Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rigid Pavement Typical Cross Section
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rigid Pavement Typical Cross Section
Uploaded by
Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruCopyright:
Available Formats
IRC:SP:83-2008
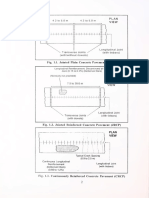
CROSS-SECTION
DEBONDING/SEPARATION MEMBRANE
LONGITIDINAL JOINT
/ Z PQC
SUB-BASE (PLC)
DRAINAGE LAWYER
Camber not Shown
SUB-GRADE
EMBANKMENT
Dowel bars across transverse Joints not shown for clarity
Fig. 1.4. Rigid Pavement Typical Cross-section
1.5. The concrete pavement slab expands with the rise in temperature
and contracts
with fall in temperature. Concrete shrinks as it cures. Concrete slabs accordingly curl and warp
due to the temperature and moisture gradients. This expansion and contraction is resisted by the
mass of the concrete slab. The natural responses due to the above, causes concrete pavement to
crack at fairly regular intervals. Keeping this in mind, contraction joints are provided at designed/
designated intervals to take care of the expected cracking. Contraction joints are thus provided to
ensure that cracking in concrete slabs do not take place at other locations except at the contraction
joint locations. It is presumed that if contraction joints are properly located, designed and
constructed, cracks at other locations will nomially not take place. However, uncontrolled (random)
cracks in the concrete pavement do take place at undesignated locations due to various factors
including deficiencies like inappropriate selection of materials, lack of timely and adequate curing,
too delayed/too early sawing of the joints, construction deficiencies etc. Faulting, Scaling, Loss of
texture etc. are other types of distresses which are normally encountered in concrete pavements.
These distresses are mainly due to improper flinctioning ofjoints, settlement of sub-grade, loosening
of tie bars and improper construction workmanship.
1.6. Cracks are not uncommon to concrete construction and, therefore, minor shallow
cracks need not be viewed as a serious problem. Many cracks can be restored easily to a condition
that will serve for the design life of the pavement, hi some cases, no repair may be required, while
in otherssome preventive repairs like reseating, retexturing will be sufficient. Only deep structural
cracks are a matter of serious concern for which repair methods are available. These guidelines
apart from suggesting various repair techniques are also aimed to offset the impression that the
repairs of the concrete pavements are something impossible and therefore, their construction should
be avoided.
You might also like
- Reinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Grade Beams, Piles & Caissons: A Practical Guide for Hillside ConstructionNo ratings yet
- Account 83403139320 PDFDocument4 pagesAccount 83403139320 PDFblackson knightsonNo ratings yet
- Structural Failures: Ankit KumarDocument21 pagesStructural Failures: Ankit KumarShikhin GargNo ratings yet
- Squeeze Cementing: Forces Cement Slurry, Under Pressure, Through Perforations or Holes in The Casing or Liner .Document41 pagesSqueeze Cementing: Forces Cement Slurry, Under Pressure, Through Perforations or Holes in The Casing or Liner .Mehdi AlizadehNo ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Cracks in BuildingsDocument25 pagesCauses and Prevention of Cracks in BuildingsDeepak MNo ratings yet
- Concrete Pavement Cracks RepairDocument18 pagesConcrete Pavement Cracks RepairRoslan 'Abok' Kamarudin100% (1)
- Technical Note 015Document4 pagesTechnical Note 015Chan Kin CheungNo ratings yet
- Cracks in ConcreteDocument4 pagesCracks in ConcreteAhmed Daahir AdenNo ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Cracks in BuildingDocument35 pagesCauses and Prevention of Cracks in BuildingharNo ratings yet
- Building Defects Ali 03Document26 pagesBuilding Defects Ali 03Ali Azhar RajputNo ratings yet
- Casting Defect in Slab PDFDocument55 pagesCasting Defect in Slab PDFBhoomaiah SunkenapalliNo ratings yet
- Draft Recommendation For Damage ClassificationDocument8 pagesDraft Recommendation For Damage ClassificationThanongsak ImjaiNo ratings yet
- Calculating Concrete Rebars QuantitiesDocument5 pagesCalculating Concrete Rebars QuantitiesJamohl Supremo Alexander100% (1)
