13 pagesEnterobius Vermicularis: Ciulla Chapter 8 - ParasitologySalve Rachelle BillenaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8: Nematodes Part 1 OverviewDocument7 pagesLesson 8: Nematodes Part 1 OverviewAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Mtap - Parasitology FinalsDocument6 pagesMtap - Parasitology FinalsMoira Pauline LibroraniaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Review: True or FalseDocument1 pageChapter Review: True or FalseJames Gabriel SalardaNo ratings yet
- Roundworms: Characteristics, Life Cycles and PathogenesisDocument18 pagesRoundworms: Characteristics, Life Cycles and PathogenesisEmmanuel AbrahamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 NematodesDocument5 pagesChapter 8 NematodesJuju GalangNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy Guide and Siemens Multistix PrinciplesDocument4 pagesClinical Microscopy Guide and Siemens Multistix Principlesjay primaNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument117 pagesNematodesBea Bianca CruzNo ratings yet
- Canizares, NematodesDocument3 pagesCanizares, NematodesJan Mark CañizaresNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Nematodes: Ancylostoma, Strongyloides, NecatorDocument4 pagesIntestinal Nematodes: Ancylostoma, Strongyloides, NecatorBlanche AltheaNo ratings yet
- Intestinal NematodesDocument1 pageIntestinal Nematodescjyulo99710No ratings yet
- 11 Parasitology - Phasmids 4Document4 pages11 Parasitology - Phasmids 4maqmmNo ratings yet
- Preventing Black Head DiseaseDocument2 pagesPreventing Black Head DiseaseSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Veterinary Helminthology MidtermsDocument4 pagesVeterinary Helminthology Midtermshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Nematodes. Nematodes Common Name Mode of Transmission Habitat Infective Stage Diagnostic Stage Definitive Host Intermediate HostDocument2 pagesLesson 2 - Nematodes. Nematodes Common Name Mode of Transmission Habitat Infective Stage Diagnostic Stage Definitive Host Intermediate HostAnjelo PerenNo ratings yet
- Lab (4) Practical Parasites The Second Stage Assistant Lecturer Muna Hashim 2014Document27 pagesLab (4) Practical Parasites The Second Stage Assistant Lecturer Muna Hashim 2014Jennifer AnatasyaNo ratings yet
- ANCYLOSTOMA DUODENALE Old World HookwormDocument2 pagesANCYLOSTOMA DUODENALE Old World HookwormScarlet AdolfoNo ratings yet
- 3 - OK Dermatite de Ácaros AviáriosDocument3 pages3 - OK Dermatite de Ácaros AviáriosYasmin S.O.MarinhoNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Animalia QuizDocument13 pagesKingdom Animalia QuizMaristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Midterm-TransesDocument11 pagesParasitology Midterm-TransesJISOO KimNo ratings yet
- Nematodes For Quiz 1 RevisedDocument6 pagesNematodes For Quiz 1 RevisedAra NuesaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10Document6 pagesLesson 10daryl jan komowangNo ratings yet
- Clinical+Parasitology-Module+8Document15 pagesClinical+Parasitology-Module+8Geresh MagsinoNo ratings yet
- 9 B Lab 9 EntrobiousDocument5 pages9 B Lab 9 EntrobiousSaadNo ratings yet
- Common intestinal parasites and their diagnostic stagesDocument5 pagesCommon intestinal parasites and their diagnostic stagesCedrick SiapnoNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Exam (HELMINTHS)Document7 pagesParasitology Exam (HELMINTHS)Tony DawaNo ratings yet
- Habronemose em Um CameloDocument4 pagesHabronemose em Um CameloTais SenaNo ratings yet
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument36 pagesParasitology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoNo ratings yet
- Abram 1987Document4 pagesAbram 1987GarethNo ratings yet
