Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histo Lect TQ
Histo Lect TQ
Uploaded by
Precious Iris Impas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views19 pagesThe document summarizes key aspects of the integumentary system. It discusses the main layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis), as well as structures found within the skin like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. It also covers cell types such as keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. Sensory receptors in the skin like Meissner's corpuscles and Pacinian corpuscles are also mentioned.
Original Description:
Original Title
histo lect tq
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of the integumentary system. It discusses the main layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis), as well as structures found within the skin like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. It also covers cell types such as keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. Sensory receptors in the skin like Meissner's corpuscles and Pacinian corpuscles are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views19 pagesHisto Lect TQ
Histo Lect TQ
Uploaded by
Precious Iris ImpasThe document summarizes key aspects of the integumentary system. It discusses the main layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis), as well as structures found within the skin like hair follicles, sebaceous glands, and sweat glands. It also covers cell types such as keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans cells, and Merkel cells. Sensory receptors in the skin like Meissner's corpuscles and Pacinian corpuscles are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
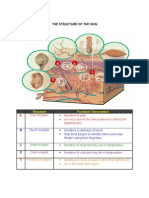
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM REVIEWER d.
Lamellar granules is important in this layer
16. Part of the hair extending beyond the skin surface
1. The skin has mainly composed of two major layers a. Hair bulb
a. Epidermis b. Hair follicle
b. Dermis c. Hair shaft
c. Sweat glands d. Hair roots
d. Both a and b 17. Which statement is true on the free nerve endings
2. Complete mixture of lipids that are hydrolyzed by bacterial enzymes a. They are not covered by a connective tissue
after secretion. b. Responses primarily to temperature, pain, and itching
a. Sebocytes c. They start in the stratum Basale and terminate in the stratum
b. Sebum granulosum
c. Pilosebaceous units d. AOTC
d. Sweat 18. Transformed and polymerized into the different forms of melanin
3. Important regulator of calcium metabolism and proper bone a. DOPA
formation. b. Dihydroxylphenylalanine
a. Sex pheromones c. Tyrosine
b. Metabolic d. Both a and b
c. Vitamin D 19. Complete the sentence
d. Vitamin D3 a. Epidermis is an epithelial layer of ___________ origin.
4. Produces the protein pigment into keratinocytes b. Dermis is a connective tissue derived from the _____________.
a. Melanocytes 20. Enumerate the epidermal derivatives of the skin.
b. Keratinocytes a.
c. Merkel cells b.
d. Langerhans cells c.
5. Source of your stem cells or the originator cells d.
a. Nail matrix 21. With several acini converging at short duct that usually empties into
b. Nail roots the upper portion of a hair follicle.
c. Eponychium a. Eccrine sweat glands
d. Hyponychium b. Apocrine sweat glands
6. Filaggrin c. Branched acinar glands
a. Aggregate the keratin filament d. Sebocytes
b. Released a process of exocytosis 22. Extension of the epidermis to the dermis
c. Cysteine rich and histidine rich proteins a. Papillary layer
d. Bundled to form keratin b. Reticular layer
7. Enumerate the five layers of thin skin in your epidermis. c. Epidermal ridges
a. d. Epidermal papillae
b. 23. These cells would form the matrix of the elongating _____
c. a. Hair roots
d. b. Skin cells
e. c. Squames
8. It can sense cold temperature which the thermoreceptor of the male d. Keratinocytes
organ. 24. It is bundled to form keratin
a. Ruffini corpuscles a. Lamellar granules
b. Pacinian corpuscles b. Tonofibrils
c. Krause end bulbs c. Squames
d. Meissner corpuscles d. Keratinocytes
9. Possess the tennis racquet shaped containing what is called _____ 25. Collagenous, fusiform capsules anchored firmly to the surrounding
a. Langerhans cells: antigen-presenting cells connective tissue that respond to stretch and torque
b. Merkel cells: birbeck cells a. Meissner
c. Merkel cells: melanosomes b. Genital
d. Langerhans cells: birbeck cells c. Lamellated
10. An enzyme that would convert tyrosine into the d. Ruffini
dihydroxyphenylalanine 26. Cells found in the sebaceous glands
a. DOPA a. Sebocytes
b. Tyrosinase b. Sebum
c. Melanin c. Acinar glands
d. Keratin d. Adipocytes
11. What does it mean if it is avascular? 27. Chemical released in the sebaceous glands
a. Lacks microvasculature a. Sebocytes
b. Does not have blood vessels b. Sebum
c. It has a thickest layer c. Acinar glands
d. Either d. Adipocytes
12. Structures that are embedded in the skin but is considered as a 28. Cells that are composed of stratified squamous keratinized e.
separate organ or tissue. a. Langerhans cells
a. Cells in the epidermis b. Keratinocytes
b. Epidermal derivatives of the skin c. Melanocytes
c. Layers of the dermis d. Merkel cells
d. Reticular layer 29. Considered the most differentiated cells in the skin
13. Epithelial tissue is _______. a. Stratum corneum
a. Regulates metabolism b. Basal layer
b. Keratinized c. Spinous layer
c. Microvasculature d. Stratum lucidum
d. Avascular 30. The distal end of the plate becomes free of the nail bed at the
14. Which statement is not true about epidermis epidermal fold called the _______
a. The thickest layer divided into papillary and reticular layer a. Eponychium
b. Composed of stratified squamous keratinized epithelium b. Hyponychium
c. Cells include keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, melanocytes, and c. Cuticle
Merkel cells d. Internal root sheet
d. AOTC 31. The secretory part is irregular stratified cuboidal epithelium
15. Which statement is true about stratum lucidum? a. Sebaceous gland
a. Consist of a thin with a translucent layer b. Sweat gland
b. Synthesize a large amount of keratin c. Eccrine sweat gland
c. Source of the skin cells and the alive skin cells d. Apocrine sweat gland
32. Precursor of melanin which catalyzed by an enzyme b. Ruffini
a. Tyrosine c. Meissner
b. Tyrosinase d. Pacinian
c. DOPA 49. Highly abundant in highly sensitive skin that is found in the stratum
d. Melanin basale
33. Enumerate the unencapsulated sensory receptors a. Keratinocytes
a. M b. Melanocytes
b. R c. Langerhans cells
c. F d. Merkel cells
34. A hair follicle and its associated sebaceous glands that make up 50. Usually produced by the apocrine sweat gland and the other skin
________. a. Sex pheromones
a. Acinar glands b. Vitamin D3
b. Apocrine c. Vitamin D
c. Holocrine d. Sexual signaling
d. Pilosebaceous unit 51. Other name for Krause end bulbs
35. This layer is very important in the skin’s ability to prevent water loss a. G
a. Basal layer b. B
b. Spinous layer 52. Why stratum granulosum is important in the body?
c. Stratum granulosum a. Because it maintains the water volume
d. Stratum corneum b. Because it is the source of skin cells and alive skin cells
36. It is usually seen or found in the spinous layer c. Starting point of the synthesis of cytoskeletal keratins
a. Keratinocytes d. AOTC
b. Melanocytes 53. Secretion from a sebaceous gland increases greatly at ____ stimulated
c. Langerhans cells primarily by _____ in men and by ____ and ____ ____ in female.
d. Merkel cells a. P
37. Derived from the neural crest which it usually scattered among the b. T
basal cells of the stratum basale c. O
a. Melanocytes 54. It connects the dermis to the epidermis
b. Keratinocytes a. Epidermal papillae
c. Merkel cells b. Epidermal ridges
d. Langerhans cells c. Papillary layer
38. Interdigitations that is considered as the peg and socket d. Reticular layer
a. Dermatoglyphs 55. Consists of a simple cuboidal with numerous secretory granules
b. Epidermal ridges a. Apocrine
c. Dermal epidermal b. Merocrine
d. Dermal papillae c. Eccrine
39. Would usually have a capsule which could be a Schwann cell d. Sweat gland
a. Unencapsulated sensory receptor 56. Collagenous corpuscles penetrated by a sensory fiber that can be
b. Papillary layer found primarily in the skin of the penis and clitoris
c. Epidermal ridges a. Bulboid corpuscles
d. Encapsulated sensory receptor b. Meissner corpuscles
40. Binds the skin to the sub adjacent organs like the muscle and contains c. Pacinian corpuscles
adipocytes d. Ruffini corpuscles
a. Hypodermis 57. Enumerate the functions of the skin.
b. Subcutaneous tissue a.
c. Epidermis b.
d. Both a and b c.
41. Layer that could vary from person to person. d.
a. Epidermal ridges e.
b. Papillary layer 58. Which statement is true about Meissner corpuscles?
c. Reticular layer a. Touch receptors
d. Subcutaneous layer b. Responsive to low frequency stimuli in the papillary layer of
42. A web of sensory fibers surrounding the bases of hair follicles in the hairless skin
reticular dermis that detects the movement of the hairs c. Found primarily in the skin of penis and clitoris
a. Merker cells d. Both a and b
b. Free nerve endings 59. Lipid found in sebum
c. Root hair plexus a. Wax, Esters
d. Pacinian corpuscles b. Squalene
43. Keratinocytes contain the _______ c. Cholesterols, Triglycerides
a. Protein filaggrin d. AOTC
b. Keratohyalin granules 60. The first line of defense against any infection
c. Melanin-pigment a. Epidermal ridges
d. AOTC b. Unbroken skin
44. It is considered as the thickest layer especially in the epidermal ridges c. Papillary layer
and characteristically exhibit spinous process. d. Reticular layer
a. Stratum basale 61. Arises from these keratinized structures within the epidermal
b. Stratum spinosum invagination. There is a portion of the epidermis that would invaginate
c. Stratum lucidum and then a structure would arise known as ______
d. Stratum granulusum a. Nail
45. ____________ pigment is linked to a matrix of structural proteins and b. Hair
accumulates in the vesicles until they form mature elliptical granules. c. Hair follicle
46. Enumerate the cells included in the epidermis d. Either
a. 62. Apocrine would release secretion connected to a ______
b. a. Sweat pore
c. b. Nail bed
d. c. Eponychium
47. The proximal part of the nail d. Hair shaft
a. Nail bed 63. These ridges intervening high form distinctive patterns unique for
b. Nail root everyone appearing as combination of loops arches and holes.
c. Nail plate a. Epidermal ridges
d. Nail matrix b. Dermal papillae
48. Corpuscle that responds when you pinch someone’s skin c. Dermatoglyphs
a. Krause end bulbs d. Dermal epidermal interdigitations
64. It is where the keratin are stored or packed d. AOTC
a. Lamellar granules 79. Between the papillary and reticular layer, there lies the ________ from
b. Squames which the capillary branches extend to the dermal papillae
c. Keratohyalin granules a. Epidermal ridges
d. Keratinocytes b. Hypodermis
65. Identify the following: c. Musculovascular subpapillary plexus
a. One-cell thick: _______________ d. Subcutaneous tissue
b. Stratum spinosum: ____________________ 80. Skin cells synthesizes vitamin D3
c. Production of keratohyalin: ___________________ a. Protection
d. Stratum corneum: ________________________________ b. Thermoregulatory
66. Granules that contain melanin c. Sex pheromones
a. Melanocytes d. Metabolic
b. Melanin-pigment 81. Nail ___ bound to a bed of epidermis known as the ____ which
c. Tyrosine contains only the basal and spinous epidermal layers
d. melanosomes a. Nail bed; nail matrix
67. Keratinocytes in this layer contain numerous keratohyalin granules b. Nail root; nail bed
which produces lamellar granules c. Nail plate; nail bed
a. Basal layer d. Nail cuticle; nail root
b. Stratum corneum 82. Wound healing: Under the influence of the growth factors and the
c. Granular layer hydrolytic enzymes released in part from ______, _____ proliferate, and
d. Spinous layer produce much new _____ to form the granulation tissue.
68. Function that skin allows you to feel tactile objects a. M
a. Protection b. F
b. Thermoregulatory c. C
c. Metabolic 83. Which statement is not true about vitamin D regulation
d. Sensory a. It has something to do with your skin cells
69. The epidermis gradually reestablishes its continuity over the wound b. Important regulator of calcium metabolism and proper bone
side but if there is an excessive collagen especially for bigger wounds, formation.
they would remain a structure known as _____ in the dermis. c. It is part of the homeostasis
a. Keloid d. It is usually broken down by UV light in the skin and travels to the
b. Scar kidney to be converted to the active form of vitamin D
c. Scar tissue 84. Which statement is true about Langerhans cells?
d. Keloid mark a. Dendritic appearing
70. Predominant cell type of epidermis b. Antigen-presenting cells
a. Keratinocytes c. Tennis-racquet shaped
b. Melanocytes d. AOTC
c. Langerhans cells 85. Collagen-rich, well-vascularized tissue in the dermis which gradually
d. Merkel cells replaces blood clot and undergoes remodeling.
