Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L1 - Assignment On Superposition Principle and Equilibrium of Charges
Uploaded by
dynamicranjan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views2 pagesOriginal Title
3. L1 - Assignment on Superposition Principle and Equilibrium of Charges
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
117 views2 pagesL1 - Assignment On Superposition Principle and Equilibrium of Charges
Uploaded by
dynamicranjanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Q1. State the principle of superposition of Q9.
Three charges −q1 , +q 2
electrostatic forces. Hence write an expression for and −q3 are placed as shown
the force on a point charge due to a distribution of N in the figure. The x-
− 1 point charges in terms of their position vectors. component of the force on
−q1 is proportional to?
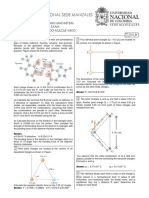
Q2. Three equally charged small objects are placed q2 q3 q2 q3
(a) 2 − 2 sin θ (b) 2 − 2 cos θ
as shown in figure below. The object A exerts an b a b a
q2 q3 q2 q3
electric force on object B equal to 3.0 x 10−6 N. (c) + sin θ (b) + cos θ
b2 a2 b2 a2
(i) What electric force does C exert on B? (ii) What
is the net electric force on B? [Ans: (i) 𝟏𝟐 𝐱 𝟏𝟎−𝟔 N Q10. Consider the charges q, q and −q placed at the
(along BA) (ii) 9 x 𝟏𝟎−𝟔 N (along BA)] vertices of an equilateral triangle. What is the force
𝟏 𝐪𝟐 𝟏 𝐪𝟐 𝟏 𝐪𝟐
on each charge? [Ans:
𝟒𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐥 𝟐, 𝟒𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐥 𝟐 , √𝟑 𝟒𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐥𝟐
]
Q11. Three equal charges (q) are placed at the
corners of an equilateral triangle of side ‘l’. Find the
Q3. For the below force on a fourth charge ‘Q’ kept at the centroid of
figure, find the the triangle? [Ans: Zero]
resultant force on
10μC charge? [Ans: Q12. Three identical charges are placed at the
18.97 N, 71.57° with corners of an equilateral triangle. If the force
horizontal] between any two charges is F, then the net force on
each will be? [Ans: 𝐅√𝟐]
Q4. Two equal positive charges, each of 2μC are
separated by a distance of 6m. Another charge 3μC Q13. Three point charges of magnitude 5μC, 0.16μC
situated on the perpendicular bisector of the line and 0.3μC are located at the vertices A, B, C of a
joining the above charges and at a distance of 4m. right angled triangle whose sides are AB = 3cm, BC
Find the magnitude and direction of the force
= 3√2cm and CA = 3cm and point A is the right
experienced by the charged of 3μC?
angled corner. Find the electrostatic force
[Ans: 3.456 x 𝟏𝟎−𝟑 N]
experienced by charge A due to other two charges?
[Ans: 17 N]
Q5. An infinite number of charges each equal to 4μC
are placed along x-axis at x = 1 m, x = 2 m, x = 4 m, Q14. Three equal charges, each having a magnitude
x = 8 m and so on. Find the total force on a charge of 2.0 x 10−6 C are placed at the three corners of a
of 1 C placed at the origin.
right-angled triangle of sides 3cm, 4cm and 5cm.
[Ans: 4.8 x 𝟏𝟎𝟒 N] Find the force on the charge at the right-angle
corner? [Ans: 45.9 N, 𝐭𝐚𝐧−𝟏 (𝟒𝟓⁄𝟗)]
Q6. Ten charged particles are kept fixed on the X-
axis at point x = 10 mm, 20 mm, 30mm,…,100mm.
