Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
Shabab ASH0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesThe document summarizes Ibn Taymiyyah's views on why the opinions of accepted Islamic scholars (imams) may differ from authentic hadiths of the Prophet Muhammad. There are several reasons for such differences:
1) A hadith may not have reached a scholar, so they issue a ruling based on other sources.
2) A hadith may have reached a scholar non-authentically, while reaching others authentically.
3) Scholars can disagree on whether a hadith is authentic through independent reasoning (ijtihad).
The document then provides several examples to illustrate these reasons for differences in interpretation among respected scholars throughout Islamic history.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes Ibn Taymiyyah's views on why the opinions of accepted Islamic scholars (imams) may differ from authentic hadiths of the Prophet Muhammad. There are several reasons for such differences:
1) A hadith may not have reached a scholar, so they issue a ruling based on other sources.
2) A hadith may have reached a scholar non-authentically, while reaching others authentically.
3) Scholars can disagree on whether a hadith is authentic through independent reasoning (ijtihad).
The document then provides several examples to illustrate these reasons for differences in interpretation among respected scholars throughout Islamic history.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesUntitled
Uploaded by
Shabab ASHThe document summarizes Ibn Taymiyyah's views on why the opinions of accepted Islamic scholars (imams) may differ from authentic hadiths of the Prophet Muhammad. There are several reasons for such differences:
1) A hadith may not have reached a scholar, so they issue a ruling based on other sources.
2) A hadith may have reached a scholar non-authentically, while reaching others authentically.
3) Scholars can disagree on whether a hadith is authentic through independent reasoning (ijtihad).
The document then provides several examples to illustrate these reasons for differences in interpretation among respected scholars throughout Islamic history.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
Notes
Ibn Taymiyyah’s The Removal of Blame From the Great Imams
by
www.thethinkingmuslim.com
I. None of the imams intentionally opposed the Prophet Muhammad (pbuh)
a. They believe that words of anyone other than the Prophet may be accepted or rejected
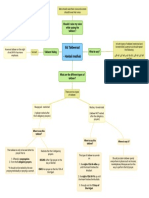
II. If the opinions of any of the accepted imams are found to be in opposition to an authentic hadith,
there is a valid excuse for it and generally falls into one of three categories
a. First Category: Scholar does not believe that the Prophet (pbuh) ever said such a thing.
There are various reasons for this
b. Second Category: Scholar does not think that the hadith is intended to refer to the issue in
question
c. Third Category: Scholar believes that the ruling is abrogated
III. Reasons for the Differences
a. Reason 1: The hadith may have never reached him
i. Hence, he gives a ruling based on a verse of Qur’an or another hadith
ii. It’s not possible for one person to know all of the hadiths
1. Mujtahaid’s objective should be to know most of the hadiths so that only a few of
the details will escape him
iii. This is the most likely reason that is found in the opinions of the pious predecessors
(salaf)
1. Ex: Abu Bakr did not know the inheritance of the grandmother even though he
spent so much time with the Prophet and Umar didn’t know the Sunnah on
seeking permission before entering a house. Similar examples are there from
Uthman and Ali’s lives.
a. Those less knowledgeable than them had the hadiths with them and told
them about it
b. If this was the case with the Sahabah, the most knowledgeable, then what
of those in later generations?
iv. The collections of hadiths that were compiled came after these imams
b. Reason 2: The hadith reached the Mujtahid but not authentically
i. But it may have reached other imams authentically
1. Ex: the hadith reaches one Mujtahid with a broken chain but to another with an
unbroken chain
ii. It may be that the Mujtahaid thinks the hadith is not authentic but it actually is
1. Ex: he considers someone in the chain as unknown but he is known to another
imam
iii. This reason was common among the Tabi’een and the Tabi’ Tabi’een up to the time of
the well-known imams
1. Because hadiths had spread wide by then and to some they reached
authentically while to others they did not
2. This is why the imams in this era would say if a hadith reaches them
authentically, they would change their ruling on a matter
c. Reason 3: The scholar makes ijtihaad and declares the hadith weak
i. But another scholar’s ijtihaad may conclude it to be authentic
1. Reasons
a. One scholar considers a particular transmitter in the hadith as not
trustworthy while another scholar disagrees
b. One scholar does not believe that the transmitter heard the hadith from
the narrator he is transmitting from while another scholar disagrees
c. One scholar thinks that a particular narrator transmitted the hadith in a
state of confusion [he may have lost his books, he became confused later
in age, etc.] while another scholar disagrees and believes the narrator
reported the hadith in his sound state
d. Transmitter forgets that he related a particular hadith and is unable to
remember it at a later date or denies that he ever related such a hadith.