71. Consist of sensory axons winding among flattened Schwann cells a. Scar tissue
arranged perpendicular to the epidermis in the dermal papillae b. Subcutaneous tissue
a. Lamellated corpuscles c. Granulation tissue
b. Pacinian corpuscles d. Either
c. Meissner corpuscles 86. Dead skin which are not metabolically active anymore because their
d. Bulboid corpuscles cytoplasm is fully cornified
72. From which the epidermal stratum corneum extends as the ____. So, a. Squames
from the nail root extends a thin piece of skin. b. Keratohyalin granules
a. Eponychium c. Keratinocytes
b. Cuticle d. Tonofibrils
c. Both a and b 87. Terminal dilation in the hair follicle
d. Nail plate a. Hair bulb
73. Epithelial tactile cells which is important in our ability to feel textures b. Hair shaft
which are also found in the stratum basale c. Hair roots
a. Langerhans cells d. Dermal papillae
b. Melanocytes 88. The sweat flows continue in the spiraling channel in excretory ____ in
c. Merkel cells the skin surface
d. Keratinocytes a. Sweat gland
74. Production of sweat b. Hair
a. Protection c. Sweat pore
b. Thermoregulatory d. either
c. Metabolic 89. Which statement is true about stratum corneum?
d. Sensory a. Composed of a layer of dead skin cells
75. It helps maintain the stratum corneum and hair shafts and exerts weak b. AOTC
antibacterial and anti-fungal properties. c. Topmost, the one we can touch or exfoliate
a. Sebocytes d. They’re just dead keratinocytes with full on keratin
b. Sweat 90. Vitamin D is usually broken down by __________ in the skin and then it
c. Sebum travels _______ to be converted to the _______ active form of vitamin
d. Sebaceous gland D which is the one that acts and regulates _________.
76. Thick skins are found in your ______ a.
a. Palm b.
b. Soles c.
c. Nails 91. Composed of a stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
d. Both a and b a. Keratinocytes
77. Specialized for sensing coarse touch, pressure, and vibrations which is b. Epidermis
found in the deep reticular dermis and hypodermis c. Melanocytes
a. Meissner corpuscles d. Dermis
b. Pacinian corpuscles 92. Why would cells receive nutrients and oxygen by diffusion?
c. Krause end bulbs a. Because it is avascular
d. Merker cells b. It doesn’t have blood vessels
78. Which statement is true about the apocrine sweat glands? c. They tend to have extra layer
a. Largely confined to skin of the axillary and perineal region d. Both a and b
b. Production of pheromones 93. Commonly known as footprints or fingerprints
c. Secretory components of the apocrine glands have much larger a. Dermal epidermal interdigitations
lumen than the eccrine. b. Tyrosinase
c. Tonofibrils a. Stratum basale
d. Dermatoglyphs b. Stratum granulosum
94. Thick layer of connective tissue that supports the epidermis c. Stratum lucidum
a. Dermis d. Stratum spinosum
b. Hypodermis 110. Tonic receptors for sustained light touch and for sensing an object’s
c. Subcutaneous tissue texture, or the tactile disc
d. Either a. Meissner corpuscles
95. Which statement is true about stratum basale b. Ruffini corpuscles
a. Contains progenitor cells for all epidermal layers c. Free nerve endings
b. Source of the skin cells and the alive skin cells d. Merker cells
c. They’re the ones that start synthesis of cytoskeletal keratins 111. Mainly composed of loose connective tissue and the one supports the
d. AOTC epidermis which is the topmost layer
96. Skin macrophage a. Hypodermis
a. Merkel cells b. Subcutaneous tissue
b. Melanin-pigment c. Reticular layer
c. Langerhans cells d. Papillary layer
d. Skin cells 112. Enumerate the two sweat glands
97. Which statement is true about reticular layer a. A
a. More of a dense irregular connective tissue b. E
b. Bundles of type I collagen 113. Which statement is true about granular layer?
c. Network of elastic fibers is present in this layer a. Formed by lamellar granules, so water cannot easily pass
d. AOTC through.
98. Subcutaneous tissue is also known as b. Undergoing the keratinization
a. Dermal layer c. Allows the skin to maintain the water volume in the human body
b. Epidermal ridges d. AOTC
c. Dermal papillae 114. Projections of the dermis and to the dermis
d. Hypodermis a. Dermal papillae
99. What is the purpose of dense irregular connective tissue in the layer of b. Interdigitations
epidermis? c. Epidermal ridges
a. Protects the hypodermis d. Hypodermis
b. Prevent water loss 115. This is where the target of when you are injected with insulin
c. Maintain water movement which is important in the human body a. Epidermal layer
d. accommodate forces from any direction b. Superficial fascia
100. Which statement is true about dermis c. Reticular layer
a. Thin layer of connective tissue d. Dermal papillae
b. It has three layers 116. Enumerate the encapsulated sensory receptors (nerve tissues)
c. Subpapillary plexus a. M
d. Both a and b b. L
101. Which statement is true about stratum spinosum c. R
a. Synthesis of a large amount of keratin would give the cell the d. K
spiny extensions and other proteins takes place. 117. Most numerous neuronal receptors in the epidermis
b. Considered a subdivision of the stratum corneum a. Krause end bulbs
c. Consists of a thin with a translucent layer of flattened eosinophilic b. Ruffini corpuscles
keratinocytes held together by desmosomes. c. Meissner corpuscles
d. AOTC d. Free nerve endings
102. A tuft of vascularized loose connective tissue 118. Identify these two corpuscles.
a. Dermal papillae a. Detects warm temperature:
b. Hair shaft b. Detects cold temperature
c. Hair roots 119. Responsible for the production and growth of hair
d. Hair follicle a. Hair bulb
103. Tissue found underneath the dermis b. Hair roots
a. Superficial fascia c. Hair follicle
b. Hypodermis d. Hair shaft
c. Subcutaneous tissue 120. Embedded in the dermis over most of the body except the skin of the
d. AOTC palms and soles.
104. Keratinocytes in this layer contain numerous keratohyalin granules a. Subcutaneous tissue
which produces lamellar granules. b. Sweat glands
a. Stratum lucidum c. Sebaceous glands
b. Stratum spinosum d. Apocrine sweat glands
c. Stratum basale 121. In most thick hairs, large vacuolated moderately keratinized cells form
d. Stratum granulosum the central portion known as ______, where the heavily keratinized
105. Water barrier cells are found. Then it is covered by the _____ then it is even covered
a. Keratohyalin granules by a ____. The cuticle will be divided into _______ and ________.
b. Lamellar granules a. M
c. Langerhans cells b. C
d. Merker cells c. C
106. Enumerate the sensory receptors d. (2)
a. U 122. Cyclic process of hair
b. E a. Catagen – telogen – anagen
107. Important in the aggregation and it is cysteine rich and histidine rich b. Anagen – catagen – telogen
proteins that is considered as the precursors of the protein filaggrin. c. Anagen – telogen – catagen
a. Lamellar granules d. Telogen – anagen – catagen
b. Keratohyalin granules 123. Hard plates of keratin on the dorsal surface of each distal phalanx
c. Keratinocytes a. Nail plate
d. Tonofibrils b. Nail root
108. The _____ would form the _____ deeper which is the source of your c. Nail bed
stem cells or the originator cells. d. Nail
a. Nail bed; nail matrix 124. Which statement is not true about blood clotting?
b. Nail root; nail matrix a. Would release the platelet derived
c. Nail plate; nail cuticle b. Recruit macrophage and neutrophils to enter the wound
d. Hyponychium; nail matrix c. Call in your immune response
109. It may be present in the thin skin but it’s only prominent in the thick skin d. AOTC
and it is considered as the subdivision of a stratum corneum. 125. Act as a lubricant of hair
a. Sebum c. Ventricular bundle
b. Sebocytes d. Atrioventricular bundle
c. Pilosebaceous unit 12. Thin layer of endothelium which is the middle myoelastic layer of
d. NOTC smooth muscle fibers and connective tissue
126. Which statement is not true about eccrine sweat glands? a. Myocardium
a. Highly acidophilic b. Endocardium
b. Widely distributed in the skin and are most numerous in the palms c. Epicardium
and foot soles. d. Pericardium
c. Produce sweat 13. It is the fenestrated elastic material which allow expansions during
d. Both a and b high blood pressures
127. A physiologic response to increased body temperature during a. Internal elastic membrane
physical exercise or thermal stress b. Attachment skeleton
a. Sweating c. Subendothelial layer
b. Sweat d. Endothelium
c. Hormone 14. Located on the atrial or blood vessel side of each valve that acts as
d. Puberty a shock absorber to dampen vibrations associated with the closing of
128. Restoring to its former structure itself the valves
a. W a. Ventricularis
b. Fibrosa
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM REVIEWER c. Spongiosa
d. Valve
1. Which statement is not true about blood 15. Generates and propagates waves of depolarization that spread
a. Carries various nutrients especially oxygen to our tissues through the myocardium to stimulate rhythmic contractions
b. Transports or can distribute itself to these said tissues in our body a. Circulatory system
via a channel b. Conducting system of the heart
c. Human body can function properly without blood c. Cardiovascular system
d. Both a and b d. Vascular system
2. Channel used in transportation of blood to various tissues using the 16. Initiate the contraction or heartbeat and will spread it through the
pumping organ which is the heart ventricular myocardium found in the right atrial wall.
a. Cardiovascular system a. SA node
b. Circulatory system b. AV node
c. Vascular system c. Electrical impulse
d. Conducting system of the heart d. Attachment skeleton
3. It is carried by the arteries or arterioles 17. Core of the value and contains fibrous extensions from the dense
a. Blood irregular connective tissue of the skeletal rings of the heart
b. Oxygenated blood a. Cardiac skeleton
c. Deoxygenated blood b. Attachment skeleton
d. Either c. Fibrosa
4. It is where the cardiac muscle will attach and for various valves d. Spongiosa
between the atria, ventricle, semilunar valves of the aorta, and 18. Consisted mainly of cardiac muscle with its fibers arranges spirally
pulmonary artery. around each heart chamber and it is thicker in the walls of the
a. Fibrous network ventricles particularly the left, than in the atrial walls
b. Cardiac skeleton a. Myocardium
c. Fibrous skeleton b. Endocardium
d. Both a and b c. Epicardium
5. Helps propel lymph towards the heart d. Pericardium
a. Contraction of muscles 19. Sinoatrial node (a. ___) – AV Node (b. ____) – Anteroventricular
b. Blood circulation bundles (of His) - ________ Conducting Network
c. Lymphatic circulation a. P
d. NOTC b. A
6. Distribution of blood and heart pumping c. S
a. Cardiovascular system 20. Slight thickening of the smooth muscle at the origin of a capillary bed
b. Circulatory system from an arteriole is called
c. Vascular system a. Venule
d. Conducting system of the heart b. Capillary
7. Identify. tunica adventitia c. Precapillary sphincter
a. Blood supply: d. Microvasculature
b. Nerve supply: 21. Continuous to the cordae tendinea which are fibrous thread-like
8. All the statements are true of endothelium except chords that also covered with endothelium
a. Presents a non-thrombogenic surface that prevents the blood a. Ventricularis
from clotting b. Spongiosa
b. The cells regulate the vascular tone and the blood flow c. Fibrosa
inflammation d. Valve
c. Consists primarily of circumferentially arranged layers of smooth 22. Why arteries have thicker tunica media?