- Ancylostoma Duodenale: What Happens When Infective Filariform Larva of Penetrates Human Skin ?Document16 pagesAncylostoma Duodenale: What Happens When Infective Filariform Larva of Penetrates Human Skin ?Ayop KhNo ratings yet
- Parasitologi: Dr. Adi Arianto, M. BiomedDocument41 pagesParasitologi: Dr. Adi Arianto, M. Biomedbayu rohmiNo ratings yet
- Dracunculus Medinensis and Filarial WormsDocument19 pagesDracunculus Medinensis and Filarial WormsAnastasiaNo ratings yet
- Art 10Document8 pagesArt 10Velazquez Rico Cinthya MontserrathNo ratings yet
- Ascaris lumbricoides Infection and TreatmentDocument10 pagesAscaris lumbricoides Infection and TreatmentJohn Carlo VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Week9&10 LEC Clinical Parasitology NEMATODESDocument18 pagesWeek9&10 LEC Clinical Parasitology NEMATODESSamuel ReyesNo ratings yet
- Multicellular Parasites: Palao, Anamarie D. Peluta, Charry Shane B. Bsed Science 3Document38 pagesMulticellular Parasites: Palao, Anamarie D. Peluta, Charry Shane B. Bsed Science 3ANAMARIE DUNGGON. PALAONo ratings yet
- The NematodesDocument17 pagesThe NematodesCherry BucalingNo ratings yet
- THE TREMATODES NotesDocument1 pageTHE TREMATODES NotesGlaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- NematodesDocument10 pagesNematodesNicolette Go100% (1)
- Helminths Tropical InfectionDocument64 pagesHelminths Tropical InfectionCut Nabila AmaniNo ratings yet
- NAGA COLLEGE FOUNDATION MEDICAL IMPORTANCE OF HELMINTHSDocument6 pagesNAGA COLLEGE FOUNDATION MEDICAL IMPORTANCE OF HELMINTHSLeslie QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Par201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFDocument27 pagesPar201 S1lab4 Midterm Phamids Aphasmids PDFHanna Alyssa Grace DimarananNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Reviewer paraDocument10 pagesLaboratory Reviewer paraDexcel concepcionNo ratings yet
- Merge AbDocument17 pagesMerge AbEricsson CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Para LabDocument22 pagesPara LabClaudine DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Nematodes (Round Worms) Lec 7 Fall 2021 PDFDocument12 pagesNematodes (Round Worms) Lec 7 Fall 2021 PDFMk KassemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - NEMATODESDocument50 pagesChapter 15 - NEMATODESmarilexdomagsangNo ratings yet
- PARA NematodesDocument23 pagesPARA Nematodes12 Newton - Cayetano, Arafe Nicole A.No ratings yet
- Class Digenea (Trematoda) - The FlukesDocument10 pagesClass Digenea (Trematoda) - The FlukesAmr EldemardashNo ratings yet
- The Treatment of Black Widow Spider EnvenomationDocument6 pagesThe Treatment of Black Widow Spider EnvenomationRoberto EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam #2 Rationalization: ParasitologyDocument5 pagesComprehensive Exam #2 Rationalization: ParasitologyJoyceNo ratings yet
- Evolution Is Wrong: A Radical Approach to the Origin and Transformation of LifeFrom EverandEvolution Is Wrong: A Radical Approach to the Origin and Transformation of LifeRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Ecology of Root PathogensFrom EverandEcology of Root PathogensS.V. KrupaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledGlaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- THE TREMATODES NotesDocument1 pageTHE TREMATODES NotesGlaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- MICROBIO NOTES Part 2Document25 pagesMICROBIO NOTES Part 2Glaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- MUMPSDocument7 pagesMUMPSGlaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY NOTES Part 1Document10 pagesMICROBIOLOGY NOTES Part 1Glaiza BolanoNo ratings yet
- Determining The Thickness of Glass in Airport Traffic Control Tower CabsDocument17 pagesDetermining The Thickness of Glass in Airport Traffic Control Tower CabsAdán Cogley CantoNo ratings yet