- Cracking in Composite-Corrugated Metal Decking Floor SlabsDocument3 pagesCracking in Composite-Corrugated Metal Decking Floor SlabsBolanle OlaawoNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction Survey FormDocument2 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Survey FormJoseNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement DistressDocument36 pagesFlexible Pavement DistressAmarjit AbujamNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignFrom EverandReinforced Concrete Buildings: Behavior and DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bridge Expansion JointDocument46 pagesBridge Expansion JointSiva Prasad MamillapalliNo ratings yet
- 16-Concrete Pavements (Part 2) - Jointing in PCC ConstructionDocument89 pages16-Concrete Pavements (Part 2) - Jointing in PCC ConstructionHimanshu SainiNo ratings yet
- Placing and Compacting ConcreteDocument8 pagesPlacing and Compacting ConcreteNorazly Awang0% (1)
- Deploying Foresight For Policy and Strategy Makers: Leonid Gokhberg Dirk Meissner Alexander Sokolov EditorsDocument285 pagesDeploying Foresight For Policy and Strategy Makers: Leonid Gokhberg Dirk Meissner Alexander Sokolov EditorsPaulo EspirituNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage, Cracking and Deflection of Concrete StructuresDocument14 pagesShrinkage, Cracking and Deflection of Concrete StructuresManoj RautNo ratings yet
- Construction Defects in ConcreteDocument13 pagesConstruction Defects in ConcreteManish KumarNo ratings yet
- Airfield Pavement1 PDFDocument8 pagesAirfield Pavement1 PDFvinay rode100% (1)
- 9.7 Pavement Evaluation - Flexible Pavement DistressDocument12 pages9.7 Pavement Evaluation - Flexible Pavement DistressvdoobooreeNo ratings yet
- 3 USIT InterpretationDocument18 pages3 USIT InterpretationAnkit Sharma100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - FailureDocument6 pagesChapter 8 - FailureThành Phương TấnNo ratings yet
- Repair of Concrete Pavement - RestorationDocument2 pagesRepair of Concrete Pavement - RestorationRana MahatoNo ratings yet
- Evaluation and Identification of Typical Defects and Failure-Modes of 110-750 KV Bushings Victor Sokolov, Boris Vanin ZTZ-Service CoDocument29 pagesEvaluation and Identification of Typical Defects and Failure-Modes of 110-750 KV Bushings Victor Sokolov, Boris Vanin ZTZ-Service CoCarlos Gabriel Quintero RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Serviceability Limit StateDocument12 pagesServiceability Limit StateMohamad Salleh YassinNo ratings yet
- Flexible Pavement DistressDocument33 pagesFlexible Pavement DistressMohammed Omer KufishahNo ratings yet
- Thermal Concrete CrackingDocument7 pagesThermal Concrete Crackingignacio_vazquez_18No ratings yet
- Cracks R.C.C Eng - Bassem JemmoDocument97 pagesCracks R.C.C Eng - Bassem JemmoMohammed FlahaNo ratings yet
- Painting Schedule PDFDocument15 pagesPainting Schedule PDFIliyanPetrovNo ratings yet
- 5 Metfloor Installation GuideDocument9 pages5 Metfloor Installation GuideTùng Hì100% (1)
- Good Construction Practise - Handouts - ConcreteDocument18 pagesGood Construction Practise - Handouts - Concretehitesh16No ratings yet
- 3770rust Vs CorrosionDocument6 pages3770rust Vs Corrosionraahul_nNo ratings yet
- Libro de Reforzamiento HORMIGON ARMADO 2022-8Document25 pagesLibro de Reforzamiento HORMIGON ARMADO 2022-8David Magne MamaniNo ratings yet
- Unit - 5Document69 pagesUnit - 5Jothi RamanathanNo ratings yet
- 1937.-CONCRETE (Autosaved)Document67 pages1937.-CONCRETE (Autosaved)EMERSON GAPUZNo ratings yet
- Causes, Evaluation and Repair of Cracks in ConcreteDocument3 pagesCauses, Evaluation and Repair of Cracks in ConcreteRajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Limit State of ServiceabilityDocument17 pagesLimit State of ServiceabilityRadhikaNo ratings yet
- Tips For Preventing and Repairing Spalled ConcreteDocument9 pagesTips For Preventing and Repairing Spalled ConcreteKevinNo ratings yet
- Steel Rust - Article 2 PDFDocument11 pagesSteel Rust - Article 2 PDFBalasubramanian MahadevanNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Concrete Slab CuttingDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Concrete Slab CuttingACCURATE BUILDING DEMOLITION L.L.C.No ratings yet
- Concrete Technolgy PDFDocument31 pagesConcrete Technolgy PDFSaqib imranNo ratings yet
