Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 4
Uploaded by
Cloviri CasjaanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lesson 4
Uploaded by
Cloviri CasjaanCopyright:
Available Formats
Saint Columban College
HIGH SCHOOL DEPARTMENT
7016 Pagadian City
S T U D E N T ’ S A C T I V I T Y S H E E T
Name: ___________________________________ Date: __________________
Year & Section: _________________________ Subject: Science 8
Lesson No. 4
Learning Content: Work
Learning Targets: At the end of the lesson, I CAN:
a. identify situations in which work is done and which no work is done,
b. solve problems by expressing work mathematically.
Learning Resources: Papa, E.C.,et. al ( 2018). Practical Science 8: Makati City, Philippines: DIWA LEARNING
SYSTEMS INC. pp. 39-46
Core Values: Taking care of the environment in every work they do
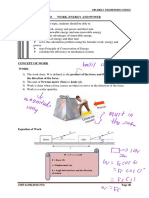
CONCEPT NOTES:
WORK
- The application of force on an object and the displacement of that object caused by force.
Formula:
W= ⃗F d⃗
SYMBOL MEANING UNIT MEANING
W WORK J Joules
⃗
F FORCE N Newton
d⃗ DISPLACEMENT m meter
Example Problems:
1. If you push a box of supplies across 5m on a floor that exerts 100N of frictional force, how
much work do you apply?
Given : Solution:
d⃗ = 5m F d⃗
W= ⃗
⃗
F = 100N W= 100N (5m)
Find : W= 500 N*m or 500J
W=? Answer: You do 500J of work on the box of supplies.
There are three ways that must be satisfied for work to be done on an object. These are the
following:
1. force – a force must be applied to the object
2. Displacement- the object must be displaced. No matter how you hard you push an object,
if the object does not move, then work is done on the object.
3. Direction of force and displacement- the force applied must be parallel to the
displacement. An applied force that is perpendicular to the displacement does not work on
the object.
You might also like
- Phy1 11 - 12 Q1 0701 AkDocument5 pagesPhy1 11 - 12 Q1 0701 AkFrancis RebancosNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in ScienceJosal Mariano JacintoNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument15 pagesWork and EnergyRonnie ValderamaNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan: Ramon Avanceña National High SchoolDocument3 pagesDaily Lesson Plan: Ramon Avanceña National High SchoolShane Catherine BesaresNo ratings yet
- Advance Montessori Education Center of IsabelaDocument8 pagesAdvance Montessori Education Center of IsabelaPrincess GuiyabNo ratings yet
- Q1Act3 Work Power and EnergyDocument29 pagesQ1Act3 Work Power and EnergyReselle AnubNo ratings yet
- 7-Unit4 Work, Energy, and PowerDocument17 pages7-Unit4 Work, Energy, and Powerelty TanNo ratings yet
- SLG 13.1 Work, Energy, and PowerDocument8 pagesSLG 13.1 Work, Energy, and PowerHaruto “kai” WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy, Power, and MachinesDocument46 pagesWork, Energy, Power, and MachinesDee Doroin50% (2)
- Activity #1: Naming of Words: ST THDocument15 pagesActivity #1: Naming of Words: ST THABDUL RAHIM G. ACOONNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter - SCIENCE 8-WEEK 1-2Document6 pages1st Quarter - SCIENCE 8-WEEK 1-2MICAH NORADANo ratings yet
- Module 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesDocument44 pagesModule 11 Work, Energy, Power and MachinesJudy Panguito Aralar100% (2)
- Summative in Science 8Document3 pagesSummative in Science 8Melvin Gayta FailagaoNo ratings yet
- SLM Gen. Physics 1 6th WKDocument16 pagesSLM Gen. Physics 1 6th WKrrNo ratings yet
- Module 8 EnergyDocument29 pagesModule 8 EnergyKismith Aile MacedaNo ratings yet
- Module Grade 8 Science First Quarter 2021Document22 pagesModule Grade 8 Science First Quarter 2021juliusvaldez07201996No ratings yet
- Contextualized Lesson Plan - WorkDocument5 pagesContextualized Lesson Plan - WorkXHiri Pabuaya Mendoza100% (1)
- Science 8Document20 pagesScience 8Gelai javilloNo ratings yet
- Work Energy PowerDocument47 pagesWork Energy PowerHemant ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- GP1 - Q1 - Week 6Document6 pagesGP1 - Q1 - Week 6Sathya CruzNo ratings yet
- GP1 Q1 Week-6 PDFDocument9 pagesGP1 Q1 Week-6 PDFmar liaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument47 pagesWork Energy and PowerPRASANNANo ratings yet