muscle cells a. Due to its function
d. Secrete various growth factors that stimulates formation of b. Since it distributes blood
vascular system c. Since this carries blood or distribute deoxygenate blood
9. VEGF stimulate branching of blood vessels from already small existing d. Both a and b
vessels through the process of ________ 23. Most common type of capillary that has distinct continuity of the
a. Vascuelogensis endothelial cells in it walls with no fenestrations, no holes, and it is
b. Angiogenesis smooth
c. P selectin a. Continuous
d. Weilbel-palade bodies b. Distinctive
10. Which statement is true about circulatory system c. Sinusoidal
a. Transports blood to various tissue d. Fenestrated
b. Carry various nutrients especially oxygen to the tissue 24. Thickest layer of vessel wall that contains longitudinally disposed
c. Human body can function properly without this system smooth muscles or bundles of smooth muscles
d. Pumps and directs blood cells and substances carried in blood a. Tunica intima
to all tissues of the body. b. Tunica media
11. Passes from the right atrium to the ventricular septum via the c. Tunica adventitia
membranous septum of the fibrous skeleton. d. Subclavian veins
a. Fibrous network 25. Form blood vascular networks that allow fluids containing gases,
b. Cardiac skeleton metabolites, and waste products to move through their thin walls
a. Precapillary sphincter c. Fibrosa
b. Capillaries d. Valves
c. Artery 39. Pacemaker
d. Arterioles a. AV Node
26. Enumerate the tissues of vascular wall b. SA node
a. E c. Atrioventricular bundles
b. S d. Either
c. C 40. Specialized epithelium that acts as a semipermeable barrier of the
27. All statements are not true about elastic arteries except blood plasma and interstitial fluid
a. Distribute blood to the organs a. Endothelium
b. The notable characteristic is the presence of elastic lamellae in b. Smooth muscle
which the thick layer allows it to expand and to accommodate c. Pericardium
pressure when the heart is pumping blood. d. Endocardium
c. It is made up of only one or two smooth muscle layers 41. Elastic arteries
d. Smallest arteries branch a. Aorta
28. A connective tissue of the endothelial cells which is a thin extracellular b. Pulmonary artery
layer composed chiefly of collagen, proteoglycans, and c. Unmyelinated nerves
glycoproteins d. Both a and b
a. Sublaminar layer 42. Which statement is true about capillaries
b. Subendothelial layer a. Consists of a single layer of endothelial cells and their basal
c. Basal lamina lamina
d. Endothelial layer b. Always function as a group
29. VEGF stimulate blood vessel formation the embryonic mesenchyme c. It has something to do with forming blood vascular networks
through a process known as ____ d. AOTC
a. Vascuelognesis 43. A simple squamous mesothelium which is supported by a layer of
b. Angiogenesis loose connective tissue containing blood vessels and nerves that
c. Weilbel-palade bodies correspond to the visceral layer of the pericardium
d. P selectin a. Myocardium
30. Storage granules of endothelial cells important in keeping blood from b. Endocardium
clotting c. Epicardium
a. Tunica media d. Pericardium
b. Weilbel-palade bodies 44. Lymph is drained in the lymphatic vessels.
c. P-selectin a. True
d. VEGF b. False: lymphatic capillaries
31. Consist primarily of circumferentially arranged layers of smooth muscle c. False: lymph nodes
cells in arteries which may have a thin external elastin lamina d. False: lymphatic circulation
separating it from the outermost tunic and has very thick for the 45. Composed primarily of longitudinally arranged collagenous tissue and
arteries few elastic fibers that contains vasa vasorum and nervi vascularis
a. Tunica adventitia a. Adventitia
b. Tunica media b. Tunica media
c. Tunica intima c. Tunica adventitia
d. Internal elastic lemina d. Either of the two
32. Enumerate the three layers of heart valves 46. The pathway of blood within the heart that is composed of
a. F connective tissue with overlying endocardium
b. S a. Cardiac muscle
c. V b. Cardiac skeleton
33. Capillaries that are found in all kinds of muscle, connective, nervous c. Heart valves
tissue, and exocrine glands d. Ventricles
a. Fenestrated 47. What is the prominent feature in elastic arteries in which elastic
b. Continuous lamellae alternate with layers of smooth muscle fiber
c. Distinctive a. Tunica intima
d. Sinusoidal b. Basal lamina
34. Why myocardium is thicker in the walls of the ventricles, particularly c. Tunica media
the left, than in the atrial walls d. Thick media
a. Since it corresponds to the visceral layer 48. Characterized by the presence of small circular fenestrate through
b. Since it contains blood vessels and nerves the very thin squamous endothelial cells. Each fenestra is usually
c. Since the ventricles are mainly the one pumping blood covered by a thin diaphragm
d. Since it corresponds to the visceral layer of the pericardium a. Sinusoidal
35. All statements are true about great saphenous vein except b. Fenestrated
a. Usually, thinner compared to another medium sized vein c. Continuous
b. Long subcutaneous vein of the lower limb that originates in the d. AOTC
foot drains into femoral vein just below inguinal ligament 49. All statements are true about arterioles except
c. Medically used for coronary-artery bypass graph a. Smallest arteries branch
d. NOTC b. Indicate the beginning of an organ’s microvasculature
36. Consists of a myocardial tissue which is difficult to distinguish from c. Flow regulators for the capillary beds
surrounding cardiac muscle d. Has bigger lumen compared to the venules
a. AV node 50. The outside covering which is directly attached to the heart
b. Pacemaker a. Myocardium
c. Conducting system of the heart b. Endocardium
d. Atrioventricular bundles c. Epicardium
37. __________ node is continuous with the specialized bundles of cardiac d. Pericardium
muscle fibers known as _____ which runs along the ______ to the apex 51. The lymphatic vessels ultimately converge as two:
of the heart, where they branch unto the conducting _______ that will a. (TD)
then extend to the myocardium of the ventricles, stimulating the b. (RLD)
heartbeat 52. A blood vessel wall would usually have the:
a. A a. Endothelial layer:
b. A b. Tunica media:
c. A c. Outside layer:
d. P 53. The space in pericardium is known as
38. Adjacent to the ventricular or atrial surface of each valve and is a. Parietal pericardium space
covered with endothelium b. Pericardium space
a. Ventricularis c. Pericardial space
b. Spongiosa d. Both a and b
54. Enumerate the two layers of pericardium b. Portal system
a. V c. Arterioles
b. P d. Arteriovenous shunts
55. All statements are true about pericardial fluid except 69. Capillaries that can be found in the tissues where there is rapid
a. Found in the pericardial activity interchange of substance occurring between tissue and blood. these
b. A fluid use for diagnosis in the enlargement of heart or infection can also be found in the kidney, intestines, choroid plexus, and
regarding the heart endocrine glands.
c. Produced by the serous mesothelial cells a. Sinusoid
d. NOTC b. Fenestrated
56. What is the main function of pericardial fluid c. Distinctive
a. Production of lubricant fluid which lessen the friction of the d. Continuous
underlying tissue during heart movements 70. Which statement is not true about sinusoidal capillaries
b. For diagnosis a. Endothelial cells have large fenestrate with no diaphragm, and
c. Deposits and cushioned adipose tissue the cells forms discontinuous layer and are separate from one
d. Both a and b another.
57. All statements are true about cardiac skeleton except b. Irregularly shaped, where developing blood tissues accumulate.
a. Made up of cardiac muscle with its fibers c. Found in tissues that are important in the regulation of blood cells
b. Anchors and supports the heat valves and those secretes substances
c. Help coordinate the heartbeat by acting as electrical insulation d. NOTC
between the atria and ventricles 71. Enumerate the large veins of tunica adventitia
d. Made up of dense irregular fibrous connective tissue a. S
58. Which statement is true about arteriovenous shunts b. P
a. Often coiled, has a relatively smooth muscle layer tissue c. V
enclosed in a connective tissue capsule and richly innervated 72. The Dural venous sinuses are medium-sized muscular arteries originate
b. Possesses numerous longitudinal smooth muscle bundles in the from the proximal part of the ascending aorta and lie on the surface
intima and in the wall developed adventitia of the heart in the epicardium surrounded by adipose tissue.
c. Long subcutaneous vein of the lower limb a. True
d. NOTC b. False: great saphenous vein
59. Pyramidal structured organs on top of the kidneys c. False: coronary arteries
a. Adrenals d. False: aorta
b. Adrenaline 73. The prominent feature of the large veins
c. Adenosine a. Bundles of smooth muscle cells
d. Aorta b. Tunica adventitia
60. Forms part of the interventricular and interatrial septa surrounding all c. Subclavian veins
valves of the heart and extends into the valve cusps and the chordae d. Endothelium
tendinea to which they are attached. 74. The blood returned via the veins to the heart unto the lungs for
a. Myocardium oxygenation
b. Endocardium a. Oxygenated blood
c. Pericardium b. Deoxygenated blood
d. Cardiac skeleton c. Blood flow
61. Type of capillaries that can be found in the liver, spleen, some d. NOTC
endocrine organs, and bone marrow 75. Directs routes between the arteries and veins that divert blood from
a. Continuous the capillaries and is usually found in sensitive tissues
b. Discrete a. Arterioles
c. Sinusoidal b. Arteries
d. Fenestrated c. Arteriovenous shunts
62. The cells in the endothelium regulate vascular tone and the blood d. Coronary arteries
flow inflammation and even is part of the local immune response 76. Regulating the motility and secretions of all types within the digestive
through: system
a. P a. Diffuse neuroendocrine system
b. W b. Enterochromaffin cells
63. Innermost layer of the blood vessel which composed of endothelium, c. Argentaffin cells
basal lamina, and subendothelial layer d. AOTCCONT
a. Tunica adventitia 77. The blood flow starts from the _____, then ____ and goes to the ____,
b. Tunica intima then unto the capillaries or capillary beds, then unto the metavenule,
c. Subendothelial layer and lastly in the ____.
d. Internal elastic lamina a. A
64. Their function is to exchange nutrients and oxygen between tissues, b. A
and they are just a simple sheath of endothelial tissue plus its basal c. P
membrane d. V
a. Arteries 78. It is usually found in tissues that are regurgitated
b. Capillaries a. Venous shunts
c. Heart valve b. Arteriovenous shunts
d. Endothelial cells c. Portal vein
65. It is called conducting arteries because their major role is to carry d. Atrioventricular shunts
blood to smaller arteries 79. The lymphatic endothelial cells are typically ______ than those of
a. Muscular arteries blood capillaries
b. Elastic arteries a. Larger
c. Arterioles b. Prominent
d. Fibrous network c. Smaller
66. Possess numerous longitudinal smooth muscle bundles in the intima d. Similar
and in the wall developed adventitia 80. Are those that do noy usually follow the usual structure and
a. Coronary arteries histological feature of the other mentioned blood vasculatures.
b. Great saphenous vein a. Blood vessels
c. Dural venous sinuses b. Atypical blood vessels
d. Central adrenomedullary vein c. Atrioventricular shunts
67. Enumerate the three types of capillaries d. Portal vein
a. C 81. Blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the blood
b. F a. Coronary arteries
c. S b. Dural venous sinuses
68. Found in the skin of the fingertips, nose, lips, and the erectile tissue of c. Atypical blood vessels
the penis and clitoris d. Blood vasculatures
a. Arteriovenal shunts 82. Enumerate the cells found in the diffuse neuroendocrine system
a. E b. Antidiuretic hormone
b. A c. Adrenocorticotrophic hormone
83. Excess interstitial fluid d. Luteinizing hormone
a. Neutrophil 8. A type of gland that possess a blood supply and their secretion is
b. Lymph directly secreted unto their blood supply.
c. Deoxygenated blood a. Exocrine
d. Oxygenated blood b. Endocrine
84. All statements are true about Dural venous sinuses except c. Paracrine
a. Blood supply for the cranial cavity d. Autocrine
b. Broad spaces within the dura mater that are lined with 9. Cells that are numerous, smaller, having less cytoplasm and exhibits
endothelial cells and devoid of smooth muscle closer proximity between their nuclei
c. Venous channels in cranial activity a. Oxyphil cells
d. NOTC b. Principal cells
85. It is medically used for coronary-artery bypass graph c. C cells
a. Great saphenous vein d. Follicular cells
b. Central adrenomedullary vein 10. Which statement is true about paracrine
c. Coronary arteries a. Common in the immune system cells
d. Dural venous sinuses b. Hormones discharge form a cell into the blood stream
86. Originate as close-ended vessels consisting of a single layer of thin c. You have one cell secreting the hormone and that hormone will
endothelial cells on an incomplete basal lamina as compared to act on the nearby or adjacent cell since it has a receptor for the
vascular capillaries hormone.
a. Lymphatics d. NOTC
b. Lymphatic capillaries 11. Fill in the blanks. The axons of the pituitary run from the ___________ and
c. Lymphatic vessels _____________ ____________ nuclei and have swellings called
d. Lymph nodes ______________________________.
87. Passes through the adrenal medulla and its tributaries have an unusual 12. The hormones discharge from a cell into the blood stream and is then
tunica media transported into the effector cell.
a. Great saphenous vein a. Juxtacrine
b. Central adrenomedullary vein b. Paracrine
c. Coronary arteries c. Endocrine
d. Dural venous sinuses d. Autocrine
88. Resembles that of veins except with thinner walls and no distinct 13. Produce somatin and somatostatin
separation among tunics a. Somatotrophs
a. Lymphatic vessels b. Somatrophs
b. Lymphatic capillaries c. Lactotrophs
c. Lymph d. Both a and b
d. Lymphatics 14. Enumerate the two acidophils of chromophils
89. The drainage of the interstitial fluid is important to keep the osmotic a. S
pressure, otherwise edema might happen and if there is a presence b. L
of a bacteria or infection, ____________ occur. 15. A concentric zone which works with the kidney for salt balance in the
a. Vasculitis body
b. Arteriosclerosis a. Zona fasciculata
c. Myocardial infarction b. Zona reticularis
d. Lymphadenitis c. Zona glomerulosa
d. Both a and b
ENDOCRINE GLANDS 16. The hormones that accumulate in axonal dilations
a. Neurosecretory bodies
1. Promotes the development of the mammary gland during puberty b. Herring bodies
and milk formation especially for pregnant women c. Neurosecretory neurons
a. Oxytocin d. Both a and b
b. Prolactin 17. An invagination or the oral ectoderm, basically an extension of the
c. Luteinizing hormone pharynx
d. Thyrotropic hormone a. Anterior pituitary
2. The secretory cells in which the hormone is stored in its cytoplasmic b. Hypophyseal pouch
granules c. Neurohypophysis
a. Somatin d. adenohypophysis
b. Somatostatin 18. Stimulates contraction of the mammary glands to eject milk and
c. Chromophils contraction of the smooth muscle during parturition
d. Gonadotrophs a. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
3. Colloid b. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
a. Contains glycoprotein thyroglobulin necessary to be added with c. Antidiuretic hormone
iodine to produce your T3 or T4 d. Oxytocin
b. Bounded by walls known as the follicular epithelium 19. A type of gland that secrete their secretion directly outside through
c. Responsible for production of the thyroid hormones their ducts
d. Both a and b a. Exocrine
4. A hormonal control mechanism that is usually common in the immune b. Endocrine
system cells c. Apocrine
a. Exocrine d. Autocrine
b. Endocrine 20. The growth hormone that stimulates the liver and other organs to
c. Paracrine secrete an insulin-like growth factor which in turn stimulates division
d. Juxtracrine insulin-like growth factor which in turn stimulates division of progenitor
5. Derived from the neuroectoderm or the neurohypophysial bud cells located in growth plates and skeletal cells resulting in body
a. Posterior pituitary growth.
b. Neurohypophysis a. somatotropin
c. Hypophyseal plate b. thyrotropic
d. Both a and b c. luteinizing
6. Enumerate the two types of endocrine glands: d. prolactin
a. 21. The increase in the level of the effector gland hormone that would
b. suppress the activity or the release of the stimulating hormones.
7. A hormone important in the reabsorption of water in the collecting a. Positive loop
ducts of the kidney and would increase especially when your b. Negative feedback loop
dehydrated. c. Antidiuretic hormone
a. Oxytocin d. Oxytocin
22. Formed in the embryo partly from the developing brain and partly 39. Enumerate the hormones of the posterior lobe of the pituitary
from the developing oral cavity a. O
a. Anterior adenohypophysis b. ADH
b. Hypophysial pouch 40. A storage site for neurosecretions
c. Neurohypophysis a. Neurohypophysis
d. Neuroectoderm b. Adenohypophysis
23. It is when your hormone is secreted from one cell and acts on c. Pars nervosa
adjacent cells that expresses specific receptors. d. Pars tuberalis
a. Autocrine 41. It is released by pinealocytes promoted by darkness and inhibited
b. Endocrine daylight
c. Paracrine a. Melanin
d. Exocrine b. Melatonin
24. Produces weak androgens c. Corpora arenacea
a. Zona fasciculata d. Gonadotrophin hormone
b. Zona glomerularis 42. Fill in the blanks. The anterior pituitary produces its __________, while the
c. Zona fasciculata posterior pituitary only acts as the _______________.
d. Zona spiralis 43. Target of adenocortitropic hormone
25. Endocrine cells of the parathyroid glands a. Glu
a. Principal cells b. Gona
b. Oxyphil cells 44. The thin zone of basophilic cells between the pars distalis and the pars
c. C cells nervosa of the neurohypophysis
d. Follicular cells a. Pars intermedia
26. Also known as the epiphysis cerebri b. Pars tuberalis
a. Adrenal gland c. Pars distalis
b. Zona fasciculata d. Pars nervosa
c. Pineal gland 45. All statements are not true about hypothalamus except:
d. Pituitary gland a. Located in the middle of the base of the brain
27. Enumerate the three parts of anterior pituitary b. Stimulates secretion and gene expression
a. P c. Encapsulates the ventral portion of the third ventricle
b. P d. Regulates pituitary gland activtiy
c. P 46. Secretory products of endocrine cells and organs that passes into the
28. Produces a mineralocorticoids circulatory system for transport to its target cells.
a. Aldosterone a. Posterior neurohypophysis
b. Testosterone b. Anterior neurohypophysis
c. Androgen c. Hormone
d. NOTC d. Neuroectoderm
29. Constitute the half of the cells in pars distalis of humans 47. Enumerate the hormonal control mechanisms
a. Corticotrophs a. P
b. Somatotrophs b. A
c. Lactotrophs c. J
d. NOTC 48. The chief cells of the pineal gland
30. Enumerate the glands that have ducts a. Pituicytes
a. S b. Corpora arenaceous
b. S c. Pinealocytes
31. An acidophil that produces prolactin d. Pinacocytes
a. Gonadotrophs 49. A signaling molecule remains on the secreting cell’s surface or
b. Thyrotrophs adjacent extracellular matrix and attracts target cells when the cells
c. Lactotrophs make contact.
d. Corticotrophs a. Juxtacrine
32. Smaller funnel-shaped region surrounding the infundibulum of b. Endocrine
neurohypophysis c. Autocrine
a. Pars distalis d. Paracrine
b. Pars intermedia 50. Consists of long cords polyhedral cells, one or two cells thick,
c. Pars tuberalis separated by fenestrated sinusoidal capillaries
33. A basophil that produces gonadotropins a. Zona reticularis
a. Corticotrophs b. Zona fasciculata
b. Chromophils c. Zona glomerulosa
c. Thyrotrophs d. Acidophil
d. Lactotrophs 51. Cells that is located in the periphery of the follicular epithelium and lie
34. Enumerate the two types of chromophils within the follicle basal lamina
a. A a. C cells
b. B b. Parafollicular cells
35. The main or master gland of the endocrine system c. Chief cells
a. Anterior lobe d. Both a and b
b. Adenohypophysis 52. Modified sympathetic postganglionic neurons. Lacking axons and
c. Neurohypophysis dendrites, and specialized as secretory cells
d. Both and b a. Epinephrine
36. It is where hormone responses to the receptor that is located on the b. Chromaffin cells
cell that produces. c. Chromophil
a. Juxtacrine d. Norepinephrine
b. Paracrine 53. A gland that is covered by a dense connective tissue capsule that
c. Autocrine sends thin trabeculae unto the gland’s parenchyma
d. Endocrine a. Master gland
37. Enumerate the two concentric regions of adrenal gland b. Epiphysis cerebri
a. Y c. Adenohypophysis
b. R d. Adrenal gland
38. The feedback system that regulates endocrine function of the 54. Features of steroid-secreting cells in the adrenal cortex
hypothalamus a. Acidophilic
a. Hormone production in the pituitary gland b. Cytoplasm rich in lipid droplets
b. Hypothalamic releasing hormone production in the c. With central nuclei
hypothalamus d. AOTC
c. Inhibits secretion of PRL by lactotrophs 55. All statements are true of adrenal gland except
d. Both a and b a. Consist of smaller cells in a network of irregular capillaries
b. Flattened structure with a half-moon shape 72. A highly branched glial cells that resemble astrocytes and most
c. Paired organs lying near the superior poles of the kidneys abundant cell type in the posterior pituitary
d. Embedded in the perirenal adipose tissue a. Pars nervosa
56. Lies below the brain in a small cavity on the sphenoid bone b. Infundibular stalk
a. Hormones c. ACT hormone
b. Hypophyseal pouch d. Pituicytes
c. Hypophysis 73. Neurons whose cell bodies lie in the supraoptic nuclei and
d. Pars tuberalis paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus
57. Enumerate the two pituitary glands: a. Oxytocin
a. P b. Neurosecretory nuclei
b. A c. ADH
58. It releases your ADH and oxytocin d. Neural stimulation
a. Adenohypophysis 74. It will trigger an increase in one of these stimulating hormones, would
b. Neurohypophysis trigger an increase of the effector gland hormone.
c. Sella turcica a. Positive loop
d. Pars distalis b. Negative feedback loop
59. It is derived embryonically from the hypophyseal pouch c. Antidiuretic hormone
a. Anterior pituitary d. Neurosecretory bodies
b. Adenohypophysis 75. A hormone that is more on the resorption of water to prevent
c. Anterior lobe dehydration
d. AOTC a. Antidiuretic hormone
60. Cords of well-stained endocrine cells interspersed with fenestrated b. Oxytocin
capillaries and supporting reticular connective tissue c. Dopamine
a. Pars intermedia d. Somatostatin
b. Pars distalis 76. It is filled lipid droplets and appear vacuolated
c. Pars tuberalis a. Zona reticularis
d. Pituicytes b. Zona fasciculata
61. Enumerate the three basophils of chromophils c. Zona glomerulosa
a. C d. Zona disparis
b. G 77. Medullary parenchymal cells arise from neural crest cells
c. T a. Chromophil
62. Secretes insulin and it is the numerous which is located centrally b. Chromaffin cells
a. D cells c. Acidophil
b. B cells d. NOTC
c. A cells 78. The one that regulates the pituitary gland
d. C cells a. Hormone
63. Most of the cells are gonadotrophs b. Pineal gland
a. Pars tuberalis c. Hypothalamus
b. Pars intermedia d. Pituicytes
c. Pars distalis 79. Secretes glucagon which is usually located peripherally
d. NOTC a. D cells
64. Form the foregut endoderm near the base of the developing tongue b. C cells
and it is located anterior and inferior to the larynx, consists of two lobes c. A cells
united by an isthmus d. B cells
a. Thyroid gland 80. The principal cells that is responsible for production of the thyroid
b. Parathyroid gland hormones tetraiodothyronine and triiodothyronine
c. Pineal gland a. Chief cells
d. Pituitary gland b. Parafollicular cells
65. Regulates calcium metabolism and the secretion is triggered by c. Follicular cells
elevated blood calcium levels and inhibits osteoclast activity d. Oxyphilic cells
a. Aldosterone 81. An endocrine or neuroendocrine gland that regulates daily body
b. T4 rhythm which is located at the posterior wall of the third ventricle near
c. Clacitonin the center of the brain.
d. Cortisol a. Anterior pituitary gland
66. The least abundant among of all basophils b. Hypothalamus
a. Corticotrophs c. Pineal gland
b. Gonadotrophs d. Both a and b
c. Thyrotrophs 82. The gland that lies at the top of the kidney
d. Lactotrophs a. Pineal
67. It is usually contained colloid-filled cysts b. Pituitary gland
a. Pars intermedia c. Adrenal gland
b. Pars nervosa d. Sebaceous gland
c. Pars tuberalis 83. Small polygonal cells with round nuclei and pale-staining slightly
d. Pars distalis acidophilic cytoplasm that secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH)
68. Enumerate the six hormones of the anterior lobe a. Oxyphil cells
a. G b. C cells
b. P c. Chief cells
c. A d. Follicular cells
d. F 84. Fill in the blanks. P__________ stimulates the production of milk.
e. L Meanwhile, O_________ stimulates the release of milk after giving birth.
f. T 85. It has three concentric that produces mainly hormone
69. A structural and functional unit of the thyroid gland which is roughly a. Anterior pituitary
spherical cyst-like compartment b. Hypothalamus
a. Follicular cells c. Adrenal cortex
b. Thyroglobulin d. Adrenal medulla
c. Thyroid follicle 86. Luteinizing hormone
d. Colloid a. Maintains the maturation of the ovarian follicle controls ovulation
70. Enumerate the neurotransmitters produced by the catecholamines b. For steroid secretion especially in males
a. E c. Maintenance of an androgen secretion of the leading cells of
b. N the testes
71. ________________ consists of pars nervosa and the infundibular stalk d. AOTC
and not an endocrine gland. 87. The somastatin which is scatted and much less abundant
a. PP cells
b. A cells b. Polygonal or rounded, smaller, and more lightly stained than the
c. C cells surrounding acinar cells, arranged in cords, separated by
d. D cells fenestrated capillaries
88. It is where the melatonin is stored and characterized by the presence c. Epithelial outgrowths from endoderm’s of the developing gut
of calcified concretions. d. NOTC
a. Corpora arenacea 103. Secrete pancreatic polypeptide located within the head of the
b. Brain sand pancreas
c. Pinacocytes a. PP cells
d. Both a and b b. C cells
89. It consists of closely packed rounded or arched cords of columnar or c. D cells
pyramidal cells with many capillaries d. A cells
a. Adrenal medulla 104. Composed of enterochromaffin cells and argentaffin cells which
b. Zona glomerulosa regulates motility and secretions of all types within the digestive system
c. Zona reticularis a. Diffuse neuroendocrine system
d. Zona fasciculata b. Pancreatic islets
90. It is filled with a glucocorticoid c. Oxyphil cells
a. Aldosterone d. PP cells
b. Cortisol 105. Enumerate thyroid hormones
c. Dehydroepiandrosterone a. T4 –
d. Testosterone b. T3 –
91. Follicle stimulating hormone | Luteinizing hormone LYMPHOID TISSUE
a. Important for the development of gonads
b. Development of egg cells and sperm cells 1. The splenic pulp which occupies most other parenchyma
c. For steroid secretion a. White pulp
d. Both a and b b. Red pulp
92. The gel-like mass 2. The secondary lymphoid structure where most lymphocytes are
a. Colloid activated by an antigen-presentation including the mucosa-
b. Corticoid associated lymphoid tissue, lymph nodes, and spleen.
