Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Peripheral Nervous System Notes
Uploaded by
Njeri MbuguaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Peripheral Nervous System Notes
Uploaded by
Njeri MbuguaCopyright:
Available Formats
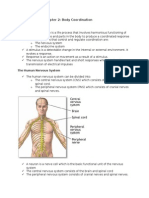
THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
The Peripheral Nervous System is made up of the following two parts:
The skeletal or somatic nervous system
The somatic nervous system is made up of motor nerves that control both voluntary and
involuntary behaviors. Voluntary behaviors are due to cognitive processes such as thinking and
reasoning. However it may initiate involuntary or reflex activities which do not need cognitive
processing.
The autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system has organs and glands such as the digestive system, bladder,
kidney, heart, adrenal glands and the lung that are connected by motor neurons or nerves to the
central nervous system. The autonomic nervous system controls the internal activities that are
important for the external behavior to take place. For example in times of danger, the internal
system are activated to generate energy necessary to manage the danger, In case a person needs
to run away from a snake or a robber, energy will be generated by breathing faster and the heart
beating faster. Adrenaline will be released into the blood stream. Consequently, increased blood
flow will enable transport of oxygen, adrenaline and nutrients such as glucose to provide energy
to the muscles. The autonomic nervous system acts on involuntary basis therefor we have no
control over its activities.
Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System
The Autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions
which operate in opposite ways. The sympathetic division mobilizes energy when needed while
the parasympathetic division conserves or stores energy when the danger is over and it is not
needed. For instance in times of danger adrenaline, oxygen and glucose are increased in the body
to energize the muscles while these activities are slowed down when one is relaxed
Examples of autonomic nervous system reactions:
When the sympathetic division is stimulated during stress or danger:
● The heart rate increases to increase the flow of blood
● Pupils dilate to increase vision
● Secretion of saliva is suppressed and the mouth feels dry
● Peristalsis slows down and the individual does not feel hungry
● Bladder muscles are relaxes
● Adrenal glands are stimulated to secrete more adrenaline and noradrenaline
● Breathing rate increases to supply more oxygen to the body
● The liver is activated to generate glucose from glycogen. The glucose is then released
into the blood stream to generate more energy
When there is no stress or danger the parasympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system
is activated. Consequently the activities of the above organs will be slowed down to conserve
energy.
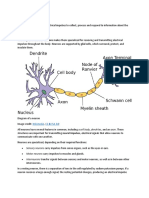
Nerves in the Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves are bundles o neurons which are either sensory or motor. There are forty three pairs of
nerves in the peripheral nervous system. Thirty one of these pairs, known as spinal nerves, enter
the central nervous system below the neck along the various levels of the spinal cord. The other
twelve pairs, known as the cranial nerves, enter the brain directly.
You might also like
- The Buccaneers BestiaryDocument74 pagesThe Buccaneers BestiaryAnonymous NqjlN5w100% (2)
- CREST English 3 Workbook-CompressedDocument83 pagesCREST English 3 Workbook-CompresseddafriaNo ratings yet
- TVBS Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesTVBS Nervous SystemAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9. Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesLecture 9. Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemJaime Japana III100% (2)
- New Scientist-3255 2019Document61 pagesNew Scientist-3255 2019SIXTO GUTIERREZ75% (4)
- Yoga For The Eyes-1Document5 pagesYoga For The Eyes-1Prajwal GowdaNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemHyacinth CorralesNo ratings yet
- Mythology and Folklore LessonsDocument11 pagesMythology and Folklore Lessonslyndon arellano100% (2)
- Natural - Selection Scenarios (1) COMPLETEDocument3 pagesNatural - Selection Scenarios (1) COMPLETEBrianna Dominguez100% (1)
- The Endocrine System: Glands That Help Control The BodyDocument10 pagesThe Endocrine System: Glands That Help Control The BodyKrishnendu WorkNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SysytemDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous SysytemDevendra RawatNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument4 pagesIntroductionRupam TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Nervous Sysytem and The Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Sysytem and The Endocrine SystemlaracanacarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Coordination and ControlDocument22 pagesChapter 12 Coordination and ControlXaundrae McDonaldNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document109 pagesChapter 3amala raviNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Biological Psychology The NSDocument25 pagesUnit 2 - Biological Psychology The NSJad KhalidNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument45 pagesHomeostasisNazrene FuaNo ratings yet
- Biological Psychology NotesDocument16 pagesBiological Psychology Notesaleeshawasfy43No ratings yet
- Central Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesCentral Nervous SystemAshleyNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Science Chapter 2Document13 pagesForm 4 Science Chapter 2Cheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- BIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR-Mbundire (2023) 2Document9 pagesBIOLOGICAL BASIS OF BEHAVIOUR-Mbundire (2023) 2Emmanuel MulengaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Week 3 NotesDocument9 pagesPsychology Week 3 Notes01234No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Biological Psychology-L!-W5-1Document16 pagesUnit 2 - Biological Psychology-L!-W5-1alialhammaditt1No ratings yet
- 1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSDocument20 pages1031 Autonomic Nervous System-BSBunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 10Document7 pagesLesson Proper For Week 10Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- How Hormones Govern Body ActivitiesDocument4 pagesHow Hormones Govern Body ActivitiesMarvin MelisNo ratings yet
- Kepy 01 09 37 EtextDocument9 pagesKepy 01 09 37 Etextmradul guptaNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument61 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemHashir SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Mental DisordersDocument35 pagesMental Disordersapi-252990108No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?Document22 pagesControl and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?So TemptedNo ratings yet
- Nervous System ReviewDocument18 pagesNervous System Reviewtherenam825No ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System: Sherwyn Hatab RNDocument14 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System: Sherwyn Hatab RNSherwyn Uy HatabNo ratings yet
- BIOPSYCHOLOGYDocument25 pagesBIOPSYCHOLOGYLizzie ShodiyaNo ratings yet
- 7 - Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument98 pages7 - Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindCikgu Diana IbnoNo ratings yet
- CHP 7 Class 10Document13 pagesCHP 7 Class 10sourabh nuwalNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument13 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemSreejesh Rk100% (1)
- Endocrine System - Part 2Document31 pagesEndocrine System - Part 2Maryem NabawiNo ratings yet
- ANS RevisedDocument31 pagesANS Revisedr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- The Receiving Mechanism: Sense Organs Are Sensitive Nerve Endings Located in Certain Body Parts. They Are Receptors ofDocument5 pagesThe Receiving Mechanism: Sense Organs Are Sensitive Nerve Endings Located in Certain Body Parts. They Are Receptors ofArlene Cerdeña SalcedaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemRashmi SainiNo ratings yet
- Nervous System FunctionsDocument10 pagesNervous System FunctionsJovi Leo PunoNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemPaige Buchanan100% (1)
- Roles of Endocrine and Nervous System in HomeostasisDocument11 pagesRoles of Endocrine and Nervous System in Homeostasislekansamuel2005No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Sympathetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesStructure and Function of The Sympathetic Nervous SystemAnthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document2 pagesNervous System 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document2 pagesNervous System 1Anthony LopezNo ratings yet
- Fight or Flight ResponseDocument2 pagesFight or Flight ResponseZahirah Amalina ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- The Biological Perspective 2Document11 pagesThe Biological Perspective 2Radhey SurveNo ratings yet
- Control and Co-Ordination in Animals Nervous System and Endocrine SystemDocument12 pagesControl and Co-Ordination in Animals Nervous System and Endocrine SystemAgastya SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4A Notes Coordination and ResponseDocument15 pages4A Notes Coordination and ResponsenatashamautsiNo ratings yet
