Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thermal Power Plant Micro For Lalu
Uploaded by
Video CloudOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thermal Power Plant Micro For Lalu
Uploaded by
Video CloudCopyright:
Available Formats
Q.1 Ans.
Draw the layout of thermal power plant ……
4. Transfer
Almost two third of electricity requirement of the world is fulfilled by thermal 5. Outdoor storage
power plants (or thermal power stations). In these power stations, steam is
produced by burning some fossil fuel (e.g. coal) and then used to run a steam 6. Covered storage
turbine. Thus, a thermal power station may sometimes called as a Steam Power 7. Inplant handling
Station. After the steam passes through the steam turbine, it is condensed in a
8. Weighing and measuring
condenser and again fed back into the boiler to become steam. This is known
as ranking cycle. This article explains how electricity is generated in thermal 9. Feeding the coal into furnace.
power plants. As majority of thermal power plants use coal as their primary fuel, i) Coal delivery
this article is focused on a coal fired thermal power plant. The coal from supply points is delivered by ships or boats to power stations situated
near to sea or river whereas coal is supplied by rail or trucks to the power stations
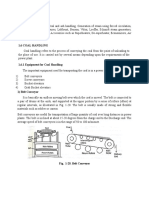
Typical Layout And Working Of A Thermal Power Plant which are situated away from sea or river. The transportation of coal by trucks is used
A simplified layout of a thermal power station is shown below. if the railway facilities are not available.
ii) Unloading
The type of equipment to be used for unloading the coal received at the power station
depends on how coal is received at the power station. If coal delivered by trucks, there
is no need of unloading device as the trucks may dump the coal to the outdoor storage.
Coal is easily handled if the lift trucks with scoop are used. In case the coal is brought
by railways wagons, ships or boats, the unloading may be done by car shakes, rotary
car dumpers, cranes, grab buckets and coal accelerators. Rotary car dumpers although
costly are quite efficient for unloading closed wagons.
(iii) Preparation
When the coal delivered is in the form of big lumps and it is not of proper size, the
preparation (sizing) of coal can be achieved by crushers, breakers, sizers, driers and
magnetic separators.
iv)Transfer
After preparation coal is transferred to the dead storage by means of the following
systems.
1. Belt conveyors
2. Screw conveyors
3. Bucket elevators
4. Grab bucket elevators
5. Skip hoists
6. Flight conveyor
Q.2 Ans. Discuss the steps involved in the coal and ash handling system .. Q.3 Ans. Discuss the factors considers for the site selection of thermal power
Coal delivery equipment is one of the major components of plant cost. The plant
1. Availability of raw material :
various steps involved in coal handling are as follows: Modern steam power plants using coal or oil as fuel require very large amount of fuel per annum.
On rough estimates, a steam power plant of 300 MW capacity requires about 3000 tonnes of coal
1. Coal delivery. per day. Therefore, it is necessary to locate the plant as far as possible near the coal fields to
reduce the cost of transportation of fuel. If the plant is located away from coal fields it may create
2. Unloading problems due to failure of transportation system, strike in mines etc.
For above reasons, atleast 15 days coal supply is needed to be stored at site. It results into :
3. Preparation (a) Increased space requirement
(b) Increased investment
(c) Additional staff requirement
(d) Losses in storage
In case it is not possible to locate the plant near the coal fields then it must be located near the
railway station to reduce the cost of road transportation cost from railway station to site of power
plant.
2. Nature of land and its cost :
The site selected should have high bearing capacity of at least 10 N / mm² to withstand dead
load of the plant. It would reduce the cost of foundation of the plant. Total space required is 1500-
2500 m² per MW capacity of plant including the space required for coal storage and ash handling
system. Therefore , the land cost must be reasonable to reduce its capital cost.
To reduce the civil engineering cost, the land selected should not need much levelling of site i.e.
it should not require filling or blasting. Also, the site selected should not have any mineral
deposits.
3. Availability of water :
Steam plants use water as working fluid which is repeatedly evaporated and condensed. It also
needs about 2% of steam generated as make up water due to its loss.
Also, considerable amount of water is needed for condensing the steam in condenser.
On rough estimates it requires about 18 x 10 litres of water per day for a 300 MW capacity plant
and 36 x 10 litres of water as make up water. Thus, it is necessary to locate a thermal power plant
near a place where required quantity of water is available throughout the year e.g. near a river,
sea or lake.
4. Load centre :
A power plant must be located near the load to which the power is supplied. However, it is not
possible to locate the power plant near all the loads. As such the centre of gravity (C.G) of all the
loads is determined with reference to reference axis where the plant is usually located. The
location of power plant at C.G. of loads reduces the cost of transmission lines and the losses
occurring in it. It should also take into account the future developments while selecting the load
centre.
5. Transport facilities :
The power plant should be located where the adequate transport facilities are available for
transportation of fuel and heavy machinery for installation.
6. Availability of labour :
Large men power is needed during the construction of plant. Therefore, labour should be
available near the construction site at cheap cost.
7. Ash disposal facilities :
Huge amount of hot ash comes out of the coal based thermal power plants which is hazardous to
human and plant life. It is corrosive and polluting in nature. Therefore, there must be sufficient
space and facilities available to dispose of large quantity of ash.
8. Future expansion :
The site selected should be such that it allows economic extensions of the plant with the
estimated growth of load.
9. Pollution :
The thermal power plants should be located away so as to avoid any nuisance from smoke, fly
ash, noise and heat discharged from the plant.
10. Away from air fields :
The power plant should be located away from the densely populated and industrial area by
taking into account the aerial warfare.
You might also like
- Chemistry and Metallurgy: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionFrom EverandChemistry and Metallurgy: Second Revised and Enlarged EditionA. SherryNo ratings yet
- WK 10 - Material Handling System (Conveyors) 2t 2020-2021Document65 pagesWK 10 - Material Handling System (Conveyors) 2t 2020-2021Mei Lamfao100% (1)
- KIET Group of Institutions, GhaziabadDocument6 pagesKIET Group of Institutions, GhaziabadSandeep ChhabraNo ratings yet
- A Case Study: Sea Borne Coal Handling System For 500 MW Power PlantDocument3 pagesA Case Study: Sea Borne Coal Handling System For 500 MW Power PlantSuhasNo ratings yet
- PPE - Coal & Ash Handling Systems: Mechanical Engineering Department SSAS Institute of Technology, SuratDocument50 pagesPPE - Coal & Ash Handling Systems: Mechanical Engineering Department SSAS Institute of Technology, SuratengineeringdesignNo ratings yet
- Fig.17 Steps in Coal HandlingDocument6 pagesFig.17 Steps in Coal HandlingBALAMBAL RNo ratings yet
- CEA - Standard - Design CRITERIA - CHPDocument29 pagesCEA - Standard - Design CRITERIA - CHPB DASNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Material Handling System (Conveyors) 2T 2021-2022Document66 pagesWeek 10 - Material Handling System (Conveyors) 2T 2021-2022Pitt Andre LozadaNo ratings yet
- Notes Ppe 16 17Document108 pagesNotes Ppe 16 17rudresh JmNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EnggDocument23 pagesPower Plant EnggMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Rohini 30162123637Document9 pagesRohini 30162123637mrdipakwaghNo ratings yet
- In-Plant Coal Handling System of Captive Power Plant at H W P, Manuguru - K. Murugappan - A.C. Mohana Rao - M.S.N. SastryDocument6 pagesIn-Plant Coal Handling System of Captive Power Plant at H W P, Manuguru - K. Murugappan - A.C. Mohana Rao - M.S.N. SastrygurumoorthiNo ratings yet
- Energy EngineeringDocument6 pagesEnergy EngineeringYashwanth H SNo ratings yet
- Steam Power PLant - CompressedDocument138 pagesSteam Power PLant - CompressedwtkovtuprNo ratings yet
- Coal Handling PlantDocument47 pagesCoal Handling PlantRajat Sharma100% (1)
- Automobile EngineeringDocument43 pagesAutomobile EngineeringShashank BiligiNo ratings yet
- SMEA1403Document157 pagesSMEA1403rrpatil1221No ratings yet
- Coal Handling 1Document18 pagesCoal Handling 1pupung182No ratings yet
- ME 522 - Power Plant Engineering - Steam Power Plant - Part 1 - LectureDocument56 pagesME 522 - Power Plant Engineering - Steam Power Plant - Part 1 - LectureJom Ancheta BautistaNo ratings yet
- Coal Handling System: Shaikh SaifDocument30 pagesCoal Handling System: Shaikh SaifKrishna SinghNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Course Material (As Per OU Syllabus)Document90 pagesPower Plant Engineering Course Material (As Per OU Syllabus)m udaya kumarNo ratings yet
- SME1304Document152 pagesSME1304187Ranjan KumarNo ratings yet
- Chute Design Jenike - Complex Calcs PDFDocument5 pagesChute Design Jenike - Complex Calcs PDFGeorge McMullinNo ratings yet
- Ppi 1Document99 pagesPpi 1Dipta BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Lres 36Document33 pagesLres 36Vikas BanjareNo ratings yet