c. Cortisol a. Lymphatic nodules
d. Follicular cells b. Diffuse lymphatic tissue
93. All statements are true about reticularis except: c. Tonsils
a. Consists of smaller cells in a network of irregular cords d. Medulla
interspersed with wide capillaries 3. The tonsil which is lack of distinct capsules and is covered by stratified
b. More heavily stained than those of the other zones because they squamous epithelium
contain fewer lipid droplets, and more function lipofuscin a. Pharyngeal
pigments b. Lingual
c. Produces weak androgens c. Palatine
d. Works with the kidney for salt balance in the body d. Corona
94. Precursor of testosterone and estrogen 4. All statements are true about antibodies except:
a. Dihydroxylphenylalanine a. The immune cells recognize and react to small molecular
b. Dehydroepiandrosterone domains of the antigen.
c. Cortisol b. Able to bind specifically and neutralize certain viral particles and
d. Androgen bacterial toxins, agglutinate many bacterial cells, and
95. Composed of large, pale-staining polyhedral cells arranged in cords precipitate most soluble antigens.
of clumps and supported by a reticular fiber network c. It is specific which makes it vastly different from innate immunity
a. Adrenal cortex and it developed through time.
b. Adrenal medulla d. NOTC
c. Adrenal gland 5. Enumerate the two types of cells of the adaptive immunity
d. Steroid-secreting cells a. A
96. Synthesized the thyroid hormones thyrozine and triiodothyronine b. L
a. Thyroid gland 6. A lymphatic vessel that conveys lymph toward the node and enter it
b. Pineal gland at various points on the convex surface of the capsule.
c. Pituitary gland a. Lymphatic nodules
d. Parathyroid gland b. Efferent lymphatic vessels
97. Precursor of production of the thyroid hormones c. Subcapsular sinus
a. Thyroglobulin d. Afferent lymphatic vessel
b. Colloid 7. The first antibody produced in initial immune response activates
c. Aldosterone complement and it is in the B lymphocyte surface as a monomer
d. Epinephrine a. Dimer
98. Enumerate the two follicular epithelia of thyroid follicle b. Pentamer
a. F c. Monomer
b. P d. Trimer with secretory component
99. Four small ovoid masses located on the back of the thyroid gland 8. Type ERC that provides the cellular framework of the medulla and to
usually embedded in the larger gland’s capsule compartmentalize groups of lymphocytes
a. Parathyroid gland a. Type VI
b. Thyroid follicle b. Type V
c. Thyroid gland c. Type IV
d. Pineal gland d. Type III
100. Enumerate the dense elongated clusters of secretory cells in 9. The _________________________ acts to supplement the central
parathyroid glands tolerance and develops in the thymosin.
a. P 10. Antibody covers biologically active portion of microbe or toxin
b. O a. Agglutination
101. The larger cell types with prominent eosinophilic cytoplasm, they may b. Neutralization
occur in small groups or in even larger masses. c. Precipitation
a. Chief cells d. Opsonization
b. C cells 11. It can be found in the submucosa of the small and large intestine
c. Oxyphil cells a. Peyer patches
d. Principal cells b. Palatine tonsil
102. All statements are true about pancreatic islets except c. Lingual tonsil
a. Compact spherical or ovoid masses of endocrine cells d. Vermiform appendix
embedded within the acinar exocrine tissue of the pancreas 12. It is bound to the surface of mast cells and basophils which destroys
parasitic worms and participates in allergies that has a 0.002%
antibody
a. IgE c. C
b. Monomer d. V
c. IgD 28. Composed of cortex and paracortex
d. Both a and b a. Lymphoid nodule
13. It has a 10-15% antibody in the serum which protects the mucosae. b. Capsule
a. Secretory component c. Reticular tissue
b. Dimer d. Parenchyma
c. Trimer with secretory component 29. Lymphatic nodules consist of small lymphocytes
d. AOTC a. Primary
14. A phenomenon wherein when the antibody binds with the bacteria, b. Secondary
it triggers phagocytic cells to phagocytose the bacterium which the c. Germinal center
antibody is found. d. Mantle zone
a. Neutralization 30. All statements are true except:
b. Agglutination a. Medulla contains the structure known as the thymic or Hassall’s
c. Precipitation corpuscles
d. Opsonization b. Parenchyma is divided into the cortex and medulla
15. All statements are true about immune system except: c. The type I ERC function as a barrier that isolates developing T
a. Provide defense or immunity against infectious agents ranging cells from the connective tissue of the organ
from viruses to multicellular parasites. d. The type VI ERC provide the cellular framework of the medulla
b. It is divided into three and to compartmentalize groups of lymphocytes
c. Not anatomical system per se because unlike other systems 31. It has approximately 80% of antibody and it can also be found in the
where it is connected, the immune system is more of a functional fetal circulation in pregnant women.
system that provides defense against infectious particles ranging a. IgG
from viruses to multicellular parasites. b. Pentamer
d. NOTC c. IgM
16. Activates phagocytosis and neutralizes antigens d. IgA
a. Monomer 32. All statements are true about lymphoid organs except:
b. Pentamer a. Group of cells and tissues
c. Secretory component b. Monitor body surfaces and internal fluid compartments
d. Both a and b c. React to the presence of potentially harmful substances
17. Most abundant cells of lymph nodes are the ________________. d. NOTC
18. Enumerate the two immune system 33. With type III cells, they create the barrier at the corticomedullary
a. A junction
b. I a. Type II
19. Forms the outer portion of the node except at the hilum, composed b. Type I
of subcapsular sinus and lymphoid nodules c. Type IV
a. Paracortex d. Type V
b. Cortex 34. Which statement is true about positive selection
c. Capsule a. CD8 and CD4 is present in the Pre-T lymphocyte
d. Parenchyma b. Associated with the development of the T cell receptor and
20. All statements are true about thymus except: binds the MHC molecules
a. It undergoes a process of shrinkage c. They can survive in the medulla but in some cases, they will die
b. Bilobed structure found in the mediastinum in apoptosis
c. It is a thyroid located at the top of the heart d. AOTC
d. The main function is for induction of central tolerance 35. Contains large immature lymphocytes and a morphologic indication
21. True or false. Type V form the most characteristic feature of the thymic of lymphatic tissue response to antigen
medulla a. Corona
a. True b. Germinal center
b. False; type IV c. Palatine
c. False; type VI d. Lingual
d. False type III 36. A protein that assists immune responses by producing cytokines that
22. Large, irregular masses of lymphoid tissue in the mucosa of posterior promote differentiation of B cells into plasma cells which activate
oral cavity and nasopharynx where their cells encounter antigens macrophages to become phagocytic and activate cytotoxic T
entering the mouth and nose lymphocytes
a. Thymus a. CTLS
b. Peyer patches b. CD4
c. Vermiform appendix c. CF8
d. Tonsils d. Both a and b
23. White pulp 37. The immunity the one that develops throughout time, and it is more
a. Splenic cords and splenic sinusoids specific compared to the other one.
b. Reticular tissue rich in macrophages and lymphocytes a. Innate
c. Consists of a thick accumulation of lymphocytes surrounding an b. Antibodies
artery c. Adaptive
d. Stave cells d. Antigen
24. Antibody cross-links cells forming a clump 38. Enumerate the three tonsils
a. Opsonization a. P
b. Precipitation b. L
c. Neutralization c. P
d. Agglutination 39. Formed largely by helper T lymphocyte and proliferating B
25. All statements are true about spleen except: lymphoblasts. It is spherical or oval that aggregates of lymphocytes
a. About the size of the clenched fist a. Subcapsular sinus
b. Only lymphoid organ involved in the filtration of blood b. Lymphoid nodules
c. Main site of old erythrocyte destruction c. Lymphatic vessels
d. NOTC d. Paracortex
26. Refers to nonspecific defenses means that it protects you in general 40. The cells or lymphocytes that is present in adaptive immunity
and it is already present to protect an individual a. T cells
a. Innate b. B cells
b. Antibodies c. APC cells
c. Adaptive d. Principal cells
d. Antigen 41. All statements are true about adaptive except:
27. Enumerate the pre-existing nonspecific defenses in innate immunity: a. It is usually the main cells in this type of immunity
a. P b. Idea behind vaccination which is the purpose is to develop
b. P one’s adaptive immunity
c. Constitute on the humoral and cellular response a. Ectopias
d. It has 4 pre-existing nonspecific defenses b. Cellular
42. More of T cells or cells mediated response by the T cells c. Epitopes
a. Humoral d. Phagocytes
b. Cellular 57. A lymphatic vessel that conveys lymph away from the node and
c. Antibodies leave at the hilum
d. Antigen a. Efferent
43. It is an antigen receptor triggering initial B cell activation which can b. Afferent
also be found in the surface of B lymphocytes 58. High endothelial venules
a. IgE a. Portal of entry of the lymphocytes into the lymph node
b. IgM b. Has an integrins that facilitates rapid diapedesis
c. IgA c. No B cell lymphoid nodules
d. IgD d. Both and b
44. Antibody cross-links circulating particles forming an insoluble antigen- 59. It has 5-10% of antibody
antibody complex a. IgM
a. Precipitation b. IgG
b. Agglutination c. IgA
c. Opsonization d. Monomer
d. Neutralization 60. Branched cordlike masses of lymphoid tissue extending from the
45. The cells which is more on inhibiting the immune response paracortex that contains T, B lymphocytes and many plasma cells.
a. Regulatory T cells a. Subcapsular sinus
b. Cytotoxic lymphocyte b. Lymphoid nodules
c. B cells c. Medullary sinuses
d. Both a and b d. Medullary cords
46. All statements are true about medullary sinuses except: 61. The tonsil which is composed of pseudostratified ciliated columnar
a. The lumen includes a meshwork of processes from reticular cells epithelium that has a thin underlying tissue, and lacks crypts which is
which represent a final lymph filter also part of the respiratory
b. Occupies most of the parenchyma a. Palatine
c. Contain many macrophages and sometimes neutrophils b. Lingual
d. Dilated spaces lined by discontinuous endothelium that c. Corona
separate the medullary cords d. Pharyngeal
47. Lined by a very thin, discontinuous endothelium penetrated by 62. The cell the one that supports the developing lymphoblasts
reticulum fibers, processes of dendritic cells, and receives lymph from a. Regulatory T cells
the afferent lymphatics b. Thymocytes
a. Cortex c. Epithelioreticular cell
b. Subcapsular sinus d. Thymic epithelial cell
c. Lymphoid nodules 63. Example of _________________ are Lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
d. Parenchyma 64. The immune cells recognize and react to small molecular domains of
48. A production site of antibodies and activated lymphocytes antigen
a. Thymus a. Ectopias
b. Medulla b. Cellular
c. Parenchyma c. Phagocytes
d. Spleen d. Epitopes
49. All statements are true about white pulp except: 65. True or false. Antibodies are the molecules that the body has
a. Contains large numbers of red blood cells that filters and recognized as foreign and would trigger an immune response or
degrades. antibody production.
b. Central artery – branch of the splenic artery a. True
c. Periarterial lymphatic sheath b. False; immunoglobulin
d. NOTC c. False; antigenic determinants
50. Enumeraration. Antibody binding Fc portion promotes: d. False; antibodies
a. C 66. A short, small diameter projection from the cecum, and the lamina
b. O propria is heavily infiltrated with lymphocytes and contains numerous
c. N lymphatic nodules
51. Composed of reticular cells and reticular fibers that form a fine a. Peyer patches
supporting meshwork throughout the remainder of the organ b. Hassall’s corpuscles
a. Trabeculae c. Vermiform appendix
b. Capsule d. Lingual tonsil
c. Cortex 67. A glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin family that interacts specifically
d. Reticular tissue with an antigenic determinant or interacts with the epitope of the
52. The inner portion of parenchyma which contains mostly large antigen which is secreted by plasma cells.
lymphocytes. a. Antigen
a. Cortex b. Antibody
b. Medulla c. Adaptive immunity
c. Thymus d. Innate immunity
d. Blood-thymus barrier 68. The cells derived from B cells
53. It protects developing lymphocytes in the thymus from exposure to a. Plasma cells
antigens b. Immunoglobulin
a. Cortex c. T cells
b. Medulla d. NOTC
c. Thymus 69. Enumerate the binding of antigen-binding site of an antibody with
d. Blood-thymus barrier antigen causes
54. Process of shrinkage that happens in the thymus a. Neutralization: microbe or toxin
a. Involution b. Agglutination:
b. Lymphoblasts c. : toxins
c. Diffuse lymphatic tissue 70. The cells that produce the antibodies and would differentiate plasma
d. NOTC cells which are more capable of antibody reactions
55. Enumerate the cells found in the lymph nodes a. Regulatory T cells
a. P b. Cytotoxic lymphocytes
b. D c. B cells
c. M d. NOTC
d. APCs 71. The T lymphocytes are also further subdivided into ____________ (Th
e. F ____) which is characterized by the presence of the ______.