- Watertite SA 15Document2 pagesWatertite SA 15Alexi ALfred H. TagoNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Behavior of Fine Grained Soils - 1999 Kocaeli Earthquake Case HistoryDocument8 pagesDynamic Behavior of Fine Grained Soils - 1999 Kocaeli Earthquake Case HistoryoceraselaNo ratings yet
- Deflection Considerations in Two-Way Reinforced CoDocument13 pagesDeflection Considerations in Two-Way Reinforced CoHamid HassanzadaNo ratings yet
- Evaluate The Extent of DamageDocument1 pageEvaluate The Extent of DamageAnonymous BAzcBzWuNo ratings yet
- Construction Joint: Sheating Stud Braces WalesDocument2 pagesConstruction Joint: Sheating Stud Braces WalesLovely BautistaNo ratings yet
- Pavement ManagementDocument100 pagesPavement ManagementJoash Normie DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0950061815305663 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0950061815305663 Mainhvthang1981No ratings yet
- Cementing 1708510900Document16 pagesCementing 1708510900Reza heidari orojlooNo ratings yet
- Tank Maintenance: Our Guide To The Economical Repair of Corroded Tank BottomsDocument4 pagesTank Maintenance: Our Guide To The Economical Repair of Corroded Tank BottomsRabah BrikaNo ratings yet
- General Information For Joints: Design Manual Chapter 5 - Roadway Design 5G - PCC Pavement JointsDocument6 pagesGeneral Information For Joints: Design Manual Chapter 5 - Roadway Design 5G - PCC Pavement JointsGiovanni ArangoNo ratings yet
- Maintenance & RepairingDocument13 pagesMaintenance & RepairingHani MenemNo ratings yet
- Drop-Off Laminate CalculationDocument12 pagesDrop-Off Laminate CalculationalfborbrNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Feb - Report 2023 - 3Document4 pagesPrelim - Feb - Report 2023 - 3Green MichaelsNo ratings yet
- Glo Backfill TBM Tunnel Boring MachinesDocument8 pagesGlo Backfill TBM Tunnel Boring Machinesjpantazis1975No ratings yet
- 2021 SMTAI What Do You Want On Your TombstoneDocument7 pages2021 SMTAI What Do You Want On Your Tombstonesouhailtbolbi14No ratings yet
- Distoration of Pavement SlabDocument1 pageDistoration of Pavement SlabSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Jointed Plain Concrete PavementDocument1 pageJointed Plain Concrete PavementSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Measurements of WorkabilityDocument1 pageMeasurements of WorkabilitySrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Fiction PileDocument1 pageFiction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Compaction PileDocument1 pageCompaction PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Piles Based On FunctionDocument1 pagePiles Based On FunctionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Distress TypesDocument1 pageDistress TypesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Classification of PilesDocument1 pageClassification of PilesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- End Bearing PileDocument1 pageEnd Bearing PileSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cause of Common Distresses PDFDocument1 pageCause of Common Distresses PDFSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity TestDocument1 pageUltrasonic Pulse Velocity TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- ApparatusDocument1 pageApparatusSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting FailuresDocument1 pageFactors Affecting FailuresSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- CreepDocument1 pageCreepSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Flexure TestDocument1 pageFlexure TestSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- MarkingDocument1 pageMarkingSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Rectangualr Portal CulvertsDocument1 pageRectangualr Portal CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Ribbed Skew Haunch CulvertsDocument1 pageRibbed Skew Haunch CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Cationic TypeDocument1 pageCationic TypeSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Precast LidsDocument1 pagePrecast LidsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Bitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Document1 pageBitumen Emulson (Cationic Type)Srinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Maximun Fill HeightsDocument1 pageMaximun Fill HeightsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- JACKING