Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer
Answer
Uploaded by
BogaleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer
Answer
Uploaded by
BogaleCopyright:
Available Formats
Powered by AI
Bing
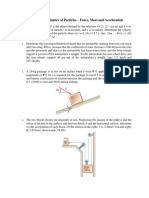
The hourly capacity (Q) can be determined by using the following formula:
Q=AxVxρ
where A is the cross-sectional area of the bulk solid on the belt in m^2^, V is
the velocity of conveyor in m/s and ρ is the density of transported material in
kg/m^3^.
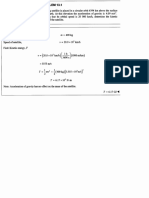
Substituting A=0.09m^2^, V=1.5m/s and ρ=593kg/m^3^ into the above
formula gives:
Q = 0.09 x 1.5 x 593
Q ≈ 80.1 kg/h.
The resultant force (F) can be determined by using the following formula:
F = Q x g x (sinθ + f x cosθ)
where Q is the hourly capacity in kg/h, g is the acceleration due to gravity in
m/s^2^, θ is the angle of repose in degrees, and f is the coefficient of friction
between the belt and material being conveyed.
Substituting Q=80.1kg/h, g=9.81m/s^2^, θ=30° and f=0.15 into the above
formula gives:
F = 80.1 x 9.81 x (sin30° + 0.15 x cos30°)
F ≈ 764 N.
The power requirement can be determined by using the following formula:
P=FxV/η
where F is the resultant force in N, V is the velocity of conveyor in m/s and η is
the electromotor efficiency.
Substituting F=764N, V=1.5m/s and η=0.85 into the above formula gives:
P = 764 x 1.5 / 0.85
P ≈ 1354 W.
I hope this helps!
You might also like
- Subsee Suction Pile Installation AnalysisDocument11 pagesSubsee Suction Pile Installation AnalysisKen KennyNo ratings yet
- Task 1 Key Answers PDFDocument3 pagesTask 1 Key Answers PDFmarsthinie sarsalejoNo ratings yet
- Parachute FormulasDocument3 pagesParachute FormulaskaranmarwahaNo ratings yet
- Hw5 Atwood Machines-SolutionsDocument10 pagesHw5 Atwood Machines-Solutionsdicksquad100% (1)
- Lab Report: Newton's Second LawDocument6 pagesLab Report: Newton's Second LawBrad Huang0% (1)
- C1Document27 pagesC1Angela Lopez100% (1)
- Final Seam ProjectDocument14 pagesFinal Seam ProjectJasper AgbuyaNo ratings yet
- Example CoagulFloccu1Document3 pagesExample CoagulFloccu1Adarsh Agrawal100% (3)
- Full Sem 2-Ship StabilityDocument189 pagesFull Sem 2-Ship StabilityYOGESH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Bugtong, Trixie Jael P.Document10 pagesBugtong, Trixie Jael P.yeng botzNo ratings yet
- Donguiz, Shiela MareDocument12 pagesDonguiz, Shiela Mareyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios TermodinamicaDocument11 pagesEjercicios TermodinamicaliaNo ratings yet
- CH-6 Linear Momentum and Impulse-11 PDFDocument13 pagesCH-6 Linear Momentum and Impulse-11 PDFvic100% (3)
- CLINT E. MOSENABRE FluidsDocument5 pagesCLINT E. MOSENABRE FluidsClint MosenabreNo ratings yet
- Antonio, Liberty Thermo PrintDocument10 pagesAntonio, Liberty Thermo Printyeng botzNo ratings yet
- Aris Fajar Yunia Putra - Forum 14Document2 pagesAris Fajar Yunia Putra - Forum 14Rindiani ChacaNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument22 pagesExercisessiakeehoNo ratings yet
- Perhitungan AtapDocument31 pagesPerhitungan AtapHanifNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Summer 2016Document9 pagesDynamics Summer 2016islamatta91No ratings yet
- ESAS Physics QuestionsDocument22 pagesESAS Physics QuestionsErika Mae OrlinaNo ratings yet
- AssignDocument10 pagesAssignkakaNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 1 and 2 Kelompok 9Document5 pagesExercise Chapter 1 and 2 Kelompok 9Puskesmas BatusepuluhNo ratings yet
- Homework 6 SolutionsDocument3 pagesHomework 6 SolutionsSean MccartneyNo ratings yet
