Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Maths Y1 4E Answers9
Uploaded by
barty22Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Maths Y1 4E Answers9
Uploaded by
barty22Copyright:
Available Formats
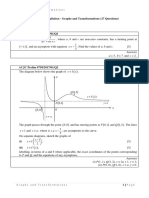
(ii) (a) LJ (b) MJ
1 0
DC2D = returns the object to (c) K2 (d) JLK
0 1
its original position 8 −4
5 (i) −3 12 (ii) (32, −33)
Answers
(iii) For example, B4, C2 or D2 0 1
6 Possible transformations are B = ,
1 0 −1 0 −1 0
2 (i) X = 0 −1 Y=
0 1 which is a rotation of 90° clockwise about the
origin, followed by
−1 0
(ii) XY = 0 −1 , rotation of 180°
3 0
A= , which is a stretch of scale factor
0 1
about the origin
3 parallel to the x-axis. The order of these is
−1 0 important as performing A followed by B leads
(iii) YX = 0 −1 0 1
to the matrix . Could also have
(iv) When considering the effect on the unit −3 0
vectors i and j, as each transformation only 1 0
affects one of the unit vectors the order of B = 0 3 . which represents a stretch of
the transformations is not important in this
case. factor 3 parallel to the y-axis, followed by
0 1
A= , which represents a rotation
3
−1 0
P=
0 1
Q= −1 0
1 0
(i)
0 −1 of 90° clockwise about the origin; again the
order is important.
0 −1
(ii) PQ = , reflection in the line 1 0
−1 0 7 (i) PQ =
y = −x −3 −1
0 −1 1 0
QP = −1 0 (ii) P = 0 −1 represents a reflection in
(iii)
(iv) The matrix P has the effect of making the the x-axis.
coordinates of any point the negative of 1 0
Q= represents a shear with the
their original values, 3 1
i.e. ( x, y ) → (−x, − y ) y-axis fixed; point B(1,1) has image (1,–4).
1 1
The matrix Q interchanges the coordinates,
2 2
i.e. ( x, y ) → ( y, x ) 8 X=
1 − 1
It does not matter what order these two 2 2
transformations occur as the result will be A matrix representing a rotation about the
the same cos θ − sin θ
1 0 0 1 0 0 origin has the form and so
sin θ cos θ
4 (i) J= 0 1 0 K = 0 0 −1
the entries on the leading diagonal would be
0 0 −1 0 1 0 equal. That is not true for matrix X and so this
−1 0 0 0 0 1 cannot represent a rotation.
L= 0 1 0 M= 0 1 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 −1 0 0 9 Y= 1 0 0
0 0 1
182
You might also like
- Homogeneous TransformDocument12 pagesHomogeneous TransformharshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 (Graphs)Document17 pagesChapter 6 (Graphs)Shubham PriyamNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous TransformDocument12 pagesHomogeneous TransformAnonymous G9t3IVfL4JNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 12975 PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment1 12975 PDFNaman HumaneNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Term 2 Assessment 2007 - EXTENSION II: Question 2 (B) Continued On Next PageDocument3 pagesYear 12 Term 2 Assessment 2007 - EXTENSION II: Question 2 (B) Continued On Next Pagenoah smithNo ratings yet
- Combain File - 2 ST, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola PDFDocument33 pagesCombain File - 2 ST, Circle, Parabola, Ellipse & Hyperbola PDFAniruddha Kawade100% (1)
- Straight Line Theory (1-27) - F24Document27 pagesStraight Line Theory (1-27) - F24neerajNo ratings yet
- Step3 2020 PaperDocument12 pagesStep3 2020 PaperEmily WrightNo ratings yet
- Straight Line: X y X yDocument3 pagesStraight Line: X y X ySayyed SohelNo ratings yet
- 2D Geometrical Transformations: Foley & Van Dam, Chapter 5Document34 pages2D Geometrical Transformations: Foley & Van Dam, Chapter 5Ashutosh JhaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Essential Mathematics For Economics and Business Teresa Bradley Paul PattonDocument5 pagesSolution Manual For Essential Mathematics For Economics and Business Teresa Bradley Paul PattonKAFIL KANWER50% (2)
- 2D Transformations: Larry F. Hodges (Modified by Amos Johnson)Document14 pages2D Transformations: Larry F. Hodges (Modified by Amos Johnson)Srinath Gm G MNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Assignment For Straight LinesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Assignment For Straight LinesNikhil HegdeNo ratings yet
- 2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)Document21 pages2017 H2 Prelim (Graphs and Transformations)toh tim lamNo ratings yet
- 1 Plane Geometric ProjectionsDocument6 pages1 Plane Geometric ProjectionsArvind RawatNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Change of AxesDocument16 pagesGeometry: Change of AxesSilvaSunnyNo ratings yet
- AriHant MATHEMATICSDocument15 pagesAriHant MATHEMATICSNareshJagathkar100% (1)
- EE 650A - Assignment 2 (2020-21-I)Document2 pagesEE 650A - Assignment 2 (2020-21-I)Pradeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Parabola - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesParabola - Short Notes - Arjuna JEE 2.0 2024dushyantsiwach3263No ratings yet
- HW2 SolDocument5 pagesHW2 SolMouliNo ratings yet
- Linear Transformation and Rank Nullity Theorem 2 LecturesDocument32 pagesLinear Transformation and Rank Nullity Theorem 2 Lecturespratyay gangulyNo ratings yet
- Co Ordinate GeometryDocument6 pagesCo Ordinate GeometryLyrics World РусскийNo ratings yet
- Conic Section RevisionDocument111 pagesConic Section RevisionBsprogrammer100% (1)
- 5ACh12 (Coordinate Treatment of Simple Locus Problems)Document45 pages5ACh12 (Coordinate Treatment of Simple Locus Problems)api-19856023No ratings yet
- PureMaths1976 Pastpaper P2Document4 pagesPureMaths1976 Pastpaper P2wltfNo ratings yet
- DefinitionDocument23 pagesDefinitionashok KumarNo ratings yet
- CG Question bank-1SHUBHAMDocument11 pagesCG Question bank-1SHUBHAMabhiamale55No ratings yet
- 2022 JC1 H2 Math Practice PaperDocument5 pages2022 JC1 H2 Math Practice PaperTimothy LauNo ratings yet
- Pair of LinesDocument58 pagesPair of LinesKahaan KakabaliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10&11Document3 pagesLecture 10&11api-3754855No ratings yet
- 11self Theory-Straight LineDocument5 pages11self Theory-Straight Lineرافت باصهيNo ratings yet
- MATH2010 Assignment 2 2019Document2 pagesMATH2010 Assignment 2 2019zaibtsu0% (1)
- 3 Straight LinesDocument21 pages3 Straight LineskalavathikathiripalliNo ratings yet
- Response CurveDocument11 pagesResponse CurveGrt grtNo ratings yet
- DHS H2 2021 Prelim P1Document5 pagesDHS H2 2021 Prelim P1猪猪侠No ratings yet
- 11 - Straight LineDocument3 pages11 - Straight LineHarsh ShahNo ratings yet
- 2019 JC1 H2 Math Rev D - Graphs and Transformations - SolutionsDocument10 pages2019 JC1 H2 Math Rev D - Graphs and Transformations - SolutionscalderteoNo ratings yet
- Vector Triple Product PDFDocument12 pagesVector Triple Product PDFdadaNo ratings yet
- Section - III: Transformations in 2-D in 2-DDocument33 pagesSection - III: Transformations in 2-D in 2-DVishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Points To RememberDocument9 pagesChapter 10 Points To RememberMokshita JainNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL P2 Exercise 3A (Solution)Document2 pagesEdexcel IAL P2 Exercise 3A (Solution)Kaif HasanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 1Document5 pagesAssignment 3 1prachikumar04No ratings yet
- Exercise - 01 Circle: Check Your GraspDocument13 pagesExercise - 01 Circle: Check Your GraspsuryaNo ratings yet
- Mat334 TD7Document5 pagesMat334 TD7jethrotabueNo ratings yet
- Section - B: Multiple Choice Type Questions: R KQ R KQ 2Document11 pagesSection - B: Multiple Choice Type Questions: R KQ R KQ 2Ajit KumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise - 01 3D-Coordinate Geometry: Check Your GraspDocument12 pagesExercise - 01 3D-Coordinate Geometry: Check Your Grasponline pathshalaNo ratings yet
- Transformations of Graphs TutorialDocument9 pagesTransformations of Graphs Tutoriallbwnb.68868No ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document8 pagesLecture 2Sukran Jamil DurjoyNo ratings yet
- CG Cheat Sheet 2020Document6 pagesCG Cheat Sheet 2020Nitesh MalviyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Assignment For Conic SectionsDocument5 pagesCBSE Class 11 Assignment For Conic SectionsAnand TripathiNo ratings yet
- Three Dimension - Chapter NotesDocument10 pagesThree Dimension - Chapter NotesDivyanshi VishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman Materi Transformasi GeometriDocument2 pagesRangkuman Materi Transformasi GeometriRanda yustamaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument14 pagesUntitledjohnyNo ratings yet
- 1 Grap TutB AnswerDocument13 pages1 Grap TutB AnswerPang Hua TanNo ratings yet
- Intersection of EllipsesDocument4 pagesIntersection of EllipsesManoj GuptaNo ratings yet
- OSM TM 4A02 e ExamDocument7 pagesOSM TM 4A02 e Exam林俊佑No ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants 1Document5 pagesMatrices and Determinants 1ym5c2324No ratings yet
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Tables of Lommel's Functions of Two Pure Imaginary Variables: Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTables of Lommel's Functions of Two Pure Imaginary Variables: Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet