Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sequences and Series 7
Uploaded by
Alexander AndradeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sequences and Series 7
Uploaded by
Alexander AndradeCopyright:
Available Formats
Math 1552 − section − 02
Prof. PhD. Hugo Leiva
Series
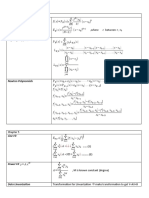
0.1. 11.10 Taylor and Maclaurin Series
Taylor Power Series Representation
Under some conditions a function f can be represented as a power series:
∑
∞
f (n) (a)
f (x) = (x − a)n , |x − a| < R.
n=0
n!
Maclaurin Power Series Representation
∑
∞
f (n) (0)
f (x) = xn , |x| < R.
n=0
n!
The nth-Degre Taylor Polynomial of f
∑
n
f (k) (a)
Tn (x) = (x − a)k , centered at x = a.
k=0
k!
∑
n
f (k) (0)
Tn (x) = xk , centered at x = 0.
k=0
k!
The Remainder Rn (x) is given by:
∑
n
f (k) (a)
f (x) = Tn (x) + Rn (x) = (x − a)k + Rn (x), |x − a| < R.
k=0
k!
∑
n
f (k) (a)
Rn (x) = f (x) − Tn (x) = f (x) − (x − a)k .
k=0
k!
Theorem
If lı́mn→∞ Rn (x) = 0 for all x such that |x − a| < R, then f admits a Taylor’s
Representation centered at x = a on |x − a| < R.
Taylor´s Inequality
If |f (n) (x)| ≤ M , on |x − a| < d, then
M
|Rn (x)| ≤ |x − a|n+1 , |x − a| ≤ d.
(n + 1)!
You might also like
- Tables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39From EverandTables of Laguerre Polynomials and Functions: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 39No ratings yet
- Taylor Series and Remainder TheoremDocument3 pagesTaylor Series and Remainder TheoremrahiedattaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 13Document7 pagesLecture 13José MendozaNo ratings yet
- Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesDocument14 pagesTaylor and Maclaurin SeriesalyssaNo ratings yet
- Modern Calculus 2Document20 pagesModern Calculus 2Dahanyakage WickramathungaNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series and Maclaurin Series: TheoremDocument9 pagesTaylor Series and Maclaurin Series: TheoremDahanyakage WickramathungaNo ratings yet
- Calculus - Telecom BCN: Chapter 13. Power SeriesDocument12 pagesCalculus - Telecom BCN: Chapter 13. Power SeriesAdrián CorralNo ratings yet
- Second Exam Sheet: Taylor Polynomial ApproximationDocument2 pagesSecond Exam Sheet: Taylor Polynomial ApproximationSameer HmedatNo ratings yet
- 6 2 Properties of Power SeriesDocument2 pages6 2 Properties of Power SeriesEmilyNo ratings yet
- Lagrange Remainder PDFDocument1 pageLagrange Remainder PDFChris BakamNo ratings yet
- Analysis II MS Sol 2015-16Document3 pagesAnalysis II MS Sol 2015-16Mainak SamantaNo ratings yet
- Module 23 0 PDFDocument32 pagesModule 23 0 PDFpankaj kumarNo ratings yet
- 13 Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesDocument3 pages13 Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesPrinceton TomasNo ratings yet
- MAT257 HW 12Document4 pagesMAT257 HW 12jiwei ZhangNo ratings yet
- 11.10 Taylor SeriesDocument6 pages11.10 Taylor SeriesMadiha KhanNo ratings yet
- Lec21Document4 pagesLec21Robert John DoodyNo ratings yet
- Taylor SeriesDocument6 pagesTaylor SeriesJunior Briones VelizNo ratings yet
- Session 7Document24 pagesSession 7Mehroze ElahiNo ratings yet
- 2009 Seemous Problems SolutionsDocument4 pages2009 Seemous Problems SolutionsHipstersdssadadNo ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1979 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument4 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1979 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- Taylor Series: N 0 N N NDocument6 pagesTaylor Series: N 0 N N NtylonNo ratings yet
- Ma207 TSCDocument38 pagesMa207 TSCAnonymous SomeoneNo ratings yet
- S. Shaimardan and N. TokmagambetovDocument13 pagesS. Shaimardan and N. TokmagambetovАйкын ЕргенNo ratings yet
- DTFT Theorems and PropertiesDocument4 pagesDTFT Theorems and Propertiessameed raheelNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Discrete Random VectorsDocument34 pagesModule 22 Discrete Random Vectorspankaj kumarNo ratings yet
- Math556 2019 Ex02Document2 pagesMath556 2019 Ex02Frankie HuangNo ratings yet