This causes one scholar to deny the hadith considering it defective while
another scholar still accepts it and does not consider it defective
e. Many Hijaazi scholars held the view that unless a hadith originated in
Hijaaz, it should not be cited as evidence. Hence, they did not accept
hadiths that originated in Iraq or Shaam.
i. Because they thought that the Hijaazi people had mastered the
Sunnah so that not a single hadith had escaped them and they
looked at hadiths originating in Iraq or Shaam with suspicion
1. Some of the Iraqi scholars thought the same about hadiths
originating in Shaam
2. Ibn Taymiyyah points out that most people of knowledge
don’t use this criteria as a basis to weaken hadiths. He
further says that the hadiths should be accepted as long as
its chain of narrators is sound no matter where it originated
from.
f. There are other reasons as well, Ibn Taymiyyah points out, but does not
mention them.
d. Reason 4: One scholar stipulates certain conditions for the acceptance of a hadith while
another scholar opposes him because he does not accept such conditions
i. Examples
1. Some say the hadith must be compared to what is in the Qur’an and established
Sunnah
2. Some say that the transmitter must be a jurist if his narration contradicts that
which can be deduced through textual principles
3. Some say that the narration of the hadith needs to be widespread and known if it
deals with an issue known to have occurred frequently at the time of the Prophet
4. There are other conditions placed as well which Ibn Taymiyyah does not mention
e. Reason 5: The hadith reaches the scholar authentically but he has forgotten about it.
i. Ex: When Umar gave a fatwa saying that a person in a state of major ritual impurity
must not pray until he finds water. Then ‘Ammar reminded him of the hadith in which
prophet allowed Umar and ‘Ammar to do Tayammum in such a case
1. After this reminder Umar still could not recall the incident
ii. Such incidents frequently occur among the early and later scholars
f. Reason 6: The scholar does not know the implication of the concerned hadith
i. Reasons
1. The scholar is unfamiliar with a particular term mentioned in the hadith or he
disagrees with other scholars with regards to its meaning
a. Ex: the word ighlaaq. Scholars differed as to what it means
2. The scholar understands a particular term in the hadith in a way which is
common in his own custom and dialect; however, it was understood differently at
the Prophet’s time
a. Usually because he views that a word retains its original meaning until
proven otherwise
b. Ex: some thought the word khamr in the Qur’an and Sunnah refers to
intoxicants made from grapes only because this was what it meant in their
own dialect. But there are hadiths which clarify that its meaning refers to
every type of intoxicating drink
3. Certain terms in the Qur’an and hadiths can be homonyms, ambivalent in their
meanings, or hovering between the literal and the metaphorical. So the scholar
takes what he thinks is the nearest to the intended meaning but is wrong
a. Ex:
i. The companion who thought the white and black thread in the
Qur’anic verse about beginning the fast was literal but it was only
metaphorical
ii. The scholars who understand the word hands in the verse dealing
with dry ablution (tayammum) to mean entire arm up to the armpit
4. Sometimes the hadith’s import is obscure
a. Indications that can be drawn from a statement are very diverse and
people differ in their ability to comprehend them
i. Ex: a scholar might know the general implication of a text but he
might not recognize that this specific case is included within that
general context
1. Or he may have realized it but had forgotten later on
5. It is also possible that a person commits a mistake by deriving from a statement
what is not conceivable within the Arabic language with which the Prophet
(peace be on him) was sent
g. Reason 7: Scholar thinks that the hadith does not carry any specific implication
i. The difference between this reason and the one before it is that in the previous
[instance] the scholar did not know that specific implication whereas in this reason he
knows the specific implication but believes that it ought not to be applied based on
some principles he had which invalidated that implication, regardless of whether he was
in reality right or wrong.
1. Ex: scholar believes that the specified general text is not a valid proof, or that the
implication is not a valid proof, or that a general ruling established for a specific
cause is applied only where that cause exists, or that a general imperative does
not necessitate obligation or immediate compliance, or that the alif and laam
[constituents of the Arabic definite article] do not denote generality, or that
negated verbs neither negate its essence nor all of its rulings, etc.
ii. Half of the disputes arisen in usul ul fiqh fall under this field [of implications]
h. Reason 8: The scholar deems that implication of the text to be opposed by something
indicating that it could not have been so intended
i. Ex: general term being opposed by a specific one, an absolute term (al-mutlaq) by a
qualified one (al-muqayyad), an absolute imperative by that which negates it, or the
literal (al-haqiqah) one by that which indicates a metaphor (al-majaz), and so on.
i. Reason 9: The scholar thinks that the hadith is opposed by contrary evidence which is
accepted by all scholars, such as a Qur'anic verse, another hadith, or consensus, thereby
indicating the hadith's weakness, abrogation, or interpretation if it is amenable to interpretation
i. Two types
1. The scholar believes that the contrary evidence is preferable (rajih) in general,
leading to one of the three possibilities without specifying any one of them
a. Weakening of the hadith
b. Its abrogation
c. Its interpretation away from the undesirable meaning
2. The scholar specifies one of the three possibilities mentioned above
a. He may err though
i. There is the possibility, however, that he might commit a mistake
regarding the abrogation by considering the later evidence to be the
earlier one
ii. He might err in interpretation by understanding the hadith in a way
which its wording does not permit, or where there is something
extraneous which rules out that interpretation
iii. It is possible that the opposing hadith is not equal in strength to the
first one in terms of the authenticity of its chain of transmitters and
the clarity of its text (matn)
ii. In most cases, the claim of a consensus is actually no more than the absence of
knowledge about any opposing opinion
1. This is due to the fact that the ultimate aim for many scholars is to know the
opinions of the scholars who were their contemporaries within their region while
not knowing the opinions of other scholars
a. Some knew opinions of only the Medinan or Kufan scholars while not
others
b. Some knew only 2-3 reputable scholars’ opinions and not others so they
thought it was a consensus
2. Fearing to go against the consensus or believing that they may be going against
the consensus led many scholars to not adhere to the obvious import of the
evidence [in some cases]
j. Reason 10: The scholar thinks the hadith was opposed by evidence indicating the hadith's
weakness, abrogation, or contrary interpretation, whereas his view that this is a contrary
evidence is not shared by other scholars, or even by those who belong to his group, or the
contrary evidence is not in reality the prevalent one
i. Ex: Kufans who, when an authentic hadith is opposed by the apparent meaning of a
Qur'anic text, believe that the apparent Qur'anic text, such as one expressing generality,
is given preference over the explicit meaning of a hadith
ii. Sometimes a scholar might consider something to be apparent which is not in reality
apparent; this is because there are many potential implications of a statement
IV. Other Issues
a. It is possible in many cases that the scholar has a proof for not acting upon a hadith which we
are not aware of because the ways of comprehending knowledge are manifold and we cannot
know all of what is in the hearts of the scholars
i. But it is not permitted for us to follow this opinion in light of an opinion that is established
with an authentic hadith and is followed by some people of knowledge
1. Because the opinion of the scholar whose evidence is unknown may be wrong
ii. Hence, he may have a valid excuse for not following the Shari’ evidence
b. The Mujtahid, despite his error, is rewarded because of his ijtihad and his mistake is forgiven
due to the fact that arriving at the correct opinion on every occasion is either impossible or
highly unlikely
c. Three possibilities for one who did not act in accordance to a given hadith. Either:
i. His leaving the hadith was permissible
1. For example, he was unaware of it
ii. His leaving the hadith was not permissible.
1. This is unlikely for the great imams. They would not leave a hadith unless due to
a legitimate reason
iii. He gave an opinion without fully comprehending the issue
1. He may be deficient in his deduction so he concludes without an evidence
though he may have used some sort of ijtihaad
a. He may be influenced by a custom or predisposition
b. He may have not taken his reasoning to its appropriate conclusion
d. Scholars sometimes disagree whether a given hadith is explicit (nass) or apparent (zaahir) in
its implication
e. Conceivable interpretation of the texts plays a role in differences as well
f. Some scholars differed whether a certain action was totally forbidden or just disliked
g. If a scholar has a reasonable interpretation for a hadith, then it cannot be said that he will be
liable for the punishment stated in the hadith
i. Ex: a hadith says such and such should not be done else will be punished in the
afterlife but scholar allows that action based on interpreting the hadith differently
ii. For the punishment to apply, there must be absence of all conditions which prevent the
blame from taking place (evidence never reached the scholar, he misunderstood
something, etc.) and the absence of all the impediments (repentance, doing good deeds
which remove bad deeds, Allah’s Mercy, trials and tribulations in life which may make
up for it, etc.)
1. It may apply to those who were aware
a. It’s case by case basis [my comment]
h. Majority of the Salaf say that Allah has only one [correct] ruling with regard to any given issue
and the one who differs from this position based on an acceptable piece of ijtihad is mistaken,
excused, and rewarded
i. Whenever it is possible for a person to know the truth and he falls short, he is not to be
excused
i. Those who fall short in their ijtihad due to invalid reasons or those who imitate with a
standard that could not make the action permissible could be liable to punishment in the
hereafter
1. Unless there are other impediments which may remove it (repentance, good
deeds which remove bad ones, etc.)
2. If however he sought the truth [to the best of his ability] and did not leave it to his
own desires, then Allah does not burden a soul beyond what it can bear
ii. Those who practice legitimate ijtihaad are not included under this because they have a
valid excuse, rather, they will be rewarded for their ijtihad even when wrong
j. In disputed matters, it is not allowed to say that specific people are cursed under the threat of
punishment mentioned in certain hadiths because there may be impediments which prevent
the threat and/or punishment from them (repentance, good deeds erasing bad ones, etc.)
i. Ex: a hadith says those who do such and such are cursed but you find a scholar who
allows that action. It may be that the scholar interprets that hadith differently [based on
sound evidence] or if the doer is a layman, he might repent or his good deeds outweigh
his bad ones or tribulations in his life might remove that sin from him or Allah may have
mercy on him, etc. These impediments could apply to the mujtahid as well.
ii. Hadiths which speak about cursing those who perform certain actions are to be
understood in general terms and not specific. So we say those who do such acts are
under the threat mentioned in the hadith but we don’t specify certain people individually
of being guilty of the curse because the curse may not apply to them due to absence of
certain conditions (ex: the knowledge did not reach him) or presence of certain
impediments (ex: repentance, Allah’s Mercy, good deeds remove bad deeds, etc.).
You might also like
- Advanced Quran StudyDocument15 pagesAdvanced Quran StudyrahimmsyedNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of AhadithDocument2 pagesEvaluation of AhadithHasan MehmoodNo ratings yet
- Principles of TafseerDocument19 pagesPrinciples of TafseerrahimmsyedNo ratings yet
- Nukhbat Al Fikar NotesDocument27 pagesNukhbat Al Fikar NotesAN101No ratings yet
- t1d-f Info BookDocument33 pagest1d-f Info Bookhossanyayesha601No ratings yet
- Introduction To Hanbali Fiqh: Overview of Imam Ahmad's LifeDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Hanbali Fiqh: Overview of Imam Ahmad's LifeHaiderNo ratings yet
- Accepting A Hadith From A Single Narrator: By: Dr. Ahmad Shafaat (May, 2004)Document19 pagesAccepting A Hadith From A Single Narrator: By: Dr. Ahmad Shafaat (May, 2004)Nafisa SumayyaNo ratings yet
- 002 BaqarahDocument56 pages002 BaqarahJannah KuNo ratings yet
- Types of HadithsDocument2 pagesTypes of HadithsMuhammad HumzaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Sunnah and HadithDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Sunnah and HadithMuhammad ArhamNo ratings yet
- Rules To Check The Authenticity of Hadith With ExamplesDocument1 pageRules To Check The Authenticity of Hadith With ExamplesBushra HanifNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat P2Document118 pagesIslamiyat P2Arsalan 08No ratings yet
- Types of HadithDocument9 pagesTypes of HadithSHAK GUILDNo ratings yet
- IqbalDocument4 pagesIqbalMuhammad Faraz ImamNo ratings yet
- Books of Hadith 1. Jami: SAHIH Is That Which Contains These Four QualitiesDocument2 pagesBooks of Hadith 1. Jami: SAHIH Is That Which Contains These Four QualitiesKnowledge Broadcast CenterNo ratings yet
- Saheefa Abu Bakr v1 0Document16 pagesSaheefa Abu Bakr v1 0imti13No ratings yet
- Usool Alhadeeth 1 PDFDocument62 pagesUsool Alhadeeth 1 PDFsamreeniqbalNo ratings yet
- Syed Hasan Shirazi: All Related (32) RecommendedDocument6 pagesSyed Hasan Shirazi: All Related (32) RecommendedAhmad SabiqNo ratings yet
- S F E P 1: EPI Inal XAM ARTDocument17 pagesS F E P 1: EPI Inal XAM ARTThe NexoNo ratings yet
- Hukum Meriwayatkan Dan Mengamalkan Hadis Daif Untuk Fa Hāil Al-A'Māl Muhammad YusramDocument11 pagesHukum Meriwayatkan Dan Mengamalkan Hadis Daif Untuk Fa Hāil Al-A'Māl Muhammad YusramMuhamad Dzikri RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Sunnat-ul-Qawliyyah: This Sunnah Is The Sayings of The Holy: SignificanceDocument8 pagesSunnat-ul-Qawliyyah: This Sunnah Is The Sayings of The Holy: SignificancealiaNo ratings yet
- Sunnat-ul-Qawliyyah: This Sunnah Is The Sayings of The Holy: SignificanceDocument8 pagesSunnat-ul-Qawliyyah: This Sunnah Is The Sayings of The Holy: SignificancealiaNo ratings yet
- Hadith Book1Document45 pagesHadith Book1Manzoor AnsariNo ratings yet
- The Defense of Hadith Scholars Against ADocument12 pagesThe Defense of Hadith Scholars Against AafridaNo ratings yet
- Authority and Importance of Sunnah - Jamal Zarabozo (Notes)Document16 pagesAuthority and Importance of Sunnah - Jamal Zarabozo (Notes)dasoundofreason1065100% (1)
- History and Importance of HadithDocument10 pagesHistory and Importance of Hadithmalkah473No ratings yet
- PBL - QH - Cep BadriDocument6 pagesPBL - QH - Cep Badriacep mahmudinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Iqtisad Fi AlDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 Iqtisad Fi AlRosli MansorNo ratings yet
- Four Prominent Imams of Ahle Sunnah Wal Jamaat and Their DifferencesDocument1 pageFour Prominent Imams of Ahle Sunnah Wal Jamaat and Their DifferencesMohammed Irfan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Types of HadeesDocument10 pagesTypes of HadeesHumtyPlaysNo ratings yet
- Hadist HasanDocument11 pagesHadist HasanAesthetic ModeNo ratings yet
- Notes On Umdat Al-Ahkam - PurificationDocument35 pagesNotes On Umdat Al-Ahkam - PurificationMohammed Shahanewz100% (1)
- Ire Paper 2 Marking Guide UaceDocument14 pagesIre Paper 2 Marking Guide UaceandreeNo ratings yet
- Critique of Shahih BukhariDocument6 pagesCritique of Shahih BukhariJUNAID FAIZANNo ratings yet
- Macam Hadist MahsyurDocument2 pagesMacam Hadist MahsyurRisky AmnurNo ratings yet
- 2a - Surat Al-FatihaDocument11 pages2a - Surat Al-FatihafarooqNo ratings yet
- Hadist Mudallas1 1Document11 pagesHadist Mudallas1 1Farah R AfidahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quran and HadithDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Quran and Hadithmaskac2727No ratings yet
- Past Paper Question On History and Importance of HadithDocument10 pagesPast Paper Question On History and Importance of Hadithsaad nadeemNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hadith Studies: Lesson NineDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Hadith Studies: Lesson NineFar DarNo ratings yet
- Biographical EvaluationDocument23 pagesBiographical EvaluationNabeelNo ratings yet
- Nely Dwi JurnalDocument12 pagesNely Dwi JurnalFajar sigit NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Islamiyat PresentationDocument26 pagesIslamiyat PresentationHira FatimaNo ratings yet
- Difference of Opinion Regarding Using Weak Hadiths For Virtues of Surahs PDFDocument15 pagesDifference of Opinion Regarding Using Weak Hadiths For Virtues of Surahs PDFjosephsharifNo ratings yet
- Adam Sbu Quran Ijiis 231031Document14 pagesAdam Sbu Quran Ijiis 231031Bharat JhunjhunwalaNo ratings yet
- 1c - Surat Al-LuqmaanDocument4 pages1c - Surat Al-LuqmaanfarooqNo ratings yet
- Final Term NotesDocument23 pagesFinal Term NotesAmara ShahNo ratings yet
- Best Principles in The Ahadith of The Rasul Saw.Document8 pagesBest Principles in The Ahadith of The Rasul Saw.Muhammad Suffyan EddieNo ratings yet
- Tayseer Al-Allam Sharh Umdah Al-Ahkam: The Book of Salaat: Part OneDocument39 pagesTayseer Al-Allam Sharh Umdah Al-Ahkam: The Book of Salaat: Part OneSimaNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 - Notes - AnnualDocument9 pagesGrade 11 - Notes - AnnualRifatNo ratings yet
- Tafseer Surah at-Teen (ﻦﯿﺘﻟا) : Notes on Nouman Ali Khan's Concise Commentary of the QuranDocument4 pagesTafseer Surah at-Teen (ﻦﯿﺘﻟا) : Notes on Nouman Ali Khan's Concise Commentary of the QuranDYNOOO GAMEING100% (1)
- Latar Belakang: Wadi1A'A-Ymfha'U Yang Memiliki Beberapa Makna, Antara Lain MenggugurkanDocument6 pagesLatar Belakang: Wadi1A'A-Ymfha'U Yang Memiliki Beberapa Makna, Antara Lain MenggugurkanPoniman SuwardiantoNo ratings yet
- (L1) Nawawi - S - 40 - Hadith - 01 - On - IntentionDocument17 pages(L1) Nawawi - S - 40 - Hadith - 01 - On - IntentionAbdoulkaremNo ratings yet
- Ibn-Daqiq's Commentary on the Nawawi Forty HadithsFrom EverandIbn-Daqiq's Commentary on the Nawawi Forty HadithsNo ratings yet
- The "Forty Hadiths" of Imam al-Nawawi: A New Translation with Accompanying Commentary and JurisprudenceFrom EverandThe "Forty Hadiths" of Imam al-Nawawi: A New Translation with Accompanying Commentary and JurisprudenceNo ratings yet
- 101 Scholars On The Permissiblity of Tawassul Istishfaa IstigathaDocument308 pages101 Scholars On The Permissiblity of Tawassul Istishfaa IstigathaShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Inheriting Falsehood 1Document9 pagesInheriting Falsehood 1Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- They Worship Shaykh Rabee MinDocument7 pagesThey Worship Shaykh Rabee MinShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Biography of The Interpreter of The Quran in Andalusia The World of Qiraat Imam Ibn Juzayy Al KalbiDocument8 pagesBiography of The Interpreter of The Quran in Andalusia The World of Qiraat Imam Ibn Juzayy Al KalbiShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- 22003-Article Text-74066-2-10-20220728Document13 pages22003-Article Text-74066-2-10-20220728Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Receiving Prizes/rewards For Tournaments and Competitions in Accordance With The Hanbali School of ThoughtDocument4 pagesReceiving Prizes/rewards For Tournaments and Competitions in Accordance With The Hanbali School of ThoughtShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- The