Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Science (05-22-23)
Uploaded by
Madeline Chloe Plata0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views1 pagePhysical Science (05-22-23)
Uploaded by
Madeline Chloe PlataCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
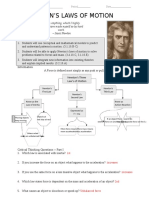
Physical Science – May 22, 2023
Newton’s Law of Force
Forces
- It is an interaction between at least two objects that
when unopposed, induces a change in the motion of
said objects.
The SI unit of force is the newton (N), which is equal to 1
kg*m/s^2
Contact Force
- When two bodies touch each other during the
exertion of the force.
Non-contact Force
- It acts upon an object even without another object
touching its surface.
Example of Contact Force
1. Friction
2. Normal force
3. Tension
4. Compression
5. Spring force
Example of Non-contact Force
1. Gravitational Force
2. Electrostatic Force
3. Magnetic
4. Electromagnetic Force
Background
SIR ISAAC NEWTON
- An English scientist and mathematician, famous for
his discovery of the law of gravity also discovered
the three laws of motion.
Newton’s Laws of Forces
1. Newton’s First Law: Law of Inertia. Objects remain at
constant velocity until and external force applied to it.
- an object at rest tends to stay at rest and an object in motion
tends to stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalance
force.
- Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist changes in its
state of motion.
Examples: Two teams are playing tug of war.
2. Newton’s Second Law: Law of Acceleration. Force equals
mass times acceleration.
- F=ma
- Acceleration – is measurement of how quickly an object is
changing speed.
3. Newton’s Third Law: Law of Interaction.
- For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
- For every force action on an object, there is an equal force
acting in the opposite direction.
You might also like
- Laws of Motion - NewtonDocument17 pagesLaws of Motion - NewtonpseudonimNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument18 pagesLaws of MotionJhen BonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 NotesDocument2 pagesChapter 4 NotesYuxin LiuNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesLaws of MotionClaudiu NicusorNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument29 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionpbayes83% (6)
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyDocument13 pagesNewton'S Laws of Motion: Name KeyMingNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesLaws of MotionGraceyxie GrasyaNo ratings yet
- NewtonDocument2 pagesNewtonglueckwunsch.liebtNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 8 NotesRocel U. GinooNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law's of MotionDocument19 pagesNewtons Law's of MotionAira YamuyamNo ratings yet
- Presentation - of MotionDocument16 pagesPresentation - of Motionharshdipraj123No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explainedrizki siwiNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws MrymDocument3 pagesNewtons Laws Mrymapi-345837027No ratings yet
- Newton LawsDocument3 pagesNewton LawsA BarrettNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawDocument10 pagesNewton's LawKyla Desiree BedienesNo ratings yet
- Untitled Document - EditedDocument1 pageUntitled Document - EditedOdeteNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument11 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionNovita Tri WidianingsihNo ratings yet
- Newtons 3rd LawDocument15 pagesNewtons 3rd LawcaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of MotionDocument11 pagesNewton's Third Law of MotionScribd-95761650% (2)
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton's Law of MotionKhawaja EshaNo ratings yet
- Interactions and ForceDocument2 pagesInteractions and Forcezhungjian586No ratings yet
- Newton NotesDocument1 pageNewton NotesSebastian RăileanuNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson ReviewDocument4 pagesPhysics Lesson ReviewШунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- Week 3 and 4 Pt. 2Document13 pagesWeek 3 and 4 Pt. 2Bradley HausNo ratings yet
- Newtons Laws and MomentumDocument20 pagesNewtons Laws and MomentumcaitlyntreacyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument8 pagesForcesapi-318478101No ratings yet
- Newtons 3rd Law of MotionDocument7 pagesNewtons 3rd Law of MotionJudiel Achilles M. Valdepena ;-;No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion Glenn Research Center NASADocument1 pageNewton's Laws of Motion Glenn Research Center NASAelenekalandadzeeeNo ratings yet
- Newtons Law Science 8Document5 pagesNewtons Law Science 8Odyfier BagonocNo ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion and ApplicationsDocument53 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion and Applicationsburner accNo ratings yet
- Physics Multiple Assignment: - S. YogavarshaDocument16 pagesPhysics Multiple Assignment: - S. YogavarshaMithu VarshaNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument17 pagesLaws of MotionMechaella Marie Maste GallazaNo ratings yet
- Verde Blanco Plantas Foto Ciencia FolletoDocument2 pagesVerde Blanco Plantas Foto Ciencia FolletoAndrea Carolina Ictech EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Who Discovered The Three Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesWho Discovered The Three Laws of MotionQUENZELLE JADE LOKINGNo ratings yet
- LM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1Document40 pagesLM5b - Newton - S Laws of Motion - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- The E Tutor - Laws of MotionDocument11 pagesThe E Tutor - Laws of Motioninfo5963No ratings yet
- 11-Woodpecker Science ReportDocument17 pages11-Woodpecker Science ReportrhaineNo ratings yet
- Subject Grade 10 Physics NotesDocument1 pageSubject Grade 10 Physics Notesjordan.shapiroNo ratings yet
- 2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1law of InertiaDocument16 pages2 G8 Science Q1-Week 1 of 1law of InertiaAn BautistaNo ratings yet
- Kabihasnan NG MesopotamiaDocument2 pagesKabihasnan NG MesopotamiaJhon Andy EsbanNo ratings yet
- 4.3newtons 1st Law and 2nd LawDocument6 pages4.3newtons 1st Law and 2nd Lawnegad607No ratings yet
- Law of Motion @moazzam - GuidesDocument1 pageLaw of Motion @moazzam - GuidesMoazzamNo ratings yet
- Nkdievid 2Document10 pagesNkdievid 2nik100% (2)
- The Focus of Lesson 1 IsDocument6 pagesThe Focus of Lesson 1 IschrizzdMNo ratings yet
- The Law of Motion Explained: Force, Inertia and EquilibriumDocument30 pagesThe Law of Motion Explained: Force, Inertia and EquilibriumNurulWardhani11No ratings yet
- Newton's Three Laws of MotionDocument7 pagesNewton's Three Laws of MotionRex Lemuel AndesNo ratings yet
- Note On Newton's Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesNote On Newton's Laws of MotionStephenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ConceptDocument15 pagesChapter 1 ConceptSiti KhalijahNo ratings yet
- Class Note 04Document1 pageClass Note 04userzeroNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsDocument12 pagesNewton's Laws: Al-Basra University College of Engineering Department of MechanicsZahra 9oNo ratings yet
- Unit2keyconcepts 1Document4 pagesUnit2keyconcepts 1ansonng16888No ratings yet
- محاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءDocument3 pagesمحاضرة 3. ـ موقع الفريد في الفيزياءMahdiTahar BrahimiNo ratings yet
- Forces and Equilibrium ExplainedDocument20 pagesForces and Equilibrium ExplainedruvinNo ratings yet
- Class Notes PhysicsDocument1 pageClass Notes PhysicsM Andika NNo ratings yet
- Week 1 ScienceDocument38 pagesWeek 1 ScienceEyphrille UmandapNo ratings yet
- The Laws of Motion: - Sir Isaac NewtonDocument51 pagesThe Laws of Motion: - Sir Isaac NewtonBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceAnastasia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Eapp Lesson 6.3Document15 pagesEapp Lesson 6.3Madeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Madeline Chloe M. Plata ABM I - Mo. Vitalis WinklerDocument1 pageMadeline Chloe M. Plata ABM I - Mo. Vitalis WinklerMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Rerum Novarum 2Document17 pagesRerum Novarum 2Madeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Madeline Chloe M. Plata - Slogan & PoemDocument2 pagesMadeline Chloe M. Plata - Slogan & PoemMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PhilosophyDocument2 pagesReviewer in PhilosophyMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Philosophy - Aguilera - PlataDocument3 pagesPhilosophy - Aguilera - PlataMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - ASSIGNMENTDocument1 pageEarth and Life Science - ASSIGNMENTMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- How Does Your Diorama Show The Interaction and Interdependence of Living Organisms From One AnotherDocument1 pageHow Does Your Diorama Show The Interaction and Interdependence of Living Organisms From One AnotherMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- EAPP Lesson 1Document26 pagesEAPP Lesson 1Madeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Lit-1-SEMIS-Reviewer 2Document7 pagesLit-1-SEMIS-Reviewer 2Madeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Mortgage For Finals PtaskDocument2 pagesMortgage For Finals PtaskMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- PSET Bus MathDocument2 pagesPSET Bus MathMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness ProgramDocument13 pagesPhysical Fitness ProgramMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- PSET Bus MathDocument2 pagesPSET Bus MathMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- PlanningDocument8 pagesPlanningMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- #43 - Plata, Madeline Chloe M.Document13 pages#43 - Plata, Madeline Chloe M.Madeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness ProgramDocument13 pagesPhysical Fitness ProgramMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Mini Task EvaluationDocument1 pageMini Task EvaluationMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet
- Mini Task EvaluationDocument1 pageMini Task EvaluationMadeline Chloe PlataNo ratings yet