Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ejemplos de Tipos de Pronouns
Uploaded by
Adriam MaciasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ejemplos de Tipos de Pronouns
Uploaded by
Adriam MaciasCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 4 Tables
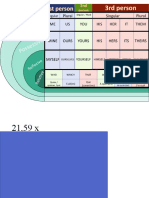
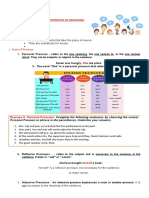
Pronouns in English
Subjective case (SUBJECT)
Possessive case
Person or subject complement after the Objective case (OBJECT)
(denotes ownership)
verb ‘to be’
st
1 I me mine
nd
Singular 2 you you yours
rd
3 he, she, it him, her, it his, hers, its
st
1 we us ours
nd
Plural 2 you you yours
rd
3 they them theirs
NB: no pronoun has an apostrophe
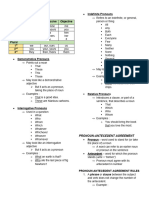
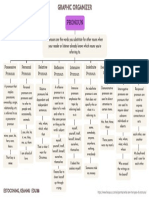
Types of Pronouns
Types of Pronouns Definition Examples
demonstrative points to this, that, these, those, such
Who? Whom?
interrogative poses questions
Which? What? Whose? Where?
who, whoever, whom, whomever, whose,
relative joins an antecedent to a modifying clause
which, that, what
whoever, everyone, everybody, everything,
someone, somebody, something, anyone,
anybody, anything, another, enough, less,
indefinite refers to no one or no thing in particular
little, all, any, much more, most, both, few,
many, several, no one, nobody, nothing,
none, one, each, either, neither, none
used when the subject of the verb is also myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself,
reflexive
its object ourselves, yourselves, themselves
myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself,
intensive provides emphasis
ourselves, yourselves, themselves
distributive refers to persons or things one at a time each, either, neither
used to introduce a sentence, without
expletive it, there
adding meaning to a sentence
You might also like
- WAJ3102 Types of PronounsDocument1 pageWAJ3102 Types of PronounsjccoccnNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronouns - Grammar Reference Sheet: (A Pronoun Is A Word That Is Used To Take The Place of A Noun.)Document1 pageTypes of Pronouns - Grammar Reference Sheet: (A Pronoun Is A Word That Is Used To Take The Place of A Noun.)Zeina M. HarfoushNo ratings yet
- Types of Pronouns - Grammar Reference Sheet: (A Pronoun Is A Word That Is Used To Take The Place of A Noun.)Document1 pageTypes of Pronouns - Grammar Reference Sheet: (A Pronoun Is A Word That Is Used To Take The Place of A Noun.)Arleth CaraballoNo ratings yet
- To StudyDocument13 pagesTo StudyMariana ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- SEMI-final Exam. Eng2.Document3 pagesSEMI-final Exam. Eng2.Allan Arancel MagsipocNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalDocument12 pagesPersonal Pronoun: You, He, She, It, We They, Me, Him, Her, Us, and Them Are All PersonalWH LimNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument10 pagesPronounstrongbmse183686No ratings yet
- 00 Parts of SpeechDocument18 pages00 Parts of SpeechBlessie Marie SamontañezNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument2 pagesParts of SpeechJhedalyn HilarionNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 pagesParts of SpeechkaztheyanoNo ratings yet
- The Pronoun: Nominative CaseDocument17 pagesThe Pronoun: Nominative CasePadhy ParthosarathiNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNS 1st Person Singular 2nd Person Singular 3rd Person SingularDocument4 pagesPRONOUNS 1st Person Singular 2nd Person Singular 3rd Person SingularShelley BerryNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument27 pagesPronounannisa nurul apNo ratings yet
- Relative Pronouns: This House Is Big That House Is BigDocument2 pagesRelative Pronouns: This House Is Big That House Is BigFaris PasovicNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech k14Document2 pagesParts of Speech k14Anis SartikaNo ratings yet