- Tuan 4.5 Powerseries TaylorexpansionDocument14 pagesTuan 4.5 Powerseries TaylorexpansionGiáp TrầnNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series: Chapter ElevenDocument7 pagesTaylor Series: Chapter ElevenRhea GoelNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series in Economics - Brief OverviewDocument4 pagesTaylor Series in Economics - Brief Overviewpinfeng100% (1)
- 11.10 Taylor Series PDFDocument7 pages11.10 Taylor Series PDFsaurav kumarNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series: N 0 N N NDocument7 pagesTaylor Series: N 0 N N NمحمدحسنفهميNo ratings yet
- Mathematic NotationDocument9 pagesMathematic NotationmdeziderioNo ratings yet
- Multiple Solutions To A (p1 (X), - . - , PN (X) ) - Laplaciantype Systems in Unbounded DomainDocument18 pagesMultiple Solutions To A (p1 (X), - . - , PN (X) ) - Laplaciantype Systems in Unbounded DomainInforma.azNo ratings yet
- Abstract:: 1 2 Definitions and Prelimiaries 3 Main ResultsDocument10 pagesAbstract:: 1 2 Definitions and Prelimiaries 3 Main ResultsAntonio Torres PeñaNo ratings yet
- 000014Document2 pages000014wiertrass2016No ratings yet
- MacalurinDocument1 pageMacalurinrootkit5678No ratings yet
- Eel2010 T10Document1 pageEel2010 T10Dikshant Gupta (B21CI014)No ratings yet
- 2018 See MousDocument1 page2018 See MousHipstersdssadadNo ratings yet
- Relation and FunctionsDocument5 pagesRelation and FunctionsSasidaran SasiNo ratings yet
- Eigenvalues and EigenvectorsDocument23 pagesEigenvalues and EigenvectorsViorel AdirvaNo ratings yet
- Hypergeometric DistributionDocument7 pagesHypergeometric DistributionChucky ChungNo ratings yet
- MATH2352 Differential Equations and Applications Tutorial Notes 4Document5 pagesMATH2352 Differential Equations and Applications Tutorial Notes 4John ChanNo ratings yet
- A Summary of Spivak's Calculus On Manifolds, Chapter On DifferentiationDocument28 pagesA Summary of Spivak's Calculus On Manifolds, Chapter On DifferentiationMarcus Joshua TorneaNo ratings yet
- Learning Materials For EE 223: Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesDocument14 pagesLearning Materials For EE 223: Taylor and Maclaurin SeriesArnel Pamaos Lopiba MontañezNo ratings yet
- 5 The Stochastic Approximation Algorithm: 5.1 Stochastic Processes - Some Basic ConceptsDocument14 pages5 The Stochastic Approximation Algorithm: 5.1 Stochastic Processes - Some Basic ConceptsAaa MmmNo ratings yet
- Module 11: Introduction To Optimal Control: Lecture Note 1Document5 pagesModule 11: Introduction To Optimal Control: Lecture Note 1salimNo ratings yet
- At Reg2Document12 pagesAt Reg2Nicolás Espinoza PeñaNo ratings yet
- Problem Sheet Manifolds 2Document4 pagesProblem Sheet Manifolds 2Borys IwanskiNo ratings yet
- Cayle y HamiltonDocument5 pagesCayle y HamiltonLakhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Power Series - Practice ProblemDocument9 pages4 - Power Series - Practice Problemzxeexz zxcecxzNo ratings yet
- Abels TheoremDocument4 pagesAbels TheoremAlsece PaagalNo ratings yet
- 11 Ma 1 A Section 1 Mid Term SolDocument2 pages11 Ma 1 A Section 1 Mid Term SolJulian Ortega RamosNo ratings yet
- Euler's Theorem For Homogeneous Functions: Division of The Humanities and Social SciencesDocument5 pagesEuler's Theorem For Homogeneous Functions: Division of The Humanities and Social SciencesNavaneethNo ratings yet
- Series and Matrices Assignment IIT MadrasDocument1 pageSeries and Matrices Assignment IIT MadrasVishwajit HegdeNo ratings yet
- Función de Probabilidad F (X) Probabilidad Acumulada: Si X, y Son Independientes: E Xy E (X) E (Y)Document2 pagesFunción de Probabilidad F (X) Probabilidad Acumulada: Si X, y Son Independientes: E Xy E (X) E (Y)Jose PinedaNo ratings yet
- 4.6. Representation of Functions As Power Series 99Document3 pages4.6. Representation of Functions As Power Series 99FernandoFierroGonzalezNo ratings yet
- CalcDocument1 pageCalcNadiaNo ratings yet
- AnalysisPrelimJanuary2023 PDFDocument2 pagesAnalysisPrelimJanuary2023 PDFrcherry calaorNo ratings yet
- Statisticsyear 1 DistributionsDocument3 pagesStatisticsyear 1 Distributionsapi-394057706No ratings yet
- Power SeriesDocument33 pagesPower SeriesAlfiyah An-NajmNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series 6Document1 pageSequences and Series 6Alexander AndradeNo ratings yet
- Paper 1Document22 pagesPaper 1Alexander AndradeNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document8 pagesPaper 2Alexander AndradeNo ratings yet
- Quantum Simulation of Black-Hole Radiation: News & ViewsDocument2 pagesQuantum Simulation of Black-Hole Radiation: News & ViewsAlexander AndradeNo ratings yet
- Rational Functions AssignmentDocument8 pagesRational Functions AssignmentSurya PappuNo ratings yet
- Olumuyiwa Oluwatomi Daniel 15CF02657 Che 522 AssignmentDocument14 pagesOlumuyiwa Oluwatomi Daniel 15CF02657 Che 522 AssignmentnelsonNo ratings yet
- Exercises 2.3Document7 pagesExercises 2.3이퓨처No ratings yet
- Las Math 6 q4 Week 2Document7 pagesLas Math 6 q4 Week 2ANGELINA RAMBOYONGNo ratings yet
- Digital SAT Suite Question Bank - Trigonometry and Geometry - Hard - AnswersDocument75 pagesDigital SAT Suite Question Bank - Trigonometry and Geometry - Hard - AnswersJonathanNo ratings yet
- Meyer PDFDocument42 pagesMeyer PDFVishnuvardhanNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed LP For Grade V MathDocument7 pagesSemi Detailed LP For Grade V MathDivine Angel Baddiri SalasNo ratings yet
- Sta404 07Document71 pagesSta404 07Ibnu Iyar0% (1)
- Activity 20: × + × + × Geometry Box, Cardboard, White Paper, Cutter, Sketch Pen, CellotapeDocument4 pagesActivity 20: × + × + × Geometry Box, Cardboard, White Paper, Cutter, Sketch Pen, CellotapeblehboNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Melcs Enhanced MathematicsDocument6 pagesGrade 10 Melcs Enhanced MathematicsMaria Eleonor BanaresNo ratings yet
- Let's Teach For Mastery - Not Test Scores: Sal KhanDocument4 pagesLet's Teach For Mastery - Not Test Scores: Sal KhanManay MhelNo ratings yet
- Ofsted Coursework LessonDocument8 pagesOfsted Coursework Lessonf5b2q8e3100% (2)
- Math Majors of America Tournament For High Schools: 2014 Individual TestDocument1 pageMath Majors of America Tournament For High Schools: 2014 Individual TestJoaquim MarquesNo ratings yet
- Hylogical StatisticsDocument52 pagesHylogical StatisticsPinaki MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Functions and GraphsDocument1 pageFunctions and GraphstawananyashaNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Buenavista, Inc.: Brgy. Poblacion, San Ildefonso, Bulacan, 3010 Philippines 326-2259Document2 pagesLiceo de Buenavista, Inc.: Brgy. Poblacion, San Ildefonso, Bulacan, 3010 Philippines 326-2259Janeyah Marie FuentesNo ratings yet
- Scopeandsequence Abeka Homeschool PDFDocument16 pagesScopeandsequence Abeka Homeschool PDFleemacale100% (1)
- Marion Scheepers Rearrangements of Numerical Series SlidesDocument18 pagesMarion Scheepers Rearrangements of Numerical Series SlidesMaria Jose de las mercedes Costa AzulNo ratings yet
- Phytagorean TheoremDocument101 pagesPhytagorean TheoremJohn Esteves GarciaNo ratings yet
- Number System Related Interview/Test QuestionsDocument3 pagesNumber System Related Interview/Test QuestionsMasterbrain BrainNo ratings yet
- MockA SL P2 MS 2014v1Document4 pagesMockA SL P2 MS 2014v1KanyaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Grade 12Document24 pagesStatistics Grade 12Reitumetse MolefeNo ratings yet
- Elementsmark of Numerical Analysis of Numerical Analysis Second Edition Radhey SDocument16 pagesElementsmark of Numerical Analysis of Numerical Analysis Second Edition Radhey SUzomah TeslimNo ratings yet
- C# - Algorithm For Simplifying Decimal To Fractions - Stack OverflowDocument12 pagesC# - Algorithm For Simplifying Decimal To Fractions - Stack OverflowsonystdNo ratings yet
- Arduino Smooth CutoffDocument3 pagesArduino Smooth CutoffVictor V. EvansNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document7 pagesLesson 5Udeshika WanninayakeNo ratings yet
- Klinik Upsr Mata Pelajaran Mte 2013Document38 pagesKlinik Upsr Mata Pelajaran Mte 2013Sneffets YdnaNo ratings yet
- Exam P Formula Sheet PDFDocument9 pagesExam P Formula Sheet PDFQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- 47 Austrian Mathematical Olympiad National Competition (Final Round, Part 2, First Day)Document2 pages47 Austrian Mathematical Olympiad National Competition (Final Round, Part 2, First Day)ElevenPlus ParentsNo ratings yet