Professional Documents
Culture Documents
How Sound Works
Uploaded by
Lucy ChrimesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
How Sound Works
Uploaded by
Lucy ChrimesCopyright:
Available Formats
How sound works.
Every sound is produced by a vibration, which is the back and forth movement of the
sound. As a person speaks, vibration is caused by the vocal cords in the throat. You
can only hear the sound when the sound reaches your ear. Sound energy travels in
the form of sound waves, the two main types of sound waves are Transverse wave
and Longitudinal wave. Transverse waves move in an up and down motion and
vibrate at a right angle to the direction of the wave. A longitudinal wave is when the
vibrations are parallel to the direction of the wave. Sound waves also travel at
different speeds in different mediums; solid, liquid or gas. In a solid the particles are
very close together so the sound energy moves as one particle hits the other
particle, because the particles are so close together sound travels quickest through a
solid. In a liquid, the particles are further apart compared to the solid particles, this
means that the sound energy will take a little longer to travel through a liquid. In a
gas particle the particles are spread out which results in the sound waves travelling
the slowest compared to liquid and solid particles. Sound vibration produces waves,
which is the distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions. Sound
waves travel in all directions and also get reflected, then bounces back on hitting a
solid surface which is called an echo.
You might also like
- How Sound Transmisson WorksDocument1 pageHow Sound Transmisson WorksJake HoughtonNo ratings yet
- How Sound WorksDocument1 pageHow Sound WorksMohammed MiahNo ratings yet
- How Sound WorksDocument1 pageHow Sound WorksAshley HillNo ratings yet
- How Sound WorksDocument1 pageHow Sound WorksNicole ForberNo ratings yet
- How Sound ProducedDocument2 pagesHow Sound ProducedMelissa De LeonNo ratings yet
- LABORATORY 12 Observing Sound WavesDocument2 pagesLABORATORY 12 Observing Sound WavesKelseyNo ratings yet
- How Sound TravelsDocument6 pagesHow Sound TravelsLeah Cortel TesorioNo ratings yet
- Acoustics 1 (Sound Theory)Document21 pagesAcoustics 1 (Sound Theory)bishal dasNo ratings yet
- Report - Lights, Camera, ActionDocument7 pagesReport - Lights, Camera, Actionrajkrishna03No ratings yet
- How Sound TravelsDocument2 pagesHow Sound Travelsellamaecariaga2021No ratings yet
- Sound WaveDocument8 pagesSound WaveMalik AyazNo ratings yet
- SPEED OF SOUND Grade 8Document2 pagesSPEED OF SOUND Grade 8Alfreda AsuqueNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Sound WavesDocument3 pagesThe Nature of Sound WavesElycris BravoNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter - Week 2 - Asynchronous TasksDocument2 pages4th Quarter - Week 2 - Asynchronous Taskssy.valNo ratings yet
- SoundessayDocument2 pagesSoundessayapi-253785202No ratings yet
- What Is A Sound WaveDocument4 pagesWhat Is A Sound WavedeepasanmughamNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves MYP4Document9 pagesSound Waves MYP4ehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 SoundDocument27 pagesChapter-12 SoundDevansh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Form 3 Physics SoundDocument5 pagesForm 3 Physics SoundChibale Mchere BandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Part 1-2 TeacherDocument60 pagesUnit 2 Part 1-2 TeacherAustin KuoNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument10 pagesSOUNDUsha DasotNo ratings yet
- Something About Sound Wave: Hui LeiDocument19 pagesSomething About Sound Wave: Hui Leimohan raoNo ratings yet
- Types of SoundsDocument24 pagesTypes of SoundsMohammad khalidNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Done by Teacher::: Misckha Babwah & Rihana Seepersad Mr. GonzalesDocument3 pagesPhysics Project Done by Teacher::: Misckha Babwah & Rihana Seepersad Mr. GonzalesMisckha BabwahNo ratings yet
- How Does Sound TravelDocument3 pagesHow Does Sound TravelGajen DemonzNo ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument24 pagesSound EnergyJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Hearing Sound: by Denise CarrollDocument41 pagesHearing Sound: by Denise CarrollarlikaNo ratings yet
- Class Viii Science Class Notes Chaptter 13 - SoundDocument6 pagesClass Viii Science Class Notes Chaptter 13 - SoundSanjay RawatNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument4 pagesPhysics Notesevelynkanuri86No ratings yet
- Sound EnergyDocument5 pagesSound EnergySherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- BuDocument15 pagesBubreycariganNo ratings yet
- I.I.T Foundation Programme: Class: VIII Sound PhysicsDocument10 pagesI.I.T Foundation Programme: Class: VIII Sound PhysicsSesha Sai KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Sound Wave? Sound Wave Is A Type of Mechanical Wave, Which Needs A MediumDocument1 pageWhat Is Sound Wave? Sound Wave Is A Type of Mechanical Wave, Which Needs A MediumnathiNo ratings yet
- Sound: Sound Is Produced When An Object Vibrates. The Vibrating Object Pushes TheDocument3 pagesSound: Sound Is Produced When An Object Vibrates. The Vibrating Object Pushes ThePablo Acierto Ragay Jr.No ratings yet
