Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7 Compilationsssss
Uploaded by
Jeric SapaulaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Compilationsssss
Uploaded by
Jeric SapaulaCopyright:
Available Formats
Jeric N.
Sapaula
BSET 3A
Chapter 7 Compilation
1. Noise immunity
The ability to detect and correct transmission errors
compatibility with time division multiplexing techniques
digital signal processing potential
Noise Immunity is the most important.
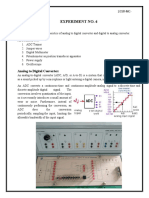
2. The process of changing analog to digital or digital to analog.
A/D and D/A
3. Sampling
4. Quantizing
5. Digitizing.
6. The signals are sampled and converted into a sequence of binary numbers that are transmitted
in parallel or serial.
7. Is a stepped approximation of the original continuously varying analog signal.
8. Reference Voltage
resistor (or capacitor) network
switches
output amplifier
9. Aliasing is a problem that happens if the sampling rate of an ADC is less than two times the
highest signal frequency.
A false signal is generated at a frequency equal to the difference between the signal and
sampling frequencies.
10. Op Amp
11. Successive approximations, flash, and sigma-delta.
The most used is Successive approximations.
12. Successive approximations converter
13. Flash. Simultaneously, an analog sample is compared to multiple voltage levels and comparator
outputs are translated into binary.
14. is digitizing a signal at more than twice the Nyquist rate.
15. Shift register
You might also like
- Digital Signal Processing: Instant AccessFrom EverandDigital Signal Processing: Instant AccessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Sampling and Baseband ModulationDocument65 pagesSampling and Baseband ModulationAbdul Qawi AnsariNo ratings yet
- What Is Widely Used Converter ? - Sigma Delta ConverterDocument3 pagesWhat Is Widely Used Converter ? - Sigma Delta ConverterMAcryan Pacquiao PactolNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PDFDocument59 pagesLecture 5 PDFJawad ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Q1. Distinguish Between Instantaneous, Natural and Flat-Top Sampling. Show DiagrammaticallyDocument6 pagesQ1. Distinguish Between Instantaneous, Natural and Flat-Top Sampling. Show DiagrammaticallyAnjali BishtNo ratings yet
- Task Chapter 4Document3 pagesTask Chapter 4Azimah Zainal OfficiqlNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication System: Analog To Digital Conversion Is Carried Out HereDocument37 pagesDigital Communication System: Analog To Digital Conversion Is Carried Out Hereahmed yuosifNo ratings yet
- Data ConversionDocument4 pagesData ConversionpauliNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Engineering Lecture 07 (ADC)Document24 pagesEmbedded Systems Engineering Lecture 07 (ADC)Nushara WedasinghaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information Technology: Lecture #9Document12 pagesIntroduction To Information Technology: Lecture #9Akäsh NåyåkNo ratings yet
- Inverters SpecsDocument11 pagesInverters SpecsbhuwaneshtakNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertermuzamiru Kahise sayumweNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital-Convesion v2 - StudentDocument43 pagesAnalog-to-Digital-Convesion v2 - StudentJysh MamusogNo ratings yet
- Full-Speed Testing of AD ConvertersDocument8 pagesFull-Speed Testing of AD ConvertersKirti Susan VargheseNo ratings yet
- Nemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1Document7 pagesNemo, Czriss Paulimer C - Problem Set 1pauliNo ratings yet
- Sigma-Delta Modulation (Σ-Δ) oldDocument20 pagesSigma-Delta Modulation (Σ-Δ) oldMustafa_elecNo ratings yet
- Introduction To FFT AnalysisDocument8 pagesIntroduction To FFT AnalysisA. VillaNo ratings yet
- Ec51 Digital CommunicationDocument18 pagesEc51 Digital CommunicationvijayprasathmeNo ratings yet
- Iii Part A BDocument115 pagesIii Part A BDivya SreeNo ratings yet
- IT 6313 Digital Communication Lab ManualDocument75 pagesIT 6313 Digital Communication Lab ManualsivagamasundhariNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 COME384Document54 pagesChapter1 COME384Sara DabajaNo ratings yet
- DC TWO MarksDocument15 pagesDC TWO MarksShanilDayalan100% (1)
- Flash AdcDocument15 pagesFlash AdcbittibssiNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Course Code: Credit Hours:3 Prerequisite:30107341Document33 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Course Code: Credit Hours:3 Prerequisite:30107341محمد القدوميNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signal Lecture Series - DSP-Based Testing Fundamentals 01Document8 pagesMixed Signal Lecture Series - DSP-Based Testing Fundamentals 01Tina HuangNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture3 ADCDocument32 pagesDSP Lecture3 ADCAlbert GenceNo ratings yet
- Using A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowDocument10 pagesUsing A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowPrakhar BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- JTD - 2C - 13 - Delta ModulationDocument11 pagesJTD - 2C - 13 - Delta Modulationhillyatul auliaNo ratings yet
- Adc and Dac: 3.1-QuantizationDocument14 pagesAdc and Dac: 3.1-Quantizationazurebirble12No ratings yet
- Villadelrey CW1 Ecea108 B14Document2 pagesVilladelrey CW1 Ecea108 B14Vivien VilladelreyNo ratings yet
- Puse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) :: ParticularDocument6 pagesPuse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) :: ParticularSubhajit DasNo ratings yet
- Intro To Digital CommunicationDocument29 pagesIntro To Digital CommunicationRyan OlaybalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 7 Digital Communications TechniquesPatrick GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document24 pagesLec 4بشير عماد كاظمNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Interfacing With Peripheral DevicesDocument36 pagesChapter 4 - Interfacing With Peripheral DeviceshuynhtrinhNo ratings yet
- Analogue and Digital Communication Lab ManualDocument95 pagesAnalogue and Digital Communication Lab ManualZara ZaraNo ratings yet
- DC Part ADocument17 pagesDC Part Apavithra PNo ratings yet
- Short Questions of Digital Communication: Unit 1: Pulse ModulationDocument7 pagesShort Questions of Digital Communication: Unit 1: Pulse ModulationSakib AhmedNo ratings yet
- Adc and Dac: Syed Khawar Hussain ShahDocument12 pagesAdc and Dac: Syed Khawar Hussain ShahM. RazaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication: Subject Name:Digital Communication Prepared by:S.Sathiya Priya AP/ECEDocument25 pagesDigital Communication: Subject Name:Digital Communication Prepared by:S.Sathiya Priya AP/ECESathiyapriya ShanmugasundaramNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing: Mustansiriyah University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department 4 ClassDocument60 pagesDigital Signal Processing: Mustansiriyah University College of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department 4 ClassPreethi ReddyNo ratings yet
- DC R16 - Unit-1Document39 pagesDC R16 - Unit-1Sivaprasad GanjiNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering Elective 2: Wireless Communications: Experiment No. 1Document7 pagesCollege of Engineering Elective 2: Wireless Communications: Experiment No. 1Mhy AcajaNo ratings yet
- Fairchild Lm7805cDocument5 pagesFairchild Lm7805cGautam BalharaNo ratings yet
- ENGD1009 Communication System Lab Session: 6 Digital Communication Chapter 2: The MODICOM 3 PCM TransmitterDocument13 pagesENGD1009 Communication System Lab Session: 6 Digital Communication Chapter 2: The MODICOM 3 PCM Transmitterعبدالله شھزادNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 6: Objective: ApparatusNioNo ratings yet
- Mechatronic ApplicationsDocument44 pagesMechatronic ApplicationsDevice SamsungNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 11Document19 pagesالمحاضرة 11هبة نبيل بالخيرNo ratings yet
- Analog-To Digital Conversion: Comsats University of Sciences and TechnologyDocument6 pagesAnalog-To Digital Conversion: Comsats University of Sciences and Technology320126512L20 yerramsettibhaskarNo ratings yet
- ADC Experiments 2019 - EditedDocument56 pagesADC Experiments 2019 - EditedchandranayakaNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Document5 pagesUnit Iii - Part-A: Course Material (Question Bank)Saravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Application: Analog and Digital SignalsDocument29 pagesEmbedded System Application: Analog and Digital SignalsMULLAIVANESH A VNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) and Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)Document23 pagesAnalog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) and Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)Pahala SamosirNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter PDFDocument4 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter PDFtowfiqeeeNo ratings yet
- A/D and D/A Conversion Testing: V G 2 V VDocument7 pagesA/D and D/A Conversion Testing: V G 2 V VRichard NewbyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 PCMDocument38 pagesLecture 5 PCMSakawa BobNo ratings yet
- Pci Final ProjectDocument10 pagesPci Final ProjectR JadhavNo ratings yet
- Data Acquisition: An Introduction: Bruxton CorporationDocument5 pagesData Acquisition: An Introduction: Bruxton CorporationkumarcvNo ratings yet
- High-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversFrom EverandHigh-Performance D/A-Converters: Application to Digital TransceiversNo ratings yet
- POVERTYDocument1 pagePOVERTYJeric SapaulaNo ratings yet
- Ramas Vs QuiamcoDocument5 pagesRamas Vs QuiamcoJeric SapaulaNo ratings yet
- Or GateDocument2 pagesOr GateJeric SapaulaNo ratings yet
- Jeric Logic Circuit Lab ReportDocument6 pagesJeric Logic Circuit Lab ReportJeric SapaulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CompilationnnnDocument1 pageChapter 6 CompilationnnnJeric SapaulaNo ratings yet
- Case DigestDocument6 pagesCase DigestJeric SapaulaNo ratings yet