- Guess The Animal!: ModelDocument2 pagesGuess The Animal!: ModelGiovanni Vilcapoma LauraNo ratings yet
- 978 613 8 91055 8 PDFDocument309 pages978 613 8 91055 8 PDFEr Sayan ParamanikNo ratings yet
- Analog Layout Design (Industrial Training)Document10 pagesAnalog Layout Design (Industrial Training)Shivaksh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Calculations To Convert Intensities Into Concentrations in Optical Emission Spectrochemical AnalysisDocument14 pagesFundamental Calculations To Convert Intensities Into Concentrations in Optical Emission Spectrochemical AnalysisPYDNo ratings yet
- FV10 Excel Flux Tutorial en 2Document36 pagesFV10 Excel Flux Tutorial en 2Ahcene BouzidaNo ratings yet
- 4.2 - Traditional Double-Walled HapaDocument25 pages4.2 - Traditional Double-Walled HapaThakur VeeruNo ratings yet
- Waste Management in Vienna. MA 48Document12 pagesWaste Management in Vienna. MA 484rtttt4ttt44No ratings yet
- GSL DIP Phase - 1 Cooler 45kWDocument1 pageGSL DIP Phase - 1 Cooler 45kWMuhasin PallikkalNo ratings yet
- #10 VHB SGT-APT Design SummaryDocument2 pages#10 VHB SGT-APT Design SummarySenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Subjects Verbs PrepositionsDocument11 pagesSubjects Verbs Prepositionsგუგა ნოსელიძეNo ratings yet
- LP PG Conversion To Thar CoalDocument3 pagesLP PG Conversion To Thar CoalRaja Zeeshan100% (1)
- Bartle Introduction To Real Analysis SolutionsDocument7 pagesBartle Introduction To Real Analysis SolutionsSam Sam65% (20)
- Bathymetry and Its Applications PDFDocument158 pagesBathymetry and Its Applications PDFArseni MaximNo ratings yet
- Caelus TT - Caelus Product TrainingDocument93 pagesCaelus TT - Caelus Product TrainingYader Daniel Ortiz CerdaNo ratings yet
- GTA San Andreas CheatDocument9 pagesGTA San Andreas CheatHatta YanuarNo ratings yet
- Ex 2013 1 (Recurrent)Document30 pagesEx 2013 1 (Recurrent)alh basharNo ratings yet
- Beneficiation of Cassiterite From Primary Tin OresDocument11 pagesBeneficiation of Cassiterite From Primary Tin OresSULMAGNo ratings yet
- Rotating Sharp Shooting Multi Target Mechanism Improves Military AimDocument13 pagesRotating Sharp Shooting Multi Target Mechanism Improves Military AimVishal GNo ratings yet
- Biomass and Bioenergy: Z.N. Akhlisah, R. Yunus, Z.Z. Abidin, B.Y. Lim, D. KaniaDocument20 pagesBiomass and Bioenergy: Z.N. Akhlisah, R. Yunus, Z.Z. Abidin, B.Y. Lim, D. KaniaPutri sinagaNo ratings yet
- Instapdf - in Bangalore Tourist Places List 674Document31 pagesInstapdf - in Bangalore Tourist Places List 674R K PathamNo ratings yet
- Fi & EiDocument3 pagesFi & EiPrasanna S Kulkarni100% (1)
- Dog Cake Recipe For Dozer's Birthday! - RecipeTin EatsDocument36 pagesDog Cake Recipe For Dozer's Birthday! - RecipeTin EatsZyreen Kate CataquisNo ratings yet
- Packaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet SinghDocument48 pagesPackaging Materials and Handling Technique: Dr. Ranjeet Singharon demagiba100% (1)
- What Is The Kingdom of GodDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Kingdom of GodSunil ChelladuraiNo ratings yet
- HymssheetDocument4 pagesHymssheettoby_wardmanNo ratings yet
- Guide 111: International Electrotechnical CommissionDocument7 pagesGuide 111: International Electrotechnical CommissionSayyid JifriNo ratings yet
- November 2010 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology A-Level PDFDocument12 pagesNovember 2010 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology A-Level PDFWiji NingNo ratings yet
- CFD Answer KeyDocument12 pagesCFD Answer KeyRaahini IzanaNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Level in A Tank Using Capacitive Type Level ProbeDocument13 pagesMeasurement of Level in A Tank Using Capacitive Type Level ProbeChandra Sekar100% (1)