- Sound Notes With Q&A VIIIDocument12 pagesSound Notes With Q&A VIIISatwikNo ratings yet
- Pitch of SoundDocument1 pagePitch of SoundFatim HamizahNo ratings yet
- Sound Waves - An EssayDocument8 pagesSound Waves - An EssayAshley RoyNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument23 pagesWavesAbdullah alifNo ratings yet
- Sound Acoustics One PagerDocument3 pagesSound Acoustics One PagerGreyBlackNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument2 pagesSoundSakshi NijhawanNo ratings yet
- Sound 8Document10 pagesSound 8Shanto NiceschoolNo ratings yet
- SoundenergyDocument13 pagesSoundenergyapi-325536819No ratings yet
- SoundDocument4 pagesSoundmahammalik20142023No ratings yet
- Waves NotesDocument5 pagesWaves NotesXtarchildNo ratings yet
- Physics NotesDocument12 pagesPhysics NotesBaseerArafaatNo ratings yet
- SOUND Verka (B) AmritsarDocument19 pagesSOUND Verka (B) Amritsarapi-3731257No ratings yet
- Sound Energy: Our Lady of Fatima University Basic Education DepartmentDocument28 pagesSound Energy: Our Lady of Fatima University Basic Education DepartmentMika MendozaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Sound WavesDocument4 pagesOverview of Sound WavesEthanNo ratings yet
- How Acoustic Levitation WorksDocument8 pagesHow Acoustic Levitation WorksclarinvalNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument8 pagesSoundHagen SeahNo ratings yet
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument2 pagesNotesRUPANo ratings yet
- Sound - Kub ReviewedDocument12 pagesSound - Kub Reviewedapi-520249211No ratings yet
- Kind of Waves (Kranz and Lemar)Document33 pagesKind of Waves (Kranz and Lemar)Jorge PalganNo ratings yet
- Sound Grade 7Document1 pageSound Grade 7Bik BokNo ratings yet
- AditiDocument12 pagesAditinnirmala2880No ratings yet
- SoundDocument16 pagesSoundRSNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris Essay YuliDocument6 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris Essay YuliYuli Putri BungsuNo ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument1 pageSOUNDElena WuNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Miah - StoryboardsDocument51 pagesMohammed Miah - StoryboardsLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- BBFC - Film RegulationDocument2 pagesBBFC - Film RegulationLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Research For EnrichmentsDocument1 pageResearch For EnrichmentsLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Own EdlDocument3 pagesOwn EdlLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- EvaluationDocument6 pagesEvaluationLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Location RecceDocument2 pagesLocation RecceLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Miah - SHOT LISTDocument6 pagesMohammed Miah - SHOT LISTLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Group BrainstormDocument2 pagesGroup BrainstormLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
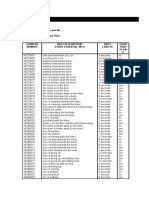
- Logging SheetDocument3 pagesLogging SheetLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Script 1 - 2Document2 pagesScript 1 - 2Lucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Music and Sound EffectDocument1 pageMusic and Sound EffectLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Broadcasting CodeDocument61 pagesBroadcasting CodeLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- How To Work in RadioDocument6 pagesHow To Work in RadioLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Task 13 - Plan of Radio Advertising Production ProcessDocument1 pageTask 13 - Plan of Radio Advertising Production ProcessLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Production PlanDocument1 pageProduction PlanLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Swot AnalysisDocument1 pageSwot AnalysisLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Competion 1Document4 pagesCompetion 1Lucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Competition 2Document3 pagesCompetition 2Lucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- OwnershipDocument4 pagesOwnershipLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Target AudienceDocument2 pagesTarget AudienceLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Job RolesDocument2 pagesJob RolesLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Audience ProfileDocument1 pageAudience ProfileLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Double Page Spread AnalysisDocument3 pagesDouble Page Spread AnalysisLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Front Cover AnalysisDocument5 pagesFront Cover AnalysisLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Production ProcessDocument4 pagesProduction ProcessLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Contents Page AnalysisDocument3 pagesContents Page AnalysisLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Legal and Ethical IssuesDocument9 pagesLegal and Ethical IssuesLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- DistributionDocument2 pagesDistributionLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- Regulatory BodiesDocument13 pagesRegulatory BodiesLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet
- AdvertisingDocument3 pagesAdvertisingLucy ChrimesNo ratings yet