- English 10 Reviewer - 4th QuarterDocument8 pagesEnglish 10 Reviewer - 4th QuarterGeromme TudNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronouns Possessive Determiners Possessive Pronouns As Subject (Nominative) As Object (Accusative and Dative)Document4 pagesPersonal Pronouns Possessive Determiners Possessive Pronouns As Subject (Nominative) As Object (Accusative and Dative)Miriam Bastos MarzalNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument1 pagePronounKeannu EstoconingNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech, English GrammarDocument17 pagesParts of Speech, English GrammarmaliknaseerNo ratings yet
- Pronombres Ojetivos, Posesivos, Reflexivos y Relativos en InglésDocument5 pagesPronombres Ojetivos, Posesivos, Reflexivos y Relativos en InglésDavid KaplanNo ratings yet
- Pronouns - Basic NotesDocument4 pagesPronouns - Basic NotesFrancis Guerrero TimbalNo ratings yet
- Sample Lesson For Pronouns Relative PronounsDocument8 pagesSample Lesson For Pronouns Relative PronounsJuniza Jahaya100% (1)
- Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesParts of SpeechMaria Alejandra VillamizarNo ratings yet
- PartsDocument17 pagesPartsLidya NurainiNo ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument13 pages8 Parts of Speechtaufikawaludin100% (4)
- PartsDocument17 pagesPartsFelipe C. CollioNo ratings yet
- Unit ThreeDocument9 pagesUnit ThreefaizaNo ratings yet
- MathDocument17 pagesMathLouise LeongsonNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - PronounsDocument6 pagesModule 3 - Pronounsfernando derosasNo ratings yet
- Words That Expresses Strong Feeling or Emotion. Exp: Aw! Oh! Phew! Well! Yea! Bravo! Gosh! Eh! Gee!, EtcDocument1 pageWords That Expresses Strong Feeling or Emotion. Exp: Aw! Oh! Phew! Well! Yea! Bravo! Gosh! Eh! Gee!, Etcdanang noviantoNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument6 pagesPronounsRizky ExterminateurNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument2 pagesPronounsMark GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Handout 2 - Pronouns (Kinds and Properties)Document5 pagesHandout 2 - Pronouns (Kinds and Properties)Sangie CenetaNo ratings yet
- Tugas PronounsDocument4 pagesTugas PronounsputuNo ratings yet
- Kinds of AdverbDocument6 pagesKinds of AdverbBryan CasidoNo ratings yet
- PronounsDocument13 pagesPronounsIqis nisaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in English: Value Focus: Teamwork/CooperationDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in English: Value Focus: Teamwork/Cooperationcy baromanNo ratings yet
- B2 Course: Unit 9 - Pronouns and DeterminersDocument9 pagesB2 Course: Unit 9 - Pronouns and DeterminersEugeniaNo ratings yet
- Unit Three 3 PronounsDocument9 pagesUnit Three 3 Pronounskatia oussNo ratings yet
- ELAReview CRCT UpdatedDocument222 pagesELAReview CRCT UpdatedAFNAN AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Pronoun PronounDocument3 pagesPronoun PronounNovia LarasantiNo ratings yet
- 08 - 09 October 2020: Understanding Noun and Its TypesDocument8 pages08 - 09 October 2020: Understanding Noun and Its TypesFitri DelitaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Cheat SheetDocument1 pageParts of Speech Cheat SheetHannaNo ratings yet
- Special English Ms. Khrisna Mae C. GelogoDocument2 pagesSpecial English Ms. Khrisna Mae C. GelogoEmz GelogoNo ratings yet
- Grammar NotesDocument10 pagesGrammar NotesKristin Chmielorski-MoffatNo ratings yet
- Presentasi Tugas Kelompok Sejarah Scrapbook CoklatDocument14 pagesPresentasi Tugas Kelompok Sejarah Scrapbook CoklatKartika Tri YamaryantiNo ratings yet
- PRONOUNSDocument3 pagesPRONOUNSleydi merinoNo ratings yet
- Pronouns PDFDocument3 pagesPronouns PDFgleeNo ratings yet
- Week 04 - Grammar - PronounsDocument3 pagesWeek 04 - Grammar - Pronounsrahma alaydaNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument4 pagesPronounmohammadadan424No ratings yet
- PronounsDocument2 pagesPronounsg-ipgp21305733No ratings yet
- PronounsDocument1 pagePronounsKeith Clouie BautistaNo ratings yet
- PronounDocument38 pagesPronounAlfa RizkiNo ratings yet