Q15. Charge 5.0 x 10−7 C, –2.5 x 10−7 C and 1.0 x
The first particle has a charge 10−8 C, the second 8
10−7 C are fixed at the corners A, B and C of an
x 10−8 C, the third 27 x 10−8 C and so on. The tenth
equilateral triangle of side 5.0 cm. Find the electric
particle has a charge 1000 x 10−8 C. Find the
force on the charge at C due to the rest two? [Ans:
magnitude of electric force acting on a 1C charge = 0.15588 N]
placed at the origin? [Ans: 4.95 × 𝟏𝟎𝟕 N]
Q16. Four equal point charges each 16μC are
Q7. Two point charges Q each are placed at a placed on the four corners of a square of side 0.2m.
distance d apart. A third point charge q is placed at Calculate the force on anyone of the charges?
a distance x from the mid-point on the perpendicular [Ans: 110.3 N, along diagonal]
bisector. Find the value of x at which charge q will
experience maximum Coulomb’s force? [Ans: Q17. Four charges +q , +q , −q and −q are placed
𝐝⁄𝟐√𝟐] respectively at the four corners A, B, C and D of a
square of side a. Calculate the force on a charge Q
Q8. Charges of +5μC, +10μC and −10μC are placed at the centre of the square?[Ans:
placed in air at the corners A, B and C of an 𝟏 𝟒√𝟐 𝐐𝐪
equilateral triangle ABC, having each side equal to , parallel to AD or BC]
𝟒𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐚𝟐
5 cm. Determine the resultant force on the charge
+5μC placed at the vertex A of the triangle. Q18. Four point charges q A = 2 µC, q B = –5 µC, q C
[Ans: 180 N] = 2 µC, and q D = –5 µC are located at the corners of
a square ABCD of side 10 cm. What is the force on Q27. Two identical charges, Q each, are kept at a
a charge of 1µC placed at the centre of the square? distance from each other. A third charge q is placed
[Ans: Zero] on the line joining the above two charges such that
all the three charges are in equilibrium. What is the
Q19. Six charges +Q each are placed at the corners magnitude, sign and position of the charge q? [Ans:
of a regular hexagon of side ‘a’. Find the force on a 𝐪 = 𝐐⁄𝟒, opposite to that of Q and position = 𝐫⁄𝟐]
charge +Q kept at the centre of the hexagon? [Ans:
Zero] Q28. Two point charges of charge values Q and q
are placed at distances x and 𝐱⁄𝟐 respectively from
Q20. Five point charges, each of value +q are placed a third charge of charge value 4q, all charges being
on five vertices of a regular hexagon of side L. What in the same straight line. Calculate the magnitude
is the magnitude of the force on a point charge of and nature of charge Q, such that the net force
value –q coulomb placed at the centre of the experienced by the charge q is zero? [Ans: Q = 4q,
𝟏 𝐪𝟐 same sign as of q or 4q]
hexagon? [Ans: ]
𝟒𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐋𝟐
Q29. Two point charges +9e and +e are kept at a
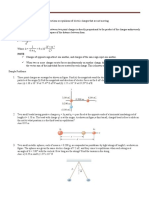
Q21. Find the force acting on a charge ‘q’ in the distance a from each other. Where should we place
following figure? a third charge q on the line joining the two charges
so that it may be in equilibrium?
[Ans: 3a/4 from +9e charge]
Q30. Two point electric charges of values q and 2q
are kept at a distance d apart from each other in air.
A third charge Q is to be kept along the same line in
such a way that the net force acting on q and 2q is
Q22. Four point charges each of value +Q are zero. Calculate the position of charge Q in terms of
placed on five vertices of a regular pentagon of side q and d. [Ans: At a distance of (√𝟐 − 1)d from
L. What is the magnitude of the force on a point charge q]
charge of value −q placed at the centre of a
hexagon? Q31. Two equal positive point charges Q are fixed at
points A(−a, 0) and B(a, 0). Another test charge q o is
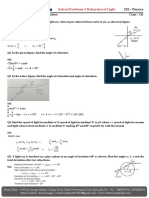
Q23. Three charged particles are placed on a also placed at O(0, 0). Check the equilibrium at O for
straight line as shown in figure. q1 and q 2 are fixed, (i) displacement along x-axis (ii) displacement along
but q 3 can be moved. Under the action of the forces y-axis. If the equilibrium is stable in any one of the
from q1 and q 2 , q 3 is in equilibrium. What is the cases, then show that test charge will perform SHM
relation between q1 and q 2 ? [Ans: 𝐪𝟏 = − 4𝐪𝟐 ] for small displacement. Also, find its time period if its
mass is ‘m’. (iii) Find the ratio of the frequencies of
oscillation in the two cases?
𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐦𝐚𝟑 𝟐𝛑𝛆𝐨 𝐦𝐚𝟑
Q24. A charge q is placed at the centre of the line [Ans: (i) T = 2𝛑 √ (ii) T = 2𝛑 √ (iii)
𝐪𝐐 𝐪𝐐
joining two equal charges Q. Show that the system
of three charges will be in equilibrium if q = −Q/ 4. √𝟐]
Q25. Two point charges +4e and +e are 'fixed' at Q32. Find the equilibrium position for a third charge
distance 'a' apart. Where should a third point charge and also find its value for which the whole system
q be placed on the line joining the two charges so will be in equilibrium. [Ans: Position is 2𝐥 and
that it may be in equilibrium? In which case the value of third charge is −36 Q]
equilibrium will be stable and in which unstable?
[Ans: Location is 2a/3, for positive charge +𝐪,
stable equilibrium, for negative charge −𝐪,
unstable equilibrium]
Q26. Two 'free' point charges +4e and +e are placed
at distance 'a' apart. Where should a third point
charge q be placed between them such that the
entire system may be in equilibrium? What should
be the magnitude and sign of q ? What type of
equilibrium will it be? [Ans: 𝐪 = 𝟒𝐞⁄𝟗, negative
charge, unstable equilibrium]
You might also like
- Deckel FPXNC Dialog 4 Dialog 11 Programming RkloppDocument260 pagesDeckel FPXNC Dialog 4 Dialog 11 Programming RkloppStelian Crisan100% (1)
- Solution Manual Complex Analysis 6th Edition by John MathewsDocument6 pagesSolution Manual Complex Analysis 6th Edition by John MathewsAviv Avraham67% (3)
- Capacitance - SL AroraDocument69 pagesCapacitance - SL Aroradynamicranjan50% (2)
- Ch.1 NumericalsDocument3 pagesCh.1 NumericalstejasNo ratings yet
- ch.1 NumericalsDocument3 pagesch.1 NumericalstejasNo ratings yet
- Ch-01 Electric Charges & Fields Daily Practice Problems - 02Document5 pagesCh-01 Electric Charges & Fields Daily Practice Problems - 02Motivation TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Daily Practice ProblemsDocument3 pagesDaily Practice ProblemsHarshitNo ratings yet
- Taller Parcial 1 - Fisica IiiDocument6 pagesTaller Parcial 1 - Fisica IiiJorge CañetesNo ratings yet
- Previous Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesDocument7 pagesPrevious Exams Questions Ch21-22-With NotesaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Assignment: Calculating Potential, Field, and WorkDocument3 pagesElectric Potential Assignment: Calculating Potential, Field, and WorkSatvik AnandNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 1 Electric Charges and Field Worksheet - 2: V M M V MDocument5 pagesCHAPTER - 1 Electric Charges and Field Worksheet - 2: V M M V Mniyathi panickerNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics ExerciseDocument20 pagesElectrostatics ExerciseUtkarsh Mittal86% (7)
- Electrostatics PS XIIDocument24 pagesElectrostatics PS XIIDark gaming liveNo ratings yet
- Jit Term 3 FinalDocument82 pagesJit Term 3 Finalpreciousrebotile133No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Short NotesDocument1 pageElectrostatics Short NotesAkanksha TiwariNo ratings yet
- Review Test 1314Document11 pagesReview Test 1314Hassan AliNo ratings yet
- TutoDocument3 pagesTutoAlees RahaizanNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Force AssignmentDocument2 pagesElectrostatic Force Assignmentrahulmatada123No ratings yet
- WS 1 (N) ForceDocument1 pageWS 1 (N) ForceMin NimNo ratings yet
- Potential AssignmentDocument2 pagesPotential AssignmentdhananjayajainNo ratings yet
- Ch21 SSMDocument18 pagesCh21 SSMFranko UrciaNo ratings yet
- Coulomb's LawDocument6 pagesCoulomb's LawAarush MishraNo ratings yet
- Partial Solution Derivations For Capa #2Document3 pagesPartial Solution Derivations For Capa #2guiana22No ratings yet
- 8b-Solution Homework The Electric Charge and Coulombs LawDocument5 pages8b-Solution Homework The Electric Charge and Coulombs Lawzainab noorNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument5 pagesSolutionAbrar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and PotentialDocument27 pagesElectric Field and Potentialthinkiit100% (1)
- 01 ElectrostaticsDocument14 pages01 ElectrostaticsAarav PatelNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics (Question Paper)Document6 pagesElectrostatics (Question Paper)anchlia12345No ratings yet
- Electrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGDocument20 pagesElectrostatics Type 2 PART 2 of 3 ENGSubhashChandraMishraNo ratings yet
- Compiled XiiDocument34 pagesCompiled XiiMridul VermaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Electric FieldDocument3 pagesAssignment Electric Fieldfahad0% (1)
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostaticsLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument3 pagesElectrostaticsLast UnknownNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1234123Document3 pagesElectrostatics 1234123Last UnknownNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Electric Field, Potential and Coulomb's LawDocument39 pagesElectrostatics: Electric Field, Potential and Coulomb's LawSANCHIT BAWEJA100% (1)
- PHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2harshitaNo ratings yet
- Phys102 Old Exam Problems Ch21-22Document2 pagesPhys102 Old Exam Problems Ch21-22Reeja MathewNo ratings yet
- ELECTROSTATICSDocument10 pagesELECTROSTATICSUrvashi RaoNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014Document21 pagesSolved Problems-Ch23-Electric Forces New Fall 2015-2014believer149No ratings yet
- Tutorials On Electric FieldDocument2 pagesTutorials On Electric FieldNkeng100% (1)
- Coulomb's Law - QuestionsDocument4 pagesCoulomb's Law - QuestionsAhamad FalahNo ratings yet
- Statics Assgnmnt)Document20 pagesStatics Assgnmnt)Mohammed AdemNo ratings yet
- Problems 2Document8 pagesProblems 2Martinez 100No ratings yet
- University of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II First Midterm Exam Questions ??/04/2003 TIME 100 MinDocument1 pageUniversity of Gaziantep Department of Engineering Physics EP 106 General Physics II First Midterm Exam Questions ??/04/2003 TIME 100 MinFatih TokgözNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument9 pagesElectric Charge and Electric FieldRehan JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics 1nUMERICALDocument5 pagesElectrostatics 1nUMERICALpavithra KumarNo ratings yet
- PanPearl2016 Solutions 1Document8 pagesPanPearl2016 Solutions 1tanNo ratings yet
- Electric PotentialDocument2 pagesElectric Potentialamanchaudhary9759No ratings yet
- Aadhar+l3+ Electric+Potential+and+Potential+Energy+Document77 pagesAadhar+l3+ Electric+Potential+and+Potential+Energy+AISHWARYA JAI SINGHNo ratings yet
- Electric Charge Multiple Choice Questions for JEE Main and AdvancedDocument14 pagesElectric Charge Multiple Choice Questions for JEE Main and Advancedbrm1shubhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsRohan Nayak-37No ratings yet
- Electrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Document14 pagesElectrostatics S1 Worksheet April 14Sameera ShanakaNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Work SheetDocument6 pagesUnit - 4 Work SheetNathan GetachewNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic For MurniDocument55 pagesElectrostatic For MurniAnonymous RMXuPuNo ratings yet
- Wuolah Free Exercises3Document14 pagesWuolah Free Exercises3Don José Antonio García-Trevijano ForteNo ratings yet
- Quest Electrostatics 4 KeyDocument5 pagesQuest Electrostatics 4 KeyCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and Force Review ProblemsDocument25 pagesElectric Field and Force Review ProblemsحمدةالنهديةNo ratings yet
- Chapter 01 PP Xii PhysicsDocument4 pagesChapter 01 PP Xii Physicsstudywithak77No ratings yet
- Physics Electrostatics MCQDocument8 pagesPhysics Electrostatics MCQSrijan Chakraborty100% (1)