56. Antigenic determinants a. CD4 protein
b. Helper T cells 88. It is when the own immune system is attacking own cells
72. The definitive cell type a. Innate immunity
a. Basophils b. Adaptive immunity
b. T cells c. Self-adaptive immunity
c. B cells d. Autoimmunity
d. Cytotoxic lymphocytes 89. True or false. Thymus is in the throat area mean while thyroid is in the
73. It is where the main production of immune cells happens mediastinum, at the top of the heart.
a. Primary a. True
b. Secondary b. False
c. Thymus c. Neither
d. Blood-thymus barrier 90. Composed of dense connective tissue which extend from the capsule
74. Enumerate the primary lymphoid organs into the substance of the node, forming a gross framework
a. T a. Trabeculae
b. B b. Capsule
75. Stimulates the secretion of LH and FSH c. Reticular tissue
a. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone d. Parenchyma
b. Dopamine 91. Enumerate the secondary lymphoid organs
c. Corticotropin-releasing hormone a. L
d. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone b. S
76. All statements are true about cortex except c. D
a. It is where the young lymphocytes are found 92. All statements are true about blood-thymus barrier except:
b. They support the growth of the lymphoblasts a. Capillary endothelium and its basal lamina
c. The cortical zone of an active thymus is packed with small highly b. Type II epithelioreticular cells with their basal lamina
basophilic lymphoblast that proliferates as well as undergo c. Perivascular connective tissue space occupied by
positive and negative selection in that region macrophages
d. NOTC d. NOTC
77. Why the vermiform appendix gets inflamed? 93. The primary or central lymphoid organ in which T cells are produced
a. Lumen gets filled with fecal material and the immune system will and originates from the embryo’s third pair of pharyngeal pouches
attack it, would get inflamed a. Spleen
b. Results in appendicitis b. Lymph nodes
c. Provide enclosed environments that facilitate production of c. Thymus
plasma cells secreting non-IgA antibodies d. Bone marrow
d. Both a and b 94. The outer portion of the parenchyma which contains an extensive
78. D__________ is the movement of the lymphocytes out of the blood into population of T Lymphoblasts or thymocytes and it is darkly basophilic.
the paracortex of the lymph nodes. a. Cortex
79. Composed of lymphocytes that aggregate around the central artery b. Thymus
a. MALTS c. Medulla
b. Periarterial lymphatic sheath d. Blood-thymus barrier
c. Splenic cords of Billroth 95. The region between the cortex and medulla
d. Both a and b a. Medullary cords
80. Serve as an important entry point for most of the lymphocytes unto b. Paracortex
the lymph nodes c. Cortex
a. High endothelial venules d. Medullary sinuses
b. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue 96. Elongated endothelial cells lining sinusoids, oriented parallel to the
c. Thymic epithelial cell blood flow and sparsely wrapped in reticular fibers and highly
d. Epithelioreticular cell discontinuous basal lamina
81. Fill in the blanks. Hypothalamic regulating hormones a. Splenic sinusoids
a. GnRH – b. Stave cells
b. CRH – c. Splenic cord of Billroth
c. TRH – d. Regulatory T cells
d. GHRH – 97. The potent source of the cytokine for T cell stimulation
82. Express MHC I and MHC II molecules, which are involved in the thymic a. Thymic
cell education b. Hassall’s corpuscle
a. Type V c. Regulatory T cell
b. Type VI d. Both a and b
c. Type II 98. Represents a cascade of events that includes activation and
d. Type I proliferation of lymphocytes, differentiation of plasma cells, and
83. Enumeration. Diffuse lymphatic tissue antibody production.
a. MALT – a. Mantle zone
b. LN – b. Corona
84. The inner part of the lymph node c. Germinal center
a. Capsule d. Both a and b
b. Medulla 99. The cells that provide a framework for the developing T cells and
c. Cortex support the growth of the lymphocytes
d. Thymus a. Epitehlioreticular cells
85. All statements are true about lymph nodes except: b. Thymic epithelial cells
a. Constitute a series of in-line filters of lymph that defend against c. Thymocytes
the spread of microorganisms and tumor cells d. T lymphoblasts
b. Covered with antibody-antigen complexes 100. ________ comes from the blood. It is the reason why the T cells can
c. There are two lymphatic vessels enter the thymus only via the bloodstream through the efferent
d. NOTC _______________.
86. Refers to the ability of the lymphocytes to recognize self-antigens 101. All statements are true except:
which also prevents autoimmunity. a. Negative selection will remove either one since they are either
a. Peripheral tolerance double positive or negative
b. Central tolerance b. Negative selection prevents autoimmunity
c. Involution c. 5% survives in this process
d. Process of shrinkage d. If the cell lymphocyte recognizes a self-antigen, it will destroy
87. It is where the immune cells develop or mature and they can also that cell which is not good.
encounter antigens 102. If it recognizes self-antigen, it will die by a program cell death known
a. Primary as ________. But if not, it will survive and mature.
b. Secondary 103. A functional system composed of various cells like white blood cells
c. Thymus and antigen-presenting cells.
d. Blood-thymus barrier a. Antigen
b. Autoimmunity 118. A group of molecules that attacks the membrane of the microbe and
c. Antibodies causes cell lysis that destroys the bacteria.
d. Immune system a. Fc portion
104. The part of the antibody that promotes complement activation, b. Opsonization
opsonization, and activation of NK cells c. Complement
a. Cell receptor binding d. Neutralization
b. Fc portion 119. Secretions like saliva, milk, tears, etc.
c. Fab portion a. IgA
d. Both a and b b. IgM
105. Enhances the antibody’s coat of the bacterium c. IgD
a. Opsonization d. IgE
b. Agglutination 120. Involves antibody production
c. Neutralization a. Self-adaptive
d. Precipitation b. Autoimmunity
106. The antibody that protects mucosae c. Humoral
a. IgA d. Both a and b
b. IgD 121. Positive selection is the recognition of the self-antigen. Meanwhile,
c. IgE negative selection is the ability to bind to MHC molecules.
d. IgG a. Both statements are true
107. Tonsils b. Both statements are false
a. Filter and trap those that enter the mouth c. First statement is true; second is false
b. Filtered the infectious foreign materials that enters the mouth d. First statement is false; second is true
c. Invaginations 122. Enumerate the five immunoglobulin classes
d. AOTC a.
108. The main effector cells in which they eat particles that are deemed as b.
potentially harmful and foreign to the human body so that they would c.
not cause damage. d.
a. Secretion e.
b. Adaptive 123. The cells that promote the differentiation of our B cells into plasma
c. Phagocytes cells, activate macrophages to become phagocytic, and activate
d. NOTC cytotoxic T-lymphocytes.
109. It has a thin capsule and doesn’t have crypts a. APC
a. Pharyngeal b. Helper T cells
b. Lingual c. Lymphocytes
c. Palatine d. Regulatory T cells
d. NOTC 124. The principle behind vaccines.
110. All statements are true except: a. Immune system
a. IgG is less or more potent as IgM b. Antibodies
b. IgM is the first antibody that is produced the body c. Antigen
c. IgD is the antibody found in the secretions d. Adaptive immunity
d. The presence of IgG denotes a past infection that can be 125. The antibody that can be found in the secretions
detected after long periods. a. IgA
111. Denoted by the presence of CD4 protein b. IgD
a. T lymphocyte c. IgM
b. B lymphocyte d. IgG
c. Helper T cells 126. Germinal center
d. Cytotoxic T cells a. Contains the lymphoblasts and plasma blasts
112. Cells that are dispersed throughout the body and they would usually b. Indicates that the lymphatic tissue responds to the presence of
concentrate in the lymphoid organs. an antigen.
a. Antigen-presenting cells c. Develops when a lymphocyte that recognizes an antigen returns
b. White blood cells to a primary nodule and undergoes proliferation
c. Both a and b d. AOTC
d. B cells 127. The primary or central lymphoid organ for T cells
113. Thymus a. Tonsil
a. Butterfly shaped structure attached to the mediastinum of the b. Spleen
sternum which is the for induction of central tolerance c. Lymph nodes
b. Organ producing T cells d. Thymus
c. Originates from the embryo’s third pair of pharyngeal pouches 128. All statements are true except:
which undergoes a process of involution. a. Partner of antibody
d. AOTC b. Range from viruses and parasites
114. The immunoglobulin that mediates hypersensitivity reaction with the c. Antigen recognizes and by recognizing as foreign
mast cells causing mast cells to degranulate so is your basophils. d. NOTX
a. IgA 129. A non-specific immunity which we have since we were born
b. IgM a. Innate
c. IgD b. Autoimmunity
d. IgE c. Antibodies
115. Special type of lymphocyte d. Antigen
a. APC 130. Activates phagocytosis and neutralizes antigens
b. T cells a. IgM
c. NK cells b. IgA
d. B cells c. IgD
116. It has something to do with acquiring CD4 or CD8 receptor which will d. IgG
designate whether they will become a helper T cell or cytotoxic T cell 131. Fill in the blanks. Preexisting non-specific defenses.
a. Positive selection a. Physical barriers: ______
b. Negative selection b. ______________________________: secretions
c. Central tolerance c. Various ________________________________
d. Both and b d. _______________: main effector cells of immune system
117. It provides defense or immunity against infectious agents. 132. Prevents autoimmunity
a. Innate immunity a. Diffuse lymphoid tissue
b. Immune system b. Central tolerance
c. Adaptive immunity c. Primary lymphoid organs
d. Antibodies d. Both and b
133. It releases perforin/granzymes which are substances that create holes a. IgM
to the viruses and bacteria infected cells. b. IgG
a. NK cells c. IgE
b. Regulatory T cells d. IgD
c. B cells 150. All statements are true except:
d. APC a. Antibodies neutralize viral particles and viral toxins
134. Young lymphoblast b. Antibodies agglutinate bacterial cells and precipitate most
a. Lymphocyte soluble antigen.
b. Thymocytes c. Antibodies is acquired gradually
c. Thymic cells d. Antibodies are Y-shaped
d. NOTC 151. Enumerate the types of lymphocytes
135. It is mediated by APCs which would determine the microbes or the a.
invader and then present that in the lymphocyte. b.
a. Self-adaptive 152. Cells that are more on inhibition of specific immune responses,
b. Adaptive monitoring peripheral tolerance
c. Innate a. B cells
d. Autoimmunity b. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
136. Denoted by CD8 protein c. Regulatory T cells
a. T cells d. Helper T cells
b. B cells 153. Enumerate the cells under T lymphocyte
c. Helper T cells a.
d. Cytotoxic T cells b.
137. Lymph node 154. Fc region of antibody binds to an NK cell, triggering release of
a. Dominated by reticular tissue because it allows easier filtration of cytotoxic chemicals.
the lymph since it’s like a meshwork or a net where the microbes a. Opsonization of NK cells
would be trapped b. Complement system
b. Extension of the capsule c. Fc portion of NK cells
c. Spherical or oval that aggregates of lymphocytes d. Activation of NK cells
d. Both a and b 155. Helper T cells
138. Antibody on the surface of the B-lymphocyte a. Represents the cell mediated immunity
a. IgG b. More on the inhibition of specific immune responses
b. IgD c. Assist in the immune responses by producing cytokines
c. IgA d. AOTC
d. IgM 156. Lymphoid organs
139. Composed of large mature lymphocytes where the thymic or Hassall’s a. Group of cells, tissues, and organs
corpuscle is located b. Monitor body surfaces and internal fluid components
a. Medulla c. React to the presence of potentially harmful substances
b. Desmosomes d. AOTC
c. Thymic epithelial cells 157. Thin connective tissue capsule that extends and divides the
d. Cortex parenchyma into lobules.
