Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flexure Test
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flexure Test
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruCopyright:
Available Formats
Page 16
which is then dropped into the second hopper and into the cylinder which is struck off
flush. The compacting factor is the ratio of the weight of concrete in the cylinder to
the weight of an equal volume of fully compacted concrete. The compacting factor for
concrete of medium workability is about 0.9.
(c) Other tests
Other tests are specified for stiff mixes and superplasticized mixes. Reference should
be made to specialist books on concrete.
2.5 TESTS ON HARDENED CONCRETE
2.5.1 Normal tests
The main destructive tests on hardened concrete are as follows.
(a) Cube test
Refer to section 2.3.1 above.
(b) Tensile splitting test
Refer to section 2.3.2 above.
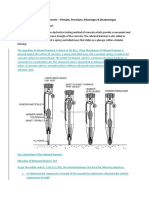
(c) Flexure test
A plain concrete specimen is tested to failure in bending. The theoretical maximum
tensile stress at the bottom face at failure is calculated. This is termed the modulus of
rupture. It is about 1.5 times the tensile stress determined by the splitting test.
(d) Test cores
Cylindrical cores are cut from the finished structure with a rotary cutting tool. The
core is soaked, capped and tested in compression to give a measure of the concrete
strength in the actual structure. The ratio of core height to diameter and the location
where the core is taken affect the strength. The strength is lowest at the top surface
and increases with depth through the element. A ratio of core height-to-diameter of 2
gives a standard cylinder test.
2.5.2 Non-destructive tests
The main non-destructive tests for strength on hardened concrete are as follows.
(a) Rebound hardness test
The Schmidt hammer is used in the rebound hardness test in which a metal hammer
held against the concrete is struck by another spring-driven metal
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 3-Quality of ConcreteDocument15 pages3-Quality of Concretesmithson JoeNo ratings yet
- Concrete Cubes and CylindersDocument3 pagesConcrete Cubes and Cylindersaecom2009No ratings yet
- RCI-Chapter 1-GeneralDocument55 pagesRCI-Chapter 1-GeneralMahlet EshetuNo ratings yet
- 3 FundamentalsDocument49 pages3 FundamentalsKetanNo ratings yet
- Hardened ConcreteDocument7 pagesHardened Concretefarah.No ratings yet
- Core Strength Variation of In-Place Concrete - tcm77-1305833Document3 pagesCore Strength Variation of In-Place Concrete - tcm77-1305833usama anterNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Structure I: References: Design of Reinforced Concrete (Jack C. Mccormac)Document45 pagesReinforced Concrete Structure I: References: Design of Reinforced Concrete (Jack C. Mccormac)Alam MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Materials and PropertiesDocument15 pagesChapter Two Materials and PropertiesAdel KhalilNo ratings yet
- Rebound HammerDocument5 pagesRebound HammerSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- CE 471-Lecture-4 (Material Properties of Concrete and Steel)Document33 pagesCE 471-Lecture-4 (Material Properties of Concrete and Steel)German VargasNo ratings yet
- M2 - Reinforced Concrete PropertiesDocument7 pagesM2 - Reinforced Concrete PropertiesKrushna LokareNo ratings yet
- Design Data: A. General. The Specific Concrete Properties Used inDocument10 pagesDesign Data: A. General. The Specific Concrete Properties Used inAnoop GuptaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete DesignDocument20 pagesReinforced Concrete DesignIvan Miranda AbadejosNo ratings yet
- Learning Material RCDDocument18 pagesLearning Material RCDChristian John BiolNo ratings yet
- Crack Formation and Fracture Energy of Normal andDocument12 pagesCrack Formation and Fracture Energy of Normal andIngénieurCivilNo ratings yet
- Lec2 Materials 2Document9 pagesLec2 Materials 2Fadi Al-QasemNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge TechnologiesDocument3 pagesRajiv Gandhi University of Knowledge TechnologiesVamsi GongallaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete - I DMU Lecture NotesDocument206 pagesReinforced Concrete - I DMU Lecture NotesAntenehNo ratings yet
- RC-II - Tutorial NOTE For Exit ExamDocument79 pagesRC-II - Tutorial NOTE For Exit Examznabugrmay20adiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three PDFDocument11 pagesChapter Three PDFshjahsjanshaNo ratings yet
- 2.ce6702 PCS PDFDocument34 pages2.ce6702 PCS PDFvignesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Strength On Recycled Concrete Using PP FiberDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Strength On Recycled Concrete Using PP FiberInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 1Ch1-Properties of Conc1Document9 pages1Ch1-Properties of Conc1yimamNo ratings yet
- Rebound Hammer Test On ConcreteDocument10 pagesRebound Hammer Test On ConcreteSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Ijresm V4 I4 47Document3 pagesIjresm V4 I4 47Shaik Asif AliNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 1.3: Response of Civil Engineering ProjectDocument43 pagesTOPIC 1.3: Response of Civil Engineering ProjectSue IlaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Introduction EditDocument38 pagesLecture 1-Introduction Editaduyekirkosu1scribdNo ratings yet
- Flexural - Strength - and - Cracking - Behavior (Kheder)Document15 pagesFlexural - Strength - and - Cracking - Behavior (Kheder)a96lhfNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Materials and Properties of Reinforced ConcreteDocument11 pages1.2 Materials and Properties of Reinforced ConcreteEveNo ratings yet
- Concrete Characteristics Using Destructive and Non-Destructive TestsDocument7 pagesConcrete Characteristics Using Destructive and Non-Destructive TestsAmanulla KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document61 pagesChapter 1ቀዳሚሃ ለጥበብ ፈሪሃ እግዚያብሔርNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Concrete StrengthDocument43 pagesLecture 5 - Concrete StrengthKaren LovedorialNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete - I-Notes and ProblemsDocument199 pagesReinforced Concrete - I-Notes and ProblemsAbrham Teklebrhan100% (1)
