Professional Documents
Culture Documents
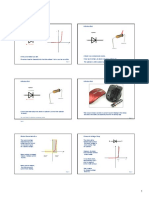
24.3 Rectification
Uploaded by
SalmanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
24.3 Rectification
Uploaded by
SalmanCopyright:
Available Formats
Physics Topic 24 (Electronics) O-Levels
RECTIFICATION
Prepared by: Sir Salman Saeed Page 1 of 2
Physics Topic 24 (Electronics) O-Levels
ELECTRICAL ENERGY Diodes, Rectification and Capacitors
Although alternating current is easier to generate and distribute, many appliances, especially those with
microchips, need direct current. The process of converting alternating to direct current is called rectification.
Alternating current Current Half-wave rectification
We now have direct
current that flows one
way around a circuit,
Time Time but it is only flowing
for half the time, and
even then the voltage
Diode - blocks current
is rising and falling.
flowing in the reverse direction
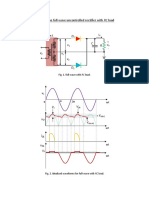
A better result is obtained with a bridge circuit.
1 Voltage
1
Current flow when 2
1 +
1 is positive and
2 Output
Time
2 is negative. - Output
1 2 2 1
1 2 2 1 2
Input This makes use of both the forward and reverse
2 Voltage current and is called full wave rectification.
Current flow when
The direct current produced still has a rising
2 is positive and Input and falling voltage. We say it is unsmoothed.
1 is negative. Time
I I
A capacitor is a component that can store charge. Charge
I + I Charge
Capacitor +
symbol
I - I
-
When the potential difference is high, Time Time
it stores some of the charge.
I I
Output +
from P.d.
bridge As the potential difference
circuit - starts to fall it releases the
charge. This helps to keep the
current and potential
difference up and we say the
direct current is smoothed.
Questions
1. What is a diode?
a. Complete the graphs in the circuit below to show the effect of the diode.
b. Why is the output an example of direct current? Why do we
say it is ‘unsmoothed’?
Current + Current
c. If the diode were reversed what would be the effect, if any,
on the direct current output?
2. What name do we give a device that stores charge? Time – Time
3. Explain the difference between full wave rectification and half-
wave rectification. Illustrate your answer with voltage-time graphs.
4. Draw a circuit that produces full wave rectification. Show how the current flows through the circuit.
Prepared by: Sir Salman Saeed Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Ayurvedic Healing A Comprehensive Guide David Frawley.07106 - 3ayurvedicdiet PDFDocument7 pagesAyurvedic Healing A Comprehensive Guide David Frawley.07106 - 3ayurvedicdiet PDFlelis2013100% (1)
- Accident Theories and Organisational FactorsDocument23 pagesAccident Theories and Organisational FactorsJorge Cronwell Montaño VásquezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Diode and Application - NewDocument78 pagesChapter 2 Diode and Application - NewPeter Yek100% (1)
- Modern Pentecostal Controversies (Fuiten)Document101 pagesModern Pentecostal Controversies (Fuiten)bratrekimNo ratings yet
- NFS (Network File System)Document9 pagesNFS (Network File System)Manish JainNo ratings yet
- SUSTAINABLE Responsible TourismDocument19 pagesSUSTAINABLE Responsible TourismJhoanna NatividadNo ratings yet
- POGIL - KinematicsDocument4 pagesPOGIL - KinematicsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Company Contact Person Mob Contact No IndustryDocument1 pageCompany Contact Person Mob Contact No IndustryDhirajNo ratings yet
- Essay About TechnologyDocument24 pagesEssay About TechnologyTemo Abashidze100% (2)
- Half Wave RectifierDocument6 pagesHalf Wave Rectifieray1574796No ratings yet
- SR - No. Questions A B C D AnswerDocument25 pagesSR - No. Questions A B C D AnswerShrikant NavaleNo ratings yet
- EE309 Notes 07 PDFDocument4 pagesEE309 Notes 07 PDFbals123456100% (1)