- Noun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction InterjectionDocument19 pagesNoun Pronoun Verb Adjective Adverb Preposition Conjunction InterjectionFerizalGunawanNo ratings yet
- Business Correspondence A Guide To Everyday Writing 2002Document161 pagesBusiness Correspondence A Guide To Everyday Writing 2002sampoyayaNo ratings yet
- Types of Speech ActsDocument3 pagesTypes of Speech Actshasria sarapilNo ratings yet
- ملخص قواعد انجليزي شامل للفصل الأول اول ثانويDocument18 pagesملخص قواعد انجليزي شامل للفصل الأول اول ثانويheba ananNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice 6 Tasks Fun Activities Games Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 51579Document3 pagesPassive Voice 6 Tasks Fun Activities Games Grammar Drills Grammar Guides - 51579FanniNo ratings yet
- Gapol - Ro 21 Tag QuestionsDocument7 pagesGapol - Ro 21 Tag QuestionsDl. PikrikNo ratings yet
- P.6 English Workbook Edited Term 2 2020 PDFDocument144 pagesP.6 English Workbook Edited Term 2 2020 PDFAlex SsembalirwaNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Tugas Tutorial Tatap Muka Ke. 3Document3 pagesRancangan Tugas Tutorial Tatap Muka Ke. 3OliviaNo ratings yet
- The Role and Importance of Terminology in The Study of Specialized LanguageDocument5 pagesThe Role and Importance of Terminology in The Study of Specialized LanguageresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Languagedevelopmentfinal 150122010309 Conversion Gate01Document31 pagesLanguagedevelopmentfinal 150122010309 Conversion Gate01Shyden Taghap Billones BordaNo ratings yet
- Nglish Presentation: Nama Nama Kelompok 3Document8 pagesNglish Presentation: Nama Nama Kelompok 3Minerva HamNo ratings yet
- Demonstrative Pronouns: This Is My New Bike. (Esta É A Minha Nova Bicicleta)Document2 pagesDemonstrative Pronouns: This Is My New Bike. (Esta É A Minha Nova Bicicleta)Aline SudréNo ratings yet
- Collins Work On Your Grammar Pre Intermediate A2Document128 pagesCollins Work On Your Grammar Pre Intermediate A2busekabanNo ratings yet
- Ready For C1 Advanced 4th Edition Student S Book Scope and SequenceDocument2 pagesReady For C1 Advanced 4th Edition Student S Book Scope and Sequencerocio50% (2)
- Genre Based ApproachDocument6 pagesGenre Based ApproachLow CscNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our English Class!Document32 pagesWelcome To Our English Class!Ruth Baong CañeteNo ratings yet
- Literary Device ChartDocument1 pageLiterary Device ChartYongqi Yang100% (1)
- Discourse - WikipediaDocument8 pagesDiscourse - WikipediaAli AkbarNo ratings yet
- Reported SpeechDocument15 pagesReported SpeechMarian ColonniNo ratings yet
- Unit 07Document11 pagesUnit 07QuanNo ratings yet
- Clasa A XII-a SeralDocument4 pagesClasa A XII-a SeralAnca IonNo ratings yet
- Low - Singable Translations of SongsDocument18 pagesLow - Singable Translations of SongsRoberto De Lucia100% (1)
- Topik 1 GrammarDocument8 pagesTopik 1 GrammarRenaldz TanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 - Reading or ListeningDocument11 pagesAssignment 3 - Reading or ListeningSuzanne Van Straaten100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Classification and Varieties of English LanguageDocument5 pagesLesson 1 Classification and Varieties of English LanguagePeter Ezekiel ReyesNo ratings yet
- RP Signature SoundsDocument3 pagesRP Signature SoundsAaron Stangarone0% (1)
- Final Examination in Eng121Document24 pagesFinal Examination in Eng121KAREN JANE BANAYATNo ratings yet
- Oet Writing Guide by E2Language 1Document6 pagesOet Writing Guide by E2Language 1Wendy SierraNo ratings yet
- Examining Code-Switching Practices in Hilman Hariwijaya's Makhluk Manis Dalam Bis and BungaDocument12 pagesExamining Code-Switching Practices in Hilman Hariwijaya's Makhluk Manis Dalam Bis and BungaKARANGGE EsportNo ratings yet
- Name: Alfini Khoirunnisa NPM: 1911040009 Class: 5DDocument2 pagesName: Alfini Khoirunnisa NPM: 1911040009 Class: 5DAlfini KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- COMPARATIVE AND SUPERLATIVE Class 6Document10 pagesCOMPARATIVE AND SUPERLATIVE Class 6Karina MoralesNo ratings yet