- Kota Super Thermal Power PlantDocument29 pagesKota Super Thermal Power Plantatul mishra75% (4)
- Thermal Power Plant ReportDocument26 pagesThermal Power Plant ReportStudent of NIT PATNANo ratings yet
- Final PPT NTPC Dadri by VikasDocument50 pagesFinal PPT NTPC Dadri by VikasTushar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 24 Solid Fuel Handling: Indiaboiler Dot Com DLP/BOE-II/ 7-II/ 01092001Document3 pagesChapter - 24 Solid Fuel Handling: Indiaboiler Dot Com DLP/BOE-II/ 7-II/ 01092001Ravi ShankarNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering Notes UNIT 1Document33 pagesPower Plant Engineering Notes UNIT 1aakashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Fuel Characteristics and Properties Coal 2020Document80 pagesChapter 5 Fuel Characteristics and Properties Coal 2020Bassam RiachiNo ratings yet
- CH-24 Coal HandlingDocument3 pagesCH-24 Coal Handlingpulakjaiswal85No ratings yet
- COAL HANDLING Tech. Information Auto Saved)Document22 pagesCOAL HANDLING Tech. Information Auto Saved)R G Sanjay PrakashNo ratings yet
- Methods of Coal StackingDocument2 pagesMethods of Coal StackingJulio César Párraga CurielNo ratings yet
- Coal Handling Plant (NTPC Farakka)Document21 pagesCoal Handling Plant (NTPC Farakka)Tadeeb AkhterNo ratings yet
- ENERGY (Detail of Power Plant)Document191 pagesENERGY (Detail of Power Plant)Bishwajit MahatoNo ratings yet
- Power Plant EngineeringDocument42 pagesPower Plant EngineeringpkvssraoNo ratings yet
- A New Simulation Method For Cargo Distribution On The Scraper Conveyor Used in Coal Plough FaceDocument8 pagesA New Simulation Method For Cargo Distribution On The Scraper Conveyor Used in Coal Plough Facehieuhuechch100% (1)
- What Is Underground Mining?Document2 pagesWhat Is Underground Mining?Taha YousafNo ratings yet
- 9 Engineering of Mechanical System and EquipmentDocument38 pages9 Engineering of Mechanical System and EquipmentMinh TríNo ratings yet
- Coal Conveyor Belt Fault DetectionDocument4 pagesCoal Conveyor Belt Fault Detectionc pawarNo ratings yet
- AshuDocument34 pagesAshuachint111No ratings yet
- Vendormeetjvrchp - Coal Handling Plant (10mtpa Capacity) On Epc ProjectDocument45 pagesVendormeetjvrchp - Coal Handling Plant (10mtpa Capacity) On Epc ProjectAnonymous R0s0Nd6yNo ratings yet
- Planning of CHP PDFDocument18 pagesPlanning of CHP PDFSamrin NaazNo ratings yet
- Powerplant Engineering NotesDocument189 pagesPowerplant Engineering NotesMilan LamichhaneNo ratings yet
- Energy Engineering Notes Module 1Document34 pagesEnergy Engineering Notes Module 1sandesh CMNo ratings yet
- Highwall in Weak Geological ConditionDocument11 pagesHighwall in Weak Geological ConditionbikamlnclNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0167903188907773 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S0167903188907773 Main88127050No ratings yet
- Coal Handling ModifiedDocument135 pagesCoal Handling ModifiedGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Analysis & Design of Junction Tower at Thermal Power Plant: Assistant Professor JIT, Davanagere, IndiaDocument9 pagesAnalysis & Design of Junction Tower at Thermal Power Plant: Assistant Professor JIT, Davanagere, IndiaArjunNo ratings yet
- Coal Handling PlantDocument38 pagesCoal Handling Plantcp6355100% (3)
- Chapter 5 Fuel Characteristics and Properties Coal 2020Document80 pagesChapter 5 Fuel Characteristics and Properties Coal 2020Bassam RiachiNo ratings yet
- Fuel and Ash Handling System PDFDocument21 pagesFuel and Ash Handling System PDFrohit choudharyNo ratings yet
- Module-1 Steam GeneratorsDocument35 pagesModule-1 Steam GeneratorsChethu ChethuNo ratings yet
- Conveyors: A. Belt ConveyorDocument19 pagesConveyors: A. Belt ConveyoryohannesNo ratings yet
- VIKRAM training-REPORT PDFDocument30 pagesVIKRAM training-REPORT PDFdixowo6103No ratings yet
- EE All ModulesDocument169 pagesEE All ModulesChethu ChethuNo ratings yet
- Report On Summer Training at NSPCL by Aniket SumanDocument41 pagesReport On Summer Training at NSPCL by Aniket SumanBACK BENCHERNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Instrumentation: Lecture NotesDocument35 pagesPower Plant Instrumentation: Lecture NotesmaanwarNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Engineering (SMEX1016) 1Document60 pagesPower Plant Engineering (SMEX1016) 1shyam sundarNo ratings yet