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec-4: Clampers, Voltage Multipliers, & Zener DiodeDocument15 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec-4: Clampers, Voltage Multipliers, & Zener DiodeRahulMondolNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicles: DC To DC ConvertersDocument31 pagesElectric Vehicles: DC To DC ConvertersSPARSH RAJNo ratings yet
- Rectifier FilterDocument12 pagesRectifier Filterengineer.chiranjitNo ratings yet
- In This Lecture:: DT Di M DT Di L VDocument5 pagesIn This Lecture:: DT Di M DT Di L VHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- DC To DC Converter (Chopper)Document26 pagesDC To DC Converter (Chopper)ATULYA ALOK 17BEE0065No ratings yet
- Diode OperationDocument3 pagesDiode OperationAnonymous FKMfvCbNo ratings yet
- Edc PPT2Document50 pagesEdc PPT2prathap_somaNo ratings yet
- Unit IiiDocument50 pagesUnit Iiisivadanams@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Module-3 (A) - Controlled Rectifiers - VII-POWER ELECTRONICS - 2015-17 SchemeDocument37 pagesModule-3 (A) - Controlled Rectifiers - VII-POWER ELECTRONICS - 2015-17 SchemeK N DEEPSHINo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - 1 - Uncontrolled Half Wave RectifierDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 2 - 1 - Uncontrolled Half Wave RectifierTan Zen YongNo ratings yet
- Analog Integrated Circuits: Linear Applications of OPAMPDocument11 pagesAnalog Integrated Circuits: Linear Applications of OPAMPSakshi ChiksheNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Current Bidirectional Switches PDFDocument7 pages4.2 Current Bidirectional Switches PDFJahangeer SoomroNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document8 pagesTutorial 1wei zhen LeongNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 JumawidDocument4 pagesActivity 1 JumawidKai JumawidNo ratings yet
- Voltage Multipliers and TransistorsDocument25 pagesVoltage Multipliers and TransistorsAbcd CanNo ratings yet
- DC To DC ConvertersDocument40 pagesDC To DC ConvertersJamir CalNo ratings yet
- Self-Lift DC-DC Converters: M Ail IlDocument6 pagesSelf-Lift DC-DC Converters: M Ail IlStudents Xerox ChidambaramNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec 3: Rectifier and Clipper CircuitsDocument12 pagesAnalog & Digital Electronics: Course No: PH-218 Lec 3: Rectifier and Clipper CircuitsRahulMondolNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics DC DC Converters: DR Taosif IqbalDocument71 pagesAdvanced Power Electronics DC DC Converters: DR Taosif IqbalTaosif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To DC-DC Conversion: A Buck Converter or A Step-Down ConverterDocument29 pagesIntroduction To DC-DC Conversion: A Buck Converter or A Step-Down ConverterAnonymous 7ZMkLN0PcNo ratings yet
- 6 Ee462l Fall2011 DC DC BuckDocument16 pages6 Ee462l Fall2011 DC DC BuckasmonovNo ratings yet
- 1 - Circuit VariablesDocument33 pages1 - Circuit VariablesBa 4xNo ratings yet
- DCM Flyback With 5 Stage Multiplier PDFDocument6 pagesDCM Flyback With 5 Stage Multiplier PDFharshalvikasNo ratings yet
- Edc PPT2Document50 pagesEdc PPT2Mohan PreethNo ratings yet
- EE2004 Fundamentals of Circuits: Lecture 2: Voltage, Current, Power Michael KnoxDocument29 pagesEE2004 Fundamentals of Circuits: Lecture 2: Voltage, Current, Power Michael KnoxVera SunNo ratings yet
- Diode Applications: EET1240/ET212 OutlinesDocument11 pagesDiode Applications: EET1240/ET212 OutlinesAhmed Noor CiiltireNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Solid-State Switching DevicesDocument35 pages1.2. Solid-State Switching DevicesMuket AgmasNo ratings yet
- Comprobar Rectificador FlukeDocument3 pagesComprobar Rectificador FlukegaplusaNo ratings yet
- Las 3Document4 pagesLas 3James Honrubia (titobibot)No ratings yet
- D.C.-D.C. Conversion (1) : Buck Converter 6.1 Operation: in This LectureDocument4 pagesD.C.-D.C. Conversion (1) : Buck Converter 6.1 Operation: in This LectureHassan FarssiNo ratings yet
- Lect 040Document5 pagesLect 040dheyaaNo ratings yet
- Topic 4a Part 1Document11 pagesTopic 4a Part 1Aftab AhmedNo ratings yet
- Topik 2 - DiodesDocument61 pagesTopik 2 - DiodesfaizahNo ratings yet
- IET Power Electronics - 2014 - Ye - Quadratic Boost Converter With Low Buffer Capacitor StressDocument9 pagesIET Power Electronics - 2014 - Ye - Quadratic Boost Converter With Low Buffer Capacitor Stressreza mohajeryNo ratings yet
- Solids and Semiconductor Devices 2Document12 pagesSolids and Semiconductor Devices 2ankit1754qNo ratings yet
- 05 DC-DC Converter - AllDocument99 pages05 DC-DC Converter - AllAsad AzharNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Power Electronics: Course: BookDocument19 pagesPower Electronics Power Electronics: Course: BooksufiiiiyanNo ratings yet
- Be Unit 1 Part 2 GVKRDocument41 pagesBe Unit 1 Part 2 GVKRvishnukanth reddyNo ratings yet
- BLE - Module 5Document65 pagesBLE - Module 5David ManiNo ratings yet
- BASIC Electronics PART 2Document10 pagesBASIC Electronics PART 2BETTY UYNo ratings yet
- 01 Theory CEDocument20 pages01 Theory CESridhar NNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Total Flyfarwd - Unit1&2.7&8Document41 pagesDC-DC Total Flyfarwd - Unit1&2.7&8Abhishek PatelNo ratings yet
- The Boost ConverterDocument5 pagesThe Boost ConverterKhafizuddin AzaziNo ratings yet
- ConverteresDocument20 pagesConverteresNedaa AltawalbehNo ratings yet
- Design of Boost ConverterDocument4 pagesDesign of Boost ConverterUsman BabarNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits Introduction To PN Junction DiodeDocument41 pagesElectronic Circuits Introduction To PN Junction DiodeAnbazhagan SelvanathanNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 - InverterDocument88 pagesMod 4 - InverterSREEHARI V ANo ratings yet
- EPE491 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument18 pagesEPE491 Introduction To Power ElectronicsAliMubarakNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Lecture NotesDocument38 pagesChapter3 Lecture Notesfarahk77737No ratings yet
- Physics at Work - Unit 02 - DC ElectricityDocument11 pagesPhysics at Work - Unit 02 - DC ElectricitySam PereraNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter - AllDocument99 pagesDC-DC Converter - AllAijaz HussainNo ratings yet
- E' Properties of Materials-AP-Fall-2016Document14 pagesE' Properties of Materials-AP-Fall-2016Muhammad RumanNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical: DEE 1113 / DMT 1113 / DEI 1003 Electrical Technology I / Electrical TechnologyDocument71 pagesBasic Electrical: DEE 1113 / DMT 1113 / DEI 1003 Electrical Technology I / Electrical TechnologyFarah Hanan AzimiNo ratings yet
- Physics Investgatory Project Full Wave Rectifier: CertificateDocument6 pagesPhysics Investgatory Project Full Wave Rectifier: CertificatearchitNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Chuong 3 - Tieng Anh - 122 BaiDocument9 pagesBai Tap Chuong 3 - Tieng Anh - 122 BaiNgọcÁnhĐặngNo ratings yet
- 24.1 CroDocument28 pages24.1 CroSalmanNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Dynamics (Scalars and Vectors, Pressure)Document4 pages3.1 Dynamics (Scalars and Vectors, Pressure)SalmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 22 O Levels PhyiscsDocument8 pagesTopic 22 O Levels PhyiscsSalmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 24 O Levels Physics ElectronicsDocument8 pagesTopic 24 O Levels Physics ElectronicsSalmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 23 O Levels Physics Electromagnetic InductionDocument7 pagesTopic 23 O Levels Physics Electromagnetic InductionSalmanNo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Physics Topic 2 (Kinematics) O-LevelsDocument10 pagesKinematics: Physics Topic 2 (Kinematics) O-LevelsSalmanNo ratings yet
- Lenses: Physics Topic 15 (Lenses) O-LevelsDocument6 pagesLenses: Physics Topic 15 (Lenses) O-LevelsSalmanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument1 pagePhysicsSalmanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 PDFDocument8 pagesTopic 2 PDFSalmanNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument2 pagesPhysicsSalmanNo ratings yet
- 3.2 DeformationDocument8 pages3.2 DeformationSalmanNo ratings yet
- Forces and EquilibriumDocument36 pagesForces and EquilibriumSalmanNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic4 (Energy, Work and Power,) O-LevelsDocument7 pagesPhysics Topic4 (Energy, Work and Power,) O-LevelsSalmanNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics Mass, Weight, DensityDocument7 pagesNotes Physics Mass, Weight, DensitySalmanNo ratings yet
- Physics Topic 25 Radioactivity MDocument5 pagesPhysics Topic 25 Radioactivity MSalmanNo ratings yet
- Notes Physics MeasurementDocument8 pagesNotes Physics MeasurementSalmanNo ratings yet
- O Levels Physics Topic 5 Turning EffectDocument6 pagesO Levels Physics Topic 5 Turning EffectSalmanNo ratings yet
- O Level Physics Topic 2 KinematicsDocument8 pagesO Level Physics Topic 2 KinematicsSalmanNo ratings yet
- 1050 Focus On AdhdDocument6 pages1050 Focus On Adhdapi-272366430No ratings yet
- SSTMZG528: Assignment 1Document4 pagesSSTMZG528: Assignment 1D V BHASKARNo ratings yet
- Marketing Psychology GuideDocument23 pagesMarketing Psychology GuideHimungshu KashyapaNo ratings yet
- EC6802 Wireless Networks Important PART-A &B Questions With AnswersDocument21 pagesEC6802 Wireless Networks Important PART-A &B Questions With AnswersohmshankarNo ratings yet
- (TP) Chapter 10 - Sound in DuctsDocument9 pages(TP) Chapter 10 - Sound in Ductsagung_123123No ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Security Chapter 1 Exam AnswersDocument5 pagesCisco CCNA Security Chapter 1 Exam Answersstu3232No ratings yet
- Scalars and VectorsDocument3 pagesScalars and VectorsnaylinaungNo ratings yet
- 3a. CONOPS Vigilancia ADS-B Base Terrestre COCESNADocument37 pages3a. CONOPS Vigilancia ADS-B Base Terrestre COCESNADairo FerrerNo ratings yet
- Daewoo CP 310Document9 pagesDaewoo CP 310quangdungvnNo ratings yet
- DPP Engine Room Log Book Page#1Document1 pageDPP Engine Room Log Book Page#1Muhammad Suleman FaizNo ratings yet
- Empowerment of Mortal and Divine Females in The Iliad - A FeministDocument21 pagesEmpowerment of Mortal and Divine Females in The Iliad - A FeministGiovanni SuárezNo ratings yet
- The Way of Tthe Cross - CPdODocument23 pagesThe Way of Tthe Cross - CPdOACCobraGNo ratings yet
- International Classi Fication of Retinopathy of Prematurity, Third EditionDocument18 pagesInternational Classi Fication of Retinopathy of Prematurity, Third EditionRameshNo ratings yet
- Heating Cable Selection GuideDocument4 pagesHeating Cable Selection Guidehassan3012No ratings yet
- GChandbook2008Document72 pagesGChandbook2008api-19918078No ratings yet
- Bending Machine Centurion ModelDocument4 pagesBending Machine Centurion ModelbharathaninNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solution For Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter 15 IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCES PDFDocument7 pagesNCERT Solution For Cbse Class 9 Science Chapter 15 IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCES PDFSanjiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Cadastral (2017 Edition Final)Document29 pagesGuidelines On Cadastral (2017 Edition Final)Olaitan RasheedNo ratings yet
- Coop Conference Proceeding (21-22aug 2022)Document585 pagesCoop Conference Proceeding (21-22aug 2022)oliviahuda75No ratings yet
- Punk Science - Inside The Mind of GodDocument3 pagesPunk Science - Inside The Mind of GodRobert Garcia0% (2)
- Annual Report Analysis - Maruti Suzuki LTD 2Document60 pagesAnnual Report Analysis - Maruti Suzuki LTD 2naman_popli50% (2)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1hbtalvi100% (1)