Salaf On Moderate Eating and The Stomach: Shaykh Dr. Abū IyādDocument7 pagesThe Salaf On Moderate Eating and The Stomach: Shaykh Dr. Abū IyādShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument497 pagesUntitledShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Biography of Muhammad Ibn Wasi From AbuDocument15 pagesBiography of Muhammad Ibn Wasi From AbuShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- The Aqīdah of Imām Al-Dāraqu NīDocument14 pagesThe Aqīdah of Imām Al-Dāraqu NīShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Notes On Al-Waraqat: Introduction To Usool Al-Fiqh Based On The Lectures of Sh. Amir BahjatDocument44 pagesNotes On Al-Waraqat: Introduction To Usool Al-Fiqh Based On The Lectures of Sh. Amir BahjatShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- 10 17120-Omuifd 570901-889388Document25 pages10 17120-Omuifd 570901-889388Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Heartrate PaperDocument5 pagesHeartrate PaperShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Laylat-ul-Qadr (The Night of Decree) : Shaykh Abdul - Aziz Ibn BaazDocument3 pagesLaylat-ul-Qadr (The Night of Decree) : Shaykh Abdul - Aziz Ibn BaazShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Https WWW - Islamweb.net Ehajj Printarticle - PHP Id 47232&lang EDocument2 pagesHttps WWW - Islamweb.net Ehajj Printarticle - PHP Id 47232&lang EShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Eid Takbeeraat - Hanbali Madhab: Should I Raise My Voice While Saying The Takbeer.?Document1 pageEid Takbeeraat - Hanbali Madhab: Should I Raise My Voice While Saying The Takbeer.?Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument12 pagesUntitledShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Principles Dealing With Tabdee and Have Not Other Scholars Spoken About Him?Document19 pagesPrinciples Dealing With Tabdee and Have Not Other Scholars Spoken About Him?Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Hanbali Fiqh & Usul Class Everything You Need in One Place Dr. Ahmad Abdel-WahabDocument7 pagesHanbali Fiqh & Usul Class Everything You Need in One Place Dr. Ahmad Abdel-WahabShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- 1 - 5022053844159300333 Notes IslamDocument6 pages1 - 5022053844159300333 Notes IslamShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- A Brief Glimpse and Overview of Early Deviant Sects and OrientationsDocument2 pagesA Brief Glimpse and Overview of Early Deviant Sects and OrientationsShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- The Ideal Way To Supplicate & Pray in The Last 10.: Ibn Rajab & Ibn Uthaymīn ( )Document11 pagesThe Ideal Way To Supplicate & Pray in The Last 10.: Ibn Rajab & Ibn Uthaymīn ( )Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Pre Uluww Al BaqillaniDocument9 pagesPre Uluww Al BaqillaniShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Hanbali Rulings On Taraweeh & Eid PrayersDocument2 pagesHanbali Rulings On Taraweeh & Eid PrayersShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Is It True That The Court of Appeal Overturned The Previous Judgement On Muhammad BN Haadi ?!Document4 pagesIs It True That The Court of Appeal Overturned The Previous Judgement On Muhammad BN Haadi ?!Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Imam Ahmad Ibn Hanbal, Takfeer Tabdee Adn SiyaasahDocument34 pagesImam Ahmad Ibn Hanbal, Takfeer Tabdee Adn SiyaasahShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- A Forum of Scholars Oversights Imam Al Suyutis Attitudes in Facing The Khilaf PDFDocument9 pagesA Forum of Scholars Oversights Imam Al Suyutis Attitudes in Facing The Khilaf PDFShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Creed Kullabi Asharis p725 PDFDocument1 pageCreed Kullabi Asharis p725 PDFShabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Imam Al-Awzai and His Humanitarian Ideas (707-774)Document9 pagesImam Al-Awzai and His Humanitarian Ideas (707-774)Shabab ASHNo ratings yet
- Fr. Alexander Schmemann - Church and State - The Orthodox Christian Experience With A View Towards The FutureDocument11 pagesFr. Alexander Schmemann - Church and State - The Orthodox Christian Experience With A View Towards The Futureromany2000No ratings yet
- Spiritual GiftsDocument6 pagesSpiritual GiftsPastor Peter I. HearneNo ratings yet
- RuqyaDocument10 pagesRuqyaFarzana ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Religion: Judaism, Christianity, and IslamDocument22 pagesReligion: Judaism, Christianity, and IslamMr. ForrestalNo ratings yet
- Al Mizan V 3Document234 pagesAl Mizan V 3www.alhassanain.org.englishNo ratings yet
- Ilmu Tasawuf Esy SukmaDocument20 pagesIlmu Tasawuf Esy Sukmahandimas amirullah PasaribuNo ratings yet
- Salome O. Siaton: DOLE-7 Regional DirectorDocument1 pageSalome O. Siaton: DOLE-7 Regional DirectorJenifer San LuisNo ratings yet
- Heroes or Zeroes? Which One Will You Choose?Document3 pagesHeroes or Zeroes? Which One Will You Choose?Km JmlNo ratings yet
- Muslim ReformersDocument4 pagesMuslim ReformersAsma RasheedNo ratings yet
- Subay'ah Al-Aslamiyyah and Abu As-Sanabil Bin Ba'kak Cosmetic Make-Up After Child BirthDocument2 pagesSubay'ah Al-Aslamiyyah and Abu As-Sanabil Bin Ba'kak Cosmetic Make-Up After Child BirthMemei RNo ratings yet
- Ramadan SlidesDocument14 pagesRamadan Slidesapi-3704968100% (1)
- Easter Tract All On One PageDocument1 pageEaster Tract All On One PageEugene SolomonNo ratings yet
- 3772 25433 1 PBDocument10 pages3772 25433 1 PBWahyudinNo ratings yet
- Ahtasham Siddique (Is) - 3378Document7 pagesAhtasham Siddique (Is) - 3378Hafsa AleemNo ratings yet
- That You May Proclaim His Excellencies. The Missional Use of The OT in 1 Peter (R. Cailing)Document18 pagesThat You May Proclaim His Excellencies. The Missional Use of The OT in 1 Peter (R. Cailing)spaghettipaulNo ratings yet
- Stay With Us, LordDocument4 pagesStay With Us, LordKennethSerpidoNo ratings yet
- G4-Islamic-Review SheetsDocument6 pagesG4-Islamic-Review SheetsAbdulrahman MohammedNo ratings yet
- اهب قلعتت تنرتنإ عقومو ةيوعدلا ةرابعلا Everything You Always Wanted to Know (but were afraid to ask)Document4 pagesاهب قلعتت تنرتنإ عقومو ةيوعدلا ةرابعلا Everything You Always Wanted to Know (but were afraid to ask)نوره الدعيلجNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Nature of ReligionDocument11 pagesUnderstanding The Nature of ReligionMarchell DennNo ratings yet
- 13 AttributesDocument5 pages13 AttributesASIF RAFIQUE BHATTINo ratings yet
- Assignment-History of India (1200-1500 C.E)Document4 pagesAssignment-History of India (1200-1500 C.E)Ujjwal YadavNo ratings yet
- Nasir Al-Albani's Slanderous Declaration That The Companions' Unanimous Practice of 20 Rak'ahs of Taraweeh Is A Reprehensible Innovation (Bid'ah) !Document13 pagesNasir Al-Albani's Slanderous Declaration That The Companions' Unanimous Practice of 20 Rak'ahs of Taraweeh Is A Reprehensible Innovation (Bid'ah) !robinNo ratings yet
- Who Was Ghazi ILM-UD-DIN PDFDocument2 pagesWho Was Ghazi ILM-UD-DIN PDFsyed_gulraiz_7100% (1)
- The Rashidun CaliphateDocument268 pagesThe Rashidun CaliphateSultan ul Faqr Publications50% (2)
- Lesson 13 - Christians in The WorldDocument12 pagesLesson 13 - Christians in The Worldgraceo_1No ratings yet
- Frank Pastore - Introduction To BibliologyDocument5 pagesFrank Pastore - Introduction To BibliologytemerloglouNo ratings yet
- Soul or SpiritDocument42 pagesSoul or SpiritSenile MonkNo ratings yet
- A Y Reporting FormDocument1 pageA Y Reporting FormGifty BaidooNo ratings yet
- Adeena (Battle of Trench)Document5 pagesAdeena (Battle of Trench)AdeenaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Liturgy of The Catholic ChurchDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Liturgy of The Catholic ChurchElsha DamoloNo ratings yet