140. Enumerate the 2 principles in adaptive community a. Trabeculae
a. H b. Medulla
b. C c. Cortex
141. The principles of adaptive immunity which is responsible for the d. Lymphoblast
cytotoxic elimination via CD8 or cytotoxic lymphocyte 158. The cells present within the lymphoid nodules
a. Innate a. Macrophages
b. Cellular b. Dendritic cells
c. Adaptive c. Follicular dendritic cells
d. Immune system d. Thymic epithelial cells
142. First antibody that is produced by the body in response to an infection. 159. A meshwork that supports lymphoblasts and creates boundary
a. IgD a. Thymic epithelial cells
b. IgM b. Cytotoxic T cells
c. IgG c. Helper T cells
d. IgE d. Both and b
143. A glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin family that interacts specially 160. Blood-thymus barrier
with an antigenic determinant a. Important structure of the thymus
a. Antigen b. Composed of the blood capillary endothelium, perivascular
b. Antibody macrophages, and the type 1 epithelioreticular cells, and their
c. More thrift basal lamina
d. AOTC c. Provided cellular framework to compartmentalize the various
144. ______________ are what the body’s triggering during vaccination. lymphocytes
145. Diffuse lymphoid tissue d. Both a and b
a. The gastric associated lymphoid tissue found in the digestive 161. Lymphatic nodules except:
tract a. Invaginations in which the epithelial lining is densely filtered with
b. Bronchi associated lymphoid tissue found in the pulmonary tract lymphocytes and other lymphocytes
c. Primary or central lymphoid organ b. Concentration of lymphocytes contained a meshwork of
d. Both a and b reticular cells
146. The immunoglobulin that participates in the destruction of parasites. c. Composed of primary, germinal center, and mantle
a. IgD d. NOTC
b. IgG 162. Fill in the blanks.
c. IgE a. Nearer to the oropharynx continuous with the respiratory tract:
d. IgA b. Continuous of the esophagus:
147. All these statements about IgG are true except: c. Nearer to the oral cavity:
a. Antibody on the surface of B-lymphocyte 163. Composed of a dense connective tissue type that surrounds the
b. Can be found in maternal milk node.
c. Most dominant antibody in the plasma or serum a. Trabeculae
d. More or less potent as IgM b. Capsule
148. Directly attacks the tumor cells c. Medulla
a. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes d. Lymph vessels
b. CD8 164. The splenic pulp which is restricted to the smaller areas especially
c. Helper T cells centering around the central arterioles near blood vessels
d. Both a and b a. White pulp
149. Antibody bound to the surface of mast cells and basophils b. Red pulp
165. The sites within the lymph nodes where the mature cells proliferate, b. Splenic cords of Billroth
differentiate, mutate their antibody genes c. Splenic sinusoids
a. Primary nodule d. NOTC
b. Mature zone 180. A functional system composed of various cells like white blood cells
c. Corona and antigen-presenting cells.
d. Germinal center a. Antigen
166. If they retain the CD4, these are the _______________. If they retain in b. Autoimmunity
the CD8, they are the ______________________________. c. Antibodies
a. Cytotoxic lymphocytes d. Immune system
b. Helper T cells 181. The part of the antibody that promotes complement activation,
c. Regulatory T cells opsonization, and activation of NK cells
d. Self-antigens a. Cell receptor binding
167. Enumerate the large immature lymphocytes found in the germinal b. Fc portion
center of secondary lymphatic nodules c. Fab portion
a. L d. Both a and b
b. P 182. Enhances the antibody’s coat of the bacterium
168. The discrete concentrations of lymphocytes contained in a meshwork a. Opsonization
of reticular cells b. Agglutination
a. Primary nodules c. Neutralization
b. Secondary nodules d. Precipitation
c. Lymphatic nodules 183. The antibody that protects mucosae
d. Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue a. IgA
169. Corona develops when a lymphocyte that has recognized an antigen b. IgD
returns to a primary nodule and undergoes proliferation. c. IgE
a. True d. IgG
b. False; mantle zone 184. Tonsils
c. False; germinal center a. Filter and trap those that enter the mouth
d. False; palatine b. Filtered the infectious foreign materials that enters the mouth
170. Deep invaginations in which the epithelial lining is densely infiltrated c. Invaginations
which lymphocytes and other leukocytes d. AOTC
a. Blood-thymus barrier 185. The main effector cells in which they eat particles that are deemed as
b. Tonsils potentially harmful and foreign to the human body so that they would
c. Tonsillar crypts not cause damage.
d. Pharyngeal tonsils a. Secretion
171. Located in the ileum which consist of numerous aggregations of b. Adaptive
lymphatic nodules containing T and B lymphocytes c. Phagocytes
a. Pharyngeal tonsil d. NOTC
b. Tonsillar crypts 186. It has a thin capsule and doesn’t have crypts
c. Vermiform appendix a. Pharyngeal
d. Peyer patches b. Lingual
172. Red pulp c. Palatine
a. Splenic cords of Billroth and Splenic sinusoids d. NOTC
b. Contains large numbers of RBC that filters and degrades 187. All statements are true except:
c. Consist of a thick accumulation of lymphocytes surrounding an a. IgG is less or more potent as IgM
artery b. IgM is the first antibody that is produced the body
d. Both a and b c. IgD is the antibody found in the secretions
173. All statements are true about vermiform appendix except: d. The presence of IgG denotes a past infection that can be
a. A morphologic indication of lymphatic tissue detected after long periods.
b. Useless organ because a person can still live without this organ 188. Denoted by the presence of CD4 protein
c. It is where the lymphocytes aggregate to protect you especially a. T lymphocyte
in the intestine b. B lymphocyte
d. The blind invagination of the cecum and a significant part of the c. Helper T cells
MALT with its lamina propria d. Cytotoxic T cells
174. Bean-shaped, encapsulated structures distributed throughout the 189. Cells that are dispersed throughout the body and they would usually
body along the lymphatic vessels and provide enclosed environments concentrate in the lymphoid organs.
that facilitate production of plasma cells secreting non-IgA antibodies a. Antigen-presenting cells
a. Lymphatic vessel b. White blood cells
b. Lymph node c. Both a and b
c. Reticular tissue d. B cells
d. Trabeculae 190. Thymus
175. Composed of dense connective tissue that surrounds the node a. Butterfly shaped structure attached to the mediastinum of the
a. Trabeculae sternum which is the for induction of central tolerance
b. Parenchyma b. Organ producing T cells
c. Cortex c. Originates from the embryo’s third pair of pharyngeal pouches
d. Capsule which undergoes a process of involution.
176. Lymphoid nodule d. AOTC
a. With germinal center: 191. The immunoglobulin that mediates hypersensitivity reaction with the
b. mast cells causing mast cells to degranulate so is your basophils.
177. Lack of B cells lymphoid nodules but rich in T cells and high endothelial a. IgA
venules b. IgM
a. paracortex c. IgD
b. Cortex d. IgE
c. Subcapsular sinus 192. Special type of lymphocyte
d. Medullary cords a. APC
178. The large lymphatic organ that is in the upper left quadrant of the b. T cells
abdominal cavity and has a rich blood supply c. NK cells
a. Stomach d. B cells
b. Spleen 193. It has something to do with acquiring CD4 or CD8 receptor which will
c. Thymus designate whether they will become a helper T cell or cytotoxic T cell
d. Tonsil a. Positive selection
179. Reticular tissue rich in macrophages and lymphocytes which is b. Negative selection
separated by the sinusoids c. Central tolerance
a. Medullary sinuses d. Both and b
194. It provides defense or immunity against infectious agents. a. Physical barriers: ______
a. Innate immunity b. ______________________________: secretions
b. Immune system c. Various ________________________________
c. Adaptive immunity d. _______________: main effector cells of immune system
d. Antibodies 210. Prevents autoimmunity
195. A group of molecules that attacks the membrane of the microbe and a. Diffuse lymphoid tissue
causes cell lysis that destroys the bacteria. b. Central tolerance
a. Fc portion c. Primary lymphoid organs
b. Opsonization d. Both and b
c. Complement 211. It releases perforin/granzymes which are substances that create holes
d. Neutralization to the viruses and bacteria infected cells.
196. Secretions like saliva, milk, tears, etc. a. NK cells
a. IgA b. Regulatory T cells
b. IgM c. B cells
c. IgD d. APC
d. IgE 212. Young lymphoblast
197. Involves antibody production a. Lymphocyte
a. Self-adaptive b. Thymocytes
b. Autoimmunity c. Thymic cells
c. Humoral d. NOTC
d. Both a and b 213. It is mediated by APCs which would determine the microbes or the
198. Positive selection is the recognition of the self-antigen. Meanwhile, invader and then present that in the lymphocyte.
negative selection is the ability to bind to MHC molecules. a. Self-adaptive
a. Both statements are true b. Adaptive
b. Both statements are false c. Innate
c. First statement is true; second is false d. Autoimmunity
d. First statement is false; second is true 214. Denoted by CD8 protein
199. Enumerate the five immunoglobulin classes a. T cells
a. b. B cells
b. c. Helper T cells
c. d. Cytotoxic T cells
d. 215. Lymph node
e. a. Dominated by reticular tissue because it allows easier filtration of
200. The cells that promote the differentiation of our B cells into plasma the lymph since it’s like a meshwork or a net where the microbes
cells, activate macrophages to become phagocytic, and activate would be trapped
cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. b. Extension of the capsule
a. APC c. Spherical or oval that aggregates of lymphocytes
b. Helper T cells d. Both a and b
c. Lymphocytes 216. Antibody on the surface of the B-lymphocyte
d. Regulatory T cells a. IgG
201. The principle behind vaccines. b. IgD
a. Immune system c. IgA
b. Antibodies d. IgM
c. Antigen 217. Composed of large mature lymphocytes where the thymic or Hassall’s
d. Adaptive immunity corpuscle is located
202. The antibody that can be found in the secretions a. Medulla
a. IgA b. Desmosomes
b. IgD c. Thymic epithelial cells
c. IgM d. Cortex
d. IgG 218. Enumerate the 2 principles in adaptive community
203. Branch of the splenic artery a. H
a. Peripheral artery b. C
b. Periarterial lymphatic sheath 219. The principles of adaptive immunity which is responsible for the
c. High endothelial venules cytotoxic elimination via CD8 or cytotoxic lymphocyte
d. Central artery a. Innate
204. Germinal center b. Cellular
a. Contains the lymphoblasts and plasma blasts c. Adaptive
b. Indicates that the lymphatic tissue responds to the presence of d. Immune system
an antigen. 220. First antibody that is produced by the body in response to an infection.
c. Develops when a lymphocyte that recognizes an antigen returns a. IgD
to a primary nodule and undergoes proliferation b. IgM
d. AOTC c. IgG
205. The primary or central lymphoid organ for T cells d. IgE
a. Tonsil 221. A glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin family that interacts specially
b. Spleen with an antigenic determinant
c. Lymph nodes a. Antigen
d. Thymus b. Antibody
206. All statements are true except: c. More thrift
a. Partner of antibody d. AOTC
b. Range from viruses and parasites 222. ______________ are what the body’s triggering during vaccination.
c. Antigen recognizes and by recognizing as foreign 223. Diffuse lymphoid tissue
d. NOTC a. The gastric associated lymphoid tissue found in the digestive
207. A non-specific immunity which we have since we were born tract
a. Innate b. Bronchi associated lymphoid tissue found in the pulmonary tract
b. Autoimmunity c. Primary or central lymphoid organ
c. Antibodies d. Both a and b
d. Antigen 224. The immunoglobulin that participates in the destruction of parasites.
208. Activates phagocytosis and neutralizes antigens a. IgD
a. IgM b. IgG
b. IgA c. IgE
c. IgD d. IgA
d. IgG 225. All these statements about IgG are true except:
209. Fill in the blanks. Preexisting non-specific defenses. a. Antibody on the surface of B-lymphocyte
b. Can be found in maternal milk 241. Composed of a dense connective tissue type that surrounds the
c. Most dominant antibody in the plasma or serum node.
d. More or less potent as IgM e. Trabeculae
226. Directly attacks the tumor cells f. Capsule
a. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes g. Medulla
b. CD8 h. Lymph vessels
c. Helper T cells 242. Covered with antibody antigen complexes bound to receptors for
d. Both a and b complement proteins and for immunoglobulin Fc region, causing B
227. Antibody bound to the surface of mast cells and basophils cells to attach, become activated and aggregate as a small primary
a. IgM lymphoid nodule
b. IgG a. Antigen-presenting cells
c. IgE b. Follicular dendritic cells
d. IgD c. Epithelioreticular cells
228. All statements are true except: d. Thymic epithelial cells
a. Antibodies neutralize viral particles and viral toxins 243. Medullary sinuses
b. Antibodies agglutinate bacterial cells and precipitate most a. Spaces which are lined discontinuous capillaries that separate
soluble antigen. the medullary cords.
c. Antibodies is acquired gradually b. It is where we can find macrophages and neutrophils
d. Antibodies are Y-shaped c. Branched-cordlike masses of lymphoid tissue
229. Enumerate the types of lymphocytes d. Both a and b
a.
b.
230. Cells that are more on inhibition of specific immune responses,
monitoring peripheral tolerance
a. B cells
b. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes
c. Regulatory T cells
d. Helper T cells
231. Enumerate the cells under T lymphocyte
a.
b.
232. Fc region of antibody binds to an NK cell, triggering release of
cytotoxic chemicals.
a. Opsonization of NK cells
b. Complement system
c. Fc portion of NK cells
d. Activation of NK cells
233. Helper T cells
a. Represents the cell mediated immunity
b. More on the inhibition of specific immune responses
c. Assist in the immune responses by producing cytokines
d. AOTC
234. Lymphoid organs
a. Group of cells, tissues, and organs
b. Monitor body surfaces and internal fluid components
c. React to the presence of potentially harmful substances
d. AOTC
235. Thin connective tissue capsule that extends and divides the
parenchyma into lobules.
a. Trabeculae
b. Medulla
c. Cortex
d. Lymphoblast
236. The cells present within the lymphoid nodules
a. Macrophages
b. Dendritic cells
c. Follicular dendritic cells
d. Thymic epithelial cells
237. A meshwork that supports lymphoblasts and creates boundary
a. Thymic epithelial cells
b. Cytotoxic T cells
c. Helper T cells
d. Both and b
238. Blood-thymus barrier
a. Important structure of the thymus
b. Composed of the blood capillary endothelium, perivascular
macrophages, and the type 1 epithelioreticular cells, and their
basal lamina
c. Provided cellular framework to compartmentalize the various
lymphocytes
d. Both a and b
239. Lymphatic nodules except:
a. Invaginations in which the epithelial lining is densely filtered with
lymphocytes and other lymphocytes
b. Concentration of lymphocytes contained a meshwork of
reticular cells
c. Composed of primary, germinal center, and mantle
d. NOTC
240. Fill in the blanks.
a. Nearer to the oropharynx continuous with the respiratory tract:
b. Continuous of the esophagus:
c. Nearer to the oral cavity:
You might also like
- Dermatology MCQDocument18 pagesDermatology MCQR Ratheesh100% (3)
- Personal Hygiene, Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Secondary School Students in IkejaDocument54 pagesPersonal Hygiene, Knowledge Attitude and Practice of Secondary School Students in IkejaBastosTemitayoStephen90% (10)
- Skin Diseases Dogs and CatsDocument10 pagesSkin Diseases Dogs and CatsMaria DumitruNo ratings yet
- Biology of The Integument 1986Document870 pagesBiology of The Integument 1986Thiago Maia CarneiroNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument2 pagesBiologyHannah laurenNo ratings yet
- Neet Test Paper 3 New PatternDocument3 pagesNeet Test Paper 3 New PatternGovindNo ratings yet
- 06 DermatologyDocument8 pages06 DermatologyMichael NyaataNo ratings yet
- Anatomy LE5 Samplex 2017BDocument6 pagesAnatomy LE5 Samplex 2017BHanako Sasaki AranillaNo ratings yet
- Q&a Properties of The Hair and ScalpDocument5 pagesQ&a Properties of The Hair and ScalpSANo ratings yet
- Part 1,2,3 With AnswersDocument27 pagesPart 1,2,3 With AnswersJonnie Rose Louise WeeNo ratings yet
- Histo ReviewerDocument21 pagesHisto ReviewerIan Iglesia100% (1)
- ALE 2014 Animal Science Autosaved - Docx 2003409664Document85 pagesALE 2014 Animal Science Autosaved - Docx 2003409664Haifa KalantunganNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 02Document3 pagesNEET Test Series 02npmishra9818No ratings yet
- Unit - 5 TESTDocument9 pagesUnit - 5 TESTmisgshlove1No ratings yet
- Sample TestDocument5 pagesSample TestPangalilingan, Bernard PaulNo ratings yet
- Revision Unit1Document3 pagesRevision Unit1anamarchalNo ratings yet
- Chitwan Multiple Institute (Cmi) Bharatpur-10, Chitwan Afu Weekly Model ExamDocument9 pagesChitwan Multiple Institute (Cmi) Bharatpur-10, Chitwan Afu Weekly Model ExamBinod BhandariNo ratings yet
- Majorship: Biological Science QuestionsDocument7 pagesMajorship: Biological Science QuestionsJun LacorteNo ratings yet
- Easy ANATDocument4 pagesEasy ANATLiza Elaine Ulep CawasNo ratings yet
- hssb2101t SecquizDocument2 pageshssb2101t Secquizfhhgghhg hggghgNo ratings yet
- Leyte CollegesDocument5 pagesLeyte CollegesMaria Jean Baclea-anNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Mcqs YT Insta Medico SlidesDocument16 pagesNervous System Mcqs YT Insta Medico SlidesNaveed KhanNo ratings yet
- Histolab Reviewer Connective TissueDocument2 pagesHistolab Reviewer Connective TissueJustine May S. ColicoNo ratings yet
- Stem 5 Gen Bio - Activity 1 May Kyla O. Parado BSN 1 - ADocument2 pagesStem 5 Gen Bio - Activity 1 May Kyla O. Parado BSN 1 - AKyla OropesaNo ratings yet
- Animal ScienceDocument19 pagesAnimal ScienceGel Mi AmorNo ratings yet
- PHYSIOLOGYDocument4 pagesPHYSIOLOGYAnne GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nursing Exam BiolagyDocument5 pagesNursing Exam BiolagysamloviniNo ratings yet
- Part 5 Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesPart 5 Bio ReviewerChester Kim DiscarNo ratings yet
- University of Tripoli HS120: - C. - D. Dense Regular Connective TissueDocument4 pagesUniversity of Tripoli HS120: - C. - D. Dense Regular Connective TissueAnn AnooshNo ratings yet
- Part I 2016 - Dermatology MCQDocument9 pagesPart I 2016 - Dermatology MCQEmma Dawod100% (1)
- Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesExam Reviewmadison.cosbyNo ratings yet
- Final MCQs For The 4th Yaer StudentsDocument49 pagesFinal MCQs For The 4th Yaer StudentseidNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1st GradingDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Exam 1st Gradingteabagman100% (2)
- Class IX Chapter 4 MCQ'sDocument2 pagesClass IX Chapter 4 MCQ'sAyesha KhanNo ratings yet
- Neurophysio Easy MCQDocument8 pagesNeurophysio Easy MCQLiza Elaine Ulep Cawas100% (1)
- Histology Reviewer With RationaleDocument7 pagesHistology Reviewer With RationaleRegine Benedicte Navarro VidalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Half Book 2Document10 pagesAnatomy Half Book 2Saeed khanNo ratings yet
- Phylum Cnidaria Test PDFDocument7 pagesPhylum Cnidaria Test PDFSHIKHAR SRVSTVNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument177 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFNishankumar JhaNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ExaminationDocument5 pages3rd Quarter ExaminationMaria Jean Baclea-anNo ratings yet
- FMGE Recall Jan 2023 (2) - 230209 - 234610Document34 pagesFMGE Recall Jan 2023 (2) - 230209 - 234610Mirthan KrishNo ratings yet
- Ati Teas 7 Biology ReviewDocument51 pagesAti Teas 7 Biology ReviewSAMUEL WAMNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grading Examination BiotechDocument2 pages3rd Grading Examination BiotechMark Bryan LoterteNo ratings yet
- Midterm SampleDocument10 pagesMidterm SampleErvin T Mile0% (1)
- Biology 1Document6 pagesBiology 1crest810No ratings yet
- BotanyDocument3 pagesBotanyStephany Mae ChiNo ratings yet
- PMC Mock Test 3Document18 pagesPMC Mock Test 3Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants-Entrance Questions N AnswersDocument6 pages6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants-Entrance Questions N AnswersNaveen Krishna M.KNo ratings yet
- Test Oral Mucosa MCQsDocument3 pagesTest Oral Mucosa MCQsDr. KashifNo ratings yet
- Test Oral Mucosa MCQsDocument3 pagesTest Oral Mucosa MCQsDr. Kashif71% (7)
- 2018 HistologyDocument100 pages2018 HistologysonsuzakadarcccNo ratings yet
- Biology Quizbee ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiology Quizbee Reviewerkim natividadNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Final ExamDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Final ExammarataningutukuNo ratings yet
- ANIMALSDocument4 pagesANIMALSSam SamNo ratings yet
- PMC Mock Test 4 by WisegotDocument19 pagesPMC Mock Test 4 by WisegotTasawar Hussain DayoNo ratings yet
- 3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDocument25 pages3 GENPATHO To Be PrintDENTAL REVIEWER ONLYNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology MCQSDocument8 pagesHuman Physiology MCQSHaris Qurashi100% (1)
- PMC Mock Test 3Document18 pagesPMC Mock Test 3hmdNo ratings yet
- 11th Biology Minimum Study Material emDocument39 pages11th Biology Minimum Study Material emJay senthilNo ratings yet
- Integumantary System TutorialDocument3 pagesIntegumantary System TutorialNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Biology Block Test Ganjil Preparation WorksheetDocument12 pagesBiology Block Test Ganjil Preparation WorksheetSMAXICLouis Bintang AlexisNo ratings yet
- Stevens Immuno Sero Answer KeyDocument18 pagesStevens Immuno Sero Answer KeyKATHERINE SHYLE MILARNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer (Biology Test)Document10 pagesScience Reviewer (Biology Test)CHRISTIAN NOE BONGALBALNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris Bu Ratih (Personal Hygiene)Document6 pagesBahasa Inggris Bu Ratih (Personal Hygiene)Listi PujiNo ratings yet
- Appendigeal TumoursDocument3 pagesAppendigeal TumourspritanuNo ratings yet
- Crim 101Document51 pagesCrim 101Aries DialinoNo ratings yet
- Week 7 - IntegumentaryDocument11 pagesWeek 7 - IntegumentaryVia Kristel ZapantaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary SystemDocument49 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary System蔡嘉慧No ratings yet
- 2nd (Integumentary Activity)Document3 pages2nd (Integumentary Activity)Yma FeelNo ratings yet
- Cosme NotesDocument9 pagesCosme NotesAlthea AlbaniaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Handout Week 7-8Document17 pagesPhysical Science Handout Week 7-8Jhay Lorraine Sadian PalacpacNo ratings yet
- 2023 Specimen Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument12 pages2023 Specimen Paper 2 Mark Schemehaardikchpubey10No ratings yet
- Health Assesment Exam ObjectivesDocument119 pagesHealth Assesment Exam ObjectivesMartha TreviñoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 27 - Histology of The Integumentary System 2Document89 pagesLecture 27 - Histology of The Integumentary System 2spitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Mid-Semster Study Notes PDFDocument32 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Mid-Semster Study Notes PDFsimone dumbrell100% (10)
- Introduction To The Human BodyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To The Human BodyRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- THE INTEGUMENT ORGAN: The Integument As An Organ and Is An Alternative Name ForDocument16 pagesTHE INTEGUMENT ORGAN: The Integument As An Organ and Is An Alternative Name ForPdianghunNo ratings yet
- The Skin (Anaphy)Document2 pagesThe Skin (Anaphy)ALEXANDRA COLLEEN ALEGRENo ratings yet
- Derma CD McqsDocument22 pagesDerma CD McqsheshamNo ratings yet
- A& P NotesDocument178 pagesA& P NotesJSeashark100% (3)
- Sweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument72 pagesSweat Glands Anatomy and PhysiologyDr Daulat Ram DhakedNo ratings yet
- PDF Fitzpatricks Dermatology 9Th Edition Sewon Kang Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Fitzpatricks Dermatology 9Th Edition Sewon Kang Ebook Full Chapterjose.hicks831100% (2)
- Integumentary SystemDocument40 pagesIntegumentary SystemFatimaKhadija AbdulNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument138 pagesIntegumentary SystemGerald John PazNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Skin and FunctionDocument2 pagesThe Structure of Skin and FunctionSiti Aliyah KarimNo ratings yet
- ADAPTATION OF GOATS by Charles Langton VanyaDocument4 pagesADAPTATION OF GOATS by Charles Langton VanyaCharles Langton Mpaso VanyaNo ratings yet
- Deodrent Project - Five BrandsDocument42 pagesDeodrent Project - Five BrandsNitinAgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Biology Mammals PPT Kel.10Document46 pagesBiology Mammals PPT Kel.10Indah BarizahhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - IntegumentDocument9 pagesChapter 6 - IntegumentBianca AmisolaNo ratings yet