Box CulvertsDocument1 pageJACKING Box CulvertsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ConfigurationsDocument1 pageManhole ConfigurationsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Culverts BasesDocument1 pageCulverts BasesSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Manhole ComponetsDocument1 pageManhole ComponetsSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Mid Girder SectionDocument1 pageMid Girder SectionSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- 6-Ways Concrete BaseDocument1 page6-Ways Concrete BaseSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- Tied Deck SlabDocument1 pageTied Deck SlabSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- I. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenDocument1 pageI. Utility Relocation Plan: Chapter 2. There Are 33 Lampposts Present Along The Project Alignment, Which Have BeenSrinivasulu Reddy KoduruNo ratings yet
- TDS Vaxo - XLDocument1 pageTDS Vaxo - XLMikey MikslNo ratings yet
- Ratana Outdoor FurnitureDocument107 pagesRatana Outdoor FurnitureNova TechieNo ratings yet
- Costing Individual Assignment Mpac518Document5 pagesCosting Individual Assignment Mpac518Anorld MunapoNo ratings yet
- Brenda Chalfin-Shea Butter Republic - State Power, Global Markets, and The Making of An Indigenous Commodity (2004)Document312 pagesBrenda Chalfin-Shea Butter Republic - State Power, Global Markets, and The Making of An Indigenous Commodity (2004)Caio Bonamigo DorigonNo ratings yet
- NOTES ON GEC TEMThe Phil - EconDocument3 pagesNOTES ON GEC TEMThe Phil - EconClarynce CaparosNo ratings yet
- Chapter IV FeasibilityDocument6 pagesChapter IV FeasibilityRomalyn MoralesNo ratings yet
- Elasticity and Tax IncidenceDocument11 pagesElasticity and Tax IncidenceKiara RamdhawNo ratings yet
- E1. The Basic Economic Problem Quiz Cards: Made by CattaystudiesDocument74 pagesE1. The Basic Economic Problem Quiz Cards: Made by CattaystudiesYashwinni VijayasekarNo ratings yet
- Acp Concrete: Heavy Duty Horizontal Prestressed Precast Concrete Wall PanelsDocument2 pagesAcp Concrete: Heavy Duty Horizontal Prestressed Precast Concrete Wall PanelsNyein ZawNo ratings yet
- Quotation For Movement From Chennai Madras To DibrugarhDocument2 pagesQuotation For Movement From Chennai Madras To Dibrugarhbirju_5191No ratings yet
- CH 10Document23 pagesCH 10Nguyễn Hữu HoàngNo ratings yet
- SICHOTS240114220Document1 pageSICHOTS240114220Sandu MonicaNo ratings yet
- Template Jawaban UTS Aplikasi Audit Ganjil 2021 - 2022Document12 pagesTemplate Jawaban UTS Aplikasi Audit Ganjil 2021 - 2022Cherry VanticaNo ratings yet
- 1 PMF 012 COM 009 - v2 - Subcontractor - Submittal - Form 029Document21 pages1 PMF 012 COM 009 - v2 - Subcontractor - Submittal - Form 029Eng hassan hussienNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sistem Politik IndonesiaDocument20 pagesJurnal Sistem Politik IndonesiaMeutia AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- BudgetingDocument29 pagesBudgetingTsega BirhanuNo ratings yet
- Accounting ErrorsDocument10 pagesAccounting ErrorsTooba HashmiNo ratings yet
- Journal, T Accounts, Worksheet and PostingDocument29 pagesJournal, T Accounts, Worksheet and Postingkenneth coronelNo ratings yet
- Zipline Conveyor SPLT1134ENWB 02Document4 pagesZipline Conveyor SPLT1134ENWB 02JrbritoNo ratings yet
- 1 P Swapna Research Article July 2011Document9 pages1 P Swapna Research Article July 2011Pratiksha JagdishNo ratings yet
- CVP QUIZ TeachersDocument5 pagesCVP QUIZ TeachersAron Ace AycoNo ratings yet
- Iron and Steel Industry Report 2018 enDocument28 pagesIron and Steel Industry Report 2018 enAlexei AlinNo ratings yet
- Oncor Joint Use Standards - Section 103 (05-2022)Document28 pagesOncor Joint Use Standards - Section 103 (05-2022)Glenda IriarteNo ratings yet
- Vergil Joseph I. Literal, DBA, CPA: Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesVergil Joseph I. Literal, DBA, CPA: Page 1 of 4hsjhsNo ratings yet
- Download pdf Economics 13Th Edition Roger A Arnold ebook full chapterDocument53 pagesDownload pdf Economics 13Th Edition Roger A Arnold ebook full chapterjohn.marshall425100% (2)
- Unit 2 (IB MBA)Document11 pagesUnit 2 (IB MBA)Megha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- EXTRA QUESTIONS ANSWERS ch-3Document3 pagesEXTRA QUESTIONS ANSWERS ch-3Sarita ChopraNo ratings yet