- JH Academy Notes RCC AND STEELDocument62 pagesJH Academy Notes RCC AND STEELKarnalPreeth100% (2)
- Regression Modeling of Breakout Strength of An Expansion Anchor Bolt As Influenced by Concrete AggregatesDocument7 pagesRegression Modeling of Breakout Strength of An Expansion Anchor Bolt As Influenced by Concrete AggregatesYuri ValenciaNo ratings yet
- CT Unit 3Document19 pagesCT Unit 3Online AdoroNo ratings yet
- Properties of Concrete Part 1Document11 pagesProperties of Concrete Part 1Muhammad Aqib ud dinNo ratings yet
- CH1 Limit State Design 10-4-13 PDFDocument30 pagesCH1 Limit State Design 10-4-13 PDFJoseph LuuNo ratings yet
- RCC 01 Pratice SheetDocument3 pagesRCC 01 Pratice SheetPiyush DasNo ratings yet
- Aggregates For ConcreteDocument15 pagesAggregates For Concretevictor mutaiNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts of ConcreteDocument19 pagesBasic Concepts of ConcreteSathish SelvaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Part 2 (Ce 361 - Advanced Concrete Technology)Document10 pagesModule 3 - Part 2 (Ce 361 - Advanced Concrete Technology)lakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Self Curing of ConcreteDocument34 pagesSelf Curing of ConcreteRAHUL DasNo ratings yet
- Rebound Hammer TestDocument8 pagesRebound Hammer TestEvello MercanoNo ratings yet
- Compressive Strength Test On Concrete Cubes: A Review: Muhammad Elhamme Abdul KarimDocument2 pagesCompressive Strength Test On Concrete Cubes: A Review: Muhammad Elhamme Abdul KarimelhammeNo ratings yet
- University of Windsor: Material PropertiesDocument15 pagesUniversity of Windsor: Material PropertiesMohammed Mudassir MirzaNo ratings yet
- The NDT Technician Vol 12 No 2Document12 pagesThe NDT Technician Vol 12 No 2Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- Dcs 1Document130 pagesDcs 1Mukesh Kumar SamotaNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation of Steel CDocument4 pagesAn Experimental Investigation of Steel CnomadiczapatoNo ratings yet
- CementDocument15 pagesCementVihar VariaNo ratings yet
- RCC SSC JE Questions 2010 To 2016Document9 pagesRCC SSC JE Questions 2010 To 2016Anirudh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Structural DesignDocument119 pagesStructural DesignKannan KandappanNo ratings yet
- Chapter1-Basic and MaterialsDocument26 pagesChapter1-Basic and MaterialsHung DuongNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Design by Professor Anthony Kwame DansoDocument131 pagesReinforced Concrete Design by Professor Anthony Kwame DansoBadu Evans NyiayeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 AggregateDocument38 pagesUnit 2 Aggregatehrushikesh dhokaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Concrete: 1.2 Properties of Concrete: 1.2.1 Increase of Strength With AgeDocument59 pagesChapter-1 Concrete: 1.2 Properties of Concrete: 1.2.1 Increase of Strength With AgeN. Neeraj kumarNo ratings yet
- Flexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsFrom EverandFlexible Glass: Enabling Thin, Lightweight, and Flexible ElectronicsSean M. GarnerNo ratings yet
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- Distoration of Pavement SlabDocument1 pageDistoration of Pavement SlabSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rigid Pavement Typical Cross SectionDocument1 pageRigid Pavement Typical Cross SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cause of Common Distresses PDFDocument1 pageCause of Common Distresses PDFSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- End Bearing PileDocument1 pageEnd Bearing PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Classification of PilesDocument1 pageClassification of PilesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Jointed Plain Concrete PavementDocument1 pageJointed Plain Concrete PavementSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Distress TypesDocument1 pageDistress TypesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Fiction PileDocument1 pageFiction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Piles Based On FunctionDocument1 pagePiles Based On FunctionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Compaction PileDocument1 pageCompaction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity TestDocument1 pageUltrasonic Pulse Velocity TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument1 pageApparatusSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting FailuresDocument1 pageFactors Affecting FailuresSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- CreepDocument1 pageCreepSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Measurements of WorkabilityDocument1 pageMeasurements of WorkabilitySrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- MarkingDocument1 pageMarkingSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rectangualr Portal CulvertsDocument1 pageRectangualr Portal CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ribbed Skew Haunch CulvertsDocument1 pageRibbed Skew Haunch CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cationic TypeDocument1 pageCationic TypeSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Precast LidsDocument1 pagePrecast LidsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Document1 pageBitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Maximun Fill HeightsDocument1 pageMaximun Fill HeightsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- JACKING Box CulvertsDocument1 pageJACKING Box CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ConfigurationsDocument1 pageManhole ConfigurationsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Culverts BasesDocument1 pageCulverts BasesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ComponetsDocument1 pageManhole ComponetsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Mid Girder SectionDocument1 pageMid Girder SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- 6-Ways Concrete BaseDocument1 page6-Ways Concrete BaseSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Tied Deck SlabDocument1 pageTied Deck SlabSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- I. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenDocument1 pageI. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet