Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eng - Book: Chem - 9 - (2nd) - PDF PDF
Uploaded by
kalam lokOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eng - Book: Chem - 9 - (2nd) - PDF PDF
Uploaded by
kalam lokCopyright:
Available Formats
distillation of liquid
for
(c)
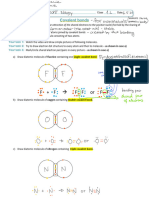
Covalent transportation
A nitrogen
its outermost
atom
(e) There are three
airhas five electrons
electronic
bonding
shell. Tonoble
nearest attain an lone pairs of
bond pairs and two
molecule.
Eng_book
atomChem_9_(2nd)_pdf.pdf
in arrangement
gas, each
shell
shares of
electrons (f)electrons
elements, the
in a
This is because
the of
three
atom. Asitsa result, nitrogen
tobond
reactbetween
with other
nitrogen
with another
bond the
outermost
a triple covalent strong
has triple
to be broken
nitrogen
forms. nitrogen
a lot of atoms
(a) Suggest a method used to obtain (g)covalent
first, which
Intermolecular
energy.
forces
(b) What gas
nitrogen typefrom
of bonding
air. is present in requires der
forces/van
(c) Describe how
a nitrogen molecule? the bonding stated in (b) Waals’
formsDraw
(d) the electron
in a nitrogen molecule. diagram (showing
(e) How many bond pairs and lone
electrons
(f) Explain whyin the outermost shells only) for a
nitrogen
pairs
(g)
is Stateof electrons
the
unreactive.attractive arethat
forces there
exist in a
nitrogen molecule.
between the nitrogen molecules. 18.
nitrogen molecule?
Section (b) (i) E. This is
(a) B conducts
18. The following table shows
9.7 because
solid itstate or
(ii)electricity
A. This isin
some physical
Substance Meltingproperties
point (°C) of five
Electrical when
the
because
solid
molten.
not conduct
it does
state but
when solid when electricity
conductivity in
substances
Solubility in A to
water
Chem_5_(2nd)_pdf.pdf
A 680 Soluble E.Good
Poor
Chem_6_(2nd)_pdf.pdf
molten conducts
(iii) B and C.
the
when
both of them
B –70 Insoluble Poor Poor This is because
electricity no
molten.
do not
solid state or
C 56 Insoluble Poor Poor matter in the
Besides, they
conduct
when
meltingmolten.
D 1610 Insoluble Poor Poor have
(iv) low is
D. This
E 660 Insoluble Good Good points.
not conduct
because it does
matter in the
electricity
when no
molten.
(a) Which of the above substances is/are solidastate
has very or
However,
point. it
(b)
not Which of thestate
in the solid aboveat 25°C? high melting
(i) 18. (c)
substances is/are (d) C.Wax does not conduct electricity no
(ii) ionic
metal(s)? B and
it isCa low-
matter it with
(iii) covalent compound(s) is in athe solid state or when
compound(s)? melting
(iv) covalent molten.Besides,
compound(s)
simple molecular structure? with a
Explain your solid.
giant covalent structure?
(c) Which of the above substance(s) is/are
answers.
(d) Which of the above substances could be
likely
wax? Explainto beyoursoluble
answer. in heptane, which is a 31
Chem_7_(2nd)_pdf.pdf Chem_8_(2nd)_pdf.pdf
non-aqueous solvent? 9
32II 44
Microscopic 19. (a)graphite;
(b) W: W: giant covalent structure; X:
X: sodium
Section
world I (c) X: ionic bonding;
19. giant
9.8 The diagrams ionic
chloride;
below Y:show
Y: covalent structure;
diamond;
the Z:
bonding Y: giant covalent
iodine
structure; Z: simple molecular structure
structures of four solids W to Z.
WXYZ
(a) What types of structures do W, X, Y
(b) ZSuggest
Chem_9_(2nd)_pdf.pdf
and four substances
have respectively?
(c) Name the types of bonding present in
that
Chem_10_(2nd)_pdf.pdf
have X the
(d)byName
solids and Ysame
these all structures
types
respectively. as W,forces
of attractive X, Y present
and
(e) Z respectively.
inforces.
solids
Which W Xand
solid, or Z, Z
hasrespectively
a higher melting and state what
(f) W andare
point? Explain Y belong
your answer. to two different forms of
particles
cannot.
19. (d) held
In solid W,forces.
the44 atoms within
carbon. Explain
Section intermolecular
molecules arewhy
31 heldW can
together conduct
In solid Z, each
electricity
the
20.
9.9while layer
Diamond,
Y byatomsare
weak linked
quartz
withinand by
each
intermolecular strong
glass covalent
are all are
molecule
hardest known natural (Answers
You might also like
- Painting and CoatingDocument20 pagesPainting and CoatingKiran D Anvekar100% (1)
- 07-Nuclear Physics IB ReviewDocument12 pages07-Nuclear Physics IB ReviewOnur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- All Pricelist SubconDocument30 pagesAll Pricelist SubcondaniNo ratings yet
- Midterm ExamDocument3 pagesMidterm Exambernadeth barajasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Midterm Practice TestDocument24 pagesChemistry Midterm Practice TestClara BetancourNo ratings yet
- Sterilization DisinfectionDocument8 pagesSterilization DisinfectionSahil ChagtiNo ratings yet
- EIL Painting Spec B16!79!41 PLS 01Document61 pagesEIL Painting Spec B16!79!41 PLS 01mANISH THIRANI100% (3)
- Span Approved Vendor Category ADocument27 pagesSpan Approved Vendor Category AyongksNo ratings yet
- RC Roofing Cladding enDocument164 pagesRC Roofing Cladding enabdalla el-saadaneyNo ratings yet
- Viscosity-Classifications Astm d2422Document8 pagesViscosity-Classifications Astm d2422Francisco TipanNo ratings yet
- Rayner-Canham 5e Answers To Odd-Numbered Questions PDFDocument25 pagesRayner-Canham 5e Answers To Odd-Numbered Questions PDFDelvia MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and PropertiesDocument7 pagesUnit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and PropertiesTAHA GABRNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument3 pagesChemistryamritasharma5319No ratings yet
- (C) Chemical BondingDocument38 pages(C) Chemical BondingAnurag RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure (Theory & Solved Ex.) Module-1Document33 pagesAtomic Structure (Theory & Solved Ex.) Module-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding (English)Document7 pagesChemical Bonding (English)PRanavNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1: Directions: Complete The Following Table: Ex.: Carbon Carbon Group Non-MetalDocument2 pagesActivity No. 1: Directions: Complete The Following Table: Ex.: Carbon Carbon Group Non-MetalJoseph Mondero RicoNo ratings yet
- SAT Chem 02 BondingDocument2 pagesSAT Chem 02 BondingTawan PetpaiboonNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure SheetDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure SheetRajeev GangwarNo ratings yet
- 04-Chemical PeriodicityDocument2 pages04-Chemical PeriodicityMohammad RussellNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Term 2 2018 Ps Worksheet Booklet PDFDocument44 pagesGR 10 Term 2 2018 Ps Worksheet Booklet PDFLucia ZeteleeNo ratings yet
- Quiz 9Document3 pagesQuiz 9James Rholdan PiedadNo ratings yet
- Bonding Short TestDocument1 pageBonding Short TestAroon SoojaniNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument30 pagesChemical Bonding - by WWW - Learnengineering.inPrakhar MishraaNo ratings yet
- Section A: Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesSection A: Chemical BondingD91Soham ChavanNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam 3Document5 pagesSample Exam 3Sonia FelixNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science (B.SC.) Semester-V (C.B.S.) Examination Physics (Atomic Physics, Free Electron Theory and Statistical Physics) Paper-1Document2 pagesBachelor of Science (B.SC.) Semester-V (C.B.S.) Examination Physics (Atomic Physics, Free Electron Theory and Statistical Physics) Paper-1Aditya BelekarNo ratings yet
- 02-Chemical Bonding-Ques-Final-EDocument32 pages02-Chemical Bonding-Ques-Final-EaavyaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bond Assig (Print) 15 10 20Document4 pagesChemical Bond Assig (Print) 15 10 20Rushikesh ThoratNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds, VSEPRDocument6 pagesCovalent Bonds, VSEPRTomáš Tommy NagyNo ratings yet