- Week 14-15 - Mechanics 7.1Document7 pagesWeek 14-15 - Mechanics 7.1Rafael Jotojot Jr.No ratings yet
- Science 8 Q1 W5 D1Document7 pagesScience 8 Q1 W5 D1Judith J. DelizoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - WORK, ENERGY AND POWERDocument20 pagesModule 4 - WORK, ENERGY AND POWERHanah ArzNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 8. ACTIVITIES in Science BNHSDocument39 pagesScience Grade 8. ACTIVITIES in Science BNHSKenneth CruzNo ratings yet
- Finals CoverageDocument9 pagesFinals CoverageShaira Isabel RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Science - 210614 - 104559Document14 pagesChapter 4 Science - 210614 - 104559Fatin AmirNo ratings yet
- Group-3 2Document4 pagesGroup-3 2Licht KnavesmireNo ratings yet
- LP Energy BasicsDocument6 pagesLP Energy BasicsJedNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science8 Sy 2015Document43 pagesLesson Plan in Science8 Sy 2015Noel PiedadNo ratings yet
- Semi - Science - Work, Energy, and PowerDocument2 pagesSemi - Science - Work, Energy, and PowerCristine ObialNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2 - Laws of MotionDocument34 pagesModule 1 and 2 - Laws of MotionLaiza GranaNo ratings yet
- University of Caloocan City: Prepared By: Arvic L. BaltarDocument6 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City: Prepared By: Arvic L. BaltarreginebonNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy - Class 9 Science SA2 NCERT Solutions Free PDF DownloadDocument20 pagesWork and Energy - Class 9 Science SA2 NCERT Solutions Free PDF DownloadmahenderdharmulaNo ratings yet
- Work, Energy & Power: Syllabus ObjectivesDocument40 pagesWork, Energy & Power: Syllabus ObjectivesBrandly NyamapnziNo ratings yet
- The World of Work and Mechanical EnergyDocument31 pagesThe World of Work and Mechanical EnergyLea Ann SuniNo ratings yet
- Work Energy and PowerDocument84 pagesWork Energy and PowerPaul Denmarc AraoNo ratings yet
- SIM AmigoDocument20 pagesSIM AmigoSheila Marie AmigoNo ratings yet
- General Physics Module 9 - 14Document5 pagesGeneral Physics Module 9 - 14Ennyliejor YusayNo ratings yet
- Oct. 2, 2023 - MRFDocument3 pagesOct. 2, 2023 - MRFmaricel fernandezNo ratings yet
- Energy Work and Power FA-KEYDocument4 pagesEnergy Work and Power FA-KEYjehehehNo ratings yet
- GP1 Q1 W5-6-MsteamsDocument13 pagesGP1 Q1 W5-6-MsteamsCleamarie RamirezNo ratings yet
- G8 SCIENCE Q1 Week 2 LAS 1Document1 pageG8 SCIENCE Q1 Week 2 LAS 1shalinee.daydayNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in SCIENCE 10-SPA - Convection CurrentDocument5 pagesLesson Plan in SCIENCE 10-SPA - Convection CurrentOpalyn Pearl Esteban100% (1)
- Q3 - Week 9 - Day 1Document4 pagesQ3 - Week 9 - Day 1Maria Ronavie Davalos MantesNo ratings yet
- HWCH 11Document9 pagesHWCH 11Eric BarberNo ratings yet
- Work 2Document18 pagesWork 2elenaNo ratings yet
- MODULE CHAPTER 7 Form 3Document21 pagesMODULE CHAPTER 7 Form 3Nurul Shafiah Mustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Notes Energy HonorsDocument42 pagesNotes Energy HonorsRonaldo ManaoatNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 - Work, Power, and EnergyDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Work, Power, and EnergymaryelNo ratings yet
- CH 11 PDFDocument14 pagesCH 11 PDFGaurav ThakareNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 9 March 29 Science Chapter 11 Work and EnergyDocument13 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 9 March 29 Science Chapter 11 Work and EnergyARHAN MIAN FACTS.No ratings yet
- Lesson 5a - Work and Energy Part 1Document34 pagesLesson 5a - Work and Energy Part 1kryzzia angelaNo ratings yet
- Coulombforce - ExplorelearninglabDocument5 pagesCoulombforce - ExplorelearninglabYoung CEONo ratings yet
- Work and Power Math in ScienceDocument4 pagesWork and Power Math in ScienceALFREDNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Potential & Kinetic EnergyDocument25 pagesLesson 3 Potential & Kinetic EnergyRonnie AbsalonNo ratings yet
- Sph4u Energy Amp Momentum Unit 2 Notes 1Document36 pagesSph4u Energy Amp Momentum Unit 2 Notes 1hNo ratings yet