- Cor 007 Day 20Document27 pagesCor 007 Day 20Rain VicenteNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) : - The ANS Consists of Motor Neurons ThatDocument26 pagesAutonomic Nervous System (ANS) : - The ANS Consists of Motor Neurons ThatDr-Abdul KhaliqNo ratings yet
- Biopsych Act#1Document3 pagesBiopsych Act#1elkanah dapulagNo ratings yet
- The Function of Nervous SystemDocument33 pagesThe Function of Nervous Systemkhairani putriNo ratings yet
- Para and SympaDocument3 pagesPara and SympajacquejackieNo ratings yet
- Module 1+2Document6 pagesModule 1+2sujaileerosado128No ratings yet
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Document4 pagesFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Misbah NoreenNo ratings yet
- Neurons and Nerves: Building The NetworkDocument6 pagesNeurons and Nerves: Building The NetworkjhustinlaurenteNo ratings yet
- NeurologicDocument33 pagesNeurologicNeil GuntingNo ratings yet
- Chap 4 - Organ Systems Nervous Muscle Endocrine and SensoryDocument3 pagesChap 4 - Organ Systems Nervous Muscle Endocrine and Sensory•[InsertnameHere]• (Aadika)No ratings yet
- SpinalDocument40 pagesSpinalVenkathachala BgNo ratings yet
- Health Psychology - Week 3 - Class 1Document17 pagesHealth Psychology - Week 3 - Class 1Behroze khalilNo ratings yet
- The Nervous and Endocrine SystemDocument6 pagesThe Nervous and Endocrine SystemNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervus System: Dr. Meida Sofyana, MbiomedDocument26 pagesAutonomic Nervus System: Dr. Meida Sofyana, MbiomedAyu Tiara FitriNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument35 pagesNervous SystemRaven MayoNo ratings yet
- 10 Systemic From Liver Necrosis To 2ry Biliary CirrhosisDocument33 pages10 Systemic From Liver Necrosis To 2ry Biliary CirrhosisadelekeyusufNo ratings yet
- EFT QuestsDocument4 pagesEFT Questszsixi bruhNo ratings yet
- Feline PanleukopeniaDocument4 pagesFeline PanleukopeniaDebora BiantiiNo ratings yet
- 38-Article Text-102-1-10-20180421Document10 pages38-Article Text-102-1-10-20180421Usman KochakNo ratings yet
- English (Respiratory System)Document16 pagesEnglish (Respiratory System)ChitraNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument3 pagesHuman AnatomyManjeet KumarNo ratings yet
- First Grading First QuizDocument10 pagesFirst Grading First QuizGhie Yambao SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Earth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test BankDocument8 pagesEarth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test Bankkathleenjonesswzrqcmkex100% (23)
- DMDave - Dungeons & Lairs 65 - Yeti Caverns - Full VersionDocument8 pagesDMDave - Dungeons & Lairs 65 - Yeti Caverns - Full VersionSimone NataleNo ratings yet
- 1 - Origin of Earth and Evolution of The EnvironmentDocument12 pages1 - Origin of Earth and Evolution of The Environmentcoolnidhi134558No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 English Literature Sample Paper Official PDFDocument14 pagesICSE Class 9 English Literature Sample Paper Official PDFDebashree MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Arta Rupestra - PaleoliticDocument26 pagesArta Rupestra - PaleoliticMirela Voiculescu100% (1)
- Dental CertificateDocument2 pagesDental Certificatesherlyn de guzman100% (1)
- Lessons Learned From The Tiger Translocation and Release in Tambling, Lampung, IndonesiaDocument7 pagesLessons Learned From The Tiger Translocation and Release in Tambling, Lampung, IndonesiaNadim KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Penalties For Prohibited Fishing Method & Practices Prohibited Fishing Method & Practices Ordinance No. 12 Series of 2018 RA 8550 RA 10654 Trawl FishingDocument8 pagesPenalties For Prohibited Fishing Method & Practices Prohibited Fishing Method & Practices Ordinance No. 12 Series of 2018 RA 8550 RA 10654 Trawl FishingPamela Joy MotasNo ratings yet
- A Party Without Music Is Lame A Bard GuideDocument18 pagesA Party Without Music Is Lame A Bard GuideMichalNo ratings yet
- Fiqh PDFDocument59 pagesFiqh PDFhabiba_il786100% (1)
- IGCSE BIology Notes PDFDocument101 pagesIGCSE BIology Notes PDFTsz Ho Lam100% (2)
- ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes: Code(s)Document2 pagesICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes: Code(s)juli hadiNo ratings yet
- English Module Section A Error IdentificationDocument9 pagesEnglish Module Section A Error IdentificationZeti Akhtar AdnanNo ratings yet
- Algoritma Tes HIVDocument31 pagesAlgoritma Tes HIVyurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Herpes Simplex Virus: The Importance of Asymptomatic SheddingDocument8 pagesHerpes Simplex Virus: The Importance of Asymptomatic SheddingatikahindraNo ratings yet