- Water Absorbing Raod PPT 2k23Document20 pagesWater Absorbing Raod PPT 2k23Video Cloud100% (3)
- 5g Wireless TechnologyDocument16 pages5g Wireless TechnologyVideo CloudNo ratings yet
- Project Report Page 1 To 4Document4 pagesProject Report Page 1 To 4Video CloudNo ratings yet
- Home AutomationDocument5 pagesHome AutomationVideo CloudNo ratings yet
- Solarworld - Magazine 2016 - en - WebDocument18 pagesSolarworld - Magazine 2016 - en - WebSamuel Arévalo GNo ratings yet
- Concept Review Chapt 17 Students 1Document5 pagesConcept Review Chapt 17 Students 1api-390763404No ratings yet
- Lesson - Exemplar - Science 9 3RD Quarter Week 3-4Document9 pagesLesson - Exemplar - Science 9 3RD Quarter Week 3-4Thartson Oliveros MagdadaroNo ratings yet
- Cost and Performance Characteristics of New Generating Technologies, AnnualDocument4 pagesCost and Performance Characteristics of New Generating Technologies, AnnualKamil M. AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marco Castillo 8kw HybridDocument3 pagesMarco Castillo 8kw HybridArlie SantosNo ratings yet
- Geothermal Power Plants: Principles, Applications, Case Studies and Environmental ImpactDocument1 pageGeothermal Power Plants: Principles, Applications, Case Studies and Environmental ImpactJuan Ponce ManríquezNo ratings yet
- AEG PS - Off - Grid - 2013 - enDocument26 pagesAEG PS - Off - Grid - 2013 - envayyikNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle AssessmentDocument3 pagesLife Cycle AssessmentHevliza TiaraNo ratings yet
- Energy and KidsDocument4 pagesEnergy and Kidsapi-270337822No ratings yet
- HPL - Solar All in One OfferingDocument2 pagesHPL - Solar All in One OfferingShivamNo ratings yet
- Energia Hazel Webinar 4 Hydrogen in A Net Zero Energy System Oct 20Document12 pagesEnergia Hazel Webinar 4 Hydrogen in A Net Zero Energy System Oct 20Mohamed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Company Profile-VisionDocument55 pagesCompany Profile-VisionABID TRADERSNo ratings yet
- EPG Micro ProjectDocument11 pagesEPG Micro ProjectTushar MoreNo ratings yet
- 8rad (2019)Document40 pages8rad (2019)Vladimiro García RiveraNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones Ups YorksDocument4 pagesEspecificaciones Ups Yorksluisgerardogonzalez8No ratings yet
- 21 MECS SteaMax Heat Recovery System DuPont - Sulfirc AcidDocument2 pages21 MECS SteaMax Heat Recovery System DuPont - Sulfirc AcidmohsanNo ratings yet
- 2018 Outlook For Energy: A View To 2040Document17 pages2018 Outlook For Energy: A View To 2040manuel cabarcasNo ratings yet
- Parabolic Solar CollectorDocument9 pagesParabolic Solar CollectorWise manNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Conventional Energy Sources and Fossil Fuel - Net ExplanationsDocument4 pagesMCQ On Conventional Energy Sources and Fossil Fuel - Net ExplanationsDr Rajesh Maharudra PatilNo ratings yet
- Leed ZeroDocument2 pagesLeed ZeroZainab KhadimNo ratings yet
- Cooling & Heating: Revomax SeriesDocument4 pagesCooling & Heating: Revomax SeriesBoonaa KiyyaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument17 pagesSeminar Reportshadan alamNo ratings yet
- Energy and Environmental Engineering: Enir 11Document10 pagesEnergy and Environmental Engineering: Enir 11cYbernaTIc enHancENo ratings yet
- Chapt0 - IC Engines - ScenarioDocument20 pagesChapt0 - IC Engines - ScenariopeterNo ratings yet
- Green Building DesignDocument6 pagesGreen Building DesignhariharanNo ratings yet
- 2nd Generation Biofuels Güssing Demo PlantDocument26 pages2nd Generation Biofuels Güssing Demo PlantTom MOt'sNo ratings yet
- Review and Comparison of Various Hydrogen Production Methods Based On Costs and Life Cycle Impact Assessment IndicatorsDocument24 pagesReview and Comparison of Various Hydrogen Production Methods Based On Costs and Life Cycle Impact Assessment IndicatorsesoubihNo ratings yet
- Unit - Iv: Geothermal & Ocean EnergyDocument83 pagesUnit - Iv: Geothermal & Ocean EnergycikhilNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh New Gen PLanDocument4 pagesBangladesh New Gen PLanRVaranasiNo ratings yet
- G7 Unit 11 Lesson 1Document3 pagesG7 Unit 11 Lesson 1Dieu VuNo ratings yet