- Differ. The Sigma and Pi. Overlap Parallel. Bond Between Single Bonds Have One Sigma Bond, Double BondsDocument20 pagesDiffer. The Sigma and Pi. Overlap Parallel. Bond Between Single Bonds Have One Sigma Bond, Double BondsSamiaNo ratings yet
- Atoms PYQ SDocument2 pagesAtoms PYQ Spatiminati2020No ratings yet
- CQ On Chap-3 (Chemistry 1 Paper)Document4 pagesCQ On Chap-3 (Chemistry 1 Paper)Mahin AzizNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument20 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular StructureWoodlem Park Calicut LRCNo ratings yet
- 7 SL-paper3Document15 pages7 SL-paper3Onur YavuzcetinNo ratings yet
- Physics Resources - From Quanta To Quarks HSC Questions PDFDocument21 pagesPhysics Resources - From Quanta To Quarks HSC Questions PDFJason BrameNo ratings yet
- Chamical BondingDocument12 pagesChamical BondingMizanur HussainNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry III (100 Items)Document15 pagesInorganic Chemistry III (100 Items)maria jeusa matiasNo ratings yet
- SHREE POKHARIYA SECONDARY SCHOOL Class 11 Tech.Document2 pagesSHREE POKHARIYA SECONDARY SCHOOL Class 11 Tech.pakheyyyNo ratings yet
- ???? ?? ???????? ???????Document8 pages???? ?? ???????? ???????chopramanya34No ratings yet
- 15-Chemical Periodicity-Set-Test - Final-EDocument2 pages15-Chemical Periodicity-Set-Test - Final-EAdhithyan MNo ratings yet
- Li Are Bombarded With Protons,: Nuclear ChemistryDocument3 pagesLi Are Bombarded With Protons,: Nuclear ChemistryANSHUNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument229 pagesChemistrypirah pirahNo ratings yet
- Practice BondingQuizDocument5 pagesPractice BondingQuiz22-Rawan AdnanNo ratings yet
- Goldengate Int'L College: First Terminal Examination-2080Document2 pagesGoldengate Int'L College: First Terminal Examination-2080sachin shahNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter3 AnswersKrishaad ManirajahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure-1 NewDocument49 pagesChemical Bonding and Molecular Structure-1 Newmohdhashim8789No ratings yet
- 05 Shapes of Molecules NDocument13 pages05 Shapes of Molecules NElongated SausageNo ratings yet
- CHT Reviewer OChemDocument223 pagesCHT Reviewer OChemChastine CruzNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Chemistry - SEM IDocument6 pagesMCQs For Chemistry - SEM IKalimuddin Siddiqui100% (1)
- INORGANIC CHEMISTRY III (100 Items)Document14 pagesINORGANIC CHEMISTRY III (100 Items)Marco SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - 254 PDFDocument27 pagesChemical Bonding - 254 PDFGa AnNo ratings yet
- Master of Science (M.SC.) Semester-IV (CBCS) Physics Examination Nuclear and Particle Physics Compulsory Paper-1Document2 pagesMaster of Science (M.SC.) Semester-IV (CBCS) Physics Examination Nuclear and Particle Physics Compulsory Paper-1Sanyam KumariNo ratings yet
- Tumbal 5Document4 pagesTumbal 5Keisha ShakiraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12: Solutions Manual Part ADocument34 pagesChemistry 12: Solutions Manual Part ADerrick JamesNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument38 pagesNomenclature of Organic CompoundsPooja DebnathNo ratings yet
- SplitPDFFile 5Document1 pageSplitPDFFile 5Abhinav ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Physics: (National Eligibility Entrance Test)Document42 pagesPhysics: (National Eligibility Entrance Test)superdummuNo ratings yet
- 9th Chem 4Document2 pages9th Chem 4Umar FarooqNo ratings yet
- Questions and Problems: Lewis Dot SymbolsDocument14 pagesQuestions and Problems: Lewis Dot SymbolsAyu AndiniNo ratings yet
- Page of Paper Trick-4-ScienceDocument2 pagesPage of Paper Trick-4-ScienceKirti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Test - 8: Time: 1 Hour Max. Marks: 25Document2 pagesSelf Assessment Test - 8: Time: 1 Hour Max. Marks: 25mystical moonbeamNo ratings yet
- 172 Bonding and Electronegativity - Van Arkel TrianglesDocument4 pages172 Bonding and Electronegativity - Van Arkel TrianglesM DiNo ratings yet
- Midterm SampleDocument14 pagesMidterm SampleTahirNo ratings yet
- Science 245 4920 841Document2 pagesScience 245 4920 841CH YNo ratings yet
- Self-Consistent Fields in Atoms: Hartree and Thomas–Fermi AtomsFrom EverandSelf-Consistent Fields in Atoms: Hartree and Thomas–Fermi AtomsNo ratings yet
- Chem 21 (2nd) PDF PDFDocument1 pageChem 21 (2nd) PDF PDFkalam lokNo ratings yet
- Chem - 19 - ... - PDF - PDF Chem - 20 - ... - PDF PDFDocument1 pageChem - 19 - ... - PDF - PDF Chem - 20 - ... - PDF PDFkalam lokNo ratings yet
- Chem 20 (2nd) PDF PDFDocument1 pageChem 20 (2nd) PDF PDFkalam lokNo ratings yet
- Chem - 17 - ... - PDF - PDF Chem - 18 - ... - PDF PDFDocument1 pageChem - 17 - ... - PDF - PDF Chem - 18 - ... - PDF PDFkalam lokNo ratings yet
- Chem - 9 - (... - PDF - PDF Chem - 10 - ... - PDF PDFDocument1 pageChem - 9 - (... - PDF - PDF Chem - 10 - ... - PDF PDFkalam lokNo ratings yet
- Inspection Certificate According To EN 10204, Type 3.1.: EN ISO 17632-A: T464MM1H5Document1 pageInspection Certificate According To EN 10204, Type 3.1.: EN ISO 17632-A: T464MM1H5Cricri CriNo ratings yet
- TWR Design Cycle 2020-2021Document23 pagesTWR Design Cycle 2020-2021Alice HuNo ratings yet
- BS 2782-10 Method 1002 1977Document11 pagesBS 2782-10 Method 1002 1977Yaser ShabasyNo ratings yet
- Goodridge Performance Parts Cat 2021Document210 pagesGoodridge Performance Parts Cat 2021Anonymous wpUyixsjNo ratings yet
- Singh-Nalwa Graphene DSSCs Review 2015Document50 pagesSingh-Nalwa Graphene DSSCs Review 2015hijerNo ratings yet
- Trislot Reactor Internal Part PDFDocument12 pagesTrislot Reactor Internal Part PDFjonathanNo ratings yet
- Coating, Laminating and Testing CapabilitiesDocument28 pagesCoating, Laminating and Testing CapabilitiesrabiulfNo ratings yet
- Precipitation Reaction (Sodium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate)Document3 pagesPrecipitation Reaction (Sodium Hydroxide and Barium Nitrate)Kim BuguinaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Manganese and MagnesiumDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Manganese and MagnesiumAluruVasuNo ratings yet
- 469 Pages, Chapters 7-15.2Document469 pages469 Pages, Chapters 7-15.2SanyaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Stoichiometry ReviewDocument2 pagesWorksheet On Stoichiometry ReviewHannah MezNo ratings yet
- EstimateDocument16 pagesEstimateAnonymous d6tUk8QZNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy& Heat Treatment of Steel Final PresentationDocument85 pagesPowder Metallurgy& Heat Treatment of Steel Final PresentationDpt HtegnNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 1Document25 pages08 Chapter 1Anonymous oyUAtpK100% (1)
- Final Year Project Report: Session 2013-2017 Group MembersDocument62 pagesFinal Year Project Report: Session 2013-2017 Group MembersNouman Ijaz Chatha67% (3)
- Check List For Inspection Before Approval To Concrete or Pouring of ConcreteDocument2 pagesCheck List For Inspection Before Approval To Concrete or Pouring of ConcreteAnil Kumar T BNo ratings yet
- Astm D1876 08 2023Document2 pagesAstm D1876 08 2023Michelle LCNo ratings yet
- Banana CutDocument8 pagesBanana Cutamir kuNo ratings yet
- Flange DimensionsDocument7 pagesFlange DimensionsDave DonohueNo ratings yet
- With Reference ToDocument45 pagesWith Reference ToSIRIGIREDDY SWETHANo ratings yet
- KL 1Document87 pagesKL 1gebru g egziabherNo ratings yet
- Concrete Test On SiteDocument12 pagesConcrete Test On SiteAnsari KhuzaimaNo ratings yet
- G16S-0205-03 - Hot Drip GalvDocument2 pagesG16S-0205-03 - Hot Drip Galvpuwarin najaNo ratings yet