- Let's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandLet's Calculate Work! Physics And The Work Formula : Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- 4 URANUS Parents Orientation SY 2022 2023Document15 pages4 URANUS Parents Orientation SY 2022 2023Cloviri CasjaanNo ratings yet
- Script For Recognition CeremonyDocument2 pagesScript For Recognition CeremonyBernard Ventenilla93% (28)
- FRAYERDocument1 pageFRAYERCloviri CasjaanNo ratings yet
- CERTIFICATES by Savanna CunninghamDocument11 pagesCERTIFICATES by Savanna CunninghamCloviri CasjaanNo ratings yet
- USAF Test Pilot School Flying QualitiesTextbook Volume 2 Part 1Document704 pagesUSAF Test Pilot School Flying QualitiesTextbook Volume 2 Part 1David Russo100% (3)
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureBawani shankerNo ratings yet
- Unit Circle ProjectDocument2 pagesUnit Circle Projectapi-3256744960% (1)
- Various Formulas Needed To Solve Energy and Power Signal ProblemDocument1 pageVarious Formulas Needed To Solve Energy and Power Signal ProblemrsrmeNo ratings yet
- Vedic Maths FAQ - YUVADocument3 pagesVedic Maths FAQ - YUVARavindran VaradarajanNo ratings yet
- Transmission Line NotesDocument140 pagesTransmission Line NotesAlessandro FantinoNo ratings yet
- BowersDocument23 pagesBowersАндрій ПономарьовNo ratings yet
- Programming Lab FileDocument71 pagesProgramming Lab FilePriyanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- 3 Geometric ConstructionsDocument12 pages3 Geometric ConstructionsRashid AlmaktoumiNo ratings yet
- Bruce Jagid Resume 2Document1 pageBruce Jagid Resume 2api-521056336No ratings yet
- Akar Persamaan Tak Linier Tunggal PPT Dy - 2 PDFDocument14 pagesAkar Persamaan Tak Linier Tunggal PPT Dy - 2 PDFazmi_faNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra and Its Applications - D. C. LayDocument71 pagesLinear Algebra and Its Applications - D. C. LayKaryl VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P1 Memo Eng March 2009 PDFDocument15 pagesMathematics P1 Memo Eng March 2009 PDFXolani KumaloNo ratings yet
- Week 4 LAB 4 Form and SpaceDocument5 pagesWeek 4 LAB 4 Form and SpaceAnotherKidNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Geometry Course OutlineDocument6 pagesCombinatorial Geometry Course OutlineApple OcampoNo ratings yet
- α t α t α α t α t α t β t αβ α t α=1,... ,N tDocument18 pagesα t α t α α t α t α t β t αβ α t α=1,... ,N tMichael ChiuNo ratings yet
- Ruler Folding Problem PaperDocument11 pagesRuler Folding Problem PaperVishnuprakash PuthiyakovilakathNo ratings yet
- Department of Mathematics Anna University, Chennai Ma5252 Engineering Mathematics-Ii Unit - II Analytic FunctionsDocument67 pagesDepartment of Mathematics Anna University, Chennai Ma5252 Engineering Mathematics-Ii Unit - II Analytic FunctionsArmahNo ratings yet
- Signals and SystemDocument2 pagesSignals and Systemjeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science 3A - CSC3A10/CSC03A3: Lecture 2: Arrays, Linked Lists and RecursionDocument66 pagesComputer Science 3A - CSC3A10/CSC03A3: Lecture 2: Arrays, Linked Lists and Recursionthapelo mokoloNo ratings yet
- Isi Mtech Qror 07Document34 pagesIsi Mtech Qror 07api-26401608No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Solving Problems Involving SetsDocument19 pagesMathematics: Solving Problems Involving SetsHazel ColaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9, Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia: Yda YDocument22 pagesChapter 9, Distributed Forces: Moments of Inertia: Yda YRushed AlamaNo ratings yet
- R NotesDocument263 pagesR Notestimothypurdy4333No ratings yet
- 2.3 Expectation of Random VariablesDocument3 pages2.3 Expectation of Random VariablesThales mathNo ratings yet
- Actex 1P-84-ACT-T Sample 5-6-11Document8 pagesActex 1P-84-ACT-T Sample 5-6-11Moisés Vicente GaldosNo ratings yet
- EE 307 Chapter 6 - Electrostatic Boundary Value ProblemsDocument34 pagesEE 307 Chapter 6 - Electrostatic Boundary Value ProblemsIzhar Ahmed NoohpotoNo ratings yet
- ML 1Document51 pagesML 1DipNo ratings yet
- PracticalsDocument29 pagesPracticalsRitik PatelNo ratings yet
- Lecture03 PDFDocument8 pagesLecture03 PDFneerajNo ratings yet