- Chap5-3 - Sediment TransportDocument19 pagesChap5-3 - Sediment TransportDarya MemonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Vivin MathewNo ratings yet
- Taller 1Document10 pagesTaller 1Sergio ManceraNo ratings yet
- Online Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - RandomDocument10 pagesOnline Engineering Mechanics Test - Engineering Mechanics Test - Randomडॉ. कनिष्क शर्माNo ratings yet
- ThermoSolutions CHAPTER01Document55 pagesThermoSolutions CHAPTER01Fred EneaNo ratings yet
- HW2Document1 pageHW2zihamidi0% (1)
- WS31Document3 pagesWS31Minte MuluNo ratings yet
- Problem Set For HydroDocument9 pagesProblem Set For HydroogulNo ratings yet
- Solutions Chapter 2Document11 pagesSolutions Chapter 2JulianneNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Week 2 Activity 5: Universal Law of GravitationDocument2 pagesQuarter 2 Week 2 Activity 5: Universal Law of GravitationJ-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Jan 13 SolutionDocument4 pagesTutorial 2 Jan 13 SolutionAlex CoolNo ratings yet
- Revision Papers For Fluid PowerDocument4 pagesRevision Papers For Fluid Poweremlynmuriuki29No ratings yet
- BAB II Perhitungan AtapDocument16 pagesBAB II Perhitungan AtapnovisuckNo ratings yet
- Impact Attenuator CalculationsDocument3 pagesImpact Attenuator CalculationsabhishekNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument7 pagesPHYSICSCherryl FloresNo ratings yet
- The Tow Truck With Attached 1200Document18 pagesThe Tow Truck With Attached 1200david caraballoNo ratings yet
- D63 CBD 01Document5 pagesD63 CBD 01Shamik MisraNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument3 pagesFluidAhmadNo ratings yet
- (PHYS1112) (2017) (F) Final R8udkjdt 62165Document18 pages(PHYS1112) (2017) (F) Final R8udkjdt 62165black.widow.010300No ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Other Applications of Newton's LawsDocument65 pagesCircular Motion and Other Applications of Newton's Lawsshark 1808No ratings yet
- Proracun Hidrdinamicke SpojniceDocument8 pagesProracun Hidrdinamicke SpojniceVojkan DamjanovićNo ratings yet
- Houston Nelson 12 Physics Chapter3.2 SolnDocument11 pagesHouston Nelson 12 Physics Chapter3.2 SolnDavid ZhenNo ratings yet
- Examples (Set 1-Traffic Flow)Document8 pagesExamples (Set 1-Traffic Flow)Madzlan NapiahNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 1 Introduction ExercisesDocument1 pagePhysics Chapter 1 Introduction ExercisesacNo ratings yet
- Tính ToánDocument5 pagesTính ToánTrần Thái ThuậnNo ratings yet
- Railway Curves 7Document21 pagesRailway Curves 7vpmohammedNo ratings yet
- 2014 CE 2710 HW 7 SolutionDocument8 pages2014 CE 2710 HW 7 SolutionAJ SaNo ratings yet
- F Ma 1000×4 4000 F Ma 1000×4 4000: Mass, M 1kg Change in Velocity 4m/s Time, T 4sDocument8 pagesF Ma 1000×4 4000 F Ma 1000×4 4000: Mass, M 1kg Change in Velocity 4m/s Time, T 4sYasmin ShaikNo ratings yet
- Rajshahi Board (CQ)Document4 pagesRajshahi Board (CQ)ismaelNo ratings yet
- Antonio Letac JRDocument15 pagesAntonio Letac JRyeng botzNo ratings yet
- 4 IGCSE MomentumDocument61 pages4 IGCSE MomentumHoracio FerrándizNo ratings yet
- In The Image On The Left, The Total Mechanical Energy IsDocument17 pagesIn The Image On The Left, The Total Mechanical Energy IsSebastian PaezNo ratings yet
- Answer Key Chapter 6Document5 pagesAnswer Key Chapter 6linNo ratings yet
- Tutorial TwoDocument5 pagesTutorial TwoParas gurungNo ratings yet
- Sol Cap 13 L7Document129 pagesSol Cap 13 L7Jesus Feijoo100% (2)
- HYDRO POWER - Working EquationsDocument13 pagesHYDRO POWER - Working EquationsJane Erestain BuenaobraNo ratings yet