- Practice Questions Chs 21-24 1Document40 pagesPractice Questions Chs 21-24 1jevanjunior0% (1)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of MatterDocument44 pagesDual Nature of MatterdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument45 pagesProjectile MotiondynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument108 pagesCurrent ElectricitydynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Electric Dipole Assignment Class 12 PhysicsDocument2 pagesElectric Dipole Assignment Class 12 PhysicsdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion Assignment - Ground to GroundDocument4 pagesProjectile Motion Assignment - Ground to GrounddynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Measurements and ErrorsDocument19 pagesMeasurements and ErrorsdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- L1 - Assignment On Electric FluxDocument3 pagesL1 - Assignment On Electric FluxdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- JEE Books Basic Math ChapterDocument12 pagesJEE Books Basic Math ChapterdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Classroom Questions - Circular MotionDocument2 pagesClassroom Questions - Circular MotiondynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument6 pagesGas LawsdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Refraction of Light Problems and SolutionsDocument20 pagesRefraction of Light Problems and SolutionsdynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Capacitance - DishaDocument86 pagesCapacitance - DishadynamicranjanNo ratings yet
- Deret TaylorDocument8 pagesDeret TaylorDaniel CaliNo ratings yet
- FinalDocument135 pagesFinalCarlos Luis Cataulin100% (1)
- Eng Math Lesson 12Document5 pagesEng Math Lesson 12Kyla Jynell SaquitonNo ratings yet
- 2 2 Rectangle 2 Square 2Document4 pages2 2 Rectangle 2 Square 2Erlyn Joyce CerillaNo ratings yet
- LG MATH Grade 5 - Geometry v2.0 PDFDocument17 pagesLG MATH Grade 5 - Geometry v2.0 PDFLevi CorralNo ratings yet
- 1.05 Geometry Foundations ActivityDocument2 pages1.05 Geometry Foundations ActivityYousef Hamdan100% (1)
- DPP (1 To 17) 11th J Maths WADocument17 pagesDPP (1 To 17) 11th J Maths WARaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry & Geometry Word ProblemsDocument7 pagesTrigonometry & Geometry Word Problemsmishita khiaraNo ratings yet
- Vector and Three DimensionDocument2 pagesVector and Three DimensionHARDIK MISHRANo ratings yet
- Trigonometric FormulasDocument5 pagesTrigonometric Formulasanshumansingh042006No ratings yet
- How To Find The IncenterDocument3 pagesHow To Find The Incenterirish xNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry Final Test - 1Document6 pagesAnalytic Geometry Final Test - 1Brenda MontañezNo ratings yet
- 3rd Preliminary Examination - Grade 8 Math 2023 - 2024Document2 pages3rd Preliminary Examination - Grade 8 Math 2023 - 2024Jerome Tala-ocNo ratings yet
- Seminar Math 2016 Students ST Mary PDFDocument40 pagesSeminar Math 2016 Students ST Mary PDFHadi Faizal Mohd RoselyNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Maths Unit 13 Angles in Parallel Lines and PolygonsDocument1 pageYear 8 Maths Unit 13 Angles in Parallel Lines and Polygonsmukona199No ratings yet
- Focus Camp 2021 VectorsDocument5 pagesFocus Camp 2021 Vectorsfairprice tissueNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade X SA II PapersDocument11 pagesMathematics Grade X SA II PapersvidyapostNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 1 Week 15 - With AnswerDocument4 pagesQ4 Week 1 Week 15 - With AnswerKizha JuanilloNo ratings yet
- CAT Quant Questions Solutions Bodhee PrepDocument12 pagesCAT Quant Questions Solutions Bodhee PrepDark HorseNo ratings yet
- Prova Selecao PG-EIA 2022-1osemDocument6 pagesProva Selecao PG-EIA 2022-1osemmarcalferreiraNo ratings yet
- How To Find CircumferenceDocument4 pagesHow To Find Circumferenceapi-150547803No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 ReviewDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Reviewmcclellanr406No ratings yet
- Proving Triangles Congruent and Statements Math ActivityDocument7 pagesProving Triangles Congruent and Statements Math ActivityLish Meremonte100% (1)
- Modul Math Form 5Document11 pagesModul Math Form 5Fujiwara Hafiz BuntaiNo ratings yet
- PLTW IED Activity 2.1.3 Sketches CADDocument20 pagesPLTW IED Activity 2.1.3 Sketches CADZanzarr100% (1)
- Similar Triangle Properties and TheoremsDocument13 pagesSimilar Triangle Properties and TheoremsShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sinus TableDocument2 pagesSinus TableMemkNo ratings yet
- Answer 1Document5 pagesAnswer 